Essence and basic principles
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics is one of the most effective techniques that helps speed up the compensation process and get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of dizziness. This set of exercises is often recommended for patients with BPPV (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo).
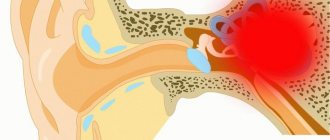
BPPV occurs when small crystals of calcium carbonate that form in the ear canals are released and move into the semicircular canals of the ears. This reaction sends mixed signals to the brain about the position of the body, and as a result, dizziness occurs.
But special exercises help break and knock out crystals, alleviating the symptoms of dizziness.
Brandt-Daroff exercises have a lot of positive aspects:
- with regular exercises, it is possible to gradually remove otolith particles from the semicircular canal in the vestibule of the labyrinth;
- during exercise, otolith particles can gradually dissolve in the endolymph;
- the maximum effect can be achieved thanks to the phenomenon of habituation: repeated provocation of dizziness leads to a significantly reduced likelihood of the central nervous system responding to an irritating factor.
Gymnastics helps restore the damaged organ of balance and helps to gradually adapt to the conditions of the outside world. This technique is quite effective, but gymnastics should be performed exactly as recommended by the doctor. It is in this case that you can achieve a positive result for a long time.
If you follow all the recommendations, vestibular exercises will help:
- reduce the likelihood of injury from a fall if you suddenly feel dizzy;
- remove symptoms of nausea and dizziness;
- improve and increase blood flow to the organs of the spinal cord and brain;
- improve quality of life;
- normalize coordination of movements;
- improve vision.
For older people, gymnastics helps them better navigate in space and maintain balance.
Such exercises not only have a positive effect on all organs of the human body, but also prepare the body for possible falls. As a result of this, the person will receive a minimal amount of injury if a situation suddenly arises.
Dizziness and vestibular gymnastics: indications for classes, basic exercises
With vestibular vertigo, in some cases the brain is able to adapt to disorders of the sensory organs.
After a certain time, dizziness may disappear. But if this does not happen, then special gymnastics will help. Let's talk about what exercises you should do.
Indications for classes
Dizziness in rare cases becomes a reason to go to the hospital.
But do not underestimate the malaise, because in some cases it is an alarming signal, warning about the likelihood of developing a serious illness.
Indications for vestibular gymnastics include diseases such as the post-stroke period, osteochondrosis, pathologies of the ear area, as well as conditions after traumatic brain injury.
But it’s not always possible to do gymnastics yourself. Self-medication can worsen the patient's condition when he has ischemic brain damage , and there is also a high likelihood of compression of the vertebral artery.
Only the doctor should decide whether gymnastics is indicated for the patient and in what way he can do it, independently or with the help of a doctor. Do not self-medicate and consult a specialist!
Contraindications
Therapeutic gymnastics is not indicated in all cases. It happens that it is better to hold off on exercise.
Vestibular gymnastics is prohibited from being performed in the following cases:
- disorientation (the period when symptoms of vestibulopathy appear);
- there are pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems;
- your health worsens after exercise.
In other cases, you can perform gymnastics, but only with serious medical supervision from a specialist who will draw up an individual training program.
General principles of vestibular exercises for dizziness
To properly carry out the therapeutic complex of exercises, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Exercise at a suitable time, but at least 2 times a day with an eight-hour break.
- Exercises are prohibited during infectious and cold diseases.
Exercise with the permission of the attending physician.
- Do all exercises in a measured rhythm. As the body begins to get used to it, gradually increase the load.
- Train in comfortable clothes that do not restrict movement and comfortable shoes.
- The complex should last from one to one and a half months.
- The complex must be adjusted by a specialist every two weeks.
Exercise instructions
At least 5 minutes are allotted for each exercise . It is recommended to perform the complex for ten to twelve days. The complete course consists of exercises for the eyes, head and balance.
Even if you are not doing the exercises under the supervision of a doctor, and in general at the beginning of classes you seem to be feeling well, be sure to ask one of your relatives or friends to stay with you for at least the first few classes. There is a chance that dizziness or fainting will occur suddenly and you will not notice a preliminary deterioration in the condition.
For balance
Balance tasks are performed while standing. You need to repeat twenty approaches.
- Lean forward. Take the item prepared in advance from the floor and go to a sitting position.
- Take the starting position while sitting. Then stand up. Return to the starting position.
- Place a small object in your hands and position it so that it is in front of your eyes. Shift from hand to hand, maintaining the original position.
- Move the item from one hand to the other under your knee.
