Rabies (rabies) is an acute zoonotic disease of viral etiology that develops after a person is bitten by an infected animal. The disease is caused by RNA viruses (rhabdoviruses). The disease manifests itself as severe damage to the central nervous system and death. There is no cure for rabies. The rabies vaccine is the only chance for a person bitten by a sick animal to survive. Therefore, vaccination should be carried out immediately.
Most cases of rabies development in patients are caused by late seeking specialized help, as well as by violation of the recommended regimen during the period of preventive vaccination or by failure to complete the course of specific immunization.
Is rabies a fatal disease?
The rabies virus affects the central nervous system of animals and humans.
Rising along the nerve pathways, it reaches the brain and causes inflammation (specific encephalitis). Until 2005, rabies was considered a fatal infection for humans. There are only a few known cases of people being cured of this terrible infectious disease. However, a timely vaccination or certain measures, which will be discussed later, can save the patient’s life. The main carriers of the rabies virus are:
- Wild animals (wolves, foxes, wild cats, lynxes, bats, hedgehogs, rodents)
- Farm animals
- Pets
Statistics of rabies incidence in Russia by animal carrier species for 1997 - 2007
The diagrams show that the main sources of rabies are wild animals. Recently, due to the spread of rabies among wild animals, the virus penetrates simultaneously into several biological species. For example, it is transmitted from a wolf to a fox or marten. Therefore, you need to be especially careful and attentive in the forest. We have previously written about safety rules in the forest.
Approximately half of all cases of rabies infection occur in domestic and farm animals that come into contact with wild animals. The most dangerous wild animals in terms of rabies infection are foxes (first diagram). Moreover, you can meet mad foxes both in the forest and in the city. When infected with rabies, foxes can manifest themselves in two ways. Some may behave aggressively and attack people. Others, on the contrary, are drawn to people and show affection, like domestic cats. This behavior is not typical for a healthy fox.
If you encounter such a fox, you must immediately leave the forest or area in which it is located. Under no circumstances should you pick them up.
What is rabies in dogs and why is it dangerous?
Rabies has a long history and a “strong association” with dogs. The first written account of rabies is contained in the Laws of Eshnunna, dated 1930 BC. e. The report contains not only a diagnosis, but also recommendations that the owner of a dog exhibiting symptoms of rabies should take all possible measures to prevent it from biting anyone.
What is rabies in dogs? It is a viral neuroinvasive disease that causes inflammation in the brain and is usually fatal. Rabies is viral in nature and primarily affects mammals.
During laboratory research, it was discovered that birds can also be infected with the virus. A minor risk group includes cold-blooded animals and insects; they become infected with the virus only unnaturally, if a person has a hand in this process.
Animals with rabies suffer from deterioration of the central nervous system and tend to behave strangely and often aggressively. Inappropriate behavior increases the likelihood that a virus carrier will bite a healthy animal or person, which will lead to transmission of the virus.
In dogs, rabies usually develops in three stages:
- Prodromal or first stage 1–3 days – characterized by behavioral changes.
- The second stage, 3–4 days , is characterized by excitement. It is this stage that is associated with "rabid animal rage" due to the affected dog's tendency to become hyper-reactive to external stimuli and bite anyone and anything that comes close.
- The third stage of 2–3 days is the paralytic stage, which is caused by damage to the neurons of the brain. There are coordination problems and other problems in the central nervous system. The dog cannot walk or does so unnaturally due to paralysis of the hind limb. At this stage, foamy drooling is observed. Further, there are difficulties with swallowing, paralysis of the facial and throat muscles. Death usually occurs due to collapse of the respiratory tract.
Note! Most people become infected with rabies from canines and wild animals. Among domestic animals, the most common carrier of the virus is the dog.
Methods and techniques of treatment
With the help of certain manipulations you can prolong life, but death will be inevitable.
Treatment for rabies in a person begins on the day he seeks professional help.
In most situations, a modern version of the vaccine is used, which can significantly shorten the duration of the treatment course and also reduce the amount of the administered dose.
It should be noted that, contrary to numerous misconceptions, the vaccine is not injected into the buttock. For children it is injected into the outer part of the thigh, for adolescents and adults directly into the deltoid muscle.
