Features of the disease
Even in the time of Hippocrates, much attention was paid to the study of pain in muscles and joints, the causes of which were unclear. But a detailed clinical description of the syndrome now called fibromyalgia appeared only 150 years ago.
In the middle of the last century, interest in this pathology increased greatly. E. Boland in 1947 proposed the concept of psychogenic rheumatism. This theory is very popular in our time, since fibromyalgia is very closely related to depression and stress.
For a long time, fibromyalgia syndrome was considered a psychosomatic disease. Today, this syndrome is one of the least studied pathologies. Few studies have identified the neurophysiological, biochemical and clinical features of fibromyalgia. This made it possible to identify the primary and secondary forms of the disease and develop diagnostic criteria, but scientists were unable to answer the question of what causes fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia affects approximately 4% of the population. This pathology can develop in any person, regardless of his place of residence, social status, nationality and race. But according to statistics, the syndrome develops more often in women. The ratio to the male sex is approximately 8-10:1. These data are still being clarified, but it is reliably known that the tendency to develop pathology increases with age. After 50 years, the frequency and intensity of pain also becomes greater.
Symptoms of the disease remain with the patient for life, but they may vary somewhat due to the influence of various factors. If you do not take any measures to heal, and also do not make significant changes in your lifestyle, then the doctors’ prognosis will be unfavorable.
Probable causes of the syndrome
As noted above, fibromyalgia was previously classified as either an inflammatory or a mental illness. But modern research has proven that the pain experienced by a person suffering from the syndrome is not caused by inflammatory processes. Increased anxiety and depression are results of the disease rather than its causes.
Today, there are several hypotheses about what could be the cause of fibromyalgia:
- pathological processes in blood vessels that led to their changes;
- heredity and genetic predisposition. Some researchers have indeed noted that there may be more than one person diagnosed with the syndrome in one family;
- stressful situations are also considered one of the most important factors in the formation of fibromyalgia, since stress often leads to the development of diseases with similar manifestations (insomnia, chronic fatigue and irritable bowel);
- too rapid serotonin metabolism;
- lack of growth hormone. The relationship between deficiency of this hormone and fibromyalgia was discovered accidentally and has not yet been sufficiently confirmed. However, during growth hormone replacement therapy, positive dynamics are observed;
- all kinds of psychogenic factors;
- physical trauma can also cause the development of fibromyalgia syndrome;
- Mercury poisoning can lead to dysfunction of the central nervous system, which provokes the development of the syndrome.
Some researchers tend to think that fibromyalgia is an idiopathic response of the immune system to certain types of bacteria that live in the human intestines.
The vast majority of these hypotheses and theories arose during the study of the characteristics of pathology, but they do not yet have a sufficient number of supporting studies.
Treatment of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome
The pain associated with fibromyalgia can almost always be relieved. Sometimes this can be troublesome, the process of selecting a treatment regimen may require more time, but treatment of fibromyalgia is real. In most cases, pain with fibromyalgia begins to subside after 2-4 weeks if 3 issues are resolved: a full night's sleep with the phases of slow-wave sleep and REM sleep represented, treatment of inflammatory triggers (autoimmune processes and infections - these are usually visible in test results), recovery normal functioning of the immune system. Why exactly 2-4 weeks? This is due to the lifespan of certain immune system cells, antibodies and other factors that support inflammation.
Prognosis for treatment of fibromyalgia. In most cases, after three or four months, you can gradually reduce your medication dosage. As physiological regulation is restored, the need for treatment gradually decreases, until all medications are completely withdrawn. Difficulties in treatment are possible if some factor continues to act on the body, again triggering fibromyalgia. For example, relapses of fibromyalgia are observed against the background of chronic viral hepatitis, when it is not possible to completely destroy the virus, in the case of “major” psychiatric pathology (schizophrenia, endogenous depression), but in these cases clinical improvement is possible, although it requires a little more effort.
Symptoms
The main symptom of fibromyalgia is pain in certain parts of the body and stiffness. In most cases, these manifestations arise gradually, the pain is aching and diffuse in nature. The pain gradually intensifies. If the patient experiences emotional and physical overload, is in a stressful situation, sleeps poorly, or has injuries, then the disease develops rapidly. The distrustful attitude of doctors, as well as cold and dampness can further intensify the pain.
In addition to pain throughout the body, the following symptoms may indicate fibromyalgia:
- Sleep problems. Studies have been conducted that have identified disturbances in the deep sleep phase in people suffering from the syndrome. After waking up, they feel tired, sleep does not bring a feeling of recovery.
- Muscle stiffness is most severe in the morning after waking up.
- The patient gets tired quickly.
- Patients with fibromyalgia syndrome react to weather changes. Weather dependence is manifested by headaches similar to migraine attacks.
- Body temperature is extremely unstable; it can change sharply from normal to high or low.