For eyes
Eye exercises: movements must be performed with a fixed head position.
- Raise your eyes first up and then down. Do twenty approaches.
- Place on the right and left those things on which you will focus your eyes.
Direct your gaze from side to side, keeping your gaze on these objects. - Slowly bring your finger 50 centimeters in front of you to your eyes.
For the head
Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness consists of three exercises . Each approach is done first with open and then with closed eyes. A total of 20 approaches.
- Tilt your head forward and back. Start carefully and gradually speed up.
- Turn in different directions.
- Perform rotation and elevation of the shoulder joints
Exercises at home
Vestibular gymnastics exercise therapy for independent performance should be built according to the following rules:
- During the first week, turn your head in different directions. Don't worry if you feel a little nauseous. This is the norm for now, so keep practicing.
- Starting next week, start bending forward and backward, left and right. Remember to control your breathing, exhale when bending over.
- After twenty days, light boxing is added to the training. You need to box with an invisible opponent with your elbows bent.
- Then walking is added. Walk forward and back without looking back. Do 10-15 repetitions.
Read more about how to cope with dizziness at home here.
Photo
Below, as a visual representation, are photos and pictures of exercises for the vestibular apparatus.
Treatment methods under the supervision of a specialist
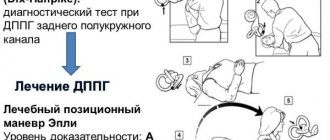
Epley maneuver
The Epley maneuver is prescribed for benign positional paroxysmal vertigo . It is necessary that the procedure be performed by a doctor for the first time. When there is a possibility that vertigo was caused by another problem, the complex is carried out only by a doctor.
In cases where neck movement has not yet been developed after a recent injury or a heart attack has occurred, the patient cannot carry out the complex himself.
- First, the doctor sits the patient facing him.
- Then he turns his head 45 degrees to the right side with a rather sharp movement.
- After this, the patient quickly lies down for thirty seconds; the position should not change. Moreover, the head should be lower than the body in a lying position.
- Now the doctor will turn your head 90 degrees in the other direction.
- Next, lie down on your left side, and the doctor sharply turns his head to the right. You should also be in this position for thirty seconds.
- After this, at the request of the doctor, you should quickly return to your original sitting position. By then the dizziness should have disappeared. If it remains, you will have to repeat the Epley maneuver again.
Semont maneuver
- The patient sits with his feet off the couch. He should turn his head to the healthy side 45 degrees.
- After holding your head with your hands, lie down on the affected side.
You need to lie there until the dizziness stops. - Then the patient is placed on the other side with his forehead down, again in a sitting position. You need to stay like this until the dizziness stops.
Conclusion
Dizziness seriously impairs quality of life. Vestibular gymnastics can improve the situation . However, remember that it must be done under the supervision of a doctor and not in preference to prescribed drug therapy.
We invite you to watch a video about dizziness, treatment methods and therapeutic exercises:
If you want to consult with the site’s specialists or ask your question, you can do this completely free of charge in x.
And if you have a question that goes beyond the scope of this topic, use the Ask a question above.
Indications for use
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics helps to concentrate attention, but does not train muscles. This type of exercise is recommended for use by all people, including the elderly, who suffer from frequent attacks of dizziness.
This set of exercises is shown to people:
- those who have had a stroke;
- those suffering from BPPV;
- with general impaired coordination of movements;
- with osteochondrosis;
- with high numbers on the tonometer;
- with chronic migraine;
- with mental disorders;
- with lung pathologies
- with minor and serious spinal injuries;
- with dyscyclic encephalopathy;
- having pathologies affecting the ear areas.
Brandt-Daroff vestibular exercises are also recommended for people who have suffered a history of brain injury.
Contraindications for use
Vestibular gymnastics performed at home is very beneficial for the human body. But before you start doing exercises using the Brandt-Daroff method or using any other method, you should definitely consult a doctor. Such activities have a number of contraindications, and if they are not taken into account, then the patient’s already serious condition can be aggravated.
You cannot use gymnastics if:
- serious disturbances in breathing rhythm are observed;
- the patient’s medical history contains records of heart problems;
- The patient has a cold or infectious disease.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a pathological condition of vestibular origin, which is characterized by paroxysmal manifestations of dizziness.
This state is provoked by changes in the spatial position of the human body.
The differences between this type of dizziness are the relative ease of treatment and the possibility of self-improvement.
Diagnostic measures
To make a definitive diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, specially developed Dix-Hallpike functional diagnostic tests are used.