The standard dosage is 1 ml, and its effect can reach up to 98%. An important point is to comply with the condition: the first injection must be given no later than two weeks after contact with the animal.
Important! Any violations in the vaccination regime can lead to dire consequences.
From the moment of the first vaccination, antibodies will begin to appear fourteen days later, and their maximum peak concentration will accumulate in a month. As the course is completed, a person develops immunity, which will protect the body for the next year.
Those undergoing treatment are prohibited from doing the following for six months after completing the course to avoid deterioration of immunity:
- drink alcohol;
- is in a sauna or bathhouse;
- supercool;
- be subject to significant physical fatigue.
In some cases, therapy using immunoglobulin is allowed. Often this course is carried out in combination with the introduction of a vaccine.
Treatment
The doctor’s first task is to conduct an urgent diagnosis. In some cases, an examination and knowledge that the person was bitten by a stray or wild animal is sufficient. Sometimes blood may be taken from the victim to conduct a minimal test, or the lining of the eye may be examined. After this, treatment is prescribed. You need to start it right away, because... When the first symptoms appear, the probability of death is one hundred percent, even with the use of all drugs.
The patient is started to be injected with a special drug “KOKAV” according to a certain scheme: day 0, day 3, day 7, day 14, day 30 and day 90. The injection is given in the deltoid muscle, and in young children the vaccine is administered through the thigh. The dosage is only 1 ml. When the course of treatment is completed, the victim will develop immunity to rabies, which will last for one year.
Sometimes it is additionally necessary to use another method of treatment. To do this, the patient is injected with rabies immunoglobulin into the wound area or buttock. However, it is used in practice quite rarely, because its use is required only in particularly severe cases. Administration schedule: day 0, day 3, day 7, day 14 and day 28.
For the period of treatment and the next six months of life, patients are prohibited from drinking alcohol, overwork, visiting the bathhouse, and getting hypothermic. If you follow all the rules and take medications, you will soon be able to start living the same way as before.
You can protect yourself with pre-exposure vaccination. However, doctors do not recommend doing this, because... This need exists only for people at risk (veterinarians, travelers, pathologists).
In 2005, doctors in the United States were able to cure a girl of rabies by putting her into a long-term artificial coma. This success is explained by the fact that the virus has only a temporary effect, after which it ceases to affect the infected person.
Symptoms
The incubation period for rabies infection lasts from 10 days to 3 months. There are rare cases where patients managed to live without any symptoms for a whole year. The exact rate at which the virus spreads depends on the method of infection, the depth of the bite or scratch if the person suffered one, the point of infection, the amount of saliva that enters the body, and the type of animal carrier. The disease itself, from the moment symptoms appear, can last from 5 to 12 days. Moreover, it occurs in three stages, each of which has special symptoms.
First stage
The duration of the first stage is from 1 to 3 days. At this time, the patient exhibits mild symptoms that can be confused with some other diseases. These include:
- Unpleasant nagging pain at the wound site;
- Inflammation and swelling if the damaged area of skin has already healed;
- Stable body temperature from 37.0° to 37.3°C;
- Weakness, nausea and vomiting, regular headaches;
- Increased anxiety, unreasonable fear;
- Irritability, apathy and depression;
- Lack of appetite, deterioration in sleep quality, frequent nightmares;
- Hallucinations (when bitten by an infectious animal in the head area).
After the first days in the initial stage, the patient's condition worsens, and rabies moves to the next level.
Second stage
The excitation stage is the second stage of virus development in the human body. It can accompany the patient for 2-3 days and, as a rule, is paroxysmal in nature. Therefore, in some cases it cannot be detected immediately. The following symptoms are characteristic of this stage:
- Strong excitability, strong reaction to any events, excessive emotionality;
- Aggressive behavior, shouting at others, frequent conflicts;
- Rare and abrupt-convulsive breathing;
- Increased heart rate, increased sweating, salivation;
- Facial muscle spasms when exposed to bright light or loud sound;
- Hydrophobia, spasms when trying to drink water, as well as at the sight or sound of it;
- Dilation of the pupils, holding the gaze at one point, protrusion of the eyeballs.
