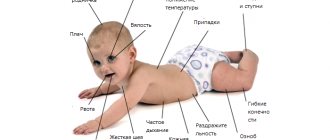
Angiopathy is an acute or chronic lesion of blood vessels, regardless of caliber (veins, arteries, capillaries suffer), accompanied by a triad of signs: a decrease in tone, which means a decrease in the quality of blood flow, paresis (partial “switching off” of the activity of the vascular muscles), spasm, that is, narrowing of the artery , veins, capillaries with impaired circulation of liquid connective tissue.
Vascular angiopathy has multiple origins, there are a number of causes for its development, which makes immediate diagnosis difficult. A well-developed research tactic is required.
Symptoms are not always typical, and disturbances in well-being are not present in all cases, especially in the early stages of the development of the pathological process.
Treatment is conservative; if necessary, surgical correction is performed, but these are extremely rare cases.
Development mechanism
The pathological process is based on a whole group of disorders. There are three main points.
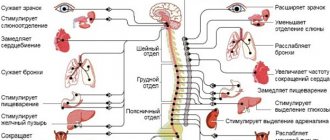
- Changes in the nervous regulation of vascular tone. As a rule, it is represented by insufficient functional activity of the central and peripheral systems.
It is accompanied by weak impulse transmission, because the arteries, veins, capillaries are in reduced tone, but at the same time a spasm often develops, that is, a narrowing of the structures and disruption of local blood flow.
- Next comes the hormonal factor. A group of specific substances is responsible for the normal functional activity of blood vessels: cortisol, adrenaline, aldosterone, angiotensin-2, and partially renin, which is an intermediate compound.
All of them, when synthesized excessively, provoke disruption of the normal functioning of arteries and other vessels.
When the factor is corrected, the pathological process quickly disappears and the blood flow returns to normal.
Metabolic abnormalities should be considered in a broader context; other metabolic processes also play a role.
- The third factor, which is somewhat less common, is infection.
In this case, narrowing and destruction of one, or very rarely several, vessels is observed; a clear localization of the disorder can be detected, which is extremely difficult, if not impossible, to do in other cases.
Typically, this form of angiopathy is the result of phlebitis, or vasculitis.
It is extremely rare that an isolated factor in the development of the disease is discovered. Much more often, doctors have to deal with a whole group of reasons.
The problem is that these disorders, one way or another, give rise to other pathogenetic mechanisms, and the longer the condition exists, the more complex it becomes both in terms of diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion - at the first symptoms of a disorder or if one is discovered during an examination, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Profile specialists - vascular surgeon (or general practitioner, if there is none in the access area), hematologist. It is possible to involve other doctors.
What is the danger of the disease?
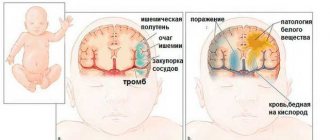
In itself, this disease is not a dangerous condition for the child, but the same cannot be said about its consequences. As is known, the thalamic nuclei are responsible for a number of important functions related to the perception and processing of information that comes from the senses. That is why, with the progression of the pathological process and an increase in the ischemic zone, the following complications are possible:
- complete or partial atrophy of the thalamus;
- child's retardation in psychomotor, mental and physical development;
- the appearance of signs of disorders on the part of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of perception (except smell);
- the appearance of pathological reflexes in the baby;
- determination during examination and instrumental examination of signs of ischemia of cerebral tissues;
- mental disorders in a child.
Classification
In medical practice, a generalized typification of process types is used. It is based on a single criterion - the localization of the violation plus its origin.
Accordingly, the following types are distinguished:
- Juvenile type. As the name suggests, it develops in young people. Years - from 13 to 18, maximum 20. In this case, it is mainly representatives of the stronger sex who suffer, the ratio with girls is almost 3:1.
Apparently, this is due to greater hormonal instability. The reasons are not completely clear; it is assumed that the restructuring of the body during puberty (puberty) is to blame.
In approximately 70% of patients, it resolves on its own, without correction; in other situations, assistance is required. The issue is resolved at the discretion of the specialist after undergoing a thorough diagnosis.
- Traumatic. It develops as a result of damage to the wall of a particular vessel.
This includes not only the gross influence of external factors such as bruises, fractures, etc., but also the operation performed, catheterization, especially careless ones.
A feature of this type of disorder also lies in the increased likelihood of the formation of blood clots, blood clots that can clog the vascular bed and lead to gangrene or death.
- Hypertensive. The result is a course of high blood pressure.