The Dix-Hallpike test is a targeted technique used to diagnose the disease.
To carry out this test, the doctor lays the patient down on the bed, then takes the head with both hands and rotates it in front to the sides around then, holding the head, lays it on the bed. After the exercise, the doctor should ask how the patient is feeling.
Usually, people who have benign positional vertigo are convinced by doctors that dizziness after such a shake is a normal condition for them.
Objectively, a patient has nystagmus that is directed toward the floor, to the side or to the top; this depends on the direct localization of the pathological process in the semicircular canals of the inner ear.
In case of a negative effect, the exercise should be repeated a few minutes after rest. Sometimes it happens that after conducting a diagnostic test in a supine position, a positive result cannot be achieved, but the condition manifests itself after the patient gets up from the couch and the body acquires a sitting position.
When repeating positional tests, the severity of the results as a rule decreases somewhat; this also must be taken into account when making a diagnosis. As an addition to the positional test, you can use not only rotation towards the head, but also the entire body.
The most difficult for patients to tolerate is a change in body position from lying to standing.
Instrumental studies
As an instrumental diagnosis of the disease, methods are used to assess the severity of nystagmus; for this purpose, methods such as electrooculography and videooculography are used.
In order to exclude organic pathology from the central nervous system or oncological pathology, patients must undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. To exclude pathology from otolaryngology, it is necessary to undergo a consultative examination with an appropriate specialist.
Differential diagnosis of benign positional paroxysmal vertigo
Unlike tumor-like formations in the brain, as well as pathologies of the posterior cranial fossa, with the benign development of vertigo, there are no signs of damage to the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system; common signs are symptoms of impaired balance and positional vertigo.
Repeated positional functional testing for ordinary dizziness is usually characterized by a decrease in the severity of the positive result, since in organic pathology, repeated testing does not affect the severity of the result.
Nystagmus of a positional nature can also manifest itself in a disease such as multiple sclerosis or acute cerebrovascular accident, while all the symptoms of damage to the nervous system remain.
Therapeutic measures to eliminate pathology and discomfort
Conservative treatment without the use of drugs includes the following methods:
Brandt-Daroff method
The patient can perform this exercise independently at home.
To carry out this technique, the patient needs to sit in the center of the bed and bend several times from side to side. Then the patient is injected back into a horizontal position and repeats the movements in a supine position.
It is necessary to rest the body for a minute, then repeat the indicated Brandt Daroff exercises.
The method for treating the disease is repeated three times throughout the day. The duration of the procedure is determined individually depending on the general well-being of the patient.
Semont maneuver
This technique can be performed either independently or with the help of a qualified specialist.
The patient sits on the bed, the doctor takes the patient's head with both hands and turns it sharply, then injects it on the same side without changing the position of the head relative to the original plane.
The patient should lie down until all discomfort disappears.
After rest, without changing the fixed position of the patient’s head, the patient is returned to a sitting position, the head is turned and placed on the opposite side, the patient should also rest. This exercise is repeated 2-3 times, once a day.
In cases where a patient suffering from benign paroxysmal vertigo has a life history of pathologies from the cardiovascular system, cardiac tonic drugs are administered before the procedure as a specific predication.
If nausea and vomiting occur during the procedure, patients are prescribed antiemetic drugs.
Epley maneuver
A procedure of this nature is carried out only by qualified specialists. The peculiarity of this method is that the procedure is carried out using smooth and slow body movements.
The patient should initially sit on the couch, the doctor takes the head with both hands and fixes the head, turning it to the side in the same position, the patient’s head is placed on his back. After this, the person’s body is turned over on its side, and then slowly seated in its original position.
This method of non-drug treatment is very effective and in most cases, repeating two or three sessions can help completely get rid of the pathological condition.
The effectiveness of this method depends entirely on how professional the specialist performing this procedure is.
Lempert maneuver
This technique is carried out exclusively by a qualified specialist. The initial position of the patient should be sitting along the couch. Turning the head forty-five degrees, fix it in the plane of the horizontal body on the side of the focus of the pathological condition.
After this, the patient is placed in a supine position on his back and the position of the head is slowly changed in the opposite direction, then the head is turned to the other side and the position of the body is changed from back to stomach, while the head should rotate together with the human body.
The exercise can be repeated several times, but with the condition of maintaining a rest period.
Surgical technique for treating the disease
Surgical intervention is performed in cases where conservative treatment of the disease has shown absolutely no positive results.
This treatment method is carried out very rarely and in quite exceptional cases.
