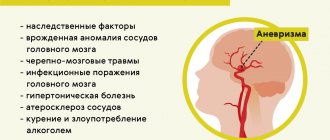
Defining true pain
Pain can be local and referred, when an inflamed structure remote from the location of the pain syndrome creates symptoms. If the junction of the sphenoid and frontal bones, in the fossa at the temple, is painful to the touch, then the cause is in the skull. If the stitch is painless, the cause should be sought in dehydration, the use of drugs that have side effects, the use of garlic or other products with essential oils, and caffeine abuse. The most common cause of discomfort in the temple is an imbalance of the musculoskeletal system, which manifests itself as scoliosis and back pain. For example, relaxation of the quadratus lumborum muscle on the right causes it to spasm on the left. To compensate for the fall to the right, the brain raises the left shoulder higher, which provokes pain in the left temple.
Migraine attacks
The classic description for migraines is a unilateral headache accompanied by nausea and incoordination. The symptoms increase over the course of an hour, reaching a peak. Possible flashing of “flies” before the eyes, photophobia, sensitivity to smells. Symptoms are directly related to irritation of the first four pairs of cranial nerves, which control vision, hearing and smell. Usually, people with asymmetry of the frontal and sphenoid bones are prone to migraines, which is corrected by manipulations by osteopaths and lifestyle changes: abandoning factors that enhance the pathology.
Tension headaches
Usually they involve half of the head and appear against the background of muscle spasm in the neck, back, and shoulders. A person complains of insomnia, a feeling of compression of the head, pain in the left temple or right one is of a shooting nature. It is necessary to be attentive to the factors that cause exacerbation and relief of symptoms. Some people find that massage of the neck and temples brings relief. Doctors prescribe muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Cervicogenic pain Caused by damage to the joints of the cervical spine, but radiating to the area above the eyes, below or behind the ear. A ring of pain surrounds the head and extends sharply to the temple. The manifestations are not associated with nausea and light intolerance and often appear after sleep. They usually develop in people who have hernias in the cervical spine or arthrosis of the joints. At night, swelling of the inflamed tissues occurs, so in the morning the symptoms intensify and resemble the feeling when the head was lying uncomfortably on the pillow while sleeping on the left or right side. It is necessary to do special exercises to restore the neck muscles.
Cluster pain Most often it shoots in the temple, but the reason lies in the eye area, provoked by overwork of the visual center. Complemented by lacrimation and redness of the face. Young men are susceptible to cluster pain syndrome. Triggering factors can be alcohol, stress, physical activity and lack of sleep. The attack lasts up to two hours. Periods of exacerbation can drag on for weeks or up to several months and disappear spontaneously.
Coin headache The pulse of the temporal artery is felt in the ear. Pain occurs after 50 years of age due to temporal arteritis - inflammation of blood vessels. Some people lose their appetite and feel severely unwell. A blood test shows an inflammatory process. Treatment includes corticosteroids to suppress abnormal immune responses where immune cells attack vascular tissues. The most severe temporal pain. Along with pain, the patient complains of sweating, loss of appetite, muscle aches, fever, blurred vision, weakness of the hip and shoulder muscles, and stiffness in the neck. Prolonged disruption of blood flow damages tissue. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor and take prescribed systemic medications that reduce the inflammatory process.
Paroxysmal hemicrania In addition to the temple, it affects the eyes and face. The burning, sharp, stabbing pain is a short-lived attack that goes away in 5 to 30 minutes, but can occur up to five times a day. Pain of moderate intensity is not associated with relapses and deterioration of general condition.
Carotid artery dissection Pain in the neck, temple and orbit, accompanied by collapse of the upper eyelid. Other neurological symptoms appear: blurred or loss of vision, weakness, difficulty speaking. The symptoms resemble a stroke due to decreased blood supply to the brain. The pain begins abruptly, which serves as the main diagnostic sign. As a rule, it is observed only on one side.
Trigeminal neuralgia A disorder that is accompanied by intermittent and shooting pain in the right temple more often than in the left. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve occurs against the background of malocclusion, inflammation after dental treatment, and bacterial infections. A rare cause is compression of the nerve by blood vessels, destruction of the protective myelin sheath. A sharp pain, reminiscent of an electric discharge, occurs along the course and exit points of the nerve: the hole on the chin, under the orbit, the notch above the orbits. Symptoms may recur several times throughout the day. The pain lasts up to two minutes and paralyzes part of the face. Provoking factors may be chewing, brushing teeth, or a gust of cold wind. Doctors prescribe anticonvulsants and antidepressants. Alternative treatment methods are used, such as osteopathy and acupuncture.
