Perinatal lesions of the central nervous system
Lebed E. P., Stoyanov V. N., Gertsev V. N., Chemeresyuk I. G.
According to statistical data given in the medical literature, in the structure of childhood disability, lesions of the nervous system account for about 50%, with 70–80% of cases accounting for perinatal lesions.
Currently, the following types of perinatal brain damage are distinguished: 1) traumatic injuries; 2) hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE); 3) infectious lesions of the brain and/or its membranes; 4) congenital anomalies of brain development; 5) dysmetabolic lesions of the central nervous system. Hemorrhagic lesions of the central nervous system are related to several groups at once, since the main cause of intracranial hemorrhage is hypoxia, and as a component of injury they are always present in traumatic hemorrhages.
The most common cause of perinatal damage to the central nervous system is hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIP) - 47%, the consequences of which occupy a leading place in the structure of morbidity and mortality in children of the neonatal period and early age. Further, the causes of perinatal brain damage, depending on the frequency of occurrence, should be distributed as follows: anomalies and dysplasia of the brain - 28%; TORCH infections - 19%; birth trauma - 4%; hereditary metabolic diseases - 2%.
Clinical syndromes associated with perinatal hypoxia depend on the period of HIE: acute period syndromes include increased neuroreflex excitability, syndromes of general depression of the central nervous system, vegetovisceral dysfunction, hydrocephalic-hypertensive, convulsive, comatose state; The structure of the recovery period of HIE includes syndromes of delayed speech, mental, motor development, hypertensive-hydrocephalic, vegetovisceral dysfunction, hyperkinetic, epileptic, cerebroasthenic.
Some authors identify syndromes of motor disorders and increased neuro-reflex excitability in the recovery period. Nelson et al. noted in their studies that children with an Apgar score of less than 3 at 10, 15, 20 minutes and those who survived were more likely to have cerebral palsy, delayed psychomotor development, and seizures than children with a higher score.
Prognostic signs depend on the severity of clinical manifestations. The mortality rate of newborns with perinatal damage to the central nervous system of a hypoxic nature is 11.5% (among children with moderate cerebral disorders - 2.5%, severe - 50%).
In children with mild hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the neonatal period, complications do not arise. According to M.I. Levene, in 80% of full-term newborns, severe CNS HIP leads to death or severe neurological impairment.
Of the clinical manifestations, the most unfavorable in terms of prognosis and long-term neurological consequences are the appearance of seizures in the first 8 hours of life, recurrent seizures, persistent muscle hypotension and the transition of the phase of lethargy and hypotension to a state of pronounced hyperexcitability and hypertension of the extensor muscles.
It was noted that in children who suffered asphyxia with the subsequent clinical picture of DIE, and also had neurological symptoms along with asphyxia, the development of cerebral palsy occurred more often.
One of the most accessible methods of brain imaging is neurosonography, with which it is possible to assess the macrostructure and echogenicity of the brain matter, the size and shape of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
The method makes it possible to objectify morphological changes in the brain in newborns, in whom routine anamnestic and clinical neurological methods may not be enough to make a diagnosis; it allows one to suspect periventricular leukomalacia on the first day, to assume the presence of peri- or intraventricular hemorrhage and to clarify its degree.
Data from neurosonographic studies at various stages of the pathological process make it possible to evaluate the results of the therapy and determine the tactics of further treatment, and are also used for clinical observation of children in the first year of life with perinatal damage to the central nervous system.
Dopplerography, which allows one to assess the amount of blood flow in intra- and extracerebral vessels, is used in HIE to assess the intensity of cerebral blood flow in different phases of the vascular response to hypoxia. Computed tomography makes it possible to diagnose selective neuronal necrosis, lesions of the thalamus and subcortical ganglia, parasagittal lesions of the ganglia, periventricular leukomalacia, focal and multifocal necrosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging makes it possible to evaluate not only disturbances in the macrostructure of the brain matter, the localization and volume of intracranial hemorrhage, and the size of the cerebrospinal fluid tracts, but also to identify areas of decreased and increased density of the brain matter, in particular white matter. Thus, this method is indispensable in the diagnosis of periventricular and subcortical leukomalacia.
The positron emission tomography method makes it possible to determine the intensity of regional metabolism and the intensity of cerebral blood flow at various levels and in various structures of the brain. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy makes it possible to reflect delayed brain death and is informative not only for the diagnosis of DIE in the acute period, but also for the prognosis of the disease.
An important prognostic criterion is electroencephalography data. Normal EEG readings are highly correlated with favorable outcomes. On the contrary, indicators such as low voltage, bursts, suppression or absence of electrocerebral activity, and paroxysmal EEG are highly associated with adverse outcomes.