- Numbness or tingling sensations may occur in different areas of the body. Spasms and cramps may occur and may vary in severity and duration.
- From time to time, memory and concentration problems may occur, and the patient feels that he cannot concentrate.
- If the disease is in a severe stage, persistent impairment of motor functions may occur. During the day, the patient cannot sit or stand normally, or move around. These symptoms may vary slightly but do not disappear completely.
Quite often, symptoms of fibromyalgia syndrome include depression, all kinds of mental disorders and sudden mood swings. But these manifestations are usually concomitant, and in most cases they are absent altogether.
Fibromyalgia has a large number of symptoms that are not justified by any disorders in the human body. A detailed study of the clinical picture of this pathology allowed researchers to classify it as a somatoform disorder. The symptoms of such pathologies are felt by a person, but he is not able to control them or cause them intentionally. Thus, fibromyalgia syndrome is a more complex problem than just muscle pain, it requires a comprehensive approach to solving the problem.
Diagnostics
To date, there are no special methods for diagnosing fibromyalgia syndrome. The doctor prescribes standard tests to determine blood sugar levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, assess the degree of activity of the thyroid gland, as well as tests for antinuclear antibodies and levels of calcium, prolactin, etc. If the results of all these studies are negative, that is, normal, then the doctor can rule out the presence of arthritis and rheumatic diseases. At this stage it is also important to exclude a disease such as migraine.
The doctor makes the diagnosis of “fibromyalgia syndrome” after checking the sensitivity of paired points on the patient’s body, as well as if the following mandatory criteria are present:
- pain and stiffness are observed in the patient for a long period of time (at least three months);
- upon palpation, pain occurs in at least 12 points out of 18. The diagnostic criterion is the occurrence of pain at the moment of pressing on a certain place, and not a violation of sensitivity;
- complete exclusion of other diseases manifested by muscle pain and stiffness;
- sleep disturbances, insomnia, morning stiffness and feeling tired after waking up.
Fibromyalgia at the time of exacerbation may have similar manifestations to an incipient stroke. At the moment, the criteria for differentiated diagnosis of these two pathologies have not been defined.
Diagnostic criteria for fibromyology
Rheumatologists have established two criteria for diagnosing fibromyalgia:
- Widespread pain that lasts more than three months. Pain affects four parts of your body - left, right, above and below.
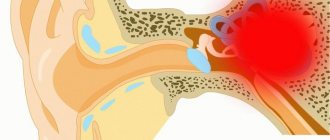
- Presence of pain points in 18 areas of the body. These areas are located in the back and front of the neck, between the neck and chest, just below the neck on the back, knees, on the inside of the elbow, just above the buttocks, below the buttocks in the upper part of the back of the thighs. At least 11 of these points must be identified to confirm the diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
Basic treatment methods
Since there is no reliable data on the causes of fibromyalgia syndrome, during treatment doctors direct all their efforts to relieving symptoms and eliminating the consequences of the disease. Therapy is based on an individual principle. First of all, the severity of pain and the condition of trigger points on the patient’s body are taken into account.
Treatment includes several therapeutic areas:
- Taking medications can eliminate pain and muscle stiffness, reduce irritability, normalize sleep and get rid of symptoms of depression, if present. The choice of medications must be approached with extreme caution, since the success of treatment largely depends on how much sleep disorders can be eliminated. And many of the drugs can cause insomnia.
- Among non-drug methods of treating the syndrome, the most effective are cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy and physical therapy. The combination of only these two methods allows you to achieve sustainable results. Massage, oxygen therapy, hypnosis and autogenic training, yoga, meditation, etc. will be useful for fibromyalgia. Maintaining a sleep and rest schedule is also a necessary condition for recovery.
- For fibromyalgia, non-traditional treatment methods can also be used. Some experts say that acupuncture can help reduce pain. Cryotherapy and a raw vegetarian diet can achieve similar results. There is also a method of treating the syndrome with popular cough tablets - guaifenesin. But in this case, the patient must completely avoid drinking tea, products containing plant oils and extracts, menthol, and bioflavonoids. You should not use cosmetics that contain salicylates, salicylic acid, disalcide and camphor. The list of substances prohibited for use and use is quite extensive, but many researchers are skeptical about this method.
It is not possible to completely get rid of the manifestations of fibromyalgia syndrome. With regular maintenance treatment, positive results can be achieved, but they do not last more than one year.
While working with the patient, the doctor supports his desire to actively resist the symptoms of the disease and develops positive thinking. The patient will be recommended to live in a dry, warm climate and be completely free from stressful situations.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a disease that comes to the attention of not only rheumatologists, neurologists, pain specialists, but also general practitioners.