Temporomandibular joint pathologies Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, which is located in the front of the ear, between the lower jaw and the skull, can be structural or functional. Symptoms of the pathology include frequent headaches, especially when chewing, stiffness in the neck and jaw muscles, and the inability to fully open the mouth. The causes of the disease are inflammation of the cartilage, compensatory muscle spasm in response to weakness in the muscles of the neck, shoulders or feet. In severe cases, surgery is performed to correct the pathology. Ice packs relieve local symptoms.
Tumors of the temporal lobe of the brain Sometimes tumors are localized directly in the temple. The pain appears in the morning and increases throughout the day, sometimes accompanied by vomiting. Magnetic resonance imaging and treatment of the underlying disease are necessary.
Treatment of neuralgia
There are not many remedies that really help with neuralgia. Usually these are drugs that reduce nerve conduction, such as carbamazepine, tegretol. But in order for treatment for shooting pain in the head to be effective, it must eliminate the irritation of the nerve.
Often the nerve is pinched as it exits the skull due to bone displacement, for example after injury, or between blood vessels or strained muscles. Special osteopathic techniques can eliminate displacement and relieve irritation (irritation) of the nerve, after which the effect appears after a few days. Osteopathic treatment for shooting pain in the head does not require drugs or surgery.
Muscle causes of pain
Trigger points are nodules in muscle fibers that cause muscle dysfunction and impair joint function. To relieve pain you need to:
- Contract the muscle or assume a position that causes it to contract.
- Gradually apply pressure on the painful point and hold for 5–60 seconds until the pain subsides.
- Stretch the muscles, repeat the pressure.
- Develop each trigger point 3-6 times a day.
The trapezius muscle attaches to the occipital bone, acromioclavicular joint, shoulder blades, and cervical and thoracic vertebrae. The formation of painful points is associated with muscle overstretching and the habit of raising the shoulders upward during prolonged sitting. The point that provokes pain in the temple is at the junction of the neck and shoulder.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is attached to the spinous process on the temporal bone and collarbone; when tense, it creates symptoms of dizziness, nausea, ringing in the ears, and headaches in the eye and visceral area. Trigger points are located along the entire length of the muscle, as well as at its attachment points on the back of the head and the inside of the collarbone. Massage in these areas brings relief. Tension in the sternocleidomastoid muscle and pain in the left temple are usually associated with weakness of the same muscle on the right.
The temporalis muscle is located above the ear and creates pain syndromes in the temples and teeth. The trigger point is felt just behind the ear and usually appears after treatment at the dentist, abuse of chewing gum, or sitting at the computer for a long time.
The semispinalis capitis muscle and the splenius neck muscle are complex small muscles that are located near the spine and can become overstrained during prolonged static loads: reading, writing, including among schoolchildren. The muscle is worked along the spine from the middle of the shoulder blades.
The suboccipital muscles are located at the base of the skull behind the ears. They become overextended when the long neck extensors listed above are relaxed. First, you need to massage the muscles along the spine at the level of the beginning of the thoracic region, and then the attachment point of the suboccipital muscles, stretching them. Avoid the habit of resting your chin on your hand.
Origin of the pathological condition
Headaches are the first symptom of many disorders in the body’s performance. Most often it shoots and hits the temple for the following reasons:
- Overwork. Patients exposed to stress, depression and leading an unhealthy lifestyle often suffer from headaches. The pathological condition usually lasts for several hours, after which it improves.
- Migraine. Unpleasant discomfort in the left temporal region often appears in pregnant women and adolescents. The syndrome is accompanied by visual impairment, vomiting, nausea, and arrhythmia.
- PMS. At this time, changes occur in the female body in the endocrine system, one of which is painful pulsation.
- Hormone synthesis disorders. This process is manifested by intense spasms in the forehead, temples, and back of the head. Often such attacks are diagnosed in patients during menopause, accompanied by sudden mood swings and hot flashes.
- Infectious pathologies and inflammation. With a cold, flu, or acute respiratory viral infection, there is often a strong pulsation in the head, which disappears after recovery.
