One of the unpleasant symptoms that causes panic thoughts in VSD is numbness in the legs. Of course, the patient does not immediately go to the doctor. First of all, he studies medical websites and finds out: most often a person’s legs go numb due to neurological diseases. And here we can safely include vegetative-vascular dystonia.
But, unfortunately, among the reasons that cause numbness in the lower extremities are such terrible things as oncology of the brain and spinal cord, stroke, diabetes, and arthritis. What facts can calm a dystonic person and erase a terrible fate from his thoughts? And is it possible to cure numb legs if the VSD is to blame?
Causes of numbness in the legs
Loss of sensation in the arms and legs can result from:
Stress – often patients who have experienced anxiety note how their right or left arm and leg become numb at the same time. The mechanism for the development of these changes is central in nature, when the physiology of certain neurons responsible for the perception of limbs in space is disrupted;
Overwork – if a person constantly works without taking breaks, characteristic neurological disorders may occur. In this case, the cause of numbness in the arms and legs is a violation of conductivity and a decrease in the excitability of the nervous tissue that occurs during overload;
Numbness of the limbs during sleep - here it is worth paying attention to the position in which you sleep, as well as the quality of the mattress.
Vitamin deficiencies - limbs often go numb due to a lack of vitamins. These substances affect blood circulation because they are part of blood vessels and nervous tissue. If their quantity is insufficient, physiological disorders occur, including sensitive ones.
What is neurosis
Neurosis is a functional mental disorder that usually arises as a result of internal and external conflicts.
The disease lasts a long time and leads to changes in a person’s mental abilities and physical condition.
The main feature of neurosis, which distinguishes it from other mental illnesses, is the preservation of an adequate perception of reality. The person is aware of his problems and is ready to be treated.
Neurosis is a mental disorder that prevents the body from adapting to environmental conditions. In severe cases, a person perceives reality in a distorted form. This causes the development of serious mental and nervous system diseases.
Causes of neurosis
Neurosis occurs for various reasons. This is usually due to hidden conflicts. They can be personal (internal), interpersonal, family. Various factors and situations have a short-term or long-term impact on the human psyche.
Internal conflicts:
- diffidence;
- inability to think rationally;
- apathy;
- dissatisfaction with the current situation;
- pressure from others.
Interpersonal conflicts:
- long-term crisis (failures at work, problems communicating with friends, in love relationships, etc.);
- dissatisfaction in relationships;
- dependence on another person - on parents, spouse, etc.;
- inflated demands of society.
Family conflicts:
- betrayal of a loved one;
- breakup of love relationships;
- quarrels and scandals in the family;
- suppression of personality by a loved one, struggle for leadership;
- lack of attention, understanding, care, affection and love in the family;
- psychosexual disharmony of spouses;
- poor financial situation.
Also, the causes of a nervous breakdown, which can lead to the development of neurosis, can be: the death of a loved one, chronic stress, past illnesses and psychological trauma, frequent overload of the nervous system and physical activity. Some doctors believe that the cause of the basic conflict in neurosis is the contradiction between incompatible personality defense mechanisms that are formed in childhood. These are ways of responding to various social factors.
Symptoms of neurosis
Symptoms of neurosis are divided into two groups: mental and physical. A sick person does not always exhibit both types of symptoms. This can make it difficult to make an immediate diagnosis. Individually, mental and physical signs can be symptoms of other diseases and disorders.
Mental symptoms
Mental symptoms appear in neurosis more often than physical ones. These include:
- emotional instability;
- sudden mood swings, irritability;
- indifference;
- isolation;
- anxiety;
- sensitivity to stress;
- unreasonable feeling of fear;
- panic attacks;
- touchiness.
With neurosis, memory may deteriorate and thinking abilities may decrease: people become inattentive, confused, and get tired quickly. They are often bothered by insomnia.
Because of this, they become irritable and aggressive. Patients with neurosis observed: low or high self-esteem, changes in life values, the appearance of phobias and a reluctance to communicate with people around them, even with loved ones.
Physical signs
Physical symptoms of neurosis are manifested by disruption of the autonomic system and pain in different parts of the body. Vegetative symptoms appear on the body and in individual body systems, but do not cause pathologies. These include:
- decreased or increased blood pressure, resulting in dizziness and dark vision;
- headaches, pain in the temporal region;
- skin rashes, redness, itching;
- allergic reactions without exposure to an allergen - rash on the face or body, edema syndrome;
- increased sweating, rapid heartbeat;
- disruption of the stomach and intestines and, as a result, problems with stool;
- rapid or difficult breathing, feeling of a lump in the throat;
- frequent urination.
