Symptoms, degrees, consequences and treatment of cerebral ischemia
Cerebral ischemia is a decrease in blood flow caused by cerebral atherosclerosis (from the Latin cerebrum - brain).
The brain performs the following functions:
processes information coming from the senses;
determines the mood, creates an emotional background;
A failure in its operation threatens the functioning of the entire organism. Numbness, a symptom of cerebral ischemia, is caused by sensory information not being processed correctly or transmitted through neurons. These are the same causes of temporary blindness. The brain is involved in decision-making, so patients with CCI - chronic cerebral ischemia - experience inhibition of thought processes.
Any pathology of the higher part of the central nervous system - the central nervous system - negatively affects many factors of life. Symptoms may be hidden - this is typical for the initial stage of the disease. The brighter they appear, the more advanced the disease.
There are two forms of the disease:
The first develops according to the principle of a transient ischemic attack - TIA, micro-stroke or an attack of acute cerebrovascular accident - ACVA. This is transient ischemia, otherwise known as transient cerebrovascular accident - TCI or ischemic stroke. The cause of the acute condition is blockage of the blood flow by an embolus or an advanced chronic form of the disease. The latter, in turn, develops gradually as the bloodstream narrows.
Cholesterol plaques are lipoproteins of the lower density limits. They are the ones who “choke” the organs, causing circulatory hypoxia. They can break away from the site of formation and circulate through the vessels. Emboli can be cholesterol or blood. Blood clots are dangerous due to the possibility of developing an inflammatory process.
Prevention of ischemia, like many other diseases, consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary, if possible, to avoid stress, not to overeat, adhere to an “anti-cholesterol” diet, play sports, give up alcohol and smoking, and spend time in the fresh air.
Possible consequences of ischemia
Since currently no single method or means of treating ischemia has been developed, its consequences can be quite serious and unpredictable. Here are just a few of them:
- Chronic headaches leading to increased irritability and depression.
- Psychological problems , and in particular mental retardation. The most common tendency is for a child to remain silent. It becomes difficult to teach him something new.
- Development of epilepsy.
As you can see, cerebral ischemia in newborns can have serious consequences . That is why this disease should in no way be treated dismissively or frivolously. A young mother should take care of the baby’s health and follow all the advice of specialists who, without a doubt, will contribute to the life of the family. Only attention to detail and subtle manifestations will help the child avoid disability and psychological trauma. Be more caring and gentle with your child, do not be afraid to consult a doctor once again and seem like an alarmist. If you doubt the well-being of your own baby and are afraid of harming his health by showing neglect, then you will most likely achieve the most undesirable results. By carefully and meticulously asking a doctor about various aspects of the disease, you are just giving yourself additional guarantees, taking note of all the necessary nuances!
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
There are many symptoms of cerebral ischemia:
nervous system dysfunction causing speech or vision problems;
sudden mood swings;
shallow and rapid breathing;
feeling of coldness in the palms and feet.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may worsen. It progresses in stages. Experts distinguish 3 stages or degrees of development of ischemia. Some also highlight a fourth.
Separately, the symptoms of an ischemic attack should be listed:
attacks of zonal loss of sensitivity;
paralysis of an area or half of the body;
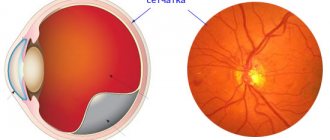
monocular vision loss (one-sided blindness).
Problems with the eyes occur because signals from them are sent to the visual cortex, located in the occipital lobe. Local numbness is due to the fact that neurons of the somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe, where tactile information is transmitted, are affected.
The red nucleus of the brain stem, basal ganglia, cerebellum and more are responsible for human motor activity. When the processes occurring in the motor areas of the cortex in the frontal lobes are disrupted, the patient has difficulty regulating movements, even to the point of paralysis. Different parts of the brain are responsible for different factors of life. Emotions are controlled by the amygdala, attention by the reticular formation, and memory by the hippocampus.
The difficulty in diagnosing some brain diseases is that their symptoms are similar to “standard” changes in well-being in older people. Another feature of cerebral ischemia is that its symptoms are very individual, because In different people, different parts of the main organ of the central nervous system are affected. Observations from the patient's relatives play an important role in diagnosis. They are able to provide a more accurate description of the changes taking place. Due to lethargy and confusion of consciousness, one cannot completely rely on the patient’s words.