Sometimes death occurs during an attack. If the manifestations stop, then the person again begins to behave adequately and returns to his business.
Third stage
The last stage lasts only one day. It is accompanied by the appearance of very serious symptoms and ends in the death of the patient. A person infected with rabies at this stage has the following symptoms:
- Stopping the manifestation of seizures and hallucinations;
- Emotional indifference, mental calm;
- Impaired sensitivity of skin and muscle tissue;
- Paralysis of muscles and some internal organs;
- Increase in body temperature to 42°C;
- Increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure.
A day after the start of the final stage, the patient’s heart or respiratory center is paralyzed, causing immediate death.
The first symptoms of rabies in humans
The first signs of rabies in humans can appear as early as a week after the bite, however, more often the incubation period of the virus ends one to three months after the bite.
In patients, the temperature rises (as a rule, low-grade fever is characteristic), the phenomenon of a scar develops, complaints of general malaise, the occurrence of inexplicable anxiety, and depression appear. There are sleep disturbances, possibly both nightmares and insomnia.
Patients also complain of severe dry mouth, poor appetite, headaches, shortness of breath, and tachycardia.
The first stage of rabies lasts from one to three days.
The second stage is accompanied by pronounced excitement. One of the most specific signs of rabies appears - severe hydrophobia. The fear of water is so strong that an attempt to bring a glass of water to the patient’s lips causes a painful spasm of the larynx and an attack of suffocation.
Patients reject water, despite severe dehydration and extreme thirst. Specifically, stretching forward of trembling hands and small twitching of the facial muscles. Such symptoms appear not only when the patient sees water, but also when he hears its sound (an open tap).
Aerophobia is manifested by the development of an attack from a breath of fresh air. In some cases, the attack may be accompanied by pronounced aggressiveness; patients try to attack hospital staff. Periods of aggression and violence are accompanied by pronounced salivation.
There is a sharpening of facial features, sunken eyes, and dilated pupils.
After periods of violence, the patient comes to his senses and is fully aware of what is happening. Also, patients fully remember everything that happened.
After the development of hydrophobia, patients live for several days (rarely more than six days).
The patient's descent into an “ominous tranquility” is a sign of imminent death. The cause of death is paralysis of the cardiac and respiratory muscles.
In isolated cases, variants of silent rabies are possible (usually after an attack by vampire bats). The disease occurs with clinical paralysis without the stage of excitation.
The total duration of rabies is from five to eight days. A longer course of the disease is extremely rare.
Prevention and vaccination against rabies in humans
After animal bites, you must immediately thoroughly wash the wound with laundry soap and running water, treat it with alcohol and iodine. It is strictly forbidden to cauterize or excise the wound, as this contributes to the spread of the virus.
After treatment in the hospital, the wound is sprinkled with powder containing anti-rabies gamma globulins.
They no longer give 40 rabies injections in the stomach. This method is outdated.
A person should be vaccinated against rabies no later than two weeks from the moment of the bite. After the specified period, it is practically ineffective.
Rabies vaccination schedule
At the moment, the following rabies vaccination schedule for humans is used: 1 milliliter of vaccine five times on the day of the bite. The drug is injected into the shoulder or thigh. Next, the rabies vaccine is administered on the third, seventh, fourteenth, twenty-eighth (or thirtieth) and ninetieth day after the bite.
The injection is given on the 28th or 30th day, depending on the vaccine manufacturer.
In case of severe bites or late treatment (10 days from the moment of the bite), anti-rabies gamma globulins are administered in addition to the vaccine.
Preventive vaccinations are recommended for people working with animals, hunters, researchers, veterinarians, etc. The rabies vaccine is valid for about a year. Therefore, for patients bitten by an animal within a year after a full course of vaccinations, vaccination is indicated only on the day of the bite + on the third and seventh days.
Preventive vaccinations are carried out upon application, as well as on the seventh and thirtieth day. A year later, the first revaccination is indicated (one administration), with further administration of the vaccine every three years (single administration of the vaccine).