For this purpose, surgical intervention techniques such as:
- filling the lumen of the semicircular bony canal of the inner ear with fragments from the bone structure, which is taken from another part of the skeleton of the human body. The most optimal bone for transplantation is the tibia;
- selective removal of nerve endings that innervate the vestibular canals of the human inner ear;
- total removal of structures and spongy substance of the bone labyrinth;
- destructive destruction of labyrinth structures using specially selected laser installations.
Absolutely all surgical methods are extremely traumatic for humans and therefore should be performed only for special medical indications.
After surgery, the patient must undergo antibacterial therapy in order to prevent the development of complications of an infectious nature.
To prevent dysentery as a side effect of antibiotics, the patient is prescribed probiotics in combination.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures for benign positional paroxysmal vertigo have not been developed to date since the etiological factors in the development of the disease have not been fully elucidated.
As a recommendation, patients should not drive a car for some time.
The pathological condition may persist for several days or weeks after treatment. As for the restoration of ability to work, it can also be difficult for several weeks, but one should take into account the fact that benign positional vertigo can recur over time and when such a moment occurs is not known.
Useful tips for patients
Vestibular gymnastics will be most effective if you follow a number of basic rules:
- The exercises should be performed in a well-lit room, so that there are no objects with sharp corners nearby, and a carpet without any folds that could lead to a fall and injury to the patient.
- The maneuver is performed using soft surfaces, such as a yoga mat, mat, blanket or thick mat.
- You need to choose comfortable clothing so that it does not constrain or limit movement. But it should not be too wide so that the patient does not get confused in it.
- Shoes must be flat-soled.
- While doing gymnastics, there must be a coach or a loved one nearby who can come to the rescue if necessary.
- You should not overload your body; as soon as even a slight feeling of fatigue appears, you need to stop.
- The load should be increased gradually to prepare the body and prevent relapses.
- Regularity is also important.
- If the patient is feeling unwell, it is better to postpone performing gymnastics until the condition improves.
- Gymnastics is not a separate type of treatment; it will only be beneficial in combination with drug treatment.
Main complex
This type of vestibular gymnastics can also be performed at home, since it does not provoke any negative reactions in the body of a person suffering from frequent attacks of dizziness.
Outside help in performing the exercise is not required, but it is better if someone is nearby, because it is unknown how the human body will react, this is especially important when performing the maneuver for the first time.
The patient should take a sitting position, you can use a regular table or ottoman, and your feet should be on the floor or simply dangling. You can just sit on the bed.
Brandt-Daroff vestibular gymnastics
And after the movement it should be like this:
- When a person calms down and feels comfortable in a sitting position, he will need to lie on his right or left side.
- You need to turn your head up, maintaining an angle of 45 degrees.
- Fix in this position for 30 seconds.
- Next, the person must again take a sitting position and stay in it for half a minute.
- Afterwards you need to repeat the procedure, but lie on the opposite side.
This is how you need to do 5 repetitions on each side. You need to rest for 15 seconds between repetitions.
If a person does not experience dizziness during the exercise, then the maneuver should be repeated, but only after a day. If dizziness occurs even for a short time in any of the positions, then the maneuver should be repeated at least 2 more times, in the evening, and then in the morning.
Vestibular exercises work in several directions at once. Their main essence is an increased supply of stimuli to the nerve endings of the central part of the vestibular apparatus, which are localized in the area of the brain stem.
gymnastics every morning for 1-2 months
- In a lying position, you need to move your eyes first horizontally, and then vertically, bring your eyes closer together, and direct your gaze to the tip of the finger approaching your nose.
- Next, you need to add gradually accelerating head movements, initially doing everything with your eyes open, and then with your eyes closed.
- Afterwards, in a sitting position, you need to turn your head, bend over, and do everything first with your eyes open, and then with your eyes closed.
- Later, you can add throwing a small ball from one hand to the other, and then complicate the task by throwing the ball under the knee.
- Next, you can add squats, also closing and then opening your eyes. As soon as all the exercises go well, without any unpleasant symptoms, you can move on to twisting your torso.
- Afterwards you need to walk on a flat surface with your eyes open and closed. You can add head turns while walking.
This whole complex helps to better navigate in space and protect against dizziness.
Vestibular gymnastics for dizziness at home in pictures, video of gymnastics
In patients with benign vertigo, the inner ear is affected. This is accompanied by paroxysmal dizziness, which worsens the quality of life.
Gymnastics for vestibular vertigo is a specially designed set of exercises that patients can perform independently at home.
