Back brain, being part of the nervous system, acts as the main coordinator of the work of all organs and muscles. It is through it that the brain receives signals from throughout the body.
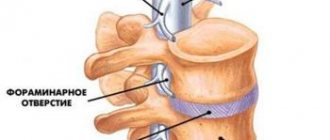
Spinal cord injury, or spinal injury, is damage to the internal contents of the spinal column: nerves, gray or white matter, meninges, blood vessels.
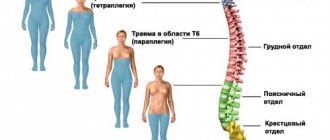
Back injuries often lead to spinal cord injuries. Spinal cord injuries account for about 15% of all nervous system injuries. Cervical spine injuries result in death in 30% of cases.
Damage can be open or closed (this depends on the integrity of the skin tissues).
Types of spinal cord injuries:
- shake,
- injury,
- hemorrhage in the spinal cord;
- destruction of the nerve roots,
- compression, displacement.
Injuries of a stable and unstable nature are distinguished separately. Fractures of the explosive type, rotation, dislocations and fractures of various degrees are considered unstable All these injuries are necessarily accompanied by rupture of ligaments, due to which the structures of the spinal column are displaced and the spinal roots or the canal itself are injured.
Spinal cord injuries are accompanied by disorders of the functions of internal organs. Immediately after receiving an injury, a malfunction of the nerve cells occurs, movement of the limbs becomes impossible, loss of sensitivity is observed, and partial paralysis .
Complications include hemorrhages into the spinal cord tissue and under the membranes of the spinal cord.
The function and integrity of the spinal cord may be impaired due to:
- falls from a height or accident;
- gunshot and knife wounds, blows;
- practicing some sports (motorsports, diving and others);
- tumors, malignant neoplasms;
- vascular aneurysm;
- congenital and postnatal abnormalities in the structure of the spinal cord;
- inflammatory processes;
- infections, neuroinfections;
- spinal circulatory disorders;
- arthritis;
- degenerative processes in the spine.
Symptoms of injuries depend on the type and location of the injury.
First aid
First aid to the victim is to maintain vital processes such as breathing and hemodynamics. It is necessary to ensure the immobility of the spinal column and eliminate bleeding, if any. It is also necessary to administer neuroprotectors and insert a catheter into the bladder if there is a delay in emptying.
Even before transportation, the medical representative must conduct a visual diagnosis (for the presence of associated injuries, open wounds, the presence of edema and reaction to the palpation process). Also at the scene of the incident, the degree of muscle tone and motor activity of the limbs are determined. Anti-inflammatory and antitetanus drugs are administered as preventive measures. If concussion is also observed, first aid tactics are based on this factor.
If the middle or lower section is injured, the person is placed on his stomach on a hard stretcher. If the upper part is damaged, the patient is transported strictly on his back.
Symptoms of concussion and spinal cord contusion
- sharp and severe pain at the site of injury;
- weakness;
- numbness in the limbs;
- pain in the spine;
- loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the body, in the area of the destroyed part of the spinal cord;
- motor dysfunction;
- involuntary emptying of the bladder or bowels ;
- breathing problems ;
- spasms below the destruction zone;
- loss of consciousness;
- curvature of the back/neck;
- partial paralysis.
Compression of the spinal cord occurs when the vertebral bodies or their fragments are displaced, as well as when hematomas form and cerebral edema. There may be loss of sensory activity and inability to move limbs or the entire body.
The most complex injuries lead to disorders of the intestinal organs, urinary system, respiratory systems and blood vessels. Often, victims suffer from chronic pain.
Spinal cord injuries affect not only the physical level, but also the psychological one. A person may experience impaired reaction speed, poor coordination, sudden mood swings, aggression, fear or a feeling of loss, anxiety, decreased appetite , and depression.
The most serious consequences of spinal cord injury are:
- paralysis of the whole body or individual parts;
- disability;
- Difficulty with digestion and bowel movements;
- deep vein thrombosis
- bedsores;
- muscle spasticity (constant tension);
- Impaired lung function (breathing problems).