Compatibility of rabies vaccination in humans and alcohol
Alcoholic beverages should not be drunk for six months after rabies vaccination and throughout the entire course of vaccination.
Drinking alcohol increases the risk of developing adverse reactions to the rabies vaccine.
The use of glucocorticosteroid drugs and immunosuppressants is also contraindicated.
Is it possible to wet the rabies vaccine?
The instructions for vaccines do not contain information about the prohibition of getting the vaccine wet. However, it is not recommended to actively rub the grafting site while swimming. Also, it is advisable to refrain from visiting the sauna (overheating is contraindicated).
During the course of preventive vaccination, overheating, hypothermia or excessive physical activity should be avoided.
Side effects of rabies vaccination in humans
Side effects of the vaccine can be manifested by the development of swelling at the injection site, pain, fever, gastrointestinal disorders of a dyspeptic nature, arthritis, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Read further: Vaccination measles, rubella, mumps - side effects, which vaccine is better, revaccination
- About
- Latest Posts
Anna Chernenko
Infectious disease doctor of the highest category with extensive experience. Specialist in the field of therapy of infectious diseases of various etiologies, methods of laboratory diagnostics of biomaterial.
Treatment of rabies in humans
There is no cure. All treatment comes down to creating the most gentle conditions for the patient and alleviating his condition until death. After death, the body undergoes mandatory cremation.
Attempts have been made to treat with rabies gamma globulins, but there is no data on their effectiveness.
To date, only six cases of rabies survival have been reported. The most famous patient is Gina Gies, who was treated according to the Milwaukee Protocol.
This is an experimental treatment developed by Dr. Rodney Willoughby. Therapy consists of putting the patient into an induced coma (to protect the central nervous system until the body produces antibodies to the virus) and using antiviral drugs.
The patient spent seven days in a coma. In total, the treatment took 31 days. Subsequent studies showed that her brain was not damaged. Mental and cognitive functions were completely preserved.
First aid
When a person has reason to believe that they may have contracted rabies, they should immediately consult a doctor
But it is equally important to provide yourself with first aid, as well as take care of safety. This is especially true in cases where the victim was bitten by a pet that became a carrier of a dangerous virus.
Immediately after the bite you need to do the following:
- Call an ambulance or choose the nearest medical facility (trauma center).
- Tie up your pet, isolating it from surrounding people and animals, or call the sanitary service through the rescue phone.
- Wash the wound with clean water and laundry soap, trying to cause heavy bleeding to remove the virus from the blood, and go to the hospital.
- Once the doctor has taken all the necessary measures, you should definitely show your pet to a veterinarian when returning home.
You can identify rabies in pets yourself. However, this can only be done after the active development of the disease begins, and the carrier becomes infectious about a week before. Therefore, in some cases, you can catch the virus even from an apparently healthy pet. Nevertheless, the symptoms will help identify a guaranteed sick animal. These include:
- Desire to chew or scratch where another animal has bitten you;
- Dilated pupils, eating inedible objects;
- Increased salivation, foam at the mouth and vomiting;
- Severe hydrophobia (not experienced by everyone);
- Aggressive behavior, attempts to run away from home.
Knowing exactly how people become infected with rabies will help many people protect themselves.
If symptoms can be detected in a pet before direct contact with it, then it must be urgently transferred to veterinarians, taking special care during transportation, because any attack from him would be extremely dangerous
After confirming the diagnosis of the animal, you should throw away all its toys that may have saliva on them.
Diagnosis of rabies in humans
To make a diagnosis of rabies, a medical history (animal bite) is extremely important. If possible, the animal should be captured and examined.
The specific symptoms of the disease are also taken into account. Diagnosis of rabies is divided into intravital and postmortem.
Test for rabies in humans
Intravital is carried out by carrying out:
- virological examination of biological material (saliva, cerebrospinal fluid);
- PCR, ELISA, RIF;
- study of corneal imprints.
For post-mortem diagnosis, electron microscopy of frozen brain tissue, immunohistochemical examination of the brain, as well as MFA or PFA are used.
All work with the rabies virus is carried out only in specialized laboratories in compliance with the strictest safety measures and protocols for working with especially dangerous infections.