This is the main therapy method that was developed by doctors Brandt-Daroff and Epley-Simon.
Properly selected rehabilitation treatment has a better therapeutic effect than medications. Before starting training, it is necessary to exclude tumor processes and ischemic brain damage. Otherwise, the underlying disease will progress and the patient’s well-being will deteriorate.
Execution Rules
Vestibular gymnastics is one of the main methods of treating benign dizziness and balance disorders. Restores compensatory mechanisms and balance. The patient is preliminarily examined: a neurological examination is recommended to identify factors that cause dizziness.
Exercises for vestibular rehabilitation
To get a positive result when performing vestibular gymnastics, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- exercise every day, morning and evening;
- The duration of classes is no more than half an hour, after which you need to rest;
- you can exercise barefoot or in shoes without heels;
- All movements are performed slowly, at a pace convenient for the patient.
It is not recommended to exercise if your health is deteriorating, or if chronic or infectious diseases are exacerbating.
The patient is in touch with the attending physician and informs him of the results of regular training. This allows you to evaluate the dynamics and adjust the treatment plan, if necessary.
Training plan
During exercise, the symptom may intensify: more intense dizziness frightens patients. However, you should not interrupt your training.
Basic exercises that patients perform daily:
- Sit on a chair, straight back, fix your gaze on an object located at a distance of 25-35 cm. Make a smooth turn of your head to the left and right. Repeat 10-15 times.
- Stand up straight, keeping your head straight, shift your center of gravity slightly forward, and then return to the starting position. Also blend back, to the left and to the right. To make the exercise more difficult, perform it with your eyes closed.
- Prepare a thick sheet of paper on which several words will be printed in standard size font. Sit down, straighten your back, place the sheet at eye level and start moving it left and right. The sheet is moved horizontally, vertically, and also diagonally. The patient follows the sheet while keeping his head still. The speed of sheet movement can be increased.
- Start walking at your usual pace, turning your head to the left and right. If you experience severe dizziness, it is better to play it safe: ask someone close to you. You can walk independently along a wall or other support to avoid falling.
Consolidate the result
Today, in the world of modern technology, dizziness is mainly treated without the use of medications. Oral medications may be prescribed if the patient is experiencing an acute period when the person’s standard of living has reached critical levels and dizziness is also accompanied by nausea and a gag reflex.
Drug treatment helps alleviate the condition and improve the condition of life.
The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- Dramamine. This is an antihistamine that inhibits the vestibular apparatus of the inner ear, affecting primarily the otoliths. The medicine has an antiemetic, sedative, anorexigenic effect, and eliminates dizziness. Take 1 tablet. up to 3 times a day. The duration is set individually. A package of 10 tablets will cost an average of 300 rubles.
- Cinnarizine. This medicine belongs to the group of vasodilators and effectively helps with migraines and dizziness. For each disease, and the drug can be prescribed for pain relief and treatment of vascular pathologies, the dosage and course are selected individually. The standard dosage for the treatment of dizziness is 1 tablet up to 3 times a day. It should be taken only after meals, as the drug can irritate the gastric mucosa. The average price for 1 unit of goods is 100 rubles.
Cinnarizine tablets - Vestibo. This is a drug from the group of vestibulolytics, prescribed to people suffering from attacks of dizziness. The medicine has similar properties to histamine, improves the flow of blood into the basilar arteries, slowing down the work of some prescriptions and relieving the symptoms of dizziness, and has a positive effect on the brain stem. Packaging the drug will cost an average of 200 rubles.
- Tanakan. This is a drug from the group of herbal nootropics. Helps improve all metabolic processes in the body, improves blood flow, increases blood flow to the brain, normalizes vascular tone, and stops the active development of thrombosis. Take the drug 1 pill three times a day. The average cost of the drug is from 500 rubles.
- Cerucal. This is an antiemetic. Acute dizziness often causes bouts of vomiting, and Cerucal helps eliminate them. The dose and course are selected individually, taking into account contraindications and features of the course of the disease. The average cost of the drug is from 200 rubles.
DPP - what is it, causes, sand in the ear, treatment options
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is more often referred to simply as BPPV. So in short. For patients, another name for the pathology is known - “sand in the ear.” Yes, it feels that way.
This sensation is given by the internal structure of the inner ear, which is part of the vestibular apparatus and is responsible, among other things, for positioning the body in space and preventing parasitic dizziness.
Let us focus on the fact that dizziness . It's not permanent. It appears occasionally when the position of the head changes.
BPPV is a common pathology. Up to 17% of all cases of dizziness are associated with this disease. This problem occurs more often in women than in men.
