- August 1, 2018
- Orthopedics and traumatology
- Natalia Penchkovskaya
In case of head injuries as a result of an accident and in case of vascular diseases, an accumulation of blood can form in the cranial cavity. As a result, an intracranial hematoma may appear. It is also called a blood tumor. Stroke, aneurysm, and thinning of blood vessels also contribute to this.
The most dangerous thing is that an intracranial hematoma affects the brain itself, severely compressing it. Also considered an unpleasant moment are clinical manifestations that, in the event of a head injury, do not make themselves felt immediately, but after some time.
Even small impacts can create pools of blood that threaten a person's vitality. They require immediate contact with a specialist and timely treatment. Often, intracranial hematomas are removed through surgery.
Causes
A brain hematoma is a dangerous pathological condition in which blood from damaged vessels accumulates in the skull. The development of a hematoma can be caused by a number of factors:
- Damage to blood vessels as a result of contusion, causing hemorrhage. In this case, the blood pouring into the cranial cavity leads to a displacement of the brain. There is also a risk of the gray matter of the brain becoming saturated with blood; in this case, as a result of the severing of connections with neurons, the entire body malfunctions.
- The development of autoimmune pathologies that promote inflammation of brain tissue with subsequent destruction and death (necrosis).
- Rupture of a vessel aneurysm due to increased blood pressure.
- Brain tumors, bleeding disorders.
- Congenital vascular diseases.
- Infectious diseases that provoke the occurrence of inflammatory processes (encephalitis, meningitis).
- Inflammations affecting blood vessels: lupus erythematosus, arteritis.
- Birth injury.
Important!
The cause of post-stroke hematoma in the brain can be sunstroke or heatstroke, as well as alcohol intoxication,
Mechanisms of education
Hematoma formation occurs when blood vessels in the brain rupture. Subdural hematomas result from damage to the cortical bridging veins and venous bleeding between the two meninges: the arachnoid and the dura mater. The source of epidural hematomas is the venous arteries that are damaged by fractures of the skull bones. In young children, the sinuses of the dura mater rupture.
There are two mechanisms of hemorrhage:
- the spilled blood permeates the gray matter of the brain, mixing with it;
- the blood provokes separation of the brain substance and forms a space filled with blood clots.
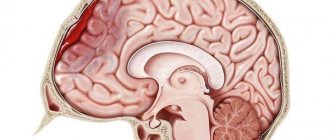
The mechanism of occurrence of cerebral hematoma
The brain located in the skull is surrounded by a special fluid that performs a protective function.
But with high-power impacts, cerebrospinal fluid cannot fully protect the brain. As a result of sharp shaking, it hits the walls of the skull, damaging the blood vessels in and around the brain. As a result, a hematoma occurs.
A cerebral hematoma is a hemorrhage in the brain accompanied by the formation of a cavity filled with coagulated or liquid blood. This injury usually damages brain tissue and blood vessels.
Injury can appear either immediately or after a certain period of time.
Classification according to all criteria
There are two groups of cerebral hematomas:
- traumatic – formed as a result of a bruise;
- spontaneous (non-traumatic).
There are a number of signs taken into account when classifying hematomas.
Depending on the location in the cranial space:
- epidural;
- subdural;
- intracerebral;
- subarachnoid;
- intraventricular.
According to the statute of limitations that determines the treatment method:
- acute – detected within 3 days from the moment of formation;
- subacute – detected between 3 and 21 days after injury;
- chronic – detected 21 or more days after the injury and hematoma formation.
Attention!
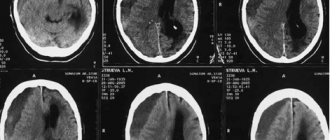
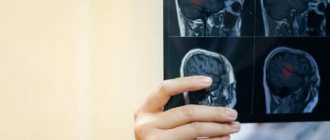
The approximate age of the hematoma can be determined by such types of diagnostics as CT and MRI.
By location:
- intracerebral;
- intracranial;
By depth:
- deep - located in the central part of the hemisphere;
- superficial - formed under the crust.
There are two groups of hemorrhages inside the brain:
- primary, accounting for about 90% of all intracerebral hematomas;
- secondary, caused by vascular pathology and bleeding disorders.
Types of cranial hematomas
Intracranial hematomas differ according to the relative extent of their manifestations, size and location in the head. They are localized near the brain itself, the bones of the skull and membranes.
By time they are divided into acute, subacute and chronic. In an acute process, signs appear within the first few days. Subacute - within 3 weeks, and chronic - even later.
The size of hematomas is also of great importance when providing assistance. Small blood accumulations are up to 50 ml, medium ones reach 100 ml, and large ones have a volume of over 100 ml.
The location of blood tumors is also different:
- Epidurals are located above the dura mater of the brain;
- Between the gray matter itself and its membrane are the subdurals.
- They also distinguish between intracerebral and intraventricular. These hematomas are located directly in the substance of the brain.
- There are hematomas formed near the brain stem.
Hematomas also form during hemorrhagic impregnation. In this case, the walls of the vessels are in an intact state.
Symptoms and signs of hematoma
There are several types of hematomas, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms and characteristics.