The consequences of perinatal CNS damage of an infectious nature are always serious. Among intrauterine infections accompanied by lesions of the central nervous system, there are a number of pathological conditions in which the detected brain disorders are of a specific nature. These include embryo- and fetopathies with TORCH infections.
Such newborns, against the background of general symptoms, are characterized by signs of multiple organ lesions with a predominance of one or another system, depending on the tropism of the pathogen. The pathogens that exhibit the greatest affinity for the central nervous system are rubella, cytomegaly, toxoplasmosis, and herpes.
Antenatal damage by representatives of this group entails severe, often irreversible organic and functional damage to the central nervous system (cerebral palsy, deafness, blindness, microcephaly, mental retardation, hydrocephalic, convulsive syndromes, impaired thermoregulation, intracerebral foci of calcification, severe meningoencephalitis).
With early diagnosis and active treatment, the prognosis for life is usually favorable; for complete recovery, it is unclear, since after an infection the pathogen can persist for months and sometimes years, predisposing to a number of diseases.
Causes of CNS pathology
The causes and consequences of damage to the central nervous system of newborns can be very different. The main factors that provoke disruption of the functioning of the nervous system are:
- lack of oxygen, or hypoxia;
- birth injuries;
- disruption of normal metabolism;
- infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy.
Lack of oxygen, or hypoxia, occurs when a pregnant woman works in hazardous work, with infectious diseases, smoking, or previous abortions.
All this disrupts general blood circulation, as well as oxygen saturation of the blood, and the fetus receives oxygen along with the mother’s blood. One of the factors leading to damage to the nervous system is considered to be birth trauma, since any injury can provoke a disruption in the maturation and subsequent development of the central nervous system.
Disruption of normal metabolism occurs for the same reasons as lack of air. Drug addiction and alcoholism of the expectant mother also lead to dysmetabolic disorders. In addition, taking potent medications can affect the nervous system.
Infectious diseases suffered by the expectant mother while carrying a child can be critical for the fetus. Among such infections it is necessary to highlight herpes and rubella. In addition, absolutely any pathogenic microbes and bacteria can provoke irreversible negative processes in the child’s body. Mostly, problems with the nervous system occur in premature babies.
Risk factors
The development of perinatal encephalopathy in the fetus and child can lead to
- chronic maternal intoxication and chronic diseases
- infectious diseases during pregnancy
- disorders of uteroplacental blood flow, placental abruption, fetoplacental insufficiency
- Umbilical cord entanglement
- maternal diseases associated with metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria, etc.)
- severe toxicosis;
- pathological course of labor, use of obstetric aid, weakness of labor, rapid labor
- prematurity;
- Fetal malformations
Periods of CNS pathologies
The syndrome of damage and depression of the nervous system combines several pathological conditions that occur during intrauterine development, during labor, and also in the first hours of a baby’s life. Despite the presence of many predisposing factors, only 3 periods are distinguished during the disease, namely:
- spicy;
- restorative;
- outcome of the disease.
In each period, damage to the central nervous system in newborns has different clinical manifestations. In addition, children may experience a combination of several different syndromes. The severity of each ongoing syndrome allows us to determine the severity of damage to the nervous system.
What is organic damage to the nervous system?
Organic damage to the central nervous system
- a pathological condition in which the brain does not function fully. The lesion can be congenital or appear due to trauma, stroke, infectious diseases of the brain, alcoholism and drug addiction.
Lesions are divided into grades 1-3. Stage 1 lesions are diagnosed in many people; they do not manifest themselves in any way and do not require treatment. Lesions of degrees 2 and 3 interfere with normal life and can provoke more dangerous diseases, so they need to be treated.
Acute course of the disease
The acute period lasts for a month. Its course directly depends on the degree of damage. With a mild form of the lesion, shuddering, increased excitability of nerve reflexes, trembling of the chin, sudden uncontrolled movements of the limbs, and sleep disturbances are observed. The child may cry very often for no apparent reason.
With moderate severity, there is a decrease in motor activity and muscle tone, weakening of reflexes, mainly sucking. This condition of the baby should definitely alert you. By the end of the first month of life, existing signs may be replaced by hyperexcitability, almost transparent skin color, frequent regurgitation and flatulence. Often, a child is diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome, characterized by a rapid increase in head circumference, increased pressure, bulging of the fontanel, and strange eye movements.
At its most severe, coma usually occurs. This complication requires the child to stay in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor.
