A child's skull is more fragile and vulnerable than that of an adult. Accordingly, the risk of serious injury increases significantly. Especially in the 1st year of life, when the bones have not yet fused and can easily move from a blow. Babies fall out of strollers and cribs, roll off the changing table and just plop down out of the blue. It’s good if everything turns out to be a bump or abrasion, but what should a mother do if the baby hits his head hard?
If a child hits his head
It is believed that head trauma is one of the most common in childhood. This is due to the fact that until the age of 5, children have a rather heavy head, which is large compared to other parts of the body.
Therefore, even with a slight push, babies can easily lose their balance and fall head down.
If the baby has learned to roll over, then he may accidentally fall. This means you can’t leave your little one on the sofa or changing table unattended for even a minute!
What parents should know about head trauma
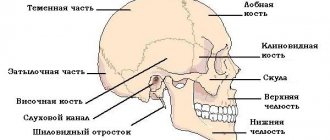
A child's head differs in structure from the head of an adult. The skull bones of babies are quite plastic and soft. This avoids serious damage upon impact.
Fontanas and a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid also protect the head from injury.
But this does not mean that head impacts can be left without treatment.
After providing medical care, you should show the child to the doctor. It is also necessary to carefully monitor the child for several days. If alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help!
After all, some head injuries lead to such dangerous consequences as concussion, compression or contusion of the brain.
The child fell and hit his head, but there were no injuries - we are monitoring the general condition of the baby
It happens that after a baby falls and hurts its head, the mother cannot find any visible injuries. What should I do?
- Over the next 24 hours , be especially attentive to your baby . The hours immediately after the fall are the most important for symptoms.
- Pay attention to whether the baby is dizzy , whether he suddenly fell asleep, whether he is feeling sick, whether he is able to answer questions, etc.
- Don't let your baby sleep so as not to miss the appearance of certain symptoms.
- If the baby calmed down after 10-20 minutes , but no visible symptoms appeared within 24 hours, most likely everything turned out to be a slight bruise of soft tissues. But if you have even the slightest doubt or suspicion, consult a doctor. It's better to play it safe once again.
- Children of the 1st year of life cannot tell what and where it hurts . As a rule, they only cry loudly, are nervous, refuse to eat, sleep restlessly after an injury, and experience nausea or vomiting. If these symptoms are prolonged and even worsen, a concussion can be assumed.
Signs of a concussion
A concussion is a mild form of traumatic brain injury that can lead to disruption of the nervous system. The peculiarity of a concussion is that the symptoms increase, and the child begins to feel worse.
With a mild concussion, the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- vomit.
However, sometimes the child can return to his games about half an hour after the blow.
For a more serious degree, the baby
- loses consciousness;
- has difficulty moving;
- does not understand where he is;
- He may vomit for several hours.
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to take the child to the emergency room as quickly as possible!
Diagnostics
A comprehensive and complete examination of a child who has sustained a head injury is possible only in an inpatient department.
A head injury is diagnosed based on the patient’s complaints, his general and neurological examination, as well as using modern instrumental examination methods, namely:
- neurosonography (ultrasound for babies);
- radiography;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and so on.
CT and MRI are rarely used in young children, because to obtain reliable data it is necessary to use anesthesia, because Maximum immobility is required during the examination procedure.
Signs of a brain contusion
A brain contusion is a type of traumatic brain injury in which a section of nerve tissue becomes necrotic. This usually occurs in the forehead, temples or back of the head.
Important! If you have a brain injury, you should not give medications!
Here are the signs of a mild brain injury:
- loss of consciousness for several minutes;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- slow or fast heartbeat.
For more severe brain contusions:
- prolonged loss of consciousness;
- Strong headache;
- repeated vomiting;
- mental disorders;
- increased blood pressure;
- slow or fast heartbeat.
Severe brain contusion can be fatal.
If there are signs of a brain injury, you should immediately seek medical help!
Traumatic brain injuries
It does not matter the age and gender of the child, the height from which he fell head down, the size of the bruise or bump on the forehead, as well as the presence or absence of abrasions and blood. All mothers and fathers should know that in all situations involving a head injury, the child needs qualified medical care.