Causes of cerebral ischemia
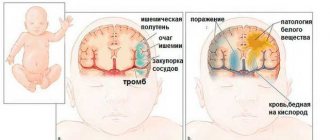
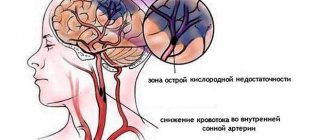
There are basic and additional prerequisites. The first include insufficient cerebral circulation, which leads to hypoxia - oxygen starvation. It occurs due to a narrowing of the lumen of the artery or its complete blockage - obturation. Without oxygen, cells cannot fully function. If this process is delayed, necrosis may begin - tissue death, otherwise called a heart attack. Brain hypoxia is characteristic of pathologies such as arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis due to the growth of fatty deposits on the inner wall of cerebral vessels.
Blocking of the lumen of a cerebral artery by a blood clot is called thrombosis. A blood clot forms directly in the brain or is carried in the blood from another part of the body. A traveling thrombus is called an embolus. It forms on the wall, but under the influence of some factors it breaks off and moves through the circulatory system until it gets stuck in the narrowest place of the arterial canal. A narrowing of the lumen can be observed not in one place, but in several at once.
Additional causes of cerebral ischemia include:
cardiovascular diseases accompanied by disturbances of central hemodynamics. For example, acute heart failure due to myocardial infarction, bradycardia, tachycardia;
vascular abnormalities, for example, compression, local spasm of the artery;
compression of the artery from the outside, for example, by a tumor;
Diagnostics
At the first stage, immediately after birth, a visual examination of the newborn is performed, an assessment of respiratory and cardiac activity, a check of reflexes, and a determination of the neurological status. To confirm the diagnosis of cerebral ischemia in an infant, the following methods are used:
- Anamnesis collection. Condition of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth. Data from the mother’s somatic and obstetric-gynecological history, as well as features of the course of pregnancy and childbirth are taken into account.
- Neurological status of the child in dynamics. Assessment of muscle-postural tone and reflexes (Infanib scale).
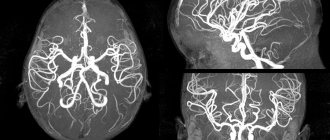
- Neurosonography.
- Dopplerography of blood vessels.
- Echoencephalography.
- CT, MRI.
Instrumental studies reflect the nature and localization of organic lesions of brain structures, as well as the dynamics of the development of disorders (progress or regression). If hypoxic or ischemic damage to areas of the brain is suspected, an electroencephalographic study is performed repeatedly, at approximately 40, 44 weeks from the moment of conception, at 6 and 12 months. Electroencephalography with topographic mapping and visualization allows us to judge the bioelectric activity of the brain of infants. EEG study shows:
- Irritation (irritation) of cortical structures, which leads to dysfunction of the cortex. Often occurs against the background of deteriorating blood supply to areas of the brain.
- Polymorphic polyrhythm (multiplicity). Several parallel basic brain rhythms, similar in amplitude.
- Diffuse vibrations that exceed normal amplitude values.
Ischemia in newborns
02/17/2015 Newborns Ischemia occurs due to the fact that in one or another organ there are disturbances in the blood supply, and, accordingly, in oxygen supply, because in this case there may not be enough of it. Subsequently, two directions of the disease can be distinguished: ischemia and hypoxia. With hypoxia, the cells of a certain organ or the body cannot receive oxygen at all or, for some reason, use it. With ischemia, there is not enough oxygen due to blockages in the vessels.
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn baby
Almost all causes that cause ischemia can be eliminated with medications or surgery. If the blockage of the vessel is removed, blood begins to flow normally to it and thus the functioning is completely restored. Of course, in order to save the organ, it is necessary to start treatment on time, otherwise all the changes can no longer be reversed. This mainly applies to the functioning of the brain, which needs a huge amount of air for normal functioning.
Causes of cerebral ischemia in a newborn baby
It is very difficult to understand that a newborn child suffers from cerebral ischemia.
He cannot tell you what hurts him or describe these pains. Most often you can find cerebral ischemia in children who were born prematurely. Such children must be carefully examined while they are in the maternity hospital. If these examinations show a problem, namely cerebral ischemia, then you need to start treating it immediately, because such a disease is considered a very serious pathology in perinatal neurology. The whole difficulty lies in the fact that there are practically no methods of therapeutic treatment of the problem. Cerebral ischemia itself can occur for several reasons:
- poor circulation in the placenta during pregnancy;
- maternal hypertension;
- anemia;
- too long and difficult childbirth;
- infection of the child during childbirth;
- birth injuries in a child.
