Changes in the nature of the functioning of the nervous system do not always have an organic, structural origin.
Often pathological processes are determined by a purely functional nature. Therefore, it is not possible to detect atomic abnormalities in the brain, which significantly complicates the diagnosis.
It is especially difficult to identify disorders of a transient nature that manifest themselves in periods, in paroxysms.
NCD of the mixed type is a chronic neurological disease, which is accompanied by severe disturbances in the functioning of the heart and fluctuations in blood pressure over a wide range.
Neurocirculatory dystonia has its own ICD-10 code, F45.3, and is considered an independent diagnosis.
Related disorders, as a rule, are not characterized as separate nosological entities. For example, vegetative-vascular dystonia is a syndrome within other diseases, but not a full-fledged independent disorder and not a diagnosis.
NCD is characterized by a group of features that qualitatively distinguish it from other disorders: primacy, that is, independence from other disorders, functional nature, therefore it is not possible to detect organic changes, cardiovascular predominant symptoms.
Types of NDC
The following types of neurocirculatory dystonia are distinguished:
- Cardiological - the heart muscle does not function properly.
- Noticeable changes in blood pressure are of the vascular type.
- Hypertensive - accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.
- Hypotonic - stable decrease in blood pressure.
- Mixed - includes several of the above symptoms.
The pathology occurs as a result of a violation of vascular tone, is recorded in adolescents (up to 80%), and is less common in people over 40 years old.
Detection of vegetative-vascular dystonia with cardialgia
One of the important tasks in diagnosing neurocirculatory dystonia of the cardiac type is the exclusion of coronary pathologies (for example, defects, myocarditis, etc.). Identification of NCD requires physical, functional and laboratory tests:
- general examination, listening to the heart, counting the pulse;
- various types of ECG: standard, complicated by exercise, with the necessary tests (change of position, taking medications, etc.);
- daily ecg examination;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- bicycle ergometry;
- general and biochemical blood tests, urine analysis.
The process of diagnosing the disease can be difficult due to the irregularity of symptoms.
Causes of hypotonic type NCD
What it is will help to understand the origin of this disease. Researchers are actively discussing the issue. This is due to the multi-vector symptoms of the disease, the onset of the development of the disease in childhood, when the development of the body should proceed quite rapidly. Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type, like many cardiac disorders, has a protracted chronic phase. The activity of the process depends on various reasons, especially external stimuli.
Predisposition to symptoms of NCD:
- heredity (the presence of similar manifestations in blood relatives);
- physical environmental factors (radiation, noise, vibration, excessive fatigue, problems at work or in the family);
- individual characteristics (the body’s adaptation to stress, the structure and specific functioning of the nervous and s/s systems);
- alcohol abuse and other bad habits.
One or more signs provoke malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs, which leads to aggravation of the disease and complication of recovery.
The root causes of NDC include:
- manifestations of a neurogenic nature;
- head injuries;
- maladaptive signs.
Neuronal dystonia manifests itself under the influence of stress that accompanies a person in everyday life. For teenagers, this is a violation of personal space on the part of parents or peers. Adult members of society face various conflict situations and mental dramas. Stressful effects manifest themselves acutely or chronically.
Disorders that are traumatic to the psyche often act as a starting point for a further crisis in parts of the nervous system. Not all people can take advantage of the right way out of conflict and overcome psycho-emotional stress on their own.
Another reason is head injuries. Sometimes a manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia occurs, accompanied by feelings of a general nature. Discomfort is expressed by decreased ability to work, weakness, increased perception of geomagnetic changes, and difficulties with physical activity.
Some experts separately highlight the therapeutic causes of this disease. Among them: infections, allergies, violation of the sports regime, long-term work with electronic devices.
How to notice violations
In general, dystonia is not a separate disease that can be treated, but only a complex of symptoms. Its manifestations are varied: from sudden surges in blood pressure and stabbing pain in the heart to digestive problems, drowsiness and fatigue.
It is generally accepted that the vast majority of VSD is associated with psychogenic causes, and not only obvious disorders. Stress, an uncomfortable work environment, and disturbances in sleep and wakefulness can lead to symptoms.
Symptoms of dystonia first of all lead a person to think about the presence of a specific disease. Because of this, patients turn to specialized specialists who, after conducting an examination, do not detect any disturbances in the functioning of individual organs. In such a situation, many refuse further diagnosis and get used to the symptoms, mistakenly believing that in the absence of the disease they will no longer be able to get rid of them.
Another problem in diagnosing dystonia is concomitant diseases. Thus, in the case of neurocirculatory dystonia of the mixed type, which is characterized by sudden surges in pressure and pain in the left side of the chest, the patient may be diagnosed with a disease of the cardiovascular system with similar symptoms. In this case, all efforts are directed towards fighting the disease, however, treatment may not be as successful as expected. The fact is that when fighting only the underlying disease, without paying attention to dystonia, symptoms may persist, which makes it difficult to determine the correct treatment tactics.