Bodily symptoms are manifested by pain in the body. Typically, pain is not felt in a specific place, as with an organic disorder of the nervous system. With neurosis, painful and unpleasant sensations alternately appear in different parts of the body and then disappear. This phenomenon depends on the psycho-emotional state of a person.
In people suffering from neurosis, performance decreases, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted, sexual desire decreases, and sometimes completely disappears. Sometimes problems with appetite arise - either a constant feeling of hunger or lack of appetite.
Often, patients experience phantom pain due to experiences caused by fear or anxiety about their health or something else. Problems with sleep appear - neurotic people find it difficult to fall asleep. They often wake up at night, have nightmares, and even after a long rest feel tired.
Pain due to neurosis
In addition to general malaise, with neurosis a person experiences pain in different parts of the body - arms, legs, back, heart, stomach, headaches, etc. Often these pains are perceived as physical diseases associated with disruption of the functioning of individual systems and internal organs.
An erroneous diagnosis is made not through the fault of doctors, but because many symptoms of neurosis coincide with signs of physical diseases. In such cases, it is advisable to consult a psychotherapist. However, pain may not mean the presence of neurosis at all, but may be a sign that precedes it.
Pain in the body and individual organs causes not only discomfort on the physical level, but also discomfort on the psychological and emotional levels. Sometimes it can be difficult to determine which parts of the body hurt. This is associated with wandering pain.
It occurs as a result of an imbalance in the autonomic system, which leads to malfunctions of organs. Due to wandering pain, when examining specific organs in which pain is present, pathology is not detected. In this case, the problem must be sought in the functioning of the nervous system.
Pain in legs and arms
Neurosis often provokes the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia, which causes headaches, pain in the heart, muscles and joints. Some people with neurotic disorder complain of back pain, which is misdiagnosed as sciatica, lumbar hernia, or vertebral misalignment. But more often pain appears in the legs or arms.
Their main difference from the usual pain, which signals physical malfunctions in the body, is the presence of other accompanying sensations, such as tingling, numbness, swelling, changes in skin color, changes in the sensitivity of the limbs, etc.
Due to severe anxiety and self-hypnosis, pain in the joints and muscles occurs without the influence of external factors and injuries. Sometimes a neurotically ill person, after communicating with people who have real physical illnesses, begins to experience the same symptoms as them, which develop into real pain.
In stressful situations or depression, pain in the arms and legs worsens, since it directly depends on the person’s mental state. During a period of peace and tranquility, the pain decreases or disappears altogether, and at a moment of slight excitement it appears again, sometimes with an increased pain threshold.
Therapy for neurotic pain
In addition to emotional and psychological factors, physical overload and sedentary work requiring the same type of actions can provoke the appearance of neurotic pain in organs, muscles and joints.
Treatment must be comprehensive.
It is selected individually and includes the use of special medications to help relieve stress, fatigue and other mental and physical symptoms, as well as psychotherapy sessions.
Sometimes, in parallel with psychotherapy, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. In some cases, a change in daily routine, diet and diet is required. Therapeutic exercises are recommended.
Prevention of the disorder
In order to prevent the appearance of neurosis, you need to lead a correct lifestyle - get rid of bad habits, play sports, observe a work and rest schedule. Sleep should be complete. Eat more vitamins and less junk food high in calories and cholesterol. Be in the fresh air more often, do physical exercises - whatever you can do.
It is useful to learn to control your emotions. Calm music will help you relax. Avoid stressful situations and try not to take problems too emotionally.
Other causes of numbness
Legs may also go numb in the following cases:
Rheumatoid arthritis. The development of the disease is accompanied by compression of the nerve endings in the knee joint. Discomfort most often occurs below the kneecap.
Gout. As a result of salt deposition in the joints of the feet, the big toe loses sensitivity, after which numbness affects the entire foot.
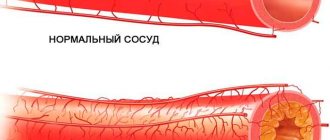
Atherosclerosis. The lower extremities may become numb as a result of impaired blood flow due to narrowing of the lumen of the femoral artery.
Vascular antiopathy, which developed against the background of diabetes. Gangrene often becomes a complication of this disease.
Polyneuropathy. The disease develops against the background of diabetes, alcoholism and heavy metal poisoning. As a result, the impulses of all nerve endings are blocked.
Multiple sclerosis. Progressive nerve disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS) cause numbness due to damage to the myelin sheath of the nerve.
Is it dangerous?
VSDeshniks are timid people. And no matter what they experience, they always worry, is it dangerous?