The presence of injury can be suspected if the child experiences clouding of consciousness, loss of consciousness of any duration and frequency. Observation is very important, since parents who know the behavioral characteristics of their child will be able to notice changes in his behavior in time. Any inadequate changes may indicate a possible head injury.
If a child stops falling asleep normally, or, conversely, sleeps for an unusually long time, or develops a headache, and it does not go away even an hour and a half after the fall, you should seek qualified medical help.
A characteristic symptom of head injury is vomiting, especially if it is repeated. The child may have a shaky and uncertain gait, dizziness, convulsions, impaired coordination of movements, weakness in the arms and legs, and the inability to move one or two paired limbs at once. In all these cases, you should definitely call an ambulance.
Discharge from the nose and ears, whether bloody, sanguineous, or clear and colorless, is a clear reason to suspect injury.
Also, symptoms of injuries may include various dysfunctions of the sense organs (hearing loss, blurred vision, complete or perhaps partial lack of response to tactile contact). The child may begin to complain that he is cold or hot. Evgeniy Komarovsky advises paying attention to each of these symptoms.
Concussion
This is a fairly simple traumatic brain injury, in which the child may lose consciousness, but such a loss will be short-term (no more than 5 minutes), nausea and dizziness are possible . The brain is not damaged, but a concussion temporarily disrupts some brain cell functions. Dr. Komarovsky claims that this is the easiest consequence of falling on his head, because after a couple of days, brain functions return to normal and the child’s condition returns to normal.
Brain contusion
This is an injury in which the membranes of the brain are directly damaged, as well as its deeper structures, with the formation of a hematoma and the occurrence of edema. How long the state of loss of consciousness lasts affects the degree of injury; it can be mild, moderate or severe. In the first degree, the symptoms are similar to a concussion, only the child’s unconscious state can last more than 5 minutes. The average severity of the injury is characterized by the duration of fainting from 10-15 minutes to an hour or a little more. In severe cases, consciousness may be absent for several hours or several weeks.
Brain compression
This is an extremely dangerous condition when, as a result of a head injury, compression occurs inside the skull. With this pathology, vomiting occurs, which is protracted and repeated. Periods of loss of consciousness are followed by so-called “light” periods, when the child behaves normally, without showing any signs of brain damage. Such periods can last up to 48 hours.
Signs of brain compression
Compression of the brain occurs due to the accumulation of blood in the cranial cavity. A hematoma forms in the skull, and the intracranial space decreases.
Symptoms do not appear immediately, but after a certain period of time. Before this, the child may feel fine.
Symptoms of brain compression are:
constant vomiting that does not bring relief;
- headache;
- interrupted sleep;
- delusions or hallucinations;
- mental arousal;
later:
- apathy and lethargy;
- loss of consciousness or coma;
- changes in the rhythm of breathing and heartbeat;
- noisy breathing, wheezing;
- periodic increasing disappearance of the pulse.
If you have symptoms of brain compression, you should immediately call an ambulance!
First aid for a child who hits his head
Here's what to do after your child hits their head.
- Calm the baby.
- Place him horizontally on the bed, so that his head and body are at the same level.
- Monitor the child's condition.
- Examine the baby: are there any bumps, abrasions, etc.
- If a lump appears, apply a cold compress to it for 3 minutes. A tall and hard bump is good. But if it is low, large and soft, you should immediately seek help from a doctor.
- Treat abrasions with hydrogen peroxide.
- If bleeding lasts longer than 10 minutes, you need to consult a doctor!
- If your baby is vomiting, you need to lay him on his side.
- Provide rest to the victim.
- If the injury is serious, do not let the child sleep until the ambulance arrives!
- Monitor the baby’s condition for a couple of days after the injury. At the slightest negative consequences, consult a doctor!
How to treat a lump at home
To treat a bump from hitting your head, use cold compresses.
To do this, take ice cubes and wrap them in a thin towel. Instead of ice, product from the freezer or a cold bottle will do.
