Motion sickness is associated with increased sensitivity of the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for maintaining balance. Our vestibular apparatus is located in the inner ear and has a complex structure. Thanks to it, we can navigate in space, hold a pose, and maintain body balance. From numerous nerve endings - receptors that are located in muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, skin - the vestibular apparatus receives information about the direction and speed of movement that we make.
These simple exercises, which reduce excitability and increase the resistance of the vestibular system to stress, can be included in your morning exercise routine or performed throughout the day. Regular training of the vestibular system will help get rid of unpleasant sensations that can overshadow any trip.
Infographics: AiF
Basic information about the functionality of the vestibular apparatus
Before talking about the symptoms and treatment of vestibular disorders, it is necessary to understand the general structure of this organ.
The vestibular apparatus is the most important organ responsible for the function of balance, body position and movement. Without the normal functioning of the apparatus, a person is prone to problems coordinating movements, with changes in the position of the head and the whole body.
The VA is located in the inner ear. It is small in size and consists of three semicircular canals and two sacs.
The channels, in turn, are responsible for the perception of height, length and width. They are filled with liquid, which allows the vestibular apparatus to determine the position of the body; accordingly, when tilted, the liquid moves.
The sacs contain lenses that press on receptors that tell the brain about acceleration, deceleration, or changes in gravity.
General information
Vestibulopathy is a disorder of the normal functioning of the vestibular apparatus , in which characteristic symptoms appear.
The ICD-10 code for vestibulopathy is H81 (Vestibular function disorders). The normal orientation of a person in space and his balance in a vertical position is ensured by the vestibular apparatus. Disturbances in its work lead to a person experiencing confusion, dizziness , and the inability to remain in a standing position. This condition is also called labyrinthopathy. It can develop due to various reasons and diseases, developing at any age in every person. Sometimes vestibulopathy is a congenital pathology.
It may manifest itself as a separate syndrome or as a sign of neuropsychiatric disorders. In the second case, it is more difficult to treat this disease. How this pathology manifests itself, and what treatment methods are advisable to practice, will be discussed in this article.
Reasons that lead to deviations in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus
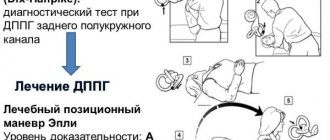
Positional vertigo
Almost everyone has experienced this feeling. This reason is especially common for people over 60 years of age. Women are most often affected by positional vertigo. It is impossible to name the exact factors influencing the occurrence of the disease. Most often, this deviation occurs after surgery or injury. Positional rotation may also provoke weakness during acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections. The following symptoms are characteristic of this disease:
- changing the position of the head, a feeling of rotation arises;
- nausea and vomiting appears;
- in some cases there is a painful sensation in the abdomen.
Dizziness due to multiple sclerosis
As the disease progresses, it may cause nausea.
Injury
A bone fracture in the temple, a concussion resulting from a head injury, causes VA disorders.
Pathologies of otolaryngology
Violations can provoke ear diseases:
- sulfur plug;
- otosclerosis;
- damage to the auditory tube;
- different forms of otitis.
Vestibular neuritis
Occurs as a result of an infectious or viral disease. This is one of the common causes of VA dysfunction, resulting from damage to the vestibular nerve. The most difficult period lasts about 3 days. Full recovery occurs after a few weeks. And for older people, it takes several months for full recovery. The following symptoms are characteristic of vestibular neuritis:
- severe dizziness;
- rapid eye movements to the sides or in a circle;
- nausea and vomiting.
Classification
Depending on the nature of its origin, vestibulopathy is divided into several types:
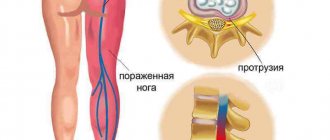
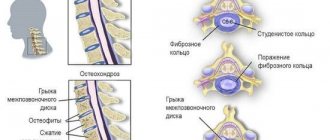
- Vertebrogenic – develops against the background of pathologies of the cervical spine. It can be observed with osteochondrosis , osteoporosis , intervertebral hernia , etc. This form is the most common. This condition is characterized by prolonged dizziness and a feeling of head instability. When trying to focus your gaze on moving objects, discomfort occurs. Spontaneous attacks of eye rotation may occur when a person tries to turn his head sharply. They last no longer than 30 seconds.
- Peripheral - develops as a consequence of the inflammatory process in the nerve ganglia in the inner ear. Most often this occurs due to allergies or infections. With such a lesion, in addition to vestibular disorders, the patient may experience tinnitus and causeless fear. Prolonged dizziness and bouts of eye rolling are noted.
- Central - develops if disturbances occur in the function and structure of the vestibular nuclei of the medulla oblongata and cortex.