It occurs in almost all patients with hypertension, but to varying degrees. These are mainly subtle changes in the lower extremities, brain and fundus.
It makes sense to undergo regular preventive examinations. By controlling the pressure, the problem is gradually eliminated; special treatment is required in extreme cases if the process is advanced.
- Hypotonic variety. Oddly enough, vascular tone also changes with low blood pressure. True, in this case the process proceeds more sluggishly. However, sudden changes in the tonometer reading are extremely dangerous and can lead to destruction of the arteries and bleeding. It’s hard to say how this will end.
- Diabetic type. It is also metabolic angiopathy, one of its varieties. Formed as a result of metabolic disorders. The processes affect the condition of the arteries of the lower extremities, coronary vessels and others, so the entire body suffers at once.
The only way to avoid complications is to normalize the activity of the endocrine system.
- Cerebral angiopathy is damage to brain vessels of various sizes: from veins and arteries to capillaries. The entire network suffers, making the condition extremely dangerous. Possible spontaneous death of nerve fibers, stroke with the development of severe neurological deficit. This variety occurs frequently.
- Vascular angiopathy of the lower extremities. Accompanied by a violation of the trophism of leg tissues, the rapid development of stagnation, in the future, over the course of years or even months, a catastrophe with tissue death, gangrene and the need for serious surgery is possible.
- Amyloid angiopathy. Another metabolic type. A characteristic feature is the deposition of the protein of the same name on the walls of blood vessels. It is extremely rare, but difficult to cure.
- Disruption of the retinal structures. Retinopathy is detected in both diabetes and hypertension. In the first case, new imperfect structures grow, which are fragile, destroy on their own and lead to bleeding. In the second, the arteries narrow, which makes adequate nutrition of the peripheral part of the retina impossible. Hence the dystrophic processes.
- Coronary type. A distinctive feature is a disruption of the normal nutrition of the heart. Sooner or later this becomes the cause of a massive heart attack. With proper treatment, a disastrous outcome can be avoided in most cases.
The classification is of key practical importance, both in terms of selecting diagnostic tactics and from the point of view of developing a therapeutic strategy for a long period.
Symptoms
Manifestations depend on the specific type of pathological process. The most common varieties should be considered.
Diabetic angiopathy
Accompanied by a systemic disturbance of blood flow throughout the body. Mainly the brain, retina, and lower extremities are affected.
Accordingly, the manifestations will be as follows:
- Decrease in visual acuity, gradual, over several years. Less commonly, the process occurs faster and is more aggressive.
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Discomfort in the legs, feeling of heaviness.
- Headaches, nausea, vomiting (rare).
- Problems with spatial orientation and coordination.
- Long-term lack of healing of wounds, even the most minor ones.
These are typical manifestations. The list is incomplete, but it reflects the complex nature of the disorder. There are dozens more signs, the specific clinic depends on the case.
Hypertensive type
It resembles that of diabetes, only the lower extremities are practically not affected. Target organs are hearts, kidneys, eyes, brain.
Signs are specific:
- Chest pain. Arrhythmias. Increased fatigue after physical activity.
- Swelling, discomfort in the lower back, frequent or, conversely, rare urination, which indicates a violation of filtration.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Headache, nausea, inability to navigate normally in space.
Symptoms of the hypertensive type of angiopathy develop gradually.
Severe dangerous damage to arteries and other vessels is noticeable already at stage 2 of hypertension, when it is difficult to correct.
Changes in the fundus and cardiac structures are detected earlier, but the patient himself does not notice them.
Retinal lesion
A typical feature of this is a disruption of the normal nutrition of fibers, including the nerve and peripheral parts of the sensitive membrane.
Accompanied by a group of violations:
- Decreased visual acuity. Gradual or rapid, depends on the specific type of pathological process.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Burning, redness of the whites.
- Problems with focusing.
Over a long period of time, scotomas develop—areas of loss of visual field. They look like large black spots that block part of the view. They are localized in the center, less often in other areas.
Attention:
The danger comes from the growth of new blood vessels in diabetes or lack of nutrition in the periphery of the retina.
Both cases increase the risks for vision in the future. Moreover, there is no effective treatment today.
Lower extremity lesions
Violation of normal nutrition of the legs gives a typical clinic:
- Feeling of heaviness, pressing pain at rest. Strengthens while walking, when changing body position.
- Impaired motor activity. Gradually, moving becomes a difficult task, and then impossible, because the limbs, as patients describe, are filled with lead and do not obey.