Development of CNS lesions
In the process of development of lesions of the central nervous system, doctors distinguish three main stages:
- spicy;
- restorative;
- Exodus.
Acute period
This period lasts about a month. Its course depends on the severity of the damage. The mildest forms of lesions are shuddering, trembling of the chin, increased excitability, sudden movements of the limbs, abnormal states of muscle tone, and sleep disturbances.
Grade 2 severity is manifested at this time by a decrease in motor activity and muscle tone, reflexes will be weakened, especially sucking, which an attentive mother will definitely notice. In this case, by the end of the first month of life, such symptoms may be replaced by hyperexcitability, marbled skin color, flatulence and frequent regurgitation.
Often at this time, children are diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome. Its most obvious symptoms include a rapid increase in head circumference, increased intracranial pressure, which is manifested by a bulging fontanel and unusual eye movements.
When the severity is greatest, coma usually occurs. Such complications leave the child in the hospital under the supervision of doctors.
Rehabilitation period
Interestingly, it is the recovery period that can be more difficult than the acute one, if there were no symptoms as such in the first months. The second period lasts approximately from 2 to 6 months. This phenomenon is expressed approximately as follows:
- the baby hardly smiles, does not show emotions;
- the baby is not interested in rattles;
- the baby's cry is rather weak;
- The child practically does not roar.
If in the first period the symptoms were present quite clearly, then from the second month of life they may, on the contrary, decrease and disappear, but this does not mean that treatment should be stopped completely. This only gives reason to understand that the child is really recovering.
Result of CNS damage
By about a year of a baby’s life, the consequences of damage to the central nervous system become obvious, although the main symptoms go away. The result is:
- developmental delay - psychomotor, physical or speech;
- hyperactivity, which affects the ability to concentrate, learn, and remember something in the future, is also expressed in increased aggressiveness and hysteria;
- cerebroasthenic syndrome – poor sleep, mood swings, weather dependence;
- epilepsy, cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus are pathologies that develop with particularly severe lesions of the central nervous system.
Rehabilitation period
Damage to the central nervous system in newborns during the recovery period has the following syndromes:
- increased excitability;
- epileptic;
- motor disorders;
- mental retardation.
With prolonged violation of muscle tone, mental development delays and the presence of motor function disorders often occur, which are characterized by involuntary movements provoked by contraction of the muscles of the trunk, face, limbs, and eyes. This prevents the child from making normal, purposeful movements.
When mental development is delayed, the baby begins much later to hold his head up on his own, sit, walk, and crawl. He also has poor facial expressions, decreased interest in toys, a weak cry, and a delay in the appearance of babbling and humming. Such delays in the development of a child’s psyche should definitely alert parents.
Perinatal CNS damage
Perinatal damage to the central nervous system in newborns is a collective concept that implies a disorder of brain functioning. Similar disorders are observed in the antenatal, intranatal and neonatal periods.
Antenatal begins from the 28th week of intrauterine development and ends after birth. Intrapartum includes the period of childbirth, from the beginning of labor to the moment of birth of the child. The neonatal period begins after birth and is characterized by the baby’s adaptation to environmental conditions.
The main reason why perinatal damage to the central nervous system occurs in newborns is hypoxia, which develops during an unfavorable pregnancy, birth injuries, asphyxia, and infectious diseases of the fetus.
The cause of brain damage is considered to be intrauterine infections, as well as birth injuries. In addition, there may be damage to the spinal cord that occurs due to trauma during childbirth.
Symptoms largely depend on the period of the disease and the severity of the lesion. In the first month after the birth of a child, an acute period of the disease is observed, characterized by depression of the nervous system, as well as hyperexcitability. Muscle tone gradually normalizes. The degree of recovery largely depends on the extent of the damage.
The disease is diagnosed in the maternity hospital by a neonatologist. The specialist conducts a comprehensive examination of the baby and makes a diagnosis based on the existing signs. After discharge from the maternity hospital, the child is under the supervision of a neurologist. To make a more accurate diagnosis, a hardware examination is performed.
Treatment should be carried out from the first hours after the birth of the child and diagnosis. In the acute form, therapy is carried out strictly in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of a doctor. If the disease is mild, treatment can be carried out at home under the supervision of a neurologist.
The recovery period is carried out comprehensively, and at the same time, together with medications, physiotherapeutic methods are used, such as physical therapy, swimming, manual therapy, massages, and speech therapy classes. The main goal of such methods is to correct mental and physical development in accordance with age-related changes.
Hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system
Since it is often hypoxia that provokes damage to the nervous system, every expectant mother should know what leads to hypoxia and how it can be avoided. Many parents are interested in what hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is in newborns. The severity of the main signs of the disease largely depends on the duration of the child’s hypoxia in the prenatal period.