- Post-traumatic – develops after traumatic brain injury if hemorrhage occurs in the labyrinth of the inner ear. As a result, tissue damage is noted. The eardrums may also be damaged, and the ganglia of the brain may be shaken and damaged. In this case, both dizziness and other characteristic signs are noted - spontaneous eye movements, nausea, vomiting. In addition, a patient with such a lesion has an unstable gait - it is difficult for him to stand on his feet.
Cochleovestibular syndrome is also distinguished . In this condition, auditory and vestibular function is impaired. Cochleovestibular disorders are accompanied by tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, and imbalance.
Sign of vertebrobasilar insufficiency
The disease most often affects people over 60 years of age. To treat vestibular disorders, it is necessary to treat cardiovascular diseases. The main causes of this type of disease are cerebellar stroke, damage to the vestibular nerve, and vascular diseases of the inner ear. The main symptoms of the disease include the following:
- unexpected dizziness for no specific reason;
- balance problems;
- accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Possible accompanying symptoms:
- deviations in visual understanding, may double;
- speech impairment, nasal voice;
- Falls may occur due to loss of balance.
The sign of vertebrobasilar insufficiency may not manifest itself for several months. Therefore, if such signs appear for a long time, this diagnosis is excluded. It is necessary to undergo a complete examination of the body.
Intoxication
There is poisoning from medications, technical ototropic fluids and alcohol. There are different groups of substances that can cause vestibular dysfunction during intoxication. First of all, these are organic and inorganic poisons of industrial origin.
These include silver, lead, nitrobenzene, mercury, nicotine and aniline. These are liquid and dense compounds. Substances in a gaseous state of aggregation cause no less harm when exposed systemically. These are carbon monoxide and acetylene. Sometimes illuminating gas is also described.
It is very important to remember about household poisons.
Alcohol has a greater affinity for the tissues of the inner ear. This group also includes nicotine and botulin. The latter is contained in improperly stored canned food. Among medicinal substances, arsenic and salicylates have an ototropic effect. Previously used Quinine is rarely found today.
Trauma and otosclerosis
Otosclerosis is a pathological process of destruction of normal tissue of the inner ear and its simultaneous replacement with denser tissue. It can be primary as part of a genetically inherited disease, as well as as a result of trauma.
Clinically, this disease also manifests itself as a triad of symptoms. These include hearing loss primarily. Without this symptom, otosclerosis cannot be diagnosed. Unlike Meniere's disease, this is a bilateral lesion. Complete deafness never develops; the patient can always hear himself.
Hearing deteriorates during meals and a high degree of concentration. And in noisy circumstances, a paradoxical improvement in audibility occurs. Tinnitus is very poorly tolerated by patients. Reminds me of the sound of leaves or dripping water.
Sound phenomena are permanent, but intensify with a runny nose, physical activity, sports, and while drinking alcohol. Noise interferes with eating and socializing. Dizziness is less common. This is usually positional vertigo, which occurs only in certain positions of the head and when turning the neck.
Multiple sclerosis
A demyelinating disease called the chameleon of neurological diseases. Develops for unknown reasons. But pathogenetically it is still a disease that develops according to an autoimmune scenario.
The first manifestations usually concern visual disturbances. Loss of visual fields, blurriness and defocus occur.
Among the complaints associated with vestibular dysfunction are dizziness and unsteadiness when walking. You can often notice small- or large-scale tremor of the upper extremities. Autonomic manifestations concern heart rate and blood pressure levels.
They may be accompanied by focal manifestations and disorders of pelvic functions. There is no specific treatment. Symptomatic correction is used, hormones and immunosuppressants are used. Options for the use of monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of multiple sclerosis are being considered.
Arterial and intracranial hypertension
When blood pressure rises, patients complain of severe headache and dizziness. With a long history of the disease, tinnitus appears or intensifies. The patient encounters difficulties when performing coordination tests.
All this indicates the presence of a hypertensive crisis. It should be differentiated from stroke. An attack of increased intracranial pressure is approximately the same. Treatment boils down to relief of hypertension, and then antihypertensive therapy is selected by a therapist or cardiologist.
Neuropathy, tumors
With metabolic disorders, the peripheral nervous system suffers greatly. This is possible with diabetes, cancer, and problems with the thyroid gland. One of the manifestations of neuropathy is dizziness and tinnitus.
The use of pathogenic therapy (metabolic drugs) leads to regression of clinical manifestations and complaints. In the presence of tumors, complaints increase. They are one-sided or two-sided, but asymmetrical. A tumor can only be detected after a full range of examinations.
Labyrinthine artery clogged
This cause of disturbance of the vestibular apparatus poses a particular threat. The fact is that the blockage interferes with the normal blood supply to the brain. The consequences can be critical: cerebellar stroke, heart attack, intracerebral hemorrhage. All of these lesions are life-threatening. If symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Signs of a blocked artery:
- severe dizziness;
- global loss of coordination;
- hearing loss in one ear.