Features of neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type in children
Students of schools, colleges and universities are at risk. This is due to the completion of a significant volume of tasks. In addition, the lack of time and preparation for exams and tests leaves its mark.
Among individuals susceptible to NCD are athletes of different ages. Overload, an accelerated pace of training, an abrupt end to a career, and injuries take their toll. These points force the human adaptation system to work under strain, which often leads to malfunctions of the body.
Pregnant patients and nursing mothers are also susceptible to dystonia. This is due to hormonal transformations, pregnancy and birth of a child, plus changes in the emotional picture of life.
Crises and symptoms of neurocircular dystonia
The development of the disease is based on disruption of the heart and blood microcirculation, expressed in a decrease in blood pressure. The body, using available resources, tries to neutralize the problems that have arisen. At the same time, oxygen starvation of tissues manifests itself, the resistance of peripheral vessels decreases, and drops in venous pressure occur.
Disease syndromes:
- General weakness. Accompanied by fatigue, exercise intolerance, and minimal efficiency.
- Orthostatic manifestations. There is a sharp decrease in pressure, even to the point of fainting. When changing body position, flickering appears in the eyes, the urge to vomit, and dizziness.
- Cardiac syndrome. This symptom occurs in 30% of patients with NCD and is marked by short-term painful squeezing sensations in the area of the heart or stabbing pain radiating to the left side of the back and arm. The pulse is usually slow, and disturbances in the rhythm and duration of the heartbeat are recorded.
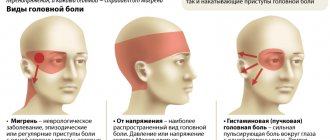
- Cerebral symptoms. This includes dull headaches in the forehead area, aggravated by any type of stress. It is often combined with dizziness and further fainting.
- A reflex type of disadaptation (numbness of the hands, decreased thermal balance of the body, cyanosis on the extremities).
- Combined syndrome combines several of the above manifestations.
NDC sometimes has a crisis course. The picture of the phenomenon is a sharp drop in blood pressure followed by fainting (collapse). Additional symptoms are unpleasant symptoms in the heart, headache. A characteristic feature of patients with NCD is an increased emotional and anxiety level.
Diagnosis
The definition of the disease is based on the detection and correct interpretation of the patient's complaints. The extent and results of special checks are also objectively assessed.
Patients must undergo consultation with a cardiologist, neurologist and therapist. Since the clinical picture of hypotonic NCD has few specific signs, an important point in diagnosis is to determine whether the detected abnormalities are symptoms of an organic disease.
Blood pressure measurement shows a hypotonic level, an ECG shows a complex of heart failures. Sometimes rheoencephalography is required to identify asymmetry of vascular blood flow and instability of rheological impulses. Also, when diagnosing, specific diagnostic tests are used.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of neurocirculatory dystonia is determined by the variant of the pathology. The most common signs of the disease:
- pressing pain behind the sternum, feeling of discomfort;
- interruptions in work, rapid heartbeat;
- headache;
- weakness, fatigue, decreased ability to work;
- noise in ears;
- “flies” before the eyes;
- pallor or redness of the skin (depending on the predominance of the component of the autonomic nervous system);
- Extrasystoles (extrasystoles) are often recorded on the cardiogram of such patients.
To diagnose the disease, a standard clinical examination by a cardiologist, measurement of blood pressure, recording of an electrocardiogram (ECG), and, if necessary, ultrasound and x-ray examination methods are used.
In some cases, special functional tests are used to exclude organic pathology.
Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type
The treatment process for this disease is based on information about the presence and severity of clinical signs. The procedure consists of correcting adaptive, neurological, and cardiac dysfunctions. The specialist prescribes a number of medications. Among them: antidepressants, sedatives, tranquilizers, substances with a high content of potassium, magnesium, vitamin B-6. Metabolic therapy is also carried out, and drugs with targeted cardiological action are administered. Additionally, supervision by a psychotherapist will be required. Alternatively, you can contact a hypnologist who will help you find the root of the problem on a subconscious level. Psychologist Nikita Valerievich Baturin has extensive experience in the treatment of various mental disorders and disorders, including hypertensive type NCD. Grateful reviews from patients further confirm the effectiveness of the courses.
Recommendations for the treatment of this disease:
- Maintaining the correct sleep schedule: getting up and going to bed at the same time, resting for at least 8 hours, taking into account individual biorhythms.
- Reduce caffeinated drinks to a minimum.
- Balanced diet.
- Carrying out dynamic physical exercises and breathing exercises to saturate the blood with oxygen.
