For many of us, headaches are not a problem as they go away easily after taking painkillers. And when the pill stops helping, we don’t go to the doctor, but switch to stronger medications and even injections.
Unfortunately, the consequences are lost time. The time when you could, but did not want to discover a problem that your body is persistently signaling. After all, a headache is not an independent disease; it can be a symptom of serious illnesses. Only a doctor should diagnose and treat them.
Why does a headache occur?
As a rule, not the whole head hurts, but some part of it. Causes of headache depending on its location:
- the temple area may hurt due to sudden changes in blood pressure, poisoning of the body with toxins or infectious diseases;
- headache in the back of the head occurs with high blood pressure, problems with the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis) or hypertonicity of the muscles of the neck and collar area;
- If your forehead hurts, it may be an inflammatory disease of the paranasal sinuses - frontal sinusitis. It may also be a sign of increased intracranial pressure or occipital nerve entrapment. Such pain accompanies very serious illnesses - meningitis, pneumonia, malaria, typhus;
- if painful sensations occur around the eyes, these are signs of migraine, vegetative-vascular dystonia. This is how eye diseases, including glaucoma, can manifest themselves.
Be careful if your head hurts regularly, with a certain cyclicity. This is a clear and specific signal - you have chronic diseases, or the level of stress and hard work is very high.
Different intensity of headaches
Headache in one area or another can be of varying intensity: from sharp and sudden attacks to long-term debilitating ones. This is also valuable diagnostic information.
The intensity of the pain in the head can be:
- Strong, sometimes unbearable. The causes of such pain are migraines, pressure changes, sinusitis, traumatic brain injuries or infections. If the pain does not subside over time, but increases, it means that the painful process is progressing.
- Long lasting. This is a very serious SOS signal that our body can only give. It may indicate infectious lesions of the nervous system, meningitis, tuberculosis, parasitic diseases, and even a brain tumor. Frequent headaches are especially concerning .
- Pulsating. This is most often how migraine manifests itself. However, these can also be vascular diseases - brain damage, impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid or venous outflow. Pulsating pain is caused by some types of infectious lesions, otitis media, and glaucoma. A severe and prolonged throbbing headache is especially dangerous.
- Sudden. As a rule, it is caused by cerebral vascular spasm. This happens in the case of a pinched nerve during cervical osteochondrosis, during a vascular crisis. Aneurysm rupture and intracranial hemorrhage are very dangerous. But a sharp headache often occurs as a result of stress, if a person is nervous or poisoned by low-quality products.
What diseases are accompanied by headaches?
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis after several stages of examination. After all, with similar symptoms, the causes of headaches are different. Here is a list of the main diseases accompanied by pain in the head area:
- Migraine. Severe headache , often throbbing, a person feels nauseous, irritated by light and smells. There is general weakness and a desire to lie down. Often the pain affects one side of the face. A migraine attack can last several hours, or maybe 2-3 days.
- Tension headache. The most common type of disease. Usually the headache is not severe, but the painful sensations return again and again. May last 6-7 days. The pain compresses the skull, is localized in the back of the head, the frontal part, the crown of the head, or spreads to all parts. This type of pain occurs in people who are engaged in sedentary work, who drive for a long time, or who are constantly in a state of stress. Their shoulder girdle is so stiff that it does not relax even during sleep. The passage of muscles, nerve impulses, and tissue nutrition are disrupted.
- Cluster disease. It is very difficult for patients to tolerate and sometimes develops into a continuous form. The pain throbs on one side of the head, compresses the eye or part of the forehead. The eye begins to water and swell. The peak of the attack lasts from half an hour to one and a half hours. Men are more likely to suffer from cluster pain.
- Pain caused by infections. She is accompanied by chills and fever. The pain presses on the temples, eyes, forehead. With ARVI, the symptoms include a cough and runny nose. With meningitis, the pain is severe, throbbing, accompanied by vomiting.
- Pain caused by injury. Their nature and intensity depends on the nature of the injury. Characteristic of concussion, skull damage, displacement of vertebrae in the cervical spine. Moreover, unpleasant sensations may arise immediately, or they may occur after some time.
- Sinus pain. Accompanies inflammation of the nasal sinuses, therefore it is localized in the frontal part of the head or near the nose. The patient experiences a runny nose and nasal congestion. You can get rid of it only by curing the underlying disease.
- Pain caused by intracranial pressure. These are massive, intense pain sensations that cover the entire surface of the head and the area around the eyes. Patients describe them as pressing or bursting. Often a person feels nauseous and has difficulty withstanding bright light.