Read further: What is the polio vaccine, what are the consequences and reactions to the vaccine
The most likely methods of infection
The rabies virus is contained in the saliva of a sick animal. Infection occurs when the virus enters the bloodstream, usually through a bite. It must be taken into account that the virus can appear in saliva 1-7 days before the first symptoms of the disease, so you can become infected even from an animal that looked healthy.
The most dangerous are bites from sick carnivores (especially wild ones, such as foxes). People rarely become infected from farm animals. Domestic birds get rabies, but they cannot infect humans due to the lack of salivary glands. Infection from birds of prey is possible, but unlikely due to their low prevalence.
But a bite is not the only way to transmit the virus, so when contacting wild or stray animals you need to be as careful as possible. Possible routes of transmission of rabies include:
- through contact with the saliva of a rabid animal on the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, mouth and damaged skin;
- through scratches caused by claws, as animals lick their paws and particles of saliva with the virus may remain on them;
- while cutting up the carcass of a sick animal through scratches and wounds on the hands.
Mad cat
Also in medicine, cases of infection through atypical or unusual routes are described - for example, through airborne droplets, which is only possible with a very high concentration of the virus in the air that is practically not found in nature.
Isolated cases of infection through the placenta during pregnancy and during tissue and organ transplantation have been recorded. There have also been cases of animals becoming infected through the digestive tract after eating raw meat; humans have not yet become infected. This is due to the fact that the virus can very rarely penetrate the blood and glandular organs, and when cooked it dies instantly.
Ways of contracting rabies
The rhabdovirus that causes the disease is transmitted by the saliva of an infected animal entering the bloodstream. Most often found in the wild, carriers are animals (foxes, ferrets, hedgehogs, badgers). Therefore, hunting dogs and animals kept near forests or plantings are at risk. There are cases of infection due to saliva getting on open or wounded areas of the skin.
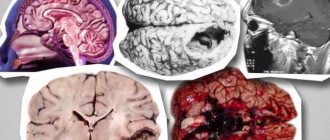
After entering the body, the virus spreads through signaling by nerve cells and concentrates in the brain and spinal cord. As a result, tissues change, swelling and hemorrhages occur.
The virus is dangerous not only for pets, but also for humans. It can be transmitted through water and food, from mother to baby and, in rare cases, through airborne transmission.
How does rabies develop?
The rabies virus appears in saliva eight to ten days before the animal shows signs of illness. Therefore, even after being bitten by a seemingly normal, healthy animal, you should urgently treat the wound with laundry soap and consult a doctor for preventative measures.
If possible, the animal should also be taken to a doctor for further observation and examination.
There are two types of rabies virus:
- street (wild variants of the virus common among animals);
- fixed (this type of rabies virus is used to create vaccines).
Both viruses have a similar antigenic nature, therefore, after administration of a vaccine made from a fixed strain, immunity to the wild virus also develops.
Once infected, rhabdovirus spreads along nerve fibers. Hematogenous and lymphogenous spread of the virus is also possible.
The virus is characterized by its tropism for acetylcholine receptors, which contributes to the damage of many groups of neurons, the development of reflex-type hyperexcitability and, subsequently, the formation of paralysis.
The brain of an infected person is affected by swelling, hemorrhage and severe necrotic and degenerative changes. Rabies causes damage to all brain structures. The area of the fourth ventricle is subject to the most severe degenerative changes.
What is rabies
Rabies is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases, which is caused by the Rabies virus. All warm-blooded creatures, including humans, are susceptible to it. The main route of transmission of rabies is through the bites of infected animals. The virus is released into their saliva and, when bitten, enters the bloodstream. In addition, it can end up in a person’s blood through scratches and injuries.
The virus travels from the site of the bite along nerve fibers to the spinal cord and then to the brain. There it multiplies and causes irreversible changes in the brain. And from there it spreads throughout the body, including in saliva. The virus affects nerve cells, causing increased excitability and aggressiveness in the patient, as well as loss of coordination, spasms, paralysis and many other symptoms.