There is a very high risk of ischemia if:
- the child’s mother was over 35 years old at the time of pregnancy;
- premature placental abruption occurred;
- the baby is lying incorrectly in the womb;
- the birth was late or premature;
- multiple births;
- with clouding of amniotic fluid.
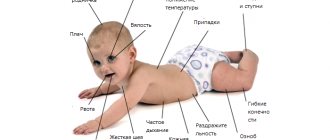
In the presence of ischemia, a newborn baby may experience a huge number of symptoms, including: tremors, restlessness, poor sleep, flinching and convulsions, weakened reflexes, hydrocephalus and enlarged head. This is not a complete list of symptoms and may vary significantly for each child.
Consequences
The consequences of cerebral ischemia in children depend on the severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the effectiveness of the therapy. After an intensive course of treatment, a rehabilitation period is needed, on which the prognosis will also depend. Among the most common consequences are:
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- mental retardation;
- constant irritability;
- epilepsy;
- isolation;
- learning difficulties.
The problem of ischemia in newborns is quite relevant in modern pediatrics. In some cases, the disease becomes a cause of disability and results in the child’s inability to further social adaptation. Complex treatment of severe forms of ischemia and its consequences is a long and complex process that requires effort, patience and attention from doctors and parents.
Degrees of ischemia in a newborn and its treatment
Ischemia
is a very dangerous disease that is quite difficult to detect and can lead to serious consequences if not treated in a timely manner. Therefore, if you have any suspicions or notice that something is wrong with your child, you need to be examined immediately.
Today, there are three types of ischemic disease in newborns. If the child has a mild degree of the disease, then during the first week of life one may notice excessive activity or severe depression. If convulsions and severe tremors have been noted for a long time, then doctors begin to talk about moderate ischemia. If a newborn child has been diagnosed with a severe degree of the disease, then he should be immediately sent to the intensive care unit. If a child has mild or moderate ischemia, then the risk of developing a neurological disorder is very low and such cases are rare today. But if there are still some disorders, they will most likely be classified as functional. If you start treating ischemia in a timely manner, you can get rid of the disorders quite quickly, without serious consequences for the child’s health. If a severe degree of coronary artery disease is detected in a newborn, it immediately leads to serious damage to the nervous system. The consequences in this case will be: convulsions, problems with hearing and vision, delays in physical and mental development.
Degrees of the disease
The consequences of oxygen starvation for the central nervous system are divided into 3 groups.
1st degree cerebral ischemia. This is a mild form. The baby is often overexcited or, on the contrary, lethargic. With a timely response, it can be protected from further progression of the disease. After the mother and child are discharged from the maternity hospital, they remain under the supervision of a specialist.
Ischemia grade 2 (moderate) in a newborn. Manifests itself in seizures and neurological disorders. These include sudden breathing problems, weakened muscle tone, decreased basic reflexes, fainting, and hydrocephalus. Treatment of this stage of the disease is carried out in a medical institution.
Cerebral ischemia grade 3. It is considered the most serious disease. Characterized by respiratory arrest, complete absence of reflexes, arrhythmia, low blood pressure, and strabismus. Sometimes the baby falls into a coma. For treatment, he is placed in the intensive care unit.
The first and second degrees of pathology are treatable. In the third case, the patient’s condition can be stabilized, but he will face a long rehabilitation period. The main thing is to notice violations in time and seek help.
How to treat cerebral ischemia in a newborn baby
Today, doctors have not only experience, but also the ability to treat cerebral ischemia in a newborn child. With the help of timely therapy, it is necessary to restore normal blood circulation and create all conditions for the full functioning and restoration of damaged areas of the brain. If mild ischemia occurs, as a rule, only massage is sufficient and there is no need to take medications. In a moderate to severe situation, you need to treat each child individually and select treatment based on the indicators and taking into account the examination results. Such children are usually hospitalized, especially for newborns up to one month of age. After all, their condition may be critical. Then, for about another year, the recovery period will continue during which the necessary treatment will be used.
Treatment of cerebral ischemia in children
In modern pediatrics, cerebral vascular ischemia in newborns is successfully treated with timely diagnosis and mild disease. The main goal of therapy is to restore blood circulation, timely resuscitation of damaged areas of the brain and save the rest. There are a few techniques:
- at first, only massage is prescribed, since medications for a small organism are stressful and the risk of multiple consequences;
- if massage does not help, medications are prescribed depending on individual indicators.