Epidural
An epidural hematoma is an accumulation of blood between the periosteum (the outer layer of the dura mater) and the inner surface of the skull. The pathology occurs as a result of strong mechanical impact, usually a blow to the head received in a car accident or a fall from a great height. The injury leads to rupture of a cerebral artery.
Note!
An epidural hematoma can cause death due to the pressure on brain tissue from a rapidly expanding cavity of blood.
The light period of pathology, lasting about 40 minutes, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- brief loss of consciousness;
- weakness;
- slight dizziness;
- asymmetry of nasolabial folds.
At the end of the light period, the victim’s condition worsens: nausea and vomiting appear, and headache increases. In some cases, rapid loss of consciousness occurs, followed by coma.
Subdural
The cause of a subdural hematoma is a rupture of an aneurysm or vein. In 70% of all cases, this occurs as a result of traumatic brain injury. As a result, the following cerebral manifestations of hematoma are observed:
- disorder of consciousness;
- headache (cephalgia), in many cases worsening after vomiting;
- nausea and vomiting;
- mental disorder.
Important!
Chronic subdural hematomas often cause decreased vision.
Subarachnoid
Subarachnoid hemorrhage occurs when there is a cerebral hemorrhage, characterized by the accumulation of blood in the space between the arachnoid and the meninges. Pathology can be caused by several factors:
- traumatic brain injury;
- rupture of a vascular aneurysm;
- dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries.
Symptoms of subarachnoid hematoma in the acute period:
- disorder of consciousness;
- intense headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- photophobia;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- disorder of consciousness for 5-10 days.
Severe bleeding with blood entering the cerebral ventricles leads to coma.
Intraventricular
Hemorrhage into the ventricles of the brain is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident caused by a head injury or hemorrhagic stroke. The pathology is characterized by a number of symptoms:
- increasing tissue swelling;
- impaired brain functionality;
- development of hydrocephalus and dropsy – causes of fainting and coma.
Intracerebral
Numerous intracerebral hematomas develop as a result of blood entering the white medulla and gradually soaking it. This leads to a breakdown of nerve connections, damage to nerve processes (neurites) and a deterioration in the regulatory effect on the functioning of the entire body.
If the hemorrhage occurs due to injury, then the capsules with blood are located near the cerebral cortex. When blood vessels rupture due to atherosclerosis and hypertension, the formation of capsules with blood occurs inside the white matter.
The main signs of intracerebral hematoma:
- speech and memory disorder;
- conduct disorder;
- convulsive epileptic seizures.
Very important!
Intracerebral hematoma with hemorrhage into the ventricles is characterized by rapidly developing depression of consciousness followed by the onset of coma.
When should you rush to the doctor?
If the blow to the head was so significant that there was loss of consciousness, then you should immediately go to the doctor. After all, symptoms do not always appear immediately. Knowing the signs of a hematoma, the victim should monitor his condition and be sure to tell his family or colleagues, since consciousness is often impaired and memory loss may occur. The person who received the blow may not even remember it.
Therefore, relatives also need to be attentive and monitor changes in the patient’s condition. At the first manifestations of a hematoma, you need to rush to the doctor and undergo the necessary examination. After all, any intracranial hematoma poses a threat to life.
First aid
After receiving an injury, the victim must bandage his head tightly and lay him in a horizontal position. In this case, there must be a pillow under your head. To prevent the patient’s condition from worsening, a number of actions will need to be taken:
- ensure fresh air enters the room;
- apply Riciniol emulsion to the bruised area;
- Apply a cold compress to the injured area every 30 minutes.
Features of hematomas on the head of a child
The formation of a hematoma on the head in childhood occurs for a number of reasons:
- mechanical damage to tissue as a result of bruises and blows;
- presence of serious illnesses;
- undergone surgical operations.
Attention!
Experts diagnose three types of hematomas in children: subdural, epidural and intracerebral.
Main symptoms of the pathology:
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- fog;
- general weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- drowsiness;
- tearfulness;
- noise in ears;
- the appearance of dark circles around the eyes.
If a child falls seriously, it is necessary to immediately show a doctor, after providing first aid:
- apply a compression bandage;
- apply a cold compress to the site of injury;
- provide the baby with bed rest.
Treatment
Based on the diagnostic results obtained, the doctor determines treatment methods. As a rule, conservative treatment is carried out for a hematoma on the head. However, in some cases surgery is required.
Conservative
Treatment with medications allows you to achieve the following:
- normalization of blood pressure, maintaining blood supply to the brain, and at the same time, not increasing the size of the hematoma;
- beneficial effect on blood clotting;
- elimination and prevention of swelling;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels.
The patient is prescribed medications:
- to eliminate vasospasm - Nifedipine, Vikasol, Aminocaproic acid, Aprotinin;
- to prevent cerebral edema - Manniol, etc.
Surgical
Surgery is performed to mechanically remove the hematoma putting pressure on the brain. There are several methods used for this operation:
- puncture;
- open;
- stereotactic;
- endoscopic;
- neuronavigation.
The tactics of surgical intervention are determined by a neurosurgeon.