- Edema.
Heart damage
The clinical picture resembles that of coronary insufficiency. Pain in the chest, heaviness, and a feeling of pressure somewhere inside are detected.
As it progresses, arrhythmias develop like tachycardia, then the reverse process with a decrease in heart rate.
The danger lies in provoking a heart attack. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, this outcome is the only possible and most threatening.
Coronary angiopathy can be detected only by diagnostic results, at least echocardiography. It will be necessary to differentiate the disorder from others.
Juvenile type
Occurs relatively often. It has an extremely unstable course. Difficult to detect, it is often necessary to hospitalize the patient and maintain constant dynamic monitoring of the condition.
As such, treatment usually does not require. It goes away on its own. But it makes sense to carefully monitor the patient so as not to miss dangerous complications. They occur in approximately 10% of cases or even less.
Brain damage
Angiopathy of cerebral vessels gives typical neurological manifestations:
- Headache.
- Disorientation in space.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting (rarely).
- Decreased vision, speech, hearing and functioning of other senses.
The symptomatic complex also largely depends on the type of vessels that change. Thus, the signs of macroangiopathy, in which arteries are involved in the process, are pronounced and difficult to miss.
Description of the pathology
There are symptoms characteristic of circulatory disorders in the brain. This:
- scattered attention and decreased concentration;
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness;
- memory impairment and restless, anxious sleep;
- short-term loss of consciousness.
It is quite difficult to identify the cause of such disorders; in this case, one cannot do without a comprehensive neurological examination. It will take a lot of time, effort and patience to get to the bottom of the truth, so a positive result depends on the professionalism of the doctors and the child’s parents.
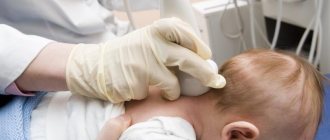
What is the diagnosis? For young children and newborns, there are several absolutely painless methods for determining cerebral circulatory disorders and checking its vascular system:
- Radiology - to identify the causes of increased pressure inside the skull, to check the condition of the fontanelles and cranial sutures of newborns.
- Computed tomography of the head - for information about the structure of the brain and the functioning of its hemispheres.
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the skull of newborns and children under 1 year of age to examine the structure of the brain, its functionality, biochemical indications, to identify vascular diseases at the initial stage.
- Dopplerography is a thorough examination of blood vessels, their direction, and the speed of blood flow. Helps identify pressure fluctuations inside the skull if cerebral circulation is impaired.
- Magnetic resonance imaging - to detect even slight displacement of the brain, tumors, hemorrhages, and injuries during childbirth.
- Electroencephalography - to study brain electrical impulses in the form of a graphic image, to obtain information about tumors, brain injuries, and the possibility of seizures in a child.
Such methods allow a specialist to see a fairly detailed picture of the existing problem, determine the condition of the vessels supplying the brain, the quality of functioning of its structures, and pathological changes (even in the absence of symptoms).
You should pay attention to the appearance of any deviations or complaints from the baby and immediately visit a specialist for consultation and a possible diagnosis. Early treatment of a developed disease is the key to successful elimination of the pathological condition of the child’s blood vessels. The indications for brain diagnostics today are quite extensive. Modern pediatrics is able to apply the latest techniques to study the brain of newborns if the following deviations from the norm exist:
- pathology in organ development;
- brain tumors or lesions;
- hemorrhage inside the skull;
- hydrocephalus of the occlusive (closed) type.
Causes
Development factors are diverse. There are over a dozen of them. A sample list looks like this:
- Diabetes mellitus in the decompensation phase. If the condition is not corrected by medications and other conservative methods.
- Intoxication with salts and metal vapors, toxic substances.
- Autoimmune diseases, especially systemic ones. Like rheumatism and others.
- Sepsis.
- Metabolic disorders other than diabetes. Endocrine diagnoses.
- Anatomical defects, abnormal development of blood vessels. It is extremely difficult to detect a problem until it makes itself known by blood flow disturbances.
- Hypovitaminosis, lack of microelements in the body.
- Smoking, alcohol abuse. Especially the use of drugs.
- Excess body weight.
- Lack of physical activity, physical inactivity.
- Harmful working conditions with elevated temperatures, background radiation, and contact with chemicals.
- Vascular injuries.
- Age 50+.
- Consumption of large amounts of salt.
Factors need to be considered in the system.
Attention:
The search for etiology (root cause) is especially important, because without knowing the origin of the disease, it is impossible to carry out proper treatment, which will become a problem.
