Headache is a concern for many people. It distracts from work, interferes with concentration, and leads to rapid fatigue. Among all types of headaches, tension-type headaches (TTH) stand out, the symptoms of which include a feeling of the head being ringed with an “iron hoop”, a feeling of pressure or tightening of the skull with “leather straps”. 50-80% of all complaints are due to this pain syndrome.
Tension headache
Characteristic
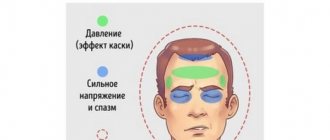
A pressing headache is a subjective sensation that occurs due to irritation of intracranial nociceptors or pain receptors located outside the cranium. The feeling of pressure on the head reflects damage (stretching, compression, displacement) of the structures:
- The hard membrane covering the brain.
- Cranial nerves.
- Arteries supplying the medulla.
- Soft tissues covering the skull (tendons, muscles, skin).
A feeling of fullness in the head, with or without pain, occurs without the participation of the brain matter and bone structures of the skull, which are not conductors of pain impulses.
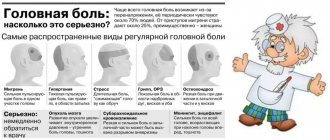
Kinds
There are primary and secondary pressure headaches. In the first case we are talking about migraine, cluster cephalgia, tension pain. In the second, painful sensations are associated with injuries in the neck and head, vascular pathologies, impaired cerebral blood flow, and the use or refusal of pharmaceuticals.
Secondary forms, which are accompanied by a feeling of constriction in the head, include pain caused by infectious and mental diseases, damage to the organs of vision, hearing, nose, and elements of the oral cavity. Taking into account etiological factors, the following types of headaches are distinguished:
- Physiological. Associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia, a violation of neurohumoral regulation of the tone of the vascular wall. They are often combined with pain in the abdominal area and occur after excessive sleep.
- Symptomatic. Correlate with the primary disease, which manifests itself with similar symptoms. These include somatic diseases, vascular pathologies, infectious lesions, and neurological disorders.
- Psychogenic. They occur as a result of physical and nervous overstrain, stress, or in a state of passion (severe excitement).
The share of symptomatic forms is about 20% in the general structure of cephalgia. The success of treatment of symptomatic forms depends on the early detection of the primary disease and the causes of the development of painful sensations.
Cervical osteochondrosis and headaches
A disease such as cervical osteochondrosis, headache is accompanied by headache constantly. However, before traveling to the nearest pharmacy for a painkiller, you need to find out what exactly is causing the pain. In a patient suffering from osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs triple their elasticity and strength
. That is why they easily move when the neck moves under physical force.
However, not only discs can shift, but also vertebrae that have lost their cartilage lining. This situation resembles a subluxation of the cervical vertebrae
.
The result of this displacement is infringement of the vertebral artery and nerve fibers of the cervical plexus. This is why there are headaches with cervical osteochondrosis
. Due to nervous and vascular syndromes.
Cervical osteochondrosis - headaches and treatment
Treatment of this disease occurs comprehensively using physiotherapy, drug therapy and therapeutic exercises. In the first case, use:
- magnetic therapy;
- medicinal baths;
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin applications.
During drug treatment, the following drugs :
- relieving muscle tension;
- inflammatory processes and pain;
- improving cerebral circulation;
- nicotinic acid;
- B vitamins;
- preparations containing magnesium, calcium and phosphorus.
as alternative therapies :
- acupuncture, acupressure and other reflexology;
- massages;
- treatment with bee products.
Causes
If the head is compressed like a hoop and dizzy, this may be due to an intracranial infectious process, which is usually accompanied by characteristic symptoms (fever, meningeal symptoms, paresis and paralysis, convulsive attacks, speech dysfunction).
In these cases, conditions where there is severe compression of the head and dizziness occur require emergency medical attention. Angiospasms in the area of small branches of the main intracranial arteries (carotid, vertebral) lead to stagnation and an increase in the volume of venous blood within the cerebral bed, which provokes the appearance of painful sensations.
Inflammatory processes localized in the head area, including respiratory viral infections, influenza, diseases of the ear (otitis and labyrinthitis), throat (pharyngitis and laryngitis), nose (rhinitis and inflammation of the paranasal sinuses), eyes (conjunctivitis and endophthalmitis) often cause pain and feeling of fullness in the head area. Common causes of the sensation of pressure on the inside of the head:
- Hypertonic disease.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Migraine, tension pain.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Stressful influences.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Disturbance in sleep and wakefulness.
- Volumetric intracranial formations (tumors, cysts).
Neurasthenia is a disease that reflects weakness and decreased functionality of the elements of the nervous system. Often neurasthenia is combined with a disorder of cerebral blood flow and chronic ischemic processes in the brain tissue. The disease is manifested by a feeling of squeezing, tightening, and pulsation in the head.