The virus is quite stable in the external environment. It easily tolerates low temperatures and can be stored frozen for several months. But when boiled, it dies instantly. Direct sunlight and ultraviolet radiation are also harmful to the virus. Almost all disinfectants can kill it.
Prevention of rabies
In the prevention of rabies, a very important role is played by the owner's compliance with the rules for keeping pets. The very first thing you need to do when you decide to take an animal into your home is to find out if it is vaccinated against rabies. Preventive vaccination using rabies vaccines for pets is mandatory in our country, and in any city or town, even a small one, they are required to do it free of charge in state veterinary clinics. The rabies vaccine is given at an early age. Repeated vaccinations must be carried out every year.
If you suspect your pet has rabies, you should immediately take it to a veterinarian for examination and testing. If an animal is not vaccinated, then it should not be allowed to participate in exhibitions and livestock farms, or go hunting with it in the forest.
If you want to sell, buy or transport dogs, you must obtain a veterinary certificate indicating that the animal was vaccinated against rabies no more than 11 months and no less than 30 days before the trip.
If your pet has been bitten by wild animals or stray dogs, you must immediately report this to the veterinary services so that it can be examined by a doctor.
The material was prepared with the participation of a veterinary paramedic
Text: Maria Pletnyova
Article updated 09.27.2019
What to do if your dog is bitten
Regardless of who bit the pet and how, it is important to be attentive, cautious and quick in examining and starting treatment:
- At home, you need to carefully examine the bite site in good lighting using a magnifying glass; it is important to first protect yourself with special barrier gloves, clothing and a medical mask;
- The site of the bite must be rid of interfering fur; it should be cut around the perimeter of the wound; treat the bite with a solution of laundry soap (the proportion is calculated according to the form 1:10 - part soap to ten parts water); the best option would be to rinse under pressure; for this, the solution is drawn into a syringe without a needle or into an enema;
- A doctor is immediately called if possible; or the pet is taken to a veterinary clinic.
If the required vaccination is available, the pet is isolated in a specially prepared home incubator or in a clinic, and an observation period is set at 2 weeks . If there are no symptoms of rabies, the dog is re-vaccinated and released.
Lack of vaccination complicates the process. The animal is immediately vaccinated with a drug that stimulates the production of immunity to the virus. After this, he is also monitored in an incubator (14 days) . Repeated vaccination is done in this case as well.
If symptoms do appear, the dog must be euthanized. Veterinarians begin to diagnose the exact infection of the virus after the death of the animal.
How to recognize a sick animal
The problem with this disease is that it is almost impossible to cure once clinical symptoms have already appeared. The progression of the disease can only be stopped through vaccination. The rabies vaccine must be given urgently, immediately after the bite.
It must be remembered that even a domestic cat can be a carrier of the virus if it has been in contact with a sick yard animal. The incubation period of the virus in animals takes 3-10 days, so it is impossible to know at an early stage of infection that the pet is already sick. He may behave calmly, but there will be a huge amount of virus in his blood. This animal is very contagious.
When the virus has captured the nerve cells, symptoms of rabies begin to appear: aggression (the animal attacks for no apparent reason, reacts painfully to any irritants), drooling (saliva can flow like a river or, like foam, collect in the corners of the mouth). It is easier for the owner to observe a pet, so if the pet suddenly becomes lethargic, hides in dark corners, or eats almost nothing, he needs to be taken to the vet immediately!
In the excited stage, the dog growls almost continuously and barks until he becomes hoarse. Everything irritates her: any shout, harsh light, etc. Due to spasms of the pharyngeal muscles, she cannot drink water. The animal is salivating profusely, its jaw is slack, and its tongue is hanging out of its mouth. Clouding of the cornea of the eyes often occurs. After the stage of excitement, a period of relative calm begins, when the animal becomes obsessively affectionate. This is the first sign of approaching paralysis and subsequent death.
A person needs to remember that the prognosis for this disease is always unfavorable. In the entire history of modern medicine, only two cases of recovery have been recorded, which doctors can only explain by the peculiarities of the body’s immune response. In both cases, these were 15-year-old teenagers, who can be called real lucky ones.
Is it possible to transmit rabies from person to person?