- Intoxication. In case of poisoning, in addition to vomiting, nausea, painful sensations may appear, severe pain in the left temple. Similar symptoms are observed with hangover syndrome.
- Vascular atherosclerosis. The disease is accompanied by an unpleasant pulsation in the temple on the left side, and can increase and then subside. The syndrome occurs against a background of impaired vision, hearing, coordination and memory.
- Low or high blood pressure. Weakness, rapid heartbeat, and pain on the left or right side of the temple may appear. Sometimes patients lose consciousness.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands. It is characterized by excessive production of adrenaline, resulting in vascular spasms and increased blood pressure.
Most patients make a mistake when they do not pay attention to the unpleasant discomfort, do not rush to see a doctor, and try to eliminate the syndrome using traditional medicine. But spasms in the left temple can be a symptom of a dangerous pathological condition that can lead to irreversible consequences.
Other causes of painful spasms in the temple include:
- VSD (nervous system disease),
- cervical osteochondrosis,
- injuries and pathologies of facial joints, cranial nerve endings,
- chronic inflammatory process of the temporal vessels,
- hunger cramps during strict diets,
- inflammatory, infectious diseases of the oral cavity,
- food throbbing pain due to the abuse of certain foods,
- inflammation of the membranes of the “gray matter”.
Reactive meningitis, what kind of disease is it?
All these conditions require immediate consultation with a doctor; you should not delay treatment, but undergo a comprehensive examination. In the early stages of the disease, painful symptoms can be eliminated and further development of the pathology can be prevented.
Diagnosis and when to get tested
Since there are many causes of spasms, only a qualified neurologist can make a correct diagnosis. Some diseases are dangerous and can lead to death. That's why you need to find out in a timely manner why it shoots in the temporal region. Correct diagnosis is the key to adequate therapy.
Comprehensive diagnostics of pathology includes the following examination methods:
- Laboratory tests.
- Ultrasonography.
- Study of the fundus.
- Examination of hormonal levels.
- CT and MRI.
- Resonance magnetic angiography.
- Cardiac monitoring.
- Consultations with specialized specialists: neurosurgeon, endocrinologist, cardiologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist.
If pain in the left hemisphere is regular, its origin should be established as quickly as possible. A general practitioner or neurologist will help determine the cause of spasms in the temporal region.
If you have the following symptoms, it is recommended to urgently undergo examination by a qualified doctor:
- uncharacteristic spasms, intense, localized in unusual places or the appearance of additional symptoms: fever, vomiting,
- cephalalgia resembling an "explosion"
- headaches accompanied by visual impairment: blurred vision, spots, darkness, slurred speech, numbness in the mouth, weakness of the limbs,
- “inaction” of analgesics after their use,
- low-grade fever,
- frequent vomiting,
- sudden increase in spasms during exercise,
- tension, soreness of the muscles of the back of the head.
Such symptoms may indicate the presence of dangerous pathologies such as stroke, meningitis or encephalitis. In this situation, you need to urgently seek medical help and call an ambulance team.
First aid for pathological conditions
Shooting pain in the right temple is a dangerous sign; when it appears, it is better to immediately consult a doctor to determine the cause of the syndrome. If you endure unpleasant discomfort for a long time, serious visual and hearing problems may develop. The patient's psychological state may deteriorate.
With intense spasms in the temple on the left, a stroke of the “gray matter” is possible. If strong lumbagoes appear in the head, you should monitor their frequency and duration. If the pain is one-time in nature and is not accompanied by additional symptoms, the following measures can be taken:
- When your temple is pulsating, it is better to take a walk in the street, a park, or ventilate the room well.
- Wash with cool water and take a shower.
- Perform a temple massage.
- Reduce lighting intensity and eliminate extraneous sounds.
- Relax, get a good night's sleep.
- Take a pain reliever.
If the patient is sure that spasms in the left temple are the result of a hangover or a cold, then you can take a medication that reduces the intensity of unpleasant symptoms of ARVI or flu. Sometimes it is recommended to use traditional medicine recipes that help eliminate vascular swelling and nourish the “gray matter” with vitamins and microelements.
When your temple throbs immediately after eating, you need to carefully study the composition of the food. If a food that causes unpleasant discomfort has been discovered, it is recommended to exclude it from the diet. If you need to buy ready-made food, it is better to give preference to baked goods, salads and pies.