If hypoxia is short-term, then the violations are not so serious; oxygen starvation that continues for a long time is more dangerous. In this case, functional disorders of the brain or even death of nerve cells may occur. To prevent nervous system disorders in infants, a woman must be very attentive to her health while carrying a child. If you suspect the presence of diseases that provoke fetal hypoxia, you should immediately consult a doctor for treatment. Knowing what it is - hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system in newborns, and what the signs of the disease are, you can prevent the occurrence of pathology with timely treatment.
How does organic damage to the nervous system manifest and what is dangerous?
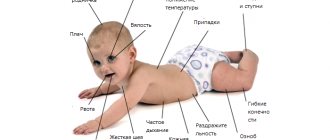
When the central nervous system is damaged, the following symptoms are observed:
- fast fatiguability;
- impaired coordination, inability to perform simple movements and actions because of this;
- problems with hearing, vision;
- inability to concentrate on a task, the need to constantly be distracted;
- trouble sleeping, insomnia, nightmares or constant awakenings;
- urinary incontinence;
- decreased immunity, which often causes colds and other diseases.
Brain lesions are especially dangerous for children who are lagging behind in physical development and cannot study normally and communicate with peers. Also, lesions lead to oligophrenia, that is, mental retardation, and dementia - loss of skills and knowledge, and the inability to acquire new ones.
Forms and symptoms of the disease
Damage to the central nervous system in newborns can occur in several different forms, namely:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
The mild form is characterized by the fact that in the first days of a child’s life, excessive excitability of nerve reflexes and weak muscle tone may be observed. A sliding squint or irregular, wandering movement of the eyeballs may appear. After some time, trembling of the chin and limbs, as well as restless movements, may be observed.
The average form has symptoms such as lack of emotions in the child, poor muscle tone, and paralysis. Convulsions, excessive sensitivity, and involuntary eye movements may occur.
The severe form is characterized by serious disorders of the nervous system with its gradual suppression. This appears in the form of seizures, kidney failure, disturbances in the functioning of the intestines, cardiovascular system, and respiratory organs.
Diagnostics
Since the consequences of damage to the central nervous system can be quite dangerous, it is therefore important to diagnose disorders in a timely manner. Sick children generally behave uncharacteristically for newborns, which is why when the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should definitely consult a doctor for examination and subsequent treatment.
Initially, the doctor examines the newborn, but this is often not enough. At the slightest suspicion of pathology, the doctor prescribes a computed tomography scan, ultrasound diagnostics, and x-rays. Thanks to comprehensive diagnostics, it is possible to identify the problem in a timely manner and carry out treatment using modern means.
Rehabilitation program for diseases of the central nervous system
Doctors of the neurological department of the St. Petersburg Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences conduct rehabilitation programs for patients with diseases of the central nervous system:
— chronic cerebrovascular accidents, consequences of stroke, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, consequences of spinal circulatory disorders;
- residual phenomena of inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system (encephalitis, arachnoiditis, meningitis, myelitis);
— consequences of brain and spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy;
- demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum diseases);
- diseases of the extrapyramidal nervous system and cerebellum (Parkinson's disease, dystonia, tremor, chorea, athetosis, tics, ataxia);
— rehabilitation of cancer patients in a multidisciplinary approach (consequences of surgical treatment, complications of chemotherapy and radiation therapy).
Purpose of rehabilitation:
► reduction in the severity of paresis (increased muscle strength),
► restoration of muscle tone,
►improving metabolism and tissue nutrition,
► improvement of cognitive functions (memory, attention, thinking),
► improved coordination,
► social and everyday adaptation.
The rehabilitation program includes:
- Stay in a 2-bed ward of the neurological department (14 days);
- Diagnostics (instrumental and laboratory);
- Consultations with specialists (initial and repeated)
- Drug therapy (nootropic, neurotrophic, metabolic, vasoactive);
- Medical massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Rehabilitation training with the inclusion of biofeedback (BFB) using several modalities (EEG, ECG, EMG, cardio, etc.)
- Physiotherapy:
- electrophoresis,
- normoxic oxygenation (pressure chamber),
- "Reabox" (dry carbon dioxide baths),
- ozokerite applications,
- electromyostimulation,
- medicinal baths
2-3 physiotherapy factors are used for 5 – 10 procedures each. The procedures are prescribed by a physiotherapist individually for each patient.
The duration of treatment is 14 days (with a stay in a single, double or multi-bed ward of the neurological department).