Traditional methods
In the prevention and treatment of autonomic hypotonic disorder, folk remedies are used, the effectiveness of which is visible only after a long period of use. Among the most popular recipes:
- Rhodiola rosea root tincture. One hundred grams of dry wort is poured into 0.5 liters of vodka. Keep in a cool place for a week, shaking occasionally. Take three times a day for 30 days.
- Angelica and St. John's wort are mixed in a ratio of 1/10. The mixture is placed in a container, which is placed in the oven for three hours. The finished powder is brewed like tea.
- Red hawthorn. A large spoonful of the plant’s fruits is infused in 200 milliliters of boiling water, and filtered after a couple of hours. Take one tablespoon before meals.
Neurocirculatory dystonia during pregnancy
In pregnant women, NCD manifests itself as memory failure, sleep disturbances, and morning fatigue. The main cause of the disease is hormonal transformations in the body. Other manifestations:
- muscle and heart pain;
- fainting conditions;
- shortness of breath;
- causeless attacks of fear or panic.
Without proper treatment, the pathology negatively affects the development or condition of the fetus. Normalization of the psychological picture, adherence to a daily routine, and avoidance of stressful situations will help improve your well-being. To relieve stress, vitamins, special breathing exercises, aromatherapy, meditation, and massage are prescribed.
Causes
Various factors can provoke the appearance of a functional disorder. Among the list of reasons why neurocirculatory dystonia of mixed type began to bother us, there is a hereditary factor. Doctors say the most common cause of the disorder is lifestyle. And a large list, where the typical culprits of neurocirculatory dystonia are noted, looks like this:
- severe diseases of internal organs;
- skull injury;
- acute infectious disease;
- excessive physical activity;
- physical inactivity;
- stress;
- lack of sleep;
- overwork.
Hypertensive type of NCD
Neurocirculatory dystonia of this type is characterized by disturbances of the autonomic nervous system. The imbalance is expressed in the dominance of the sympathetic department over the parasympathetic part. Many people are concerned about NCD of the hypertensive type, what is it like during pregnancy? The disease manifests itself with standard symptoms:
- increase in blood pressure parameters;
- headaches and dizziness, aggravated by exercise;
- sensitivity to meteorological changes;
- increased heart rate;
- tendency to constipation;
- increased body temperature, especially in infectious diseases;
- drying of the lacrimal glands;
- mood swings;
- rapid fatigue.
With improper or untimely treatment, the course of the disease worsens and is fraught with various complications.
NCD is a multi-vector disease that has not been fully studied by specialists. It is a significant illness because it often affects people of working age. You can get rid of the problem only with the help of an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Causes and diagnosis
Symptoms of mixed NCD, which are diagnosed in 70% of patients with dystonia, can develop in a person of any age. In adolescents, it is observed in connection with the growth of the body, hormonal changes, and overwork - physical and mental - also has a great influence on the condition.
In adults, there are many more factors for the development of mixed type NCD - it can be caused by stress, disturbances in sleep and rest patterns, intoxication, including alcohol and tobacco, unhealthy diet, and serious physical activity. In addition, in women, hormone-dependent dystonia often occurs during pregnancy, as well as after abortion, due to impaired functioning of the ovaries, during menopause.
According to statistics, the most common cause of the syndrome is prolonged psychological stress, serious stress or psychological trauma. However, if the symptoms appeared precisely after stress, the presence of other causes of dystonia cannot be immediately ruled out. In addition, there is a high probability that mixed NCD developed against the background of other diseases of the cardiovascular system. For a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a number of examinations, including:
- electrocardiogram;
- echocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and thyroid gland;
- chest x-ray;
- hormonal blood test.
These examinations help to simultaneously exclude diseases, the symptoms of which can be mistaken for manifestations of mixed type NCD, and also to identify the causes of dystonia. For the same purpose, it is worth contacting a cardiologist, endocrinologist, therapist, vertebrologist, infectious disease specialist - those specialists who diagnose and treat diseases that can cause the symptoms that appear.
Patients with any type of NCD generally experience fatigue, weakness, sleep disturbances, irritability, decreased concentration and attention.
The cardiac type of NCD is characterized by rapid heartbeat, arrhythmia, tachycardia and cardialgia. Neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypertensive type is characterized by an increase in pressure, which, as a rule, occurs unnoticed by a person. This symptom can only be detected by regularly measuring blood pressure. Hypotensive NCD, in turn, is characterized by vascular insufficiency. In addition to low blood pressure, it is characterized by headaches and muscle weakness, and patients often complain of chills.
Neurocirculatory dystonia of a mixed type combines symptoms of a cardiac type with symptoms of a hypotensive or hypertensive type. It is the symptoms of mixed type NCD that cause the most problems in diagnosis: they are characteristic of a very wide range of diseases.