Features of complex therapy of the syndrome
Depending on the type of pathology that provoked the appearance of spasms in the left hemisphere of the head, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. Treatment of the pathological condition may include the following medications:
- sorbents,
- if your temple is throbbing, medications that eliminate swelling of blood vessels will help,
- anti-inflammatory drugs,
- if your temple hurts, antipyretic tablets are prescribed,
- sedative medications that have a sedative effect,
- antibacterial drugs.
Complex treatment may include warming creams if spasms occur due to prolonged exposure to cold or drafts. Physiotherapy is also often prescribed, including:
- Therapeutic baths.
- Wraps using special mud.
- If your temple hurts, a course of massages is indicated.
- Electric phoresis.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Treatment through acupuncture.
When headaches in the left temple are the result of overwork, a strict diet or excess food, a person should change their diet and lifestyle to eliminate the pathological factors causing the malaise.
Prevention measures for the syndrome
To get rid of unpleasant discomfort, you need to follow the correct regime: get enough sleep, eat well, do not overload yourself with work and mental stress, and take walks in the fresh air. Sometimes following these simple tips is enough to avoid resorting to the use of potent medications.
If it shoots in the left temple, the following recommendations will help:
- after a hard day at work, it’s good to take a relaxing bath or perform water treatments for your feet,
- in case of severe spasms provoked by VSD or sharp fluctuations in blood pressure, acupressure on the hands, neck, head will help restore blood circulation,
- if your temple hurts constantly, you need to eat only healthy foods: always have breakfast, drink 200 ml of water on an empty stomach 30 minutes before, eat a green apple,
- It is recommended to include in the diet lean meats, cereal porridges, sea fish and cottage cheese, fruits and fresh vegetables, grain baked goods,
- patients suffering from frequent temporal spasms are recommended to consume natural fruit juices, kefir,
- If you have a headache, you should give up seasonings, various spices, sugar, replace it with natural honey, and limit your salt intake.
For pain in the right or left temple, nutritionists recommend consuming at least 150 grams of sauerkraut, as well as black currants (a tablespoon) and a bee product with vegetable oil.
When should you see a doctor?
Serious illnesses such as meningitis or stroke can cause pain in the temple. You need to pay attention to the symptoms:
- visual impairment;
- difficulty pronouncing words;
- nausea and vomiting;
- problems with speech recognition;
- fainting;
- temperature rise above 39 degrees;
- neck muscle tension;
- numbness and weakness on one side of the body.
Isolated cases of pain are usually caused by muscle strain. It is necessary to understand why it shoots in the temple if the symptoms intensify over time, become regular and disrupt the usual way of life.
Why does it shoot in the left temple and what to do
Many people are familiar with the sharp pain that hits the left temple.
This trouble can be a manifestation of a large number of different diseases, since a significant number of muscles, veins, nerve endings and receptors are located in the temporal region. It happens that throbbing pain is the only symptom that worries a person. But sometimes other ailments are added to this problem. In any case, such symptoms cannot be ignored, since they may be signs of serious disorders in the body.
Mechanism of occurrence
Painful sensations occur due to irritation of the nerve trunks. First, a pathological impulse is formed in the nerve fibers, as a rule, this occurs due to some provoking factor, mechanical damage or inflammatory process affecting nerve processes or muscle tissue.
As a result, the pathological process affects the structure of neurons, and the nerve fibers cease to perform the function of “inhibition”.
As a result, a short-term pain impulse is formed that spreads throughout the entire nerve trunk. This is how a sharp pain arises, which is often accompanied by pulsation.
It is important to realize that pain in the temporal region of the head is not an independent disease, it is a concomitant symptom indicating some kind of disorder in the body.
Why it shoots in the left temple: 18 common reasons
If the left temple hurts and throbs, this may be a concomitant sign of a number of disorders. As a rule, trouble occurs under the following conditions:
- Physical and emotional fatigue . People who are stressed and lead an unhealthy lifestyle often experience headaches, and their face may go numb during an attack. As a rule, the painful condition lasts for 1–2 hours, after which improvement occurs.