Cerebral ischemia in a newborn is a serious disease that can only be cured with timely and correct treatment. The consequences of pathology are determined by its severity.
Why does ischemia occur in a newborn and what is its danger?
Ischemia in a newborn (cerebral ischemia) develops when there is insufficient supply of oxygenated blood to the baby’s brain.
Nervous tissue reacts extremely sensitively to oxygen starvation, so disruption of the blood supply quickly leads to the development of metabolic disorders and brain damage. In the first stages, perinatal hypoxia (oxygen starvation) promotes the redistribution of blood flow between organs to maintain sufficient cerebral blood supply.
However, prolonged deficiency of O2 in the blood (hypoxemia) and progressive hypercapnia (increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood) contribute to impaired vascular autoregulation and the development of cerebral hypoperfusion (decreased blood flow in the cerebral vessels).
What is HIE and cerebral ischemia?
A decrease in SMC leads to damage to endothelial cells and a sharp narrowing of the capillaries of the brain. As a result of this, the resistance of the vascular bed to blood flow increases, contributing to:
- disruption of autoregulation of blood supply;
- significant worsening of ischemia in the newborn;
- development of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE).
The term HIE implies the presence of acute damage to the brain, as a result of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and ischemia (lack of blood supply). That is, the term cerebral ischemia in newborns is considered to have a broader meaning, including both primary O2 deficiency and impaired cerebral perfusion.
Neonatal cerebral ischemia also includes ischemia caused by blue-type congenital heart defects ( tetralogy of Fallot , Ebstein's anomaly).
The severity of damage to brain structures is determined by the duration and severity of hypoxia and ischemia, as well as the primary cause of tissue oxygen starvation.
Main signs of the disease
Ischemic disease affecting the brain in newborns is accompanied primarily by neurological symptoms. Assessment of the newborn's condition on the Apgar scale of 2-5 points indicates the presence of intrapartum (during childbirth) asphyxia. In especially severe cases, a coma and severe depression of the central nervous system may develop, which requires immediate resuscitation measures with connection to a ventilator. Other signs:
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Bulbar disorders. Dysfunction of swallowing and sucking.
- Alternation of muscle hypotonia and muscle hypertonicity of the pyramidal, pyramidal-extrapyramidal type.
- Spastic tetraplegia. Partial or complete paralysis of the limbs.
- Spastic tetraparesis. Weakness of motor activity of all limbs as a result of dysfunction of the nervous system.
- Dystonic episodes (spasmodic contraction of muscles of a constant nature) with a characteristic freezing in the posture of an asymmetrical tonic neck reflex.
- Hyperkinesis (involuntary movements of one or a group of muscles) with athetosis (involuntary twitching) of the hands.
- Muscle rigidity. Stiffness, hardness of muscles.
- Sleep disturbance, frequent crying.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns. Causes
In the vast majority of cases, ischemia in a newborn is perinatal, that is, it occurs in the womb.
Less commonly, it is a consequence of asphyxia during childbirth. Cerebral ischemia is more typical for premature babies, since their vascular system is not yet fully formed. This diagnosis is rare in full-term babies.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns may be associated with:
- maternal pathologies leading to fetoplacental insufficiency: anemia,
- diabetes,
- coagulopathies accompanied by a tendency to thrombosis,
- thyroid disease (thyroid gland),
- kidney pathologies,
- endometriosis,
- myometrial hypoplasia,
- hypovolemia,
- hypoxemia,
- Congenital heart defect,
- low or high blood pressure,
- late gestosis, including preeclampsia and eclampsia;
Risk factors for ischemia in a newborn are divided into antenatal and intrapartum.
Antenatal factors include:
- mother's age is over 35 years old,
- premature and prolonged labor,
- non-compliance by the mother with the principles of a healthy lifestyle (smoking, drinking alcohol or taking drugs during pregnancy),
- refusal to see a doctor, as well as the presence of: endocrine diseases (especially diabetes mellitus);
- long-term toxicosis;
- threats of abortion;
- multiple pregnancy;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases (especially in the second and third trimester of pregnancy);
- autoimmune pathologies.
Treatment methods
When choosing a course of treatment for cerebral ischemia in a newborn and infant, the specialist takes into account several factors:
- how the disease manifests itself;
- severity of symptoms;
- the weight of the child, which plays an important role in premature and low birth weight children;
- presence/absence of intrauterine developmental pathologies;
- how the pregnancy progressed;
- method of delivery (natural birth or cesarean section).