Important! Any back injury requires urgent contact with a doctor, an ambulance or the nearest emergency room. After any spinal injury, immediate care is extremely important. The sooner a qualified neurosurgeon stops the pathological process in the spine, the less pronounced the consequences will be. Do not delay rehabilitation measures to eliminate long-term consequences of a spinal cord injury.
To clarify the diagnosis, radiography , and, if necessary, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (CT, MRI), which can help identify blood clots in the spinal substance. An X-ray of the spine will help determine the location of the injury and the type of injury. A lumbar puncture (lumbar puncture, spinal tap, lumbar puncture) and myelography may also be needed.
Hematomyelia is bleeding in which blood may accumulate in a hematoma, or fill a component of the spinal cord. It spreads along it, causing the destruction of nerve tissue, compression of motor pathways and brain structures. Causes partial damage to the spinal cord, but can affect the entire diameter. Accompanied by excessive bleeding into the space of the brain.
Types of injuries
As already mentioned, spinal injuries come in different types, which is why it is important to identify a specific variant during diagnosis. It will be useful for people to know common pathologies in order to roughly understand what they might encounter.
A disease such as hematomyelia often occurs. In such a situation, hemorrhages occur in the spinal cord, causing a hematoma. Various symptoms occur, in particular, loss of temperature and pain sensitivity.
Such manifestations remain for about 10 days, after which regression begins. If treatment is started in time, then it will be possible to restore impaired functions. It should be understood that a person often remains with neurological disorders.
It also happens that damage to the spinal cord roots occurs. In such a situation, a person begins to suffer from paralysis or paresis of the limbs. They are often accompanied by autonomic disorders, sensory disturbances, and problems with the functioning of the pelvic organs. Specific symptoms directly depend on which part of the spine is affected. For example,
If the collar area is affected, then paralysis of the upper and lower extremities begins, breathing becomes significantly more difficult, and sensitivity is also impaired.
Compression is a common spinal cord injury that occurs due to foreign bodies, joint appendages, and tendon problems that damage the spinal cord. As a result, a person may completely or partially lose motor activity in the upper or lower extremities.
Crush injury represents an injury in which the integrity of the organ in question is compromised. It ruptures, and symptoms of spinal shock are observed for two to three months. As a result, paralysis of the limbs may occur, and muscle tone may also decrease. A person’s reflexes, both somatic and vegetative, disappear. In this case, sensitivity will be completely absent, and the pelvic organs work uncontrollably.
When a concussion occurs, a reversible disruption of the spinal cord occurs, with a significant decrease in muscle tone, and a complete or partial loss of sensitivity in the parts of the body for which the damaged section is responsible. Such symptoms do not last long, after which complete restoration of the spine occurs.
As you can understand, spinal cord injuries can be different, which is why you should definitely consult a doctor for diagnosis. Just focusing on the symptoms will not be enough to find out a specific diagnosis.
At the same time, it is not recommended to self-medicate, because in this case you can not only not improve your well-being, but also worsen your health condition.
Danger of spinal cord rupture
Spinal cord rupture is an extremely serious and painful condition that leads to disability and threatens a person’s life. When the spinal cord is ruptured in areas of the body below the rupture site, communication with the brain is disrupted and they lose their functions. Also, many patients are interested in the question: will there be spasticity if the spinal cord is ruptured? If such a phenomenon is observed, then the likelihood of restoring lost functions increases. However, spastic phenomena require strict control and should not be neglected.
Spinal shock is a particularly serious condition when the spinal cord is ruptured. The spinal cord is temporarily “switched off,” and along with it the entire body. In this state, only the heart and lungs work, acting autonomously. During spinal shock, it will not be possible to test reflexes, sensitivity , and determine the degree of damage to nerve fibers. This condition cannot be predicted and can last from several weeks to several months. At this time, it is necessary to support the body and take measures to prevent bedsores and muscle atrophy.
A rupture of the spinal cord poses a direct threat to human life. If the most difficult period can be survived, the person will need to undergo a long course of rehabilitation to adapt to life with a disability.
Treatment
First aid consists of combating traumatic shock (see), which occurs in almost half of such patients, as well as violations of vital functions. In case of injury to the cervical and upper thoracic parts of the spinal cord due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, severe breathing disturbances may occur, up to its complete stop, and therefore it is necessary to apply artificial respiration, followed by intubation and transfer of the victim to mechanical respiration (see Artificial respiration).