This compress is kept at the site of impact for 3-5 minutes. Then they take a short break.
These manipulations are performed alternately within an hour.
Do not give painkillers without consulting a doctor!
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
There are common warning signs that indicate you need to take your child to the hospital or emergency room immediately.
These include:
- disturbance of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- drowsiness;
- vomit;
- inappropriate behavior;
- speech disorder;
- Strong headache;
- dizziness;
- heat;
- loss of balance;
- different size pupils;
- weakness in the limbs or inability to move them;
- bleeding from the nose or ears;
- dark spots behind the ears or under the eyes;
- discharge of colorless fluid from the ears or nose;
- disturbances in the functioning of the sense organs.
Symptoms and signs of injury
The signs of a concussion vary among children of different ages. The baby cannot talk about how he feels. Therefore, adults need to focus on external manifestations. The student will report pain quite coherently, but may hide information about the injury if he is afraid of punishment.
Infant
A newborn with a head injury does not lose consciousness. The main signs indicating a concussion in an infant are identified:
- The skin of the face and limbs turns pale.
- The child cries loudly, excitedly, and does not calm down for 15-20 minutes.
- Cold sweat appears on the skin.
- Sometimes the temperature rises.
- After crying, a newborn may quickly fall asleep.
Another sign of damage to the gray matter is swelling and pulsation of the large fontanel. In addition, the newborn's regurgitation becomes more frequent and vomiting appears like a fountain. After sleep, the child remains irritable, whiny, and does not eat well.
Preschooler
At the age of 2-3 years, a child reacts to injury and pain with loud crying. He still cannot describe in words what exactly is bothering him, but he will hold on to the bruise. The following symptoms are noted when a child has a concussion:
- The baby turns pale.
- There may be a brief loss of consciousness.
- Vomiting occurs, many times in children under 3 years of age.
- Drowsiness, weakness, and apathy are noted.
- Body temperature rises.
- Cold sweat appears.
If a child hits the back of the head, temporary blindness and other vision problems may occur. Looking carefully into the baby’s eyes, you will notice that the pupils diverge in different directions and do not focus on a specific object. The victim's movements become sluggish, he may have poor orientation in space, stagger when walking, and bump into objects.
Schoolboy
With a concussion due to a bruise in older children, the symptoms of injury are pronounced. First of all, brain damage is manifested by loss of consciousness immediately after receiving a blow. There may be a delayed manifestation of signs of a concussion - fainting, vomiting, loss of orientation appear several hours after hitting the head. Victims have symptoms:
- Increased heart rate, tachycardia.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Cold sweat.
- Headache, dizziness, nausea.
- Loss of orientation in space and time.
- Impaired vision and hearing.
- Short-term memory loss.
A schoolchild may complain of red circles before the eyes, trembling of limbs, and nausea. Some time after the injury, vomiting may begin and the temperature may rise. Insomnia, irritability, and tearfulness appear.
What to do if a child hits his arm or leg hard
Being kicked or kicked is another common childhood injury.
It is important for adults to learn how to correctly identify the symptoms of injury and correctly provide first aid.
Most often, such blows lead to bruises.
Causes
The most common causes of limb impacts in children are:
- mastering walking;
- immature coordination;
- active and careless games with peers;
- participation in children's brawls and fights;
- running in uncomfortable or slippery shoes.
Make sure there is no sprain, dislocation, crack, or fracture
Before providing first aid, you need to find out if there are signs of a more serious injury to the limb. If so, then the child must be urgently taken to the emergency room!
Signs of a fracture
So, with an open fracture there will be the following signs:
- open wound;
- protruding bone fragments.
For a closed fracture:
- swelling;
- swelling at the site of impact;
- redness or bluishness of the skin;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- abrasions, hematoma;
- unnatural mobility in the area of impact,
- change in bone shape
- protrusion of bone through the skin.
Signs of a crack
A bone fracture has the following symptoms:
- swelling of the injured area;
- severe pain when trying to move, as well as pressing on the site of impact;
- at rest the pain is muted or throbbing;
- It is possible to easily lean on the injured limb.