If the weakness in the legs is associated solely with a violation of the vegetative system and does not appear so often, then there is no danger in this. Perhaps, except for the likelihood of falling with severe weakness in the lower extremities. But this is unlikely to happen either.
Even in an absolutely healthy person, during times of strong excitement or sudden fear, his legs can give way. Most people have experienced this condition at least once in their lives.
Symptoms that may occur along with numbness in the legs
Numbness in the leg may occur along with other symptoms or a combination of symptoms. For example, if your legs are numb due to compression of a nerve root in the lumbar spine, you may also experience pain in your legs or lower back. Leg numbness as a consequence of multiple sclerosis can go hand in hand with tingling and lack of coordination. Any symptom that occurs along with numbness in the leg can help your doctor make a correct diagnosis.
Symptoms that may occur along with numbness in the leg
Numbness in the leg may occur along with other symptoms, including:
- anxiety, restlessness;
- burning sensation;
- frequent urination;
- itching;
- increased numbness in the leg, tingling or pain when walking;
- pain in the lumbar spine;
- muscle spasm;
- tingling;
- rash;
- increased sensitivity to touch.
Symptoms
Characteristic signs of this condition are:
- a feeling that the legs are cottony, or rubber, or even made of jelly;
- fear of loss of balance and a feeling of unsteadiness in gait (weakness in the legs often manifests itself simultaneously with psychogenic dizziness);
- a feeling that your legs are about to bend at the knees, and an inevitable fall will occur, after which you will not be able to get up;
- paresthesia, numbness in the lower extremities;
- trembling in the legs, sometimes imaginary, sometimes actually noticeable.
All of the above symptoms may appear simultaneously, or they may occur one after another. Sometimes just one manifestation can be annoying.
The intensity of symptoms can vary from extremely strong to subtle. The condition can change hour by hour, day by day, etc. Sometimes the problem can disappear for several days, months, or even years, and then return again.
Symptoms of leg weakness are often accompanied by poor general health, drowsiness, dizziness, and muscle pain throughout the body. In most cases, there are other bodily manifestations of chronic anxiety, often called VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia): rapid pulse, sweating, chest pain, nausea, etc.
Tingling and numbness in the leg
In common peroneal nerve compression syndrome, numbness or tingling is felt in the top of the foot or inner leg. The peroneal nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the toes, feet, and legs. A knee injury, a broken fibula, a tight shin cast, and even frequent crossing of the legs can lead to this syndrome. Treatment for numbness involves eliminating the cause. But sometimes a corticosteroid injection may be needed to reduce the swelling, and in some cases surgery is performed.
How to deal with body pain after stress
Stress causes irreparable damage to the health of every person. In this case, the body responds to negative emotions and excess tension based on nervousness. In addition to this is muscle pain (myalgia) throughout the body. According to experts, this is a completely natural reaction to external physical and psychological stimuli. These problems can and should be dealt with. If the disease is not treated in time and proper prevention is not followed, the progression of coronary heart disease or heart attack is high. Body pain due to stress is called myalgia
Only true opinion
So there they said that the vegetative-vascular system is responsible for all sorts of inexplicable paralysis, for example, due to nervousness, my legs once gave out!
This happens for the following reason: the brain communicates emotional stress to the muscles, and then to the joints via nerve endings. During emotional experiences, changes occur in the human body, which are mainly associated with the expansion and contraction of blood vessels. Neuropsychic injuries contribute to the occurrence of atherosclerosis of the lower extremities. People who experience leg pain are advised to stop smoking if they smoke, as nicotine is a major risk factor for vascular ischemia.
If you feel aching pain in your legs and feet, especially in the late afternoon, you should consult an orthopedist. Wear arch supports or special insoles prescribed by your doctor. Joint diseases include diseases such as arthritis and arthrosis.
Which doctor should I contact?
A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders, such as sensory loss and numbness in the extremities. In order to correctly assume what was the possible cause and choose the right direction of the diagnostic search, the neurologist must examine the patient, find out in which parts of the body numbness occurs (only in the fingers, in the hands or feet, in the entire arm or leg, in one limb , or right and left symmetrically), are there any other neurological symptoms or concomitant diseases.
Depending on the results of the examination, the neurologist may refer you to other specialists:
- For vasculitis, Raynaud's disease - see a rheumatologist.
- For cardiovascular pathologies, see a cardiologist.
- For diabetes mellitus, see an endocrinologist.
- In case of tumors or injuries, see a neurosurgeon.
- For infectious diseases - see an infectious disease specialist.
- In case of poisoning with harmful substances at work, contact an occupational pathologist.