DPP - what is it?
BPPV is, as stated above, an abbreviation for the term “benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.” An attack of this type of dizziness is associated with a change in the position in space of the body and head. However, it differs from, for example, orthostatic collapse in the duration and condition after the attack.
For reference. That is, BPPV is a short-term vestibular disorder observed when turning the head.
It is accompanied by nausea, and in some cases, vomiting. The cause of the pathology is the presence of freely floating otoliths (crystallized calcium bicarbonate) in the endolymph. Their displacement causes irritation of the ciliated cells and, accordingly, dizziness.
For diagnostic purposes, special tests are used, and for therapeutic purposes, vestibular gymnastics, Epley and Semont maneuvers are used. The effectiveness of drug therapy has not been proven, so prescribing medications is advisable only as an adjunct.
DPP - causes
To imagine the mechanism of development of an attack of dizziness with BPPV, you should familiarize yourself with the structure of the vestibular apparatus.
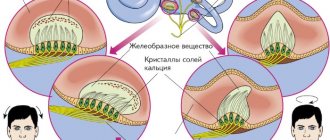
It consists of the superior, posterior and horizontal semicircular canals with extensions (ampoules), as well as a pair of sacs - oval and round. All these structures, forming the so-called labyrinth, are filled with endolymph and contain accumulations of sensitive ciliated cells.
In the ampoules, the receptor cells are covered with gelatinous caps - the cupula, and in the channels - with a special membrane with inclusions of crystallized calcium.
The main cause of so-called benign positional vertigo or otolithiasis is a disorder of metabolic processes in the inner ear. By the way, otolithiasis is another name for BPPV.
Normally, these crystals (otoliths or otoconia) are localized in the membrane, and there is a constant dissolution of old formations and their replacement by new ones.
If production increases or their utilization slows down, undissolved otoliths move freely in the endolymph, periodically causing malfunctions of the vestibular apparatus.
Typically, otoconia accumulate in the lumen of the posterior semicircular canal or ampoules, sticking to the cupula. During movement, they irritate the hair cells directly or dislodge their jelly-like covering.
For reference. As a result, the perception of angular accelerations is disrupted, and a short-term attack of dizziness occurs. When the movement of the otoliths stops and they settle to the bottom of the canal (they stop moving the cupula), the head stops spinning.
Factors that disrupt the process of formation and dissolution of otoconia are:
- TBI leading to damage to the otolithic membrane;
- viral inflammation of the labyrinth of the inner ear;
- Meniere's disease;
- taking antibiotics that have an ototoxic effect (Gentamicin and other aminoglycosides);
- spasm of the artery supplying the vestibular apparatus with blood;
- surgical operations.
In accordance with the localization of free otoliths, otolithiasis is divided into two types. The accumulation of crystallized calcium in the channels is called canalolithiasis, in the ampoules - cupulolithiasis. The disease is called benign because it is caused by mechanical irritation, and not by organic damage to the structures of the inner ear.
DPP - symptoms
The main symptoms of BPPV include the following:
- rotational vertigo,
- short duration (paroxysmal): dizziness lasts seconds or minutes,
- Nausea and vomiting are sometimes recorded.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo begins when the head is thrown back or turned, since such movements provoke movement of the otoliths. The attack most often occurs when the body is in a horizontal position, so patients usually complain of morning dizziness associated with turning over in bed.
Why dizziness occurs, causes and types
Night attacks lead to awakening.
For reference. Subjectively, paroxysm, which is the main symptom of BPPV, is felt as rotation of surrounding objects in different planes.
The duration of an individual attack is on average half a minute, but it is perceived as longer (about 5 minutes). The frequency of occurrence during an exacerbation period varies from weekly repetition to several paroxysms per day.
In some cases, BPPV attacks are isolated. Remissions, as a rule, last a long time, amounting to months and even years.
There are no additional signs of vestibular disorders such as hearing loss or hearing loss, headache, or tinnitus in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.
Attacks may only be accompanied by nausea or, less commonly, vomiting. In the intervals between them or after a single paroxysm, patients note symptoms characteristic of dizziness of a non-systemic nature.
There are sensations of instability, swaying, and so-called “lightheadedness.”
BPPV in itself does not pose a danger to human health and life, has no negative consequences, and the prognosis of the disease is favorable. However, if the attack occurs in conditions that require fine-tuned coordination or increased concentration, an accident is likely.