Traditional methods
To treat hematomas, products based on vinegar, salt and alcohol are most often used. Methods for preparing the most common compresses:
- Mix apple cider vinegar with ice water in a 2:1 ratio. Apply the resulting composition to the site of injury.
- Dissolve 1 tbsp in 100 g of vinegar. l. salt.
- Dilute 1 tbsp in 100 g of water. l. salt.
- Mix 100 g of vinegar, 100 g of vodka and 500 g of water.
Decoctions for the treatment of hematomas can be prepared from fresh herbs, for example:
- plantain;
- parsley;
- wormwood;
- wild rosemary, etc.
Birth hematomas
Cafelogematoma does not require therapy in every case, since it resolves on its own within one month. If there is a grade II hematoma, treatment is necessary, which includes the following:
- keeping the child under constant medical supervision;
- administration of hemostatic drugs.
An indication for surgical intervention may be a grade III hematoma.
Treatment of subdural hematoma
Treatment methods:
- Immediate hospitalization;
- Conservative treatment: Decongestants imupret and others);
- Drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain (verapamil, dilacor, felodipine, nifedipine, cavinton and others);
- Drugs to improve brain metabolism (Cerebronorm, Neo-Cerebron, Thiocetam, Cytoflavin);
- Painkillers (pentalgin, rapten, movaisn, meloxam and others);
- Antiemetic drugs (metoclopramide and others);
- Vitamins (groups A, C).
- Conservative treatment is carried out under constant monitoring of blood pressure.
With severe cerebral edema, which does not go away after blood suction, there are signs of melting of the nerve fiber and suspicion of the formation of intracerebral hemorrhages and blood accumulation. You can also
Recovery
The rehabilitation period after a hematoma in an adult takes about 6 months, in children much less. A number of rules will help speed up this process:
- strict adherence to sleep schedule;
- ensuring balanced nutrition;
- taking only those medications prescribed by the doctor;
- gradual return to normal activities.
Note!
Drinking alcoholic beverages is possible only after final recovery.
Recovery prognosis
A mild brain injury has a favorable outcome, in which mental and neurological functions are completely restored. A moderate bruise with timely and correct treatment also ends in complete recovery. In some cases, after it there is a slight lack of coordination of movements, vegetative-vascular dystonia and hydrocephalus.
Severe traumatic brain injury causes death in approximately 30% of cases. In addition, there is a high percentage of disability among surviving patients.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for the appearance of hematomas in the brain include:
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when there is a blow to the head or the head and a fall, which disrupts the integrity of the blood vessels of the brain.
- Hypertension (arterial hypertension), especially hypertensive crises.
- Anomalies in blood vessels (for example, aneurysms, as well as similar arteriovenous malformations), reducing the resistance of the walls of blood vessels, including capillaries.
- Disorders in the body accompanied by decreased blood clotting (such as hemophilia, etc.).
- Taking anticoagulant drugs (inhibiting blood clotting processes).
- Diseases of an allergic nature and/or infectious-allergic (such as rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, and others).
- GM tumors.
- Birth injuries.
The most common causes are TBI and hypertension (arterial hypertension). During a hypertensive crisis, accompanied by a rise in pressure to high levels, the blood vessels of the brain may burst, unable to withstand the stress.
No pattern was found, for example, between the appearance of a hematoma and its size depending on the severity of the injury.
Possible consequences of TBI
A hematoma on the head can lead to a number of consequences, such as:
- asthenia;
- frequent depression;
- impairment of motor activity: paralysis, numbness;
- chronic fatigue;
- impaired coordination of movements and speech function;
- uncontrolled bowel movements;
- urinary incontinence;
- decreased brain activity;
- sleep disturbance;
- dementia as a consequence of TBI.
Patients who have suffered a traumatic brain injury feel worse when weather conditions change.
Consequences after surgery
With timely treatment, the consequences of subdural hematoma and surgical treatment may be completely absent. The patient's postoperative period takes place in the intensive care unit under the round-the-clock supervision of a doctor and nursing staff.
CT scans are also routinely performed to promptly detect and prevent recurrent hemorrhage. Drug therapy and antibiotics are also used to prevent infection.
The postoperative period depends on the care:
- the head area should be clean;
- scar – no change in color;
- physical activity should be minimal;
- Regular ventilation is carried out.
Consequences of the operation:
- Intracranial hypertension;
- Partial or complete loss of mental and physical performance;
- Frequent headaches;
- Deformation of the area where the operation was performed;
- Hearing impairment;
- Visual impairment;
- Impaired speech, thinking, memory;
- Lability of behavior;
- Dizziness;
- Breathing and heartbeat disorders;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Disruption of the excretory system;
- Paralysis;
- Convulsions;
- Various neurological disorders depending on the location of the brain damage;
- Infectious diseases of the brain;
- Brain swelling;
- Bleeding.
After the operation, the patient is recommended to undergo long-term rehabilitation in medical resort institutions that specialize in the rehabilitation of brain functions.
Also recommended:
- undergo courses of therapy and diagnostics;
- avoid stressful situations and physical strain;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- Healthy food.
After the operation, the patient is assigned disability for three years. If there are no consequences, the disability may be revoked.