Rabies is an acute viral infection from the zoonotic group. It causes pronounced symptoms of damage to the nervous system, and its development always leads to death. Animals are believed to be the main carriers. But many people are concerned about whether the rabies virus is transmitted from person to person. To understand this issue, we need to look at the infection a little closer.
Picture of the disease
The disease develops in stages. At the first stage, the infected person begins to experience itching, pain and burning in the bite area. The wound may heal, but the swelling does not go away for a long time. Painful sensations spread up the limb if the arm or leg was bitten. If a person is bitten on the face, they experience hallucinations.
Damage to the nervous system begins almost immediately. The infected person experiences severe depression, is in a depressed state, sees terrible dreams, and suffers from lack of appetite. The temperature remains elevated throughout the entire period. Sometimes a reverse reaction can be observed - psychomotor agitation.
In the second stage, the patient develops an insurmountable fear of hydrophobia. Even trying to drink a glass of some drink or the sound of running water provokes spasms in the throat and fear of suffocation. The patient is almost constantly in a state of strong excitement, suffers from hallucinations, and sweats profusely.
Signs of rabies in humans
Severe damage to the central nervous system leads to:
- development of convulsive contractions of the respiratory and swallowing muscles;
- a sharp increase in salivation (secretion of saliva and profuse sweating;
- severe disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Further migration of the rabies virus throughout the body is accompanied by its penetration into all organs and the development of multiple organ failure.
The first signs of rabies in humans are the appearance of a scar phenomenon, unclear fears, and depression. Subsequently, the addition of paroxysms of rabies and various phobias is noted.
The scar phenomenon consists of a strong burning sensation, as well as nagging and aching pain at the site of the bite. The pain spreads along the nerve fibers located at the site of the bite. Severe redness and swelling of the scar is also noted.
Paroxysms of rabies are called a specific reaction of the patient to the action of any irritants. The patients shudder, stretch their trembling arms forward (the body also goes through a slight trembling) and throw their heads back. The appearance of inspiratory dyspnea (inability to take a full breath) is also characteristic.
The most indicative phobias (fears) with rabies will be the occurrence of hydrophobia (fear of water), aerophobia (fear of air), acousticophobia (fear of various sounds), photophobia (fear of light).
Prevention and treatment
This fatal disease requires preventive measures. Even a minor animal bite to a person can cause infection. This is an important point in understanding how rabies is transmitted. In any case, immediate medical attention is necessary. The subsequent course of action will be determined by the doctor. Emergency treatment is often used by administering a vaccine with active or passive action.
Prevention of rabies in humans is also an important process that regularly requires attention
It is recommended to use soap, detergent or other available substances that can kill the virus.
This procedure must be started as soon as possible after the bite and continued for at least fifteen minutes.
It should be remembered that infection can occur not only through a bite and scratch, but also through saliva.
Persons who, for various reasons, may have regular or direct contact with sick animals are recommended to receive a mandatory preventive vaccine.
Vaccination is carried out when:
- a person is bitten by wild rodents;
- saliva gets on the skin;
- there was a bite or scratch from an animal suspected of carrying the virus;
- the bite was applied through a thin tissue layer;
- after being injured by any object contaminated with the saliva of a known infected animal.
Vaccination is not carried out when:
- the wound was caused by a bird;
- a bite occurred on a dense layer of tissue, without damaging the skin;
- dairy or meat products from an infected animal were consumed without heat treatment;
- your pet was bitten by a rodent;
- received a bite from a wild rodent in places where the disease has not been noticed for two years;
- there was contact with a person infected with rabies without damaging the skin or contacting the mucous membranes with infected saliva.
How not to get rabies
Sometimes people's fear of contracting rabies reaches such a level that they come to the hospital for vaccination, even when there is no threat of infection. The possibility of infection is excluded when:
- the animal's saliva came into contact with intact skin;
- the bite fell on the fabric of the clothing, and it was not damaged;
- the wound was left by the claws of a bird;
- boiled meat or milk of a sick animal was consumed;
- bitten by a domestic animal that has been vaccinated against rabies for a year and has no dangerous signs, with a non-dangerous localization of the bite.