Fibromyalgia is a fairly common disease, affecting about 20 million people worldwide (about 4% of the population), mostly middle-aged women. However, despite its prevalence, the diagnosis of fibromyalgia in the world, particularly in Russia, is extremely rare. This is due to unusual manifestations of the disease, insufficient awareness of doctors and the lack of clear diagnostic criteria. Fibromyalgia is understood as a syndrome of non-articular widespread symmetrical musculoskeletal pain, which is chronic in nature and accompanied by depression, sleep disturbances and the presence of specific tender points. In neurological practice, this is also a fairly common pathology. Nevertheless, there is a paradoxical situation in which the actual diagnosis of fibromyalgia, even syndromic, is, in principle, absent in the daily practice of medical specialists. The reason for this, on the one hand, most likely lies in the variety of clinical manifestations of fibromyalgia. Neurologists most often evaluate such patients in accordance with the leading comorbid manifestations (“panic attacks”, tension headaches, widespread osteochondrosis, myofascial syndrome, osteoarthritis, etc.). On the other hand, the reason lies in the underestimation of the significance of mental disorders and stress for these patients and the lack of generally established ideas and views on this symptom complex as a single suffering. Undoubtedly, such patients are also encountered in the practice of psychiatrists, who, however, do not diagnose patients with FM, since they do not subject the patient’s somatic state to a detailed analysis and do not examine their sensitive points.
Story
Although the term “fibromyalgia” was coined relatively recently, this condition has long been described in the scientific literature. In 1904, William Gowers coined the term fibrositis. The modern concept of fibromyalgia was created by Smythe and Moldofsky in the mid-1970s. They coined a new term, fibromyalgia. The authors identified the presence of local hypersensitivity, so-called “tender points,” as a characteristic symptom of fibromyalgia. They also found that patients with fibromyalgia often experience sleep disturbances. The next stage in fibromyalgia research was the development of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia, which were published in 1990. Significant progress in the study of fibromyalgia has been made after researchers concluded that the condition is not caused by damage or inflammation of peripheral tissues. Therefore, all efforts were aimed at studying the central mechanisms of pathogenesis.
Etiology and pathogenesis
One of the most important mechanisms for the formation of chronic pain in fibromyalgia is the phenomenon of central sensitization (CS). It is characterized by the fact that after prolonged peripheral nociceptive stimulation, a certain level of excitation remains in the central sensory neurons of the dorsal horn, which maintains pain even in the absence of further peripheral pathology. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that CS can develop in the presence of disorders in the central nervous system without peripheral damage. Fibromyalgia is such an example. Often, patients with fibromyalgia who do not show peripheral changes are considered by doctors as malingerers or patients with hysteria. Some doctors, in situations where they cannot find an organic cause of pain, prefer to use diagnostic labels such as psychosomatic and somatoform disorders. However, today it has been convincingly shown that central sesitization, as well as impaired descending (noradrenergic and serotonergic) inhibitory control of pain, occur in fibromyalgia not as a result of peripheral changes in muscles, fascia, ligaments or connective tissue, but as a result of neurodynamic disorders in the central nervous system in individuals with a genetic predisposition under the influence of a large number of stressful (physical and mental) events. Research into fibromyalgia over the past two decades has shown that the pain threshold depends on the degree of distress. Many psychological factors, such as hypervigilance, suspiciousness, catastrophizing, and external locus of pain control, may play an important role in the severity of fibromyalgia symptoms. Special studies have shown that patients with fibromyalgia have reduced serotonergic and noradrenergic activity. It has also been found that patients with fibromyalgia have decreased levels of serum serotonin and its precursor L-tryptophan. This evidence is supported by the fact that drugs that simultaneously increase serotonin and norepinephrine levels (tricyclic antidepressants, duloxetine, milnacipram and tramadol) are effective in treating fibromyalgia.
The main symptoms of fibromyalgia are pain (100%), stiffness (77%) and fatigue (81.4%). The onset of fibromyalgia in most patients is gradual. The onset of the disease is often associated with emotional factors, stress, changes in the family, injuries, surgical interventions, etc. The most common symptoms of fibromyalgia are pain, which worsens in a state of fatigue, tension, excessive physical activity, immobility and cold. The pain is usually bilateral and symmetrical. Pain and stiffness in the head and neck area are typical in the morning. Complaints of calf muscle cramps, paresthesia and sensations of fullness in the upper and lower extremities are quite common. Fatigue is one of the most common complaints. Often the patient wakes up more tired than before going to bed.
American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia (N. Smyth, M. Yunus, 1990):
- The presence of generalized symmetrical pain (spreading to the right and left, upper and lower halves of the body, or axial), lasting for at least the last 3 months.
- Pain on palpation of at least 11 out of 18 (9 pairs) specific tender points.