Rice. 1. A patient with a cervical spine injury, prepared for transportation: a splint is applied to immobilize the cervical spine.
The victim is transported from P.-s. i.e. only on a rigid stretcher or on various kinds of shields in a position on the back or stomach with immobilization of the damaged part of the spine. Immobilization in case of damage to the cervical spine is reliable; the edges are achieved using a special splint (Fig. 1).
Rice. 2. A patient with a fracture of the cervical spine due to skeletal traction by the tuberosities of the parietal bones.
The basis of conservative treatment of patients with closed injuries of the spine and spinal cord who are not subject to surgical treatment is traction on an inclined plane (see Traction). Such an inclined plane can be a rigid bed or a shield with the head end raised by 20-30°. In this case, traction is carried out due to the patient’s own body weight, which is fixed to the head end of the bed using cotton-gauze rings for the armpits (in case of a fracture of the thoracic or lumbar spine), or a load fixed to the bones of the skull (Fig. 2) or behind the zygomatic arches (in case of a fracture of the cervical spine). To reposition displaced vertebrae, place a bag of sand or a thick cotton swab under the fracture area. To restore impaired function of the spinal cord (in cases of concussion or bruise), medications are prescribed that increase the excitability and conductivity of the spinal cord (dibazole, proserine, strychnine, etc.), absorbable agents (aloe, vitreous, FIBS, lidase, pyrogenal, trypsin , iodine preparations, etc.). Much attention is paid to massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy, in particular applications of ozokerite, paraffin, and mud to the area of injury. Longitudinal galvanization of the spine, iontophoresis of iodine, novocaine, and proserine are also used. Measures to prevent trophic disorders are important, including: placing the patient on a mattress made of porous rubber, foam rubber or an air mattress, systematically turning him in bed, general quartz irradiation.
In case of compression of the spinal cord, surgical treatment is indicated to eliminate compression of the brain and restore normal topographic-anatomical relationships between the spine and spinal cord. Surgical tactics are determined by the nature of the compression and its location.
Rice. 3. Radiographs (and their diagrams) of the cervical spine in case of fracture-dislocation. At the cervical vertebra (lateral projection): a - before surgery, b - after corporedesis (arrows indicate the area of the fracture). Rice. 4. Schematic representation of the placement and fixation of bone grafts for a spinal fracture: 1 - spinous processes of the vertebrae, 2 - bone grafts placed on the skeletonized vertebral arches on both sides of the spinous processes, 3 - silk sutures.
With the help of forced closed reposition, by skeletal traction of the skull bones, deformity of the cervical spine and bone compression of the spinal cord are eliminated. After this, a spinal puncture with liquorodynamic tests and venospondylography are performed for diagnostic purposes. If disturbances in the patency of the subarachnoid spaces are detected, a laminectomy (see) is performed with revision, elimination of possible compression of the spinal cord and simultaneous posterior fixation of the spine (see Spondylodesis). If venospondylograms reveal signs of impaired venous blood flow, indicating anterior compression of the spinal cord, removal of part or the entire body of the damaged vertebra along with one or two adjacent discs (so-called anterior decompression) with mandatory fixation of the adjacent vertebral bodies using bone grafts — corporodesis (Fig. 3). In some cases, if indicated, open reduction of the fracture-dislocation is performed, followed by posterior fixation of the cervical spine. In case of fracture-dislocations of the thoracic and lumbar spine, it is fixed using a Tsivyan-Ramich fixator or bone grafts placed on skeletonized arches on both sides of the spinous processes and fixed with silk sutures through the interspinous ligaments (Fig. 4). Various metal structures can be used to fix the spine. In the presence of a depressed vertebral arch fracture, emergency decompressive laminectomy is indicated. The remaining signs of spinal cord compression after eliminating the spinal deformity, as well as the presence of a penetrating wound with liquorrhea (see) are an indication for revision of the spinal cord.
Rice. 5. Schematic representation of the stage of the operation (removal of cerebral detritus) for spinal cord injury: 1 - dura mater, 2 - spinal cord, 3 - cerebral detritus washed from the bulb with isotonic solution, 4 - retractor, 5 - suction.