For example, while driving a car or working at height. In addition, frequent exacerbations negatively affect the patient’s psycho-emotional state. The result can be depression, hypochondria, and neuroses.
Diagnosis of BPPV
When contacting a neurologist, a medical history is taken and a series of specific tests are performed. The diagnosis of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is made primarily on the basis of clinical data. To confirm it, the doctor performs the Dix-Hallpike test.
The person being tested, sitting on the couch and turning his head to the affected side (the angle of rotation should be 45⁰), fixes his gaze on the bridge of the nose of the person conducting the test. Then you quickly need to lay him down on his back so that the fixed head hangs down slightly.
After 20 seconds, return to its original state, repeat on the other side and evaluate the result:
- If after 1-5 seconds in a lying position the patient becomes dizzy and rotatory nystagmus (rotation of the eyeballs) occurs, BPPV is diagnosed. When returning to the starting position, the eyes move in the opposite direction.
- The absence of both symptoms indicates that the test is negative.
- A positive bilateral result indicates a traumatic origin of the pathology.
- Dizziness without nystagmus is confirmation of the diagnosis, but with the prefix “subjective”.
If the test is repeated several times in a row, the accumulation of otoliths that irritate the ciliated cells will dissipate. Accordingly, the head will no longer feel dizzy when tilted, and the nystagmus will be exhausted.
To fix the latter during diagnostics, special techniques are used. Electronystagmography or videooculography.
Recording equipment is needed because eye movements during the Dix-Hallpike test cannot always be recorded visually.
For reference. To further confirm benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, a so-called rotation test is performed.
The patient, lying on his back, throws his head back at an angle of 30⁰. The doctor sharply turns it to the affected side and observes the horizontal nystagmus that occurs after a short latent interval.
By the nature, speed and direction of movement of the eyeballs, one can determine the localization of otoliths, and in the case of canalolithiasis, in which particular canal the accumulation of otoliths is located.
The main symptoms of BPPV are characteristic of some other vestibular disorders, diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Differential diagnosis is required if vestibular neuronitis, multiple sclerosis, Meniere's disease, arterial hypotension, Barré-Lieu and vertebral artery syndromes are suspected.
With these pathologies, in addition to dizziness, hearing loss, neurological disorders, tinnitus, cephalalgia, and neck pain are also observed.
DPP - treatment
Therapy used for BPPV is predominantly conservative. Surgical intervention is a radical measure, fraught with complications and advisable only if there is no effect from other methods.
For reference. The basis of treatment is various techniques that allow you to move otoliths in the labyrinth and stop exacerbations of the disease, as well as performing special Brandt-Daroff gymnastics.
Taking medications is indicated only in the acute phase of the disease and has the nature of an adjunct.
How to get rid of dizziness - what to do
Epley maneuver
This method, by sequentially changing the position of the head in space, allows the otoconia to be moved from the semicircular canals to one of the sacs.
It is used for canalolithiasis to eliminate the cause of dizziness – irritation of the ciliated cells.
It goes like this:
- Turning the head towards the problematic ear by 45⁰, the patient lies on his back from a sitting position. The head must hang over the edge of the couch, and it must be fixed in this way for a minute and a half.
- Then turn 90⁰ in the other direction, simultaneously turning over from your back to the same side.
- Then the face turns towards the floor for a while.
- The technique is completed by moving to the initial sitting position, but with the head lowered to the chin.
For reference. This sequence of manipulations allows you to change the orientation of the labyrinth in space and gradually move the otoliths into the sac from the posterior semicircular canal.
Semont's reception
In case of cupulolithiasis, the ampoules of the labyrinth must be freed from otoconia. For this purpose, another technique is used.
Sitting on the couch with his legs down, the patient must fix his head turning towards the healthy ear and not change its position the entire time the technique is being performed.
First, the doctor abruptly places the person on the affected side, then returns to the previous position and lies down on the other side.
Correct, quick execution helps to free the cupula from crystals adhering to it.
Vestibular gymnastics
If the diagnosis is confirmed, you should regularly perform a set of Brandt-Daroff exercises.
It is performed in the morning, after waking up, and consists of the following sequence of movements:
- sit across the bed with your feet on the floor;
- turn your head to the left (rotation angle is about 45⁰);
- without changing its position, lie on your right side;
- lie there for half a minute or until the dizziness disappears;
- return to original position;
- repeat for the other side.
You need to repeat the complex daily, and if you have dizziness, several times a day.
Surgery
For reference. The Semont maneuver, the Epley maneuver used for dizziness, as well as regular vestibular exercises usually provide the required therapeutic effect, which allows you to get rid of BPPV paroxysms for a long time.