Signs of stretching
A sprain is a tear in the fibers of the ligaments, most often in the area of the middle joints of the limbs.
Here are its symptoms:
- Severe pain that gets worse over time;
- loss of limb mobility;
- the pain is slightly muffled if you apply cold;
When mobility is limited and compresses are applied, the condition improves after a few days.
Signs of dislocation
A dislocation has the following distinctive features:
- deformed joint;
- the limb is in an unnatural position;
- motor activity is severely limited;
- When flexing and extending a limb joint, severe pain occurs in the joint.
Important! The dislocation must be corrected no later than 2-3 hours after the injury!
Alarming symptoms
Every baby can fall down to the floor or hit his head on furniture or any other objects. If this happens, parents should monitor him. In this case, any physical activity should be kept to a minimum. Older children need to limit their brain activity - prohibit them from reading, playing on the computer or watching TV. A child who complains of weakness or dizziness should be seen by a doctor.
After hitting the forehead
Children can often hit their foreheads. A visit to the doctor should not be postponed if parents notice:
- A depression has formed in the place where the bump was.
- The baby complains of nausea and vomiting.
- Cannot calm down for a long time.
- The lips turned blue and the skin became pale.
Tatyana Gurevich, head of the movement disorders clinic at the Tel Aviv Medical Center, talks in detail about head injuries:
- The pupils have greatly increased in size or squint has appeared.
- A too large lump appeared at the site of the impact.
- He cannot turn his head to the side, it is difficult for him to move.
- There is bleeding from the nose or ears.
If at least one of the above signs is noticed, you should immediately show the child to a doctor. Even in cases where adults think that the injury is insignificant, consultation with a pediatrician is mandatory!
Before the doctor arrives, the victim should not be given medications so that the doctor can assess the real picture of the damage. The baby should lie on its side while awaiting examination.
After being hit with the back of the head
If the blow falls to the back of the head, the symptoms that should alert you will be almost identical. Additionally, numbness of the limbs, loss of consciousness (can be prolonged), blurred vision (cloudedness, complete absence, etc.), tinnitus, severe dizziness, impaired coordination of movements and memory loss may occur.
Such impacts often cause concussions. And even if the baby just fell on the floor, hitting the back of his head, this condition cannot be ignored. To avoid negative consequences, it is better to immediately show the child to a doctor.
Older children and teenagers can be injured by falling backward while roller skating, biking, or fighting. To avoid trouble, it is important to teach your child how to fall correctly as early as possible, and when riding a bicycle, you must use a protective helmet.
First aid for a bruised arm or leg
- Calm the baby.
- Sit or lay it down so that it is convenient to provide first aid.
- Examine the site of the injury to ensure there is no more serious injury.
- Disinfect the skin if there are abrasions or cuts. Apply cold to the injury site. This will help reduce capillary bleeding and reduce pain and swelling. If there is no ice, a cold bottle or frozen food will do.
- They must be wrapped in cloth before being applied to the baby's skin.
- Keep this cold compress for about 30 minutes, then take a 15-minute break. During the “respite”, keep the bruised limb in an elevated position. Then the cold is applied again.
- If the pain is very severe, you can give children's painkillers, but only after consulting a doctor.
- If the pain does not go away, the swelling intensifies, or complications arise, you need to take the child to the emergency room!
Possible consequences
Children can fall in any direction. The types of injury, signs and consequences will depend on where the blow lands. Even if the child seems healthy, adults still need to monitor his condition and behavior for several days.
It is possible that your health will begin to deteriorate after some time. Children may complain of headaches and memory problems. They become moody, sleep and appetite are disturbed.
When hit with the forehead
Children are most likely to fall forward and hit their forehead. In such situations, the simplest manifestation of injury will be a lump. There are 2 types of traumatic brain injuries:
- Closed - without violating the integrity of the bones of the skull and skin. There are mild injuries (not threatening the baby) and complex injuries (when treatment is necessary).