- Pain that occurs when the trigeminal nerve is damaged. Sharp, short-lived (from 2 to 5 seconds), but very painful. Occurs suddenly in any part of the face. Most often, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs in people with unhealthy teeth and oral problems.
Pathological causes
Sometimes pain in the bridge of the nose spreads to other parts, which makes it very difficult to understand its location. The pain itself can be pressing or aching. There are many reasons why your forehead hurts:
| Causes | Clinical picture |
| Frontitis (inflammation of the frontal sinuses) | Pain syndrome is a consequence of excessive accumulation of fluid and pus. As a result, pressure occurs on the mucous membrane of the frontal sinuses. It manifests itself most strongly immediately after waking up, since during sleep there is stagnation in the frontal sinuses, and gradually subsides. Frontal sinusitis is accompanied by difficulty breathing, high fever and thick nasal discharge (sometimes pus). In a neglected state, photophobia and eye pain occur |
| Sinusitis | Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. Severe pain occurs due to narrowing of the lumen in the nose and stagnation of secretions. The pain subsides noticeably after the fluid leaves the nose. Additional signs of pathology: cough, high fever and pain in the bridge of the nose and eyes |
| Ethmoiditis | An ENT disease, its symptoms are similar to frontal sinusitis, in which inflammation (purulent) occurs in the ethmoid sinuses located in the area of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx |
| ARVI | Due to general intoxication of the body after penetration of the virus into the central nervous system and blood, the following are observed: inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, high temperature (up to 39 degrees), chills, muscle and joint pain |
| Fever | Pain is a consequence of general poisoning of the body with decay products of pathogenic microbes that affect the functioning of the nervous system. A feature of the disease is a two-stage manifestation with an increase in temperature, the level of leukocytes in the blood, bloody skin hemorrhoidal rashes |
| Meningitis | This is an inflammation of the meninges, accompanied by intracranial pressure. This occurs due to excessive production of spinal cord fluid, leading to swelling of the membranes. The pain becomes diffuse and spreads to the temples, parietal part and back of the head. Symptoms: increased muscle tone, temperature, nausea, convulsive state up to coma |
| Encephalitis | When the brain becomes inflamed and its frontal lobes are damaged, constant pain occurs. Symptoms of the pathology: cerebral edema, plethora, fever, general malaise, increased body temperature, insomnia, vomiting, dizziness |
| Cluster headaches | Periodic pain in the orbit occurs. The causes of the pathology are still unknown, but most doctors believe that it is associated with the inability of the hypothalamus to control the biological clock of the human body. This condition is usually observed in the autumn-spring period and lasts from several hours to several months. Attacks are accompanied by congestion in the ears and increased sweating |
| Ophthalmological pathologies | Myopia (farsightedness), glaucoma and astigmatism are accompanied by pain in the frontal part and orbit. This occurs due to constant stress and often leads to decreased vision or complete loss of vision. |
| Osteochondrosis (cervical) | A person feels constant pain in the forehead (left or right side), intensifying with anxiety and insomnia |
| Migraine | Intense pain occurs due to impaired vascular tone, which causes insufficient blood to flow to the brain. Neurological symptoms, nausea, irritability, photophobia and dizziness are often observed. Migraine develops against the background of physical fatigue, stress, and alcohol abuse |
| Tumor | Due to the ongoing process, a gradually progressive pain occurs, which begins immediately after waking up and becomes stronger with every movement of the head, sneezing and defecation. Symptoms of the pathology: mental disorders, verbosity, lack of a sense of shame during the development of metastases and their penetration into the frontal bone, tissues and blood vessels of the brain. The nature depends on the location of the tumor, its size, stage and the presence of concomitant diseases |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | Pain is a consequence of pressure from altered blood vessels, a tumor, or a previous injury. Symptoms: the face turns red, tearing begins, sweating increases and the pupils dilate |
| Allergy | Discomfort is a consequence of cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure. The nature of the pain is similar to migraine pain; angioedema and urticaria may be observed |
What examinations need to be completed
If you complain of a headache, you should consult a therapist. First, the doctor collects an anamnesis - clarifies the nature, location, and duration of the headache. Remember when it first occurred and how often it recurs. In order to exclude additional factors that may provoke attacks, you need to undergo an examination by a neurologist, ENT doctor, ophthalmologist and visit a dental office. They will be able to accurately identify the causes and types of headaches and prescribe treatment.