Therapy directly depends on the stage of ischemia. During the first, massage and gymnastics are indicated. They will help improve blood circulation and, as a result, oxygen supply to the brain. It is also necessary to ensure that there is enough fresh air in the children's room. Medications are not useful here.
For stage 2 ischemia, special treatment is required. Physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, electropheresis, should be added to the massage. In cases where there are blood clots in the vessels, they are removed.
To improve the condition, the doctor prescribes several groups of medications:
Anticonvulsants. They not only relieve cramps, but also protect against them.
Diuretics. Helps remove fluid accumulated in the body. Prescribed for the development of hydrocephalus or mild cerebral edema.
Anticoagulants. Provoke blood thinning.
Drugs to dilate blood vessels. Effectively reduce intracranial pressure.
If cerebral edema does not go away as a result of treatment, bypass surgery is performed. After taking medication, this is the only way to cure the disease.
The third stage is more difficult to treat than others. The course of treatment consists of several procedures:
- Ventilate your lungs if you have breathing problems.
- Surgery to remove blood clots blocking blood vessels.
- As in the second stage, shunting is performed to help cope with the swelling.
- Taking medications to thin the blood and dilate blood vessels.
Symptoms, degrees, consequences and treatment of cerebral ischemia
Cerebral ischemia is a decrease in blood flow caused by cerebral atherosclerosis (from the Latin cerebrum - brain).
The brain performs the following functions:
processes information coming from the senses;
determines the mood, creates an emotional background;
A failure in its operation threatens the functioning of the entire organism. Numbness, a symptom of cerebral ischemia, is caused by sensory information not being processed correctly or transmitted through neurons. These are the same causes of temporary blindness. The brain is involved in decision-making, so patients with CCI - chronic cerebral ischemia - experience inhibition of thought processes.
Any pathology of the higher part of the central nervous system - the central nervous system - negatively affects many factors of life. Symptoms may be hidden - this is typical for the initial stage of the disease. The brighter they appear, the more advanced the disease.
There are two forms of the disease:
The first develops according to the principle of a transient ischemic attack - TIA, micro-stroke or an attack of acute cerebrovascular accident - ACVA. This is transient ischemia, otherwise known as transient cerebrovascular accident - TCI or ischemic stroke. The cause of the acute condition is blockage of the blood flow by an embolus or an advanced chronic form of the disease. The latter, in turn, develops gradually as the bloodstream narrows.
Cholesterol plaques are lipoproteins of the lower density limits. They are the ones who “choke” the organs, causing circulatory hypoxia. They can break away from the site of formation and circulate through the vessels. Emboli can be cholesterol or blood. Blood clots are dangerous due to the possibility of developing an inflammatory process.
Prevention of ischemia, like many other diseases, consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary, if possible, to avoid stress, not to overeat, adhere to an “anti-cholesterol” diet, play sports, give up alcohol and smoking, and spend time in the fresh air.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
There are many symptoms of cerebral ischemia:
nervous system dysfunction causing speech or vision problems;
sudden mood swings;
shallow and rapid breathing;
feeling of coldness in the palms and feet.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may worsen. It progresses in stages. Experts distinguish 3 stages or degrees of development of ischemia. Some also highlight a fourth.
Separately, the symptoms of an ischemic attack should be listed:
attacks of zonal loss of sensitivity;
paralysis of an area or half of the body;
monocular vision loss (one-sided blindness).
Problems with the eyes occur because signals from them are sent to the visual cortex, located in the occipital lobe. Local numbness is due to the fact that neurons of the somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe, where tactile information is transmitted, are affected.
The red nucleus of the brain stem, basal ganglia, cerebellum and more are responsible for human motor activity. When the processes occurring in the motor areas of the cortex in the frontal lobes are disrupted, the patient has difficulty regulating movements, even to the point of paralysis. Different parts of the brain are responsible for different factors of life. Emotions are controlled by the amygdala, attention by the reticular formation, and memory by the hippocampus.
The difficulty in diagnosing some brain diseases is that their symptoms are similar to “standard” changes in well-being in older people. Another feature of cerebral ischemia is that its symptoms are very individual, because In different people, different parts of the main organ of the central nervous system are affected. Observations from the patient's relatives play an important role in diagnosis. They are able to provide a more accurate description of the changes taking place. Due to lethargy and confusion of consciousness, one cannot completely rely on the patient’s words.