. A situation where a headache and shooting in the left temple often occurs in adolescents and young women, especially during pregnancy. Often the malaise is accompanied by visual disturbances, and “spots” flash before the eyes, and some patients experience nausea, vomiting and an increased heart rate.
Migraine- Premenstrual syndrome . During these periods, neuroendocrine changes occur in a woman’s body, one of the manifestations of which is pain in a certain part of the head.
- Disruptions in the production of hormones . This process can manifest itself as sharp pain in the back of the head, temples or frontal area. Often such attacks occur in women during menopause, accompanied by hot flashes and mood swings.
- Inflammatory processes and infectious diseases . With influenza and ARVI, severe pain in the head often occurs, disappearing after recovery. These same symptoms are characteristic of colds, when the patient could simply be exposed to a draft. In such cases, pain may appear not only in the temples, but also in the neck or ear.
- Poisoning . During intoxication, in addition to nausea and vomiting, an unpleasant sensation often occurs when the right or left temple throbs and severely hurts. The same symptoms are characteristic of a hangover.
- Atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the brain . Such “deposits” are often the cause of pain that knocks in the left temple , and can periodically intensify and then subside. Such conditions are accompanied by disorders of hearing, vision, memory and coordination of movements.
- High or low blood pressure . These conditions may be accompanied by loss of consciousness, weakness, arrhythmia and pulsation in the right or left side of the head.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands . This condition is characterized by increased activity of adrenaline synthesis, resulting in vascular spasms and blood pressure “jumping up.” This provokes the disease.
- Vegetovascular dystonia . This disorder can be accompanied by unpleasant manifestations from all organs and systems of the body, including headaches.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine . Due to this disorder, the diameter of the vertebral artery decreases, which can cause discomfort when the head hurts and the left temple twitches.
- Diseases and injuries of the facial joints . With such a disorder, pain appears in the corresponding part of the head, as well as in the cheekbones. Sometimes when the jaw moves, clicks occur and a crunching sound is heard in the joints.
- Damage to cranial nerves . This condition is caused by compression of the processes, which provokes sensations reminiscent of an electric shock.
- Chronic inflammation of the temporal arteries (arteritis) . This disease affects older people: both women and men. The condition is manifested by pain in the temple area, which is often pulsating in nature. In some cases, there is redness in this part of the face.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity . Many patients note that when a tooth hurts, the unpleasant sensation spreads throughout the entire head, including the temporal region. The same thing happens with painful processes in the mucous membrane, for example, stomatitis.
- Inflammation of the meninges . These conditions are characterized not only by headache and fever, but also by symptoms accompanying poisoning.
- "Hungry" pains . People who eat irregularly or practice strict diets are prone to frequent ailments in the form of headaches. This is a consequence of a lack of certain microelements in the body.
- Food headaches. This is the opposite situation, when the disease occurs in people who abuse certain foods, for example, fast food, chocolate, Chinese processed foods, cheeses, and others.
Many people make the mistake of not paying attention to unpleasant sensations and not turning to doctors, but trying to treat the ailment with folk remedies or pills. This should not be done, since pain in the left temple area may be a sign of the development of serious diseases, and delay in this case will lead to catastrophic consequences.
In what cases should you not postpone a visit to the doctor?
The patient requires urgent medical attention if headaches are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomiting and nausea;
- visual impairment;
- loss of consciousness;
- difficulties in pronouncing words and recognizing someone else's speech;
- increased body temperature;
- numbness or weakness on one side of the body;
- tension in the neck muscles.
Symptoms such as these may be signs of serious illnesses such as meningitis, encephalitis, or stroke. In this case, you cannot delay contacting a doctor, and you should immediately call an ambulance.
Diagnostics
Since there are many reasons that provoke a headache in the left temple, a comprehensive examination is required to identify them. As part of diagnostic measures, the following are prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- electroencephalography of blood vessels in the brain and cervical region;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- lipid profile;
- consultation of specialized specialists (ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, neurologist and others).
After a diagnostic study, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Features of therapy
Depending on what disease is causing the pain in the left side of the head, a specialist will prescribe treatment. The following medications can be used as part of therapy:
- sorbents;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs that relieve swelling of blood vessels;
- antipyretic substances;
- antibacterial medications;
- sedatives.
Warming ointments can also be prescribed if the pain appears as a result of prolonged exposure to a draft. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out, including:
- mud wraps;
- baths;
- massages;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture.