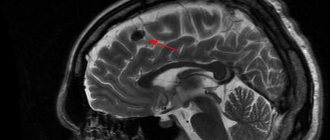
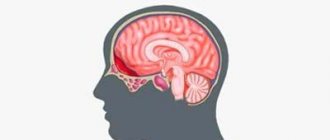
Brain sarcoma is a malignant oncological disease that develops from poorly differentiated connective tissue cells. The neoplasm penetrates into neighboring tissues and organs and is a metastatic form of cancer. Brain sarcoma is diagnosed in only 2% of patients. The disease can manifest at any age. The danger is that the tumor is detected in late stages, when even surgery does not help.
Causes of the disease
Modern medicine finds it difficult to give an exact answer to the question of why symptoms of spinal sarcoma occur. Doctors have not yet figured out the reason why healthy cells degenerate into malignant ones. However, there are a number of factors that can influence the development of spinal cancer in a person:
- spinal column injuries;
- influence of radiation;
- genetic defects that affect cell division and can cause spinal sarcoma;
- exposure to carcinogens on the body - contact with arsenic, asbestos, vinyl chloride and other harmful substances increases the risk of developing sarcoma;
- unhealthy diet with high levels of carcinogens;
- long-term exposure of a person to ultraviolet rays - in the sun or in artificial conditions;
- smoking;
- diseases of the spine of a congenital or acquired nature.
All of the above can cause spinal sarcoma, but these factors are not a direct threat. The occurrence of tumors in any part of the body and the appearance of metastases can lead to secondary lesions in the tissues of the spine.
Treatment for a common process
Chemotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for advanced disease because the drugs injected enter the bloodstream and reach cancer cells throughout the body.
The most common chemotherapy drugs used for soft tissue sarcomas are doxorubicin, trabectedin, gemcitabine, docetaxel, and paclitaxel. These drugs may be prescribed alone or in combination.
Chemotherapy in patients with progressive disease should be based on doxorubicin or epirubicin, both drugs belong to the anthracyclines. In patients with angiosarcoma, paclitaxel or docetaxel may be offered instead of doxorubicin.
Adding another drug(s) to doxorubicin or epirubicin may enhance the effect of systemic chemotherapy in some patients. This choice primarily depends on the histological type of cancer.
If the first chemotherapy does not give the expected result, then another chemotherapy may be offered. The choice of one or more drugs will depend on previously used drugs, as well as on the histological type of the tumor. Drugs that may be considered include ifosfamide, trabectedin, gemcitabine, docetaxel, and paclitaxel.
Targeted therapy
This treatment works by binding to a specific protein or structure involved in tumor growth and progression. Side effects differ from traditional chemotherapy and depend on the mechanism of action of the drug. Targeted drugs approved for use in soft tissue sarcomas in Russia are:
- pazopanib – for soft tissue sarcomas other than liposarcomas;
- imatinib – for dermatofibrosarcoma, when systemic therapy is required.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy may be used to relieve symptoms or prevent complications, such as bone metastases.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of metastases may be considered depending on their location and medical history. For example, when lung metastases appear long after initial treatment and when, in the opinion of the surgeon, they can be completely removed.
Types of sarcomas
There are several types of the disease that are worth knowing about.
Spinal osteosarcoma
The patient may experience signs and symptoms of spinal sarcoma affecting bone tissue. This type of disease is more often diagnosed in men, as well as in childhood and adolescence. The disease begins with mild pain, which patients rarely pay attention to in time. As the situation worsens, the pain does not go away at night, does not depend on physical activity and is not relieved by taking medications. Often the tumor grows into adjacent bone tissue. May affect one or more vertebrae at the same time.
Chondrosarcoma of the spine
This type of disease affects cartilage tissue. It often affects males aged 25-59 years. The development of the tumor begins with the vertebral arches and processes, often occurring in the sacral and lumbar regions. Can spread to other parts of the body - ribs, other vertebrae, etc.
Fibrosarcoma of the spine
Spinal sarcoma, the symptoms and manifestation of which begin with pain in the skin near the spinal column, can affect connective tissue. Where such a tumor occurs, a brown-blue node forms, which quickly increases in size. In addition, the tumor quickly spreads metastases throughout the body, which complicates further treatment of the patient.
Classification
Classification by tissue from which tumor formation occurs:
- Fatty – liposarcoma;
- Muscular:
- striated muscle tissue - rhabdomyosarcoma,
- unstriated muscle tissue – leiomyosarcoma;
- Vessels:
- circulatory – hemangiosarcoma,
- lymphatic – linfangiosarcoma;
- Connective – fibrosarcoma;
- Synovial membrane – synovial sarcoma;
- Nervous – neurogenic sarcoma;
- Skin – fibrosarcoma.
Symptoms
At first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but as the tumor grows, a person begins to complain about his health. How sarcoma manifests itself will depend on the location of the process. It can be located in:
- Thoracic department.
- Neck.
- Lumbar region.
However, general clinical manifestations of the disease can be identified. These include the following:
- symptoms associated with compression of the nerve endings of the spinal cord - a person complains of pain of a different nature from shooting to burning, the pain syndrome can intensify in a supine position, and the disease itself is easily disguised as neuralgia, chondrosis, radiculitis and others;
- paresthesia – the sensitivity of the skin is impaired, a tingling sensation, “goosebumps” occurs on the skin;
- the neoplasm can cause temporary paralysis, as well as numbness of the tissue around the tumor;
- a person complains of decreased sensitivity of the limbs and weakness.