Inspection of the spinal cord is carried out after laminectomy and opening of the dura mater of the spinal cord with a linear incision along the midline. In this case, blood clots are removed using anatomical tweezers or cotton balls. If the substance of the spinal cord is damaged, the brain detritus is washed with an isotonic solution and suctioned with an aspirator through a cotton-gauze ball (Fig. 5). During an anatomical break of the spinal cord, necrotic areas of its proximal and distal sections are removed. Putting sutures on the ends of the interrupted spinal cord did not justify itself. When the roots of the cauda equina are ruptured, they are sutured under an operating microscope (see) using microsurgical instruments. The dural incision is carefully sutured.
In case of open injuries of the spine and spinal cord, primary surgical treatment of wounds is performed (see), laminectomy, removal of bone fragments, accessible foreign bodies, revision and elimination of compression of the spinal cord, and in the presence of a penetrating wound - suturing or plastic surgery of the defect of the dura mater of the spinal cord (see . Meninges).
Rice. 6. Schematic representation of the stage of meningomyeloradiculolysis during the adhesive process after spinal cord injury: 1 - resected vertebral arches, 2 - dura mater, taken on supports and opened, 3 - spinal cord, 4 - fusion dissected with a spatula.
In the postoperative, as well as in the late period of both closed and open trauma, repeated courses of conservative treatment are carried out using absorbable, stimulating drugs and physiotherapy. Indications for late laminectomy with revision of the spinal cord are all types of compression, severe pain, as well as persistent trophic disorders that are not amenable to conservative treatment. The operation in this case consists of disconnecting the meningeal adhesions around the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots (meningomyeloradiculolysis), restoring the patency of the intrathecal spaces and eliminating compression of the brain (Fig. 6). Rehabilitation of impaired functions is facilitated by the dignity of chickens. treatment in specialized sanatoriums for patients with spinal cord damage (Saki, Sergievskie Mineral Waters, Kemeri, etc.), which is carried out in the late period of injury.
Treatment of trophic disorders is aimed at normalizing the trophic influence of the nervous system and directly affecting bedsores and trophic ulcers. Surgical intervention on the spine with revision, elimination of compression and foci of irritation of the spinal cord, as well as conservative measures to restore the function of the spinal cord help to normalize the trophic influence of the nervous system on tissues.
Forecast
determined primarily by the degree and level of spinal cord damage. The higher the level of injury and the more significant the damage to the spinal cord, the greater the danger to life. In most patients with P.-s. t. persistent neurol, disturbances remain, the severity of which also depends on the degree of damage to the spinal cord.
Causes
Factors that provoke back injuries can be:
- Injuries sustained in road accidents. They are more often observed in pedestrians or motorcyclists, since their back is not protected by a hard seat back.
- Injuries caused by a person falling from a height, including falls from bridges or other structures, or jumping into water.
- Domestic injuries. These include falls from stairs, knife wounds, and gunshot wounds. In older people, brain ruptures can occur even as a result of falling from their own height.
Also, serious back injuries can be sustained by a child during natural childbirth or during a caesarean section.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of spinal cord injuries should begin with a history. During the interview, primary neurological signs are revealed:
- physical activity for the first time minutes after injury;
- manifestation of shock;
- paralysis.
In the hospital, a specialist conducts a detailed external examination with palpation. At this stage, the patient’s complaints are taken into account:
- location and strength of pain;
- problems with memory and perception;
- impaired skin sensitivity.
Palpation reveals bone displacement, swelling, unnatural muscle tension and all kinds of deformities. Neurological examination reveals changes in reflexes.
Spinal cord injury requires accurate diagnosis. To do this, an instrumental examination is carried out:
- CT, MRI.
- X-ray of bone tissue in several projections: through the oral cavity, anterior, lateral and oblique.
- Myelography using a contrast agent.
- CT myelography.
- Study of somatosensory evoked potentials. This method measures the conductivity of nerve tissue.
- Vertebral angiography is a study of the blood vessels that supply brain tissue.
- Electroneuromyography to assess the condition of muscles and nerve endings.
- Lumbar puncture with liquorodynamic tests to study the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Used on patients with spinal cord injuries, these diagnostic techniques make it possible to distinguish various spinal cord injuries from each other, depending on their severity and cause. These examinations directly influence the choice of therapy.