Types of VA lesions
Dizziness is recognized as the main accompanying factor of vestibular apparatus disorder. Experts identify several forms.
- Peripheral. The most popular type occurs with disease of the auditory nerve tubules in the vestibular apparatus.
- Central. Diseases of the vestibular parts of the brain: brainstem, cerebellum, cortical parts.
- Afferentative. Dizziness occurs due to problems with vision, hearing, and dysfunction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Symptoms of VA disease
Signs of violation appear in two forms: direct and concomitant.
Direct manifestations:
- dizziness;
- nystagmus (involuntary movement of the eyes horizontally or in a circle).
Associated manifestations:
- nausea of varying degrees, vomiting;
- pallor or redness of the face and neck;
- problems with balance, coordination;
- sweating;
- problems with the heart and breathing;
- change in pressure indicators.
Signs of vestibular dysfunction occur in attacks and can have varying degrees of impact. Symptoms may be caused by smell, food, or weather changes.
Determining the diagnosis
For diagnosis, it is very important to consult a doctor at the initial stage of manifestation of disorders. Defects in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus are often a consequence of other diseases. An otolaryngologist will help determine the initial causes and make a diagnosis.
During diagnosis, a full examination is carried out using additional drugs:
- Audiometry will help determine the level of auditory perception;
- To determine the condition of the vertebral arteries, an ultrasound examination is performed;
- The presence of brain pathologies is checked using tomography.
List of sources
- Zamergrad M.V., Grachev S.P., Gergova A.A. Acute vestibular vertigo in old age: stroke or peripheral vestibulopathy. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2018; 118(6-2): 46-49.
- Parfenov V.A., Abdulina O.V., Zamergrad M.V. Differential diagnosis and treatment of vestibular vertigo // Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics. - 2010. - No. 2. - P. 49-54.
- Suslina Z.A., Varakin Yu.Ya., Vereshchagin N.V. Vascular diseases of the brain. M. 2006.
Treatment of the disease
Drug therapy
Most often, the first thing doctors do when the vestibular organ is damaged is to prescribe treatment that eliminates the main symptoms. Vasoactive medications are used for this. Drug treatment consists of antiemetics and vestibular suppressants. This includes 3 subtypes of medications:
- anticholinergic;
- benzodiazepines;
- antihistamines.
After a thorough diagnosis, other diseases that provoke the disease of the vestibular apparatus are discovered. For example, sensorineural hearing loss, accompanied by hearing loss. Therefore, the main task of the doctor is to correctly determine the root cause and prescribe effective therapy.
ethnoscience
It is effective in complex treatment with the implementation of recommendations from the doctor. Folk remedies are not a reason to abandon traditional methods of treatment.
There are several folk remedies.
Ginger. For 4 teaspoons add a pinch of mint, fennel, crushed pumpkin seeds, celery, a little chamomile flowers and orange zest. The mixture is poured with boiling water and infused for about 15 minutes.
Balm based on 3 tinctures. The first is prepared from clover: pour 40 g of flowers into 500 ml of alcohol. Leave for 2 weeks in the dark. For the second, you need Dioscorea roots: 50 g, pour 500 ml of alcohol. Let it stand for 2 weeks in a dark place. The third tincture is prepared from propolis and alcohol. The mixture should infuse for 10 days in a dark place. And then strain the composition. Use 1 tablespoon of mixed tinctures, 3 times every day after meals.
Diet
Salt-free diet
- Efficiency: 5-10 kg in 13 days
- Time frame: 13 days
- Cost of products: 4500-8000 rubles for 13 days
For some diseases that provoke vestibulopathy, it is recommended to adhere to a salt-free diet or limit the amount of salt in the menu.
In general, nutrition should be rational and varied, and the diet must include fresh fruits and vegetables, meat, fish, dairy products, nuts, and vegetable oils.
You should give up alcohol.
Prevention of violations
Special therapeutic exercises will help cope with coordination problems. A set of exercises trains the vestibular apparatus. Classes last for 15 minutes. At first they are performed at a very slow pace.
- Movement of the eyes horizontally and vertically. The head is motionless.
- Tilt your head in different directions, first with your eyes open and then closed.
- Shrug.
- Throwing a ball from hand to hand.
- Walking around the room with your eyes open, then closing them.
Rules for performing vestibular gymnastics
- Vestibular gymnastics should be done daily, 2 times a day.
- The duration of the lesson should be 20–30 minutes, after which rest is necessary.
- Standing exercises should be performed barefoot or in comfortable shoes without heels.
- During vestibular gymnastics, you should not rush, so as not to fall.
- You should not exercise if you are feeling unwell due to another illness (for example, a cold or migraine).
- To evaluate the results and adjust the exercise program, you must contact your doctor every two weeks (by phone or in person).