Doctors will be forced to deal with the investigation, and this is the path to progression and constant relapses.
Diagnostics
It is carried out under the supervision of a vascular surgeon, hematologist, and if necessary, other specialists are involved.
The survey tactics include the following activities:
- Oral questioning of the patient and collection of anamnesis. It is necessary to obtain primary information about well-being and health throughout life.
This is important because it allows us to draw up a clinical picture and a portrait of the patient himself over the course of many years.
Without a differentiated approach, it is impossible to talk about effective diagnosis. A person’s task is to answer doctors’ questions in detail and to the point.
At this stage, it is important to detect the intended localization of the disorder, damage to the vessel. Further, targeted research is aimed at identifying the pathology itself.
- Ophthalmoscopy. Fundus examination.
- Ultrasound Dopplerography of blood vessels. Duplex scanning. Allows you to evaluate the speed of blood flow, its quality, possible disorders and their nature.
- X-ray.
- Angiography.
- ECHO-KG, ECG.
- MRI with or without gadolinium (contrast enhancement).
This is usually enough to make a diagnosis.
Is it necessary to treat lenticulostriate angiopathy?
As is known, the thalamo-striatal region of the brain is responsible for a number of important functional aspects on which the normal functioning, growth and development of the child’s body depends. That is why, after discovering pathological inclusions of calcium salts in a given area, most neurologists suggest the baby’s parents undergo a course of treatment. The main goal of such therapy is to restore adequate blood circulation in the cerebral tissue and eliminate the consequences of ischemia.
What happens if, during the first neurosonographic study, calcifications were discovered in a child aged one month, which affected the striatal zone?
Such young patients are registered with a pediatric neurologist, and at three months of age they undergo a repeat ultrasound examination with monitoring of changes. Sometimes it happens that pathological inclusions resolve on their own; in other cases, calcifications increase in size and provoke an expansion of the ischemic zone.
In the latter case, the child is prescribed drug treatment aimed at correcting disorders, improving trophism and metabolism of cerebral structures.
If there are calcifications along the striatal vessels, the child is recommended to take daily medications to help restore normal blood flow in ischemic tissues. This treatment is carried out for three months, after which its results are assessed. As a rule, young patients take the drugs Cortexin and Pantogam, against which the inclusions either completely disappear or decrease in size.
In cases where the baby is resistant to the therapy and calcifications increase to large sizes, the child’s parents are recommended to consult a pediatric neurosurgeon, who will offer the option of the most correct surgical intervention to eliminate the pathological formations.
Treatment
To treat angiopathy, medications from several pharmaceutical groups are used:
- Means for normalizing microcirculation. Pentoxifylline and analogs.
- Medicines against high blood pressure. ACE inhibitors (Perindopril), centrally acting agents (Moxonidine, Physiotens), beta blockers (Carvedilol, Metoprolol, Anaprilin and others), calcium antagonists (Diltiazem, Verapamil).
- Blood thinners. Aspirin and its analogues for long-term use. In dangerous cases - Heparin and similar drugs.
- Statins. At risk of developing atherosclerosis with the deposition of cholesterol plaques. Atoris and others.
If necessary, antiarrhythmic drugs (Amiodarone, Quinidine), cardiac glycosides (Corglicon, Digoxin, tincture of lily of the valley) are used.
To normalize brain nutrition, nootropics (Glycine), cerebrovascular and antihypoxic drugs (Piracetam, Actovegin) are prescribed.
In extreme cases, surgery is required. Fortunately, these are exceptional situations.
Other methods, such as exercise therapy, physiotherapy, diet, are not always required. This question needs to be clarified by a specialist.
Possible complications
- If the brain is damaged, there is a stroke and severe neurological deficit.
- Heart attack.
- Eye - blindness.
- Kidney - insufficient filtration.
- Lower extremities - tissue death, necrosis or gangrene.
- Possible involvement of abdominal vessels. In this case, massive bleeding.
The natural outcome in the absence of therapy is severe disability or death. Both options are common. You can avoid such a sad outcome if you start treatment on time.
Useful video
At the first symptoms of neurological abnormalities in a newborn, consultation with a neurologist is not only desirable, but also recommended. If there are any abnormalities in the newborn, the pediatrician will refer you to a specialist. Striatal angiopathy at one month of age does not require treatment, but at 3 months, special therapy is needed to eliminate it. If there is no clinical effect from treatment, gentle surgical intervention may be prescribed.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.