- Open – damage to the skin and bone occurs. As a result of the fall, the baby's consciousness is impaired and bleeding appears.
Neurologist M. M. Shperling talks about traumatic brain injuries. We listen to the doctor:
Closed injuries include the following:
- Brain concussion. The victim may lose consciousness (usually this lasts several minutes). After this, dizziness, nausea and vomiting will appear. Pale skin and blue lips are observed. Although, it is possible that the child will not have any manifestations of a concussion. But it’s too early to rejoice. Parents in such situations should analyze the baby’s behavior during sleep. When a concussion occurs, sleep is disturbed and he often wakes up. If this is the case with your child, then he needs to be shown to a doctor. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the child needs bed rest.
- Brain contusion. In this case, after the blow, the children lose consciousness. The skin around the eyes darkens, and the ears and nose may bleed. In this case, you need to call an ambulance. Other signs of brain contusion include: impaired speech and facial expressions, damage to the facial nerve.
- Soft tissue bruise. This injury is the easiest and most harmless. In this case, a lump or hematoma appears at the site of the impact. The child quickly calms down and his condition returns to normal.
Consequences of hitting your head
When hit with the back of the head
Falling on the back of your head is very dangerous. Therefore, after such an injury, the baby should be immediately shown to a doctor to avoid serious consequences:
- Impaired perception. When the blow comes from the left side, the baby may not perceive the space that is on the left and vice versa. This condition is considered very serious and dangerous, but it is diagnosed extremely rarely.
- Children may become inattentive. Sleep is disturbed, memory deteriorates. The baby suffers from constant headaches.
Dr. Komarovsky talks about childhood head injuries and in which cases it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor:
Such consequences can be avoided if you show the child to a doctor as soon as possible after the injury occurs.
How to treat bruises with folk remedies
For minor bruises, you can help your child with folk remedies.
For example, like this.
- Add a solution of magnesium sulfate (bitter Epsom salt) to a hot water bath. This bath is taken 2-3 times a week for an hour.
- Crush the wormwood until smooth, spread it in a thick layer and cover with a bandage. It should be damp, so periodically you need to moisten the fabric with wormwood juice.
- Rinse the cabbage leaf with cold water and place it on the bruised site, and apply a bandage on top.
- Grate raw potatoes. Place this paste on the bruised area and cover with thick cotton cloth on top.
- An aloe leaf is smeared with honey and then applied to the injured area.
- Wash the plantain leaf, mash it until the juice appears and apply to the bruise.
What to do immediately after the impact?
If there are no obvious injuries to the scalp and skull bones , a cold compress (wet towel or medical ice pack) should be applied to the site of the impact. Keep for 5 to 15 minutes. This will reduce pain and stop tissue swelling and bleeding.
- If there is a wound and bleeding, apply a cotton swab to the area. If it becomes heavily saturated with blood, change it. However, if bleeding continues after 15 minutes, call an ambulance immediately.
- If a child has an open head injury , cover the damaged area with a sterile gauze bandage and immediately call an ambulance. In this case, a cold compress cannot be applied.
- Pay attention to the child's pupils : if they are different sizes, most likely the baby has suffered severe brain damage. Call 103 urgently.
- If the child has lost consciousness after the blow, and you have already called an ambulance, place the baby on his side so that in case of vomiting, he will not choke on the vomit. If the fall was serious and you suspect that the spine may have been damaged (the child fell from a great height on his back or on his head), you should turn him very carefully so that the torso and head are on the same axis.
- After any head injury, the baby needs rest, but to assess the severity of the condition over time, do not let the child fall asleep for an hour . If the child does not respond to simple questions (this applies to older children), his coordination is impaired, and vomiting recurs, call an ambulance. If you suspect a serious injury, but the baby still falls asleep, you should not wait for him to wake up - call the specialists.
Prevention measures
To protect your baby from blows, it is important to follow these recommendations.
- Always stay close to your child on the playground, especially near swings, slides and ladders.
- Try not to leave a small child unattended, even at home.