One of the main symptoms and manifestations of spinal sarcoma is pain.
At first it appears occasionally, then it becomes constant. Sometimes body temperature can rise to 38 degrees. At night, the pain can intensify; taking medications does not help. As the disease progresses, the gait changes, coordination problems occur, incontinence may begin, the person loses weight, becomes weak and irritable, and apathy occurs. Hematomas may appear throughout the patient's body for no reason. Occasionally, the disease manifests itself only as compactions in the spine.
Examples of soft tissue sarcomas of the head and neck
Kaposi's sarcoma
Osteogenic sarcoma of the alveolar process of the maxilla
Osteogenic sarcoma of the mandible
Pleomorphic sarcoma of the soft tissues of the neck on the right
How to diagnose
Only an experienced specialist can determine sarcoma of the soft tissues of the spine. Neurologist
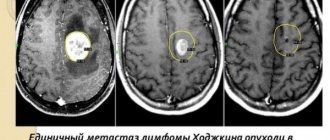
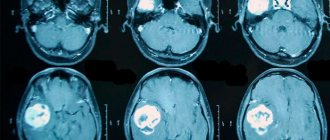
conducts an examination and interview, and based on the data obtained, can refer a person to an MRI, CT scan, or other procedure that allows visualization of spinal tissue. Using these methods, the doctor will determine the location of the tumor, its size, whether it has affected neighboring tissues, etc.
A blood test for tumor markers is often prescribed. Histology will help to refute or confirm the diagnosis. Often a puncture of the vertebral contents is performed for further examination.
Diagnostics
The presence of one or more symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a neurologist. For sarcoma, diagnosis can be invasive or non-invasive. Patients are prescribed the following non-invasive diagnostic methods: ultrasound, computed tomography and scintigraphy. Magnetic resonance imaging provides the most accurate results. Using it, you can determine the localization of the tumor, as well as the area of affected tissue.
Invasive types include measurement of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, as well as its cytological examination. For an accurate diagnosis, an immunochemical blood test and angiography (X-ray examination of blood vessels) may be necessary. When diagnosing sarcoma, a puncture is taken.
Treatment of spinal sarcoma
After looking at a photo of spinal sarcoma and learning about its symptoms and manifestations, it is also worth learning that surgical treatment of such a disease is not always possible. The fact is that often the neoplasm grows into nearby tissues and organs, which makes removal impossible. Doctors usually prescribe combination therapy, which includes radiotherapy and polychemotherapy. If metastases are present, high doses of radiation are required, after which the patient needs a bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
Prevention
Preventive measures help prevent the development of the disease. Under no circumstances should you expose your body to radiation even for therapeutic purposes.
Do not forget about routine magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, which can detect sarcoma in the early stages. Preventive measures include:
- Keeping a diary in which the duration, time of onset and intensity of headaches are noted, if they become bothersome. This information will help the neurologist.
- Following an anti-cancer diet, which includes a large amount of fresh vegetables and the absence of carcinogenic foods (bacon, smoked fish, salted meat).
- Giving up bad habits, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, getting a full eight hours of sleep, no stress, regular rest.
Recovery prognosis and survival
In general, if the tumor is small, does not grow quickly and does not metastasize, after treatment remission occurs in almost 70% of patients. If treatment is successful, survival after diagnosis of spinal sarcoma is high, and almost half of patients can live up to 7 years. About 30% of people diagnosed with sarcoma recover after chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
It is worth understanding that treatment should be carried out by an experienced doctor who has all the necessary knowledge and skills. Self-treatment will not bring positive results. If you are faced with manifestations of the disease, you should not hesitate to contact the clinic, because the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the higher the chances of successful treatment.
Advantages of treatment at Top Ikhilov
- Accuracy of diagnosis.
The clinic makes a diagnosis with 100% accuracy. - Highly professional medical staff.
Experienced oncologists work here, who have been dealing with the problems of treating brain sarcoma for many years. Many of them are world-class experts. - Innovation.
Here they use the latest methods of combating sarcoma, sometimes unavailable in other countries. Only those products that have proven their effectiveness are used. - Gentle therapy.
The selection of therapy is carried out in such a way as to minimize side effects and preserve the functioning of all systems and organs to the maximum. This applies to safe chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and the least traumatic brain surgeries. - Moderate cost.
Reasonable prices and an optimal ratio of quality and price attract medical tourists from all over the world. - Personal accompaniment.
The patient is accompanied by a representative of the international department, who helps resolve organizational issues, translate medical documents, etc.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(5 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Forecast
The prognosis for soft tissue sarcomas of the head and neck largely depends on the size of the tumor, primary location, etiology, and the presence of local or distant secondary foci of malignancy. With early diagnostic measures and adequate timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable.
Bibliography:
- NCCN Guidelines for Patients: Soft Tissue Sarcoma, 2021.
- Shah. Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology 5 ed., 2021.
- Soft tissue sarcomas: a guide for patients – Information based on ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines – v.2016.1
- Fedenko A. A., Bokhyan A. Yu., Gorbunova V. A., Makhson A. N., Teplyakov V. V. Practical recommendations for drug treatment of soft tissue sarcomas. Malignant tumors: Practical recommendations RUSSCO #3s2, 2021 (volume 9). pp. 272–282.