What to do if your legs go numb
If numbness and tingling become regular, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The therapist will conduct an examination, ask you questions about your lifestyle, social habits (for example, he will probably be interested in your Friday meetings with friends over a bottle or two), place and working conditions, and the health of close relatives.
Based on the results, the doctor will most likely prescribe tests, which may include:
- Blood tests. They will help identify possible diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, signs of abnormal immune system activity, liver dysfunction, kidney dysfunction, or other metabolic problems.
- Electromyogram (EMG). This is a test for electrical muscle activity.
- Cerebrospinal fluid studies. They will help identify antibodies associated with peripheral neuropathy.
Depending on what the studies show, the doctor will prescribe treatment for you. It’s all very simple, the main thing is not to put off visiting the doctor!
Drug treatment
Medical treatments for long-term numbness in the legs and feet include:
- Antidepressants. Some antidepressants, such as duloxetine and milnacipran, have been approved for the treatment of fibromyalgia.
- Corticosteroids. Some corticosteroids may help reduce chronic inflammation and numbness associated with diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
- Gabapentin and pregabalin. Medicines that block or alter nerve signaling may help relieve numbness in fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and diabetic neuropathy.
There are contraindications, you need to consult a specialist!
What treatments are there for varicose veins?
Over the years, veins lose their elasticity, their capacity deteriorates and varicose veins develop. But not only age-related changes cause the disease. Here are the factors that increase the risk of varicose veins:
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- Hypertension;
- Obesity;
- Liver diseases;
- Taking hormonal drugs that affect vascular tone.
Many older people complain of rapid fatigue and swelling of the feet, venous network, and heaviness in the legs. For varicose veins, an integrated approach is effective:
- Taking venotonics and angioprotectors that improve blood circulation and increase vascular tone;
- Use of local therapy. These are cooling or, conversely, warming creams, ointments and gels that reduce swelling and increase blood flow (Venitan, Troxevasin, Lyoton);
- Taking non-steroidal medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect and eliminate pain and anticoagulants - medications that thin the blood.
Physiotherapy
In order to strengthen the nervous tissue and reduce the signs of various pathologies that cause numbness in the legs, physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed. These include:
- Warm-up sessions;
- Shock wave therapy;
- Drug electrophoresis;
- Laser treatment;
- Magnetotherapy.
Radon baths and contrast showers to activate blood flow have proven themselves well.
How to help yourself
To improve your well-being on your own, it is recommended:
Use ointments that have a warming or cooling effect. These include Capsicam and Apizartron. They contain components that help not only activate skin receptors, but also reduce pain, eliminate swelling and inflammatory reactions.
Before going to bed, take a contrast shower - in most cases, numbness of the arms and legs at night is caused by poor circulation, which improves with a temperature difference during ablution;
Use alternative medicine. In this case, we are talking about the use of rubs and applying compresses based on pepper or garlic. They have a warming effect, stimulate blood circulation and improve tissue nutrition.
Related posts:
- Nightmares and how to get rid of panic attacks at night Nightmares are one of the sleep disorders (parasomnias) and are associated...
- What are phobias? Many things that surround us every day can cause phobias. A dog bit me...
- Hallucinosis Hallucinosis (syn. hallucinatory syndrome) is a pathological condition that is characterized by the appearance...
- Xenophobia: what kind of disease? Xenophobia is the fear of strangers or strangers. This term…
How is treatment for swelling of the legs in older people carried out?
Swelling of the legs in the elderly is a common occurrence. In most cases, puffiness of the feet is caused by a long walk or dietary errors, for example, eating pickles or a small portion of alcohol.
Physiological edema goes away on its own, without leaving a trace, without causing irreversible pathological processes in the body. But there are a number of diseases in which pastiness of the lower extremities is observed with enviable regularity:
- Kidney failure;
- Phlebeurysm;
- Disorders of the lymphatic system;
- Cardiovascular disorders;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Soft tissue injuries, sprained tendons in the foot area.
Pathological conditions require a comprehensive examination, as well as timely treatment in order to prevent the progression of the underlying disease.
You can cope with minor swelling of the legs yourself at home, for which you should:
- Take diuretics (diuretics) recommended by your doctor to remove excess fluid from the body;
- Use topical veinotonics in the form of gels or ointments if the puffiness is caused by varicose veins;
- Follow a diet, perform gymnastics to improve blood circulation;
- Do not wear tight shoes and clothes, monitor your activity and rest schedule.
To relieve swelling of the feet, folk recipes will also help, for example, taking a decoction of horsetail, lingonberry, rosehip, bearberry. Treatment of the feet of older people with complex edema is carried out in specialized institutions.