But in some cases, conservative therapy is ineffective, and surgery is prescribed.
Surgical intervention is carried out taking into account the severity of the pathology, the age characteristics of the patient using various techniques. So, you can fill the semicircular canal, which contains clusters of otoliths, or cross some vestibular fibers.
Sometimes complete removal of the labyrinth is indicated, which is carried out using laser destruction.
Drug therapy
Many experts doubt the advisability of using medications. Medicines used for BPPV are not able to eliminate the causes of dizziness, but only alleviate the symptoms of the disease during acute periods.
The basis of treatment consists of techniques and gymnastics that dispel clusters of otoconia. However, an otolaryngologist may recommend tablets that improve cerebral circulation and metabolic processes in brain tissue as a supplement.
For reference. Such drugs as Betahistine, Cinnarizine, and products based on the gingko biloba plant are considered quite effective and safe.
Conclusion
Vestibular disorder, caused by the movement of free otoliths in the canals and ampullae of the labyrinth of the inner ear, is considered an age-related disease. The majority of patients who consult a doctor with characteristic complaints are people aged 70 to 78 years.
For reference. The slowdown of metabolic processes, characteristic of older people, is the main reason for the excess amount of crystallized calcium in the vestibular apparatus. The proportion of young patients with this diagnosis is insignificant.
Only an otolaryngologist or neurologist can recognize the symptoms characteristic of BPPV and prescribe treatment; differential diagnosis is also necessary. Typically, conservative non-drug therapy methods provide positive results in the form of relief of dizziness attacks and long-term remission.
Pathology is treated surgically only in exceptional cases when its manifestations cannot be eliminated by other methods. Medicines are used only as an additional remedy during an exacerbation.
Source: https://neuromed.online/chto-takoe-dppg/
When to expect an effect
As experts and patients themselves say, a positive result after using gymnastics using the Brandt-Daroff method can be expected after completing the first set. You need to perform the maneuver 5 repetitions each morning, afternoon and evening.
Each set should take no more than 10 minutes. If an episode of dizziness has occurred, then it is better to perform the maneuver for 2 weeks. But doctors say that within a day after the gymnastics, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Vestibular gymnastics, regardless of which of the Brandt-Daroff or Epley maneuvers was used, is a safe and most effective way to independently reduce, and in some cases completely get rid of, the symptoms of dizziness.
If maneuvers do not help, then it is better to seek qualified help. The doctor will help you choose a different set of exercises and, if necessary, prescribe medication.
BPPV: causes of vertigo, diagnosis and treatment, Brand Daroff exercise
About 75% of people who suffer from vertigo actually experience it due to a disease of the inner ear and vestibular system.
BPPV or benign paroxysmal (frequently recurring) positional (starts in a certain position of the body) vertigo is characterized by sudden attacks of dizziness due to changes in head position or body posture.
According to statistics, about 40% of people over the age of 50 suffer from this disorder. Also, women complain much more often about its manifestations. The disease mainly manifests itself during physical activity, during morning rises, etc.
Etiological factors in the development of functional dizziness (causes)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), a very complex condition in etiology, in some cases it is not possible to establish the true cause of the disease.
The most common causes of BPPV include:
- traumatic injuries of the skull and concussions;
- inflammatory processes in the labyrinth of the inner ear;
- undergone surgical interventions in the head area.
Features of symptomatic manifestations
Symptomatically, benign paroxysmal vertigo manifests itself in the form of a feeling that objects around are rotating, this feeling appears after a sudden change in body position.
Paroxysmal dizziness usually manifests itself in the morning after sleep; it is difficult for a person to navigate in space after getting out of bed.
The duration of the paroxysmal period is, as a rule, no more than three minutes, then it goes away on its own without the use of auxiliary techniques.
Additionally, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo manifests itself in the form of dyspeptic disorders, which is a common symptomatic component for all types of vertigo.
An important aspect in diagnosing the disease is that benign positional vertigo is not accompanied by syndromes of organic disorders of the nervous system.
With this pathology, no pathologies develop in the organs of hearing, vision or smell. Thus, the disease does not pose a particular threat to human life, but causes some discomfort.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery is usually favorable; this condition does not pose a particular danger to the patient’s life. Depending on what disease or injury could have triggered the development of this condition, further recovery and the effect of the treatment will depend.
The prognosis for full recovery also depends on how promptly the patient sought qualified medical help.
Source: https://neuro-orto.ru/bolezni/epylepsyya/manevr-epli.html