Your doctor may recommend the following tests:
- Electroencephalography is a study of the state of the brain. This is how vascular and tumor pathologies and hematomas are detected;
- X-ray will show whether there are signs of hydrocephalus, whether there has been a head injury or sinusitis;
- magnetic resonance imaging - this can detect a tumor, cerebral circulation problems, sinus diseases, and the consequences of a stroke.
- computed tomography - this way you can determine whether there are hemorrhages in the brain, what is the structure of the brain tissue and blood vessels;
- electromyography - determines damage to neural connections and nerves;
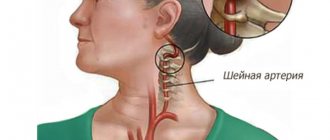
- Ultrasound of neck vessels with Doppler - a popular procedure reveals atherosclerosis, pathologies of blood vessels and blood flow, aneurysms;
- laboratory tests - tests will help detect the inflammatory process, the presence of infection, cholesterol metabolism problems and autoimmune processes.
Treatment
The consequences of headaches can be very serious. The more frequent and severe the headaches become, the more pronounced their consequences will manifest themselves - up to muscle spasms and brain hypoxia. And besides, the underlying disease will inevitably begin to progress.
Treatment of headaches is not limited to the use of medications - although taking anti-inflammatory, painkillers and local analgesics is an important part of the treatment. For example, a course of drug blockades greatly alleviates the patient’s condition.
A good help in treating headaches will be:
- manual therapy is a method of applying manual massage techniques to the spine. Particularly effective for migraines and tension pain;
- massage techniques. Effective for recovery from injuries and chronic migraines;
- acupuncture - exposure to medical needles through special points on the body. This way you can activate the work of organs associated with certain nerve endings and start the self-healing process;
- osteopathy - in this case, muscle tension and changes in joints and organs are worked out using special massage techniques on points on the patient’s body;
- physiotherapy - treatment with ultrasound, alternating or constant weak electric and magnetic fields, and heat. Effective for different types of headaches;
- physical therapy - moderate physical activity, especially good for the treatment of post-traumatic conditions and pain from overexertion;
- Botox injections - if the muscles are constrained by spasm, a Botox injection will relax the area of the body and relieve headaches;
- Extracorporeal hemocorrection is a method based on cleansing the blood of excess cholesterol and toxic substances. Has proven itself in the treatment of multiple sclerosis and pathologies of the immune system;
- folk remedies. For the most part, grandmother’s lotions and spells cannot be recommended in every case and only as a method of self-soothing. By preparing decoctions and compresses, you can waste precious time and miss the early stage of the disease. Therefore, in any case, consult your doctor first.
Folk remedies
For headaches, you can also use folk remedies. The most popular is a cold compress. Apply it to the location of pain. But it is not used for colds.
Rosemary, lavender and lemon balm oils are useful for headaches. They are rubbed into the temples and forehead area. A relaxing effect is also achieved through a gentle massage.
You can relieve headaches with green tea or propolis tincture. But before using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
How to prevent headaches
The best prevention of headaches is a healthy lifestyle and the ability to avoid stress.
The main conditions for this:
- proper nutrition. Food should not contain toxins, not cause excess weight, and supply the body with the necessary vitamins and amino acids;
- physical activity. Strong and moderate exercise, warm-ups during the working day, swimming, running, hippotherapy will keep muscles toned and prevent the occurrence of muscle tension;
- absence of bad habits. Alcohol, smoking, abuse of coffee and energy drinks are the first harbingers of imminent headaches. Take care of yourself.
- a full night's sleep. Only in this way can the body have a quality rest and restore its strength.
Prevention
In order to avoid headaches, it is recommended to follow certain preventive measures:
- Normalize your work and rest schedule. For an adult, sleep duration is at least 8 hours.
- Eat properly. The diet must include vegetables and fruits. They will help maintain immunity and reduce the risk of developing infectious and viral diseases.
- Avoid stress, anxiety and neuroses.
- Get rid of bad habits. These include smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Walk outdoors and exercise every day. It is important to dress appropriately for the weather conditions and not overexert yourself.
- After waking up, take a contrast shower.
Compliance with the rules of prevention will significantly reduce the risk of headaches when they are localized in the temples and forehead area.
If unpleasant sensations occur regularly, you should consult a doctor who will conduct a diagnosis, determine the cause of their occurrence and, if necessary, prescribe a course of therapy.