The following points are used:
- occipital region - place of attachment of m. suboccipitalis;
- neck region - anterior sections of the space between the transverse processes CV - CVII;
- trapezius muscle - middle of the upper edge;
- supraspinatus muscle at its insertion;
- the zone of articulation of the second rib with the sternum along its upper edge;
- a point located 2 cm distal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus;
- in the gluteal region - the upper outer quadrant of the buttock along the anterior edge of the muscle;
- greater trochanter of the femur;
- in the area of the knee joint there is a medial fat pad.
The pressure applied at these points should be 4 kg/cm, the pressure at which the examiner's nail beds turn white. When palpating 18 painful points, it is recommended to apply even pressure on paired points and, with the same force, palpate other areas of the body to compare sensitivity. Patients with fibromyalgia experience increased sensitivity in tender spots compared to other areas of the body. Painful points reflect areas of increased sensitivity to painful stimuli, and are not a consequence of local inflammation or tissue damage. In addition, it is necessary to determine pain sensitivity at control points (in the frontal, above the head of the fibula).
The presence of a positive reaction in more than 11 of 18 painful points was determined by the diagnostic criterion based on the analysis of statistical data from large populations of patients. However, not all patients with fibromyalgia will have increased sensitivity in more than 11 points. Once again, we note that the ACR criteria for fibromyalgia are intended for research purposes and not for making diagnoses for specific patients. However, examination of tender points is considered an important part of studying the functioning of the musculoskeletal system in patients with generalized pain syndrome. Palpation of soft tissues and joints allows you to identify areas of increased sensitivity. This examination allows you to exclude synovitis or myositis and is very important in the diagnosis of fibromyalgia. Along with the described most characteristic complaints of pain, fatigue and stiffness, patients with fibromyalgia have a whole symptom complex of psychovegetative, psychosomatic and various algic disorders, which occur in FM several times more often than in the population. The high association with FM allows us to consider them as comorbid. The most common among them are the following: “panic attacks”, hyperventilation syndrome, tension headaches, migraines, lipothymic conditions, irritable bowel syndrome, cardialgia, abdominalgia, Raynaud’s syndrome. It should be emphasized that in one patient, as a rule, one can detect a whole symptom complex of the mentioned disorders, the dominance of which in the clinical picture often makes it difficult to identify “fibromyalgic phenomena proper,” which is reflected in the interpretation of these patients and, as a consequence, in the leading diagnosis (tension headaches). , chronic myofascial syndrome, etc.). Recently, the FiRST (Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool) questionnaire has been proposed to screen for fibromyalgia (Table 3). The advantages of the questionnaire are its brevity and ease of completion. It should be emphasized its high sensitivity (90.5%) and specificity (85.7%). It is important to note that the questionnaire is intended for screening and a diagnosis cannot be made using it alone. Patients who score 5 or more on the FiRST questionnaire should be carefully evaluated to make a definitive diagnosis of fibromyalgia.
FiRST questionnaire for screening for fibromyalgia
| Yes | No |
| I have pain all over my body | |
| Pain combined with a constant feeling of exhaustion | |
| The pain is like a burning sensation, electric shock, or cramping | |
| The pain is combined with other unusual sensations throughout the body such as pins and needles, tingling, and numbness. | |
| The pain is combined with other disorders (problems with digestion, urination, headaches, sleep disorders, depression) | |
| The pain greatly affects my life, especially my sleep and ability to concentrate, I’m kind of slow |
Fibromyalgia Treatment
The presence of pronounced psychological disorders dictates the need to include antidepressants in the treatment of fibromyalgia. The most commonly used are amitriptyline and melipramine at a dose of 10-25 mg 1 time per night. The course of treatment is 4-6 weeks. Fluoxetine is prescribed 20 mg 1 time in the morning. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have found widespread use in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Long-term oral administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is undesirable due to possible side effects. Recently, preference has been given to local therapy in the form of ointments, gels, as well as local injections in combination with painkillers, in particular lidocaine. In a recent RCT of patients with fibromyalgia, lidocaine 50 mg was injected into a painful point in the trapezius muscle. As a result, not only a local reduction in pain at the injection site was noticed, but also a general analgesic effect. This study demonstrated the important role of peripheral tissues in the development of hyperalgesia in fibromyalgia and demonstrated the clinical utility of local anesthetic injections for the management of pain in fibromyalgia. It is considered appropriate to include so-called local muscle relaxants: baclofen at a dose of 15-30 mg per day or dantrolene at a dose of 25-75 mg per day help reduce muscle tone and have an analgesic effect. There are reports of the effectiveness of antioxidants (ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol) in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Among non-drug treatments, various physiotherapeutic procedures are widely used, in particular massage, balneotherapy, and cryotherapy. In recent years, much attention has been paid to physical exercise, namely aerobics, as an effective way to eliminate chronic muscle pain and fatigue. Importance is also attached to methods of psychological rehabilitation of patients with fibromyalgia - psychotherapy and autogenic training.