The estimated cost of rehabilitation, taking into account hospital stay, is 85,000 – 112,000 rubles. depending on the selected program duration and number of services.
At the St. Petersburg Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, you can undergo the entire range of necessary diagnostics.
Sign up for rehabilitation by phone. contact center 323 45 35.
Treatment of central nervous system lesions
Some pathological processes occurring in the baby’s body may be irreversible in an advanced stage, and therefore require urgent measures and timely therapy. Treatment of newborns should be carried out in the first months of their life, since during this period the baby’s body is able to completely restore impaired brain functions.
Deviations in the functioning of the central nervous system are corrected with the help of drug therapy. It contains drugs that help improve the nutrition of nerve cells. During therapy, drugs that stimulate blood circulation are used. With the help of medications, muscle tone can be reduced or increased.
To help sick children recover faster, osteopathic therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures are used in combination with medications. To carry out a rehabilitation course, massage, electrophoresis, reflexology and many other techniques are indicated.
After stabilization of the child’s condition, an individual program of supportive complex therapy is developed and regular monitoring of the baby’s condition is carried out. Throughout the year, the dynamics of the child’s condition are analyzed, and other therapy methods are selected to promote rapid recovery and development of the required skills, abilities and reflexes.
Treatment and rehabilitation for PCNSL
Treatment of PPCNS begins with measures to prevent it.
Before birth, mandatory monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out and, if any abnormalities are present, treatment is immediately prescribed. In severe cases, surgical delivery may be required.
During the perinatal period, children with suspected PPCNS are observed by a neonatologist. At this stage, intensive therapy is carried out, the child is in a specialized department.
After stabilization of the condition, in the absence of a threat to life, the recovery process begins - rehabilitation. The goal of this stage is to minimize the effects of brain damage.
At this stage, medications are used that improve trophic processes in brain tissue, massage to normalize tone and stimulate tactile and proprioceptors, exercise therapy and kinesiotherapy (Bobat, Vojta, etc.) to develop motor skills and prevent the development of contractures, it may also be necessary the use of special orthopedic devices to prevent or correct limb deformities. Botulinum therapy can be used to reduce tone.
The most important thing is to remember that all rehabilitation activities are carried out for one purpose - to provide an opportunity for the child to develop skills and make him as independent as possible in adulthood. Each child’s body is unique and the result of recovery in each specific case is very difficult to predict, however, the correct and consistent use of rehabilitation methods and techniques allows you to achieve maximum results. Cases of partial or complete restoration of central nervous system functions after PCNSL are far from uncommon.
Prevention of central nervous system damage
In order to prevent the occurrence of a serious and dangerous disease, it is necessary to prevent damage to the infant’s central nervous system. To do this, doctors recommend planning your pregnancy in advance, undergoing the required examinations in a timely manner and giving up bad habits. If necessary, antiviral therapy is carried out, all necessary vaccinations are given, and hormonal levels are normalized.
If damage to the baby’s central nervous system does occur, then it is important to provide assistance to the newborn from the first hours of his life and to constantly monitor the baby’s condition.
Consequences of central nervous system damage
The consequences and complications of central nervous system damage in a newborn child can be very serious, dangerous to health and life, and they are expressed in the form of:
- severe forms of mental development;
- severe forms of motor development, cerebral palsy;
- epilepsy;
- neurological deficit.
Timely detection of the disease and proper therapy will help get rid of serious health problems and prevent complications from occurring.
Causes of central nervous system damage in newborns
Suppression of the central nervous system of a newborn during and after childbirth can occur for three main groups of reasons: ischemic-hypoxic lesions, traumatic and infectious-toxic. Let's look at each group in more detail.
- Ischemic and hypoxic lesions of the central nervous system in newborns
are caused by a lack of oxygen in the child’s blood during childbirth. This may be due to long and protracted labor, weakness of labor, abnormalities of the placenta and umbilical cord. With ischemia (complete absence of oxygen), brain cells die, and the further picture of the disease depends on which part of the cortex this happens. - Traumatic lesions of the central nervous system
- in the vast majority of cases occur during childbirth. The immediate cause may be an early birth (the baby’s head is born very quickly and is injured), a large fetus, unskilled actions of the obstetrician, etc. - Infectious and toxic lesions
can be associated with viral infection, alcohol, smoking during pregnancy, etc.
Brain lesions most often have an ischemic-hypoxic nature, while the spinal cord is more often affected by physical trauma to the child’s neck during childbirth. To prevent this, it is very important to give birth in a good maternity hospital with a competent obstetrician, and in the first days after discharge, go to see an osteopath.