- In my apartment, I should have heavy, loose objects on the shelves that could fall on the baby.
- Furniture should be securely fastened.
- If your little one is learning to walk, you should use protective pads on sharp furniture corners.
- Make sure that the shoes you buy have non-slip soles.
- Fasten your baby in the stroller with seat belts.
What to do if your child hits his back hard
A blow from the back can pose a serious risk to a child's health. After all, in this area of the body there are not many compensatory mechanisms that could mitigate the results of injury.
Therefore, it is necessary to carefully examine the child who hit him in order to understand the consequences.
Most often, the result of such an injury is a bruise that affects the soft tissue in the spine.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a back injury are:
- throbbing pain;
- edema, swelling;
- hematoma or bruise at the site of the injury;
- severe pain, especially during movement.
Types of bruises
- Contusion of the upper back affects the cervical vertebrae. Sometimes this can lead to respiratory arrest, decreased muscle tone, and impaired sensitivity.
- A mid-back contusion can cause discomfort when breathing, and the child may feel pain in the heart and may lose sensation and coordination.
- A bruise to the lower back leads to urination problems and decreased sensation in the legs.
- The most dangerous are those bruises that affect the spinal cord. They can lead to poor circulation, rupture of nerve endings and paralysis.
What parents need to know
The bruise can be caused by falling on your back, during a road accident or playing sports.
It is important to be able to distinguish a bruise from other, more serious back injuries. This will allow appropriate treatment to be provided.
How to distinguish a back injury from a spinal injury
- With an injury such as a dislocated vertebrae, mobility in the damaged area will be limited, or movement will cause severe pain.
- When a fracture occurs, the body often takes an unnatural position.
- If the spinal cord is damaged, there may be tingling in the limbs, disruption of internal organs, weakness, loss of sensation and inability to move.
First aid for a back injury
If a child hits his back hard, what should he do?
In medicine, there is a rule in this case: until the opposite diagnosis is proven, the patient may have a damaged spine. Therefore, any movement can worsen the baby’s condition.
The child cannot be put on his feet, sat down, moved, etc. We need to call the doctors.
To provide assistance, doctors immobilize the patient and carry him on a rigid stretcher with a head holder and straps.
Warning signs of injury. What to do?
It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance if the child exhibits the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing or heartbeat;
- constriction of the pupils;
- sensory disturbance;
- inability to move limbs;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- severe fatigue, desire to lie down;
- a feeling of tingling, burning or numbness in the bruised area.
This indicates that the child has suffered a serious spinal injury!
Features of the regime after a back injury
- It is worth observing bed rest.
- If the doctor recommends, you will need to wear a rigid corset.
- You can engage in physical therapy and breathing exercises approximately on the second day after the injury.
- Your doctor may also prescribe physical therapy.
Danger of head impacts
As soon as the baby has learned to move independently, he often falls and bumps appear on his head. Parents, as a rule, do not pay attention to this, considering this condition normal. How do you know if you should worry?
Forehead strike
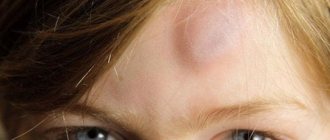
The consequence of a child falling head down and hitting his forehead is the appearance of a bump. This occurs due to injury to small vessels and filling of surrounding tissues with blood. The result is swelling and hematoma. Due to the fact that the forehead bones are quite strong, these injuries are not dangerous. But, if a baby develops a lump after a fall, then it must be shown to a doctor who can determine the extent of the damage and rule out serious consequences.
Hit with the back of the head
Sometimes, a child may fall on his back and hit the back of his head. In this case, parents should hurry to see a doctor. This is because such injuries can cause serious problems in the future. Due to the fact that in the back of the head there are nerve endings that affect the functioning of the organs of vision, it can be disrupted. The child may lose consciousness, experience trembling in the legs and general weakness of the body. And all this can happen even with a small bump.
If you see that your child has hit the back of his head, rush with him to the doctor, even if he does not make any complaints. There are times when signs of such injuries may take a long period of time to appear.