The feeling of pressure on the head is often associated with pathologies of the spine. Vertebrogenic (associated with the spine) pain and a feeling of compression in the head area develop according to the principle of compression-irritation or reflex-angiospastic course.
In the first case, the mechanism of development of cephalgia is associated with irritation and compression of the nerve roots in the spinal column, in the second - with a reflex spasm of the vascular wall of the vertebral arteries. The reasons for the feeling of pressure on the back of the head can be associated with intoxication, poisoning with nitrates, carbon monoxide, arsenic and other neurotoxic substances. The feeling of squeezing the head occurs as a result of many of the primary diseases discussed below.
Arterial hypertension
If the head is bursting from the inside with or without pain, this may indicate a sustained increase in blood pressure, which correlates with diseases of the heart (heart failure, atrial fibrillation) and blood vessels (atherosclerosis, developmental abnormalities). Acute encephalopathy of hypertensive origin leads to disruption of neurohumoral regulation of cerebral blood flow and cerebral edema, which causes a feeling of constriction in the head, but not pain.
It is believed that the feeling of squeezing and squeezing the head, as if in a vice, is caused by a reflex contraction of the muscles lying next to the skull, difficulty in venous outflow, and increased pulsation of the main cerebral arteries. Provoking factors: alcohol consumption, excessive physical activity, strong emotional experiences.
Cerebral blood flow disturbance
The head hurts, as if it were pressing and bursting from the inside, often due to an acute disturbance of cerebral blood flow, which is more common among elderly patients. Any form of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke causes a headache.
Less commonly, such sensations occur in the prodromal (preceding) period or for 2-4 weeks after stroke. If the feeling of tightness and cephalalgia last longer, there is a high probability of the influence of psychogenic factors, for example, depression. Associated symptoms: speech impairment, motor dysfunction, nausea, vomiting.
Arterial hypotension
If the pressure is 100 to 70 mm. Hg Art. or lower, patients are often haunted by the feeling that the head does not hurt, but there is pressure inside, which is due to a persistent decrease in the tone of the walls of arterioles and cerebral arteries. In this state, pulse stretching of the arterial walls and sustained expansion of the vascular bed occurs. The nature of the pain is dull, generalized.
In this case, the skull seems to shrink and tighten under the influence of provoking factors - physical and mental fatigue, stress, oxygen starvation of brain tissue. Associated symptoms: lethargy, a feeling of heaviness in the area of the skull, as if it were pressing and pulled from the inside.
Giant cell arteritis
Systemic inflammation of the blood vessels begins with damage to the temporal arteries. Usually combined with myalgia of the rheumatic type. It is more often detected among women over 50 years of age. Pain, sometimes throbbing, localized in the forehead and temples with irradiation to other parts of the head is the first symptom of the disease.
Painful sensations often intensify while eating. Associated symptoms: loss of appetite, soreness in the jaw muscles, reflex tension of the spinal muscles, aching pain in the joints and skeletal muscles.
Cerebrovascular diseases
The feeling of constriction and pressure in the head in cerebrovascular pathologies is caused by a constant lack of blood supply to the brain tissue. Associated symptoms: sleep disorder, muscle and general weakness, increased fatigue.
Traumatic brain injuries
After suffering traumatic injuries to the skull and intracranial structures, there may be pressure in the head when the patient bends over or makes sudden movements. Painful sensations are caused by hemodynamic disturbances and damage to soft tissues located in the cranium and neck.
A feeling as if the head is being squeezed may be accompanied by anxiety, nausea, and repeated vomiting. With severe injuries, neurological symptoms appear (aphasia, paresis, epileptic seizures), the severity of which depends on the nature of the damage.
Increased intracranial pressure
A feeling of pressure in the head from the inside, with or without pain, often occurs as a result of increased intracranial pressure. More often, painful sensations appear in the morning or at night, which is due to a deterioration in the outflow of venous blood. The nature of the pain is intense, bilateral, bursting.
What to do, how to treat?
Preliminary diagnosis is usually not required; your description of the nature of the headache is sufficient. If the pain is episodic, short-term and not chronic, you can get rid of tension headaches at home.
Otherwise, you need to contact your doctor. He will prescribe you a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scan, as well as an appropriate course of therapy.
Chronic tension headaches are a reason to see a doctor.
Helping ourselves
So how can you get rid of tension headaches on your own?
- Rest
Give yourself a few hours of peace. A relaxing massage, pleasant music, and warm baths with essential oils are very helpful in relieving tension. It is necessary to treat not only the body, but also the mood - take time for your hobby, reflect in silence.
- Need to cope with stress
Breathing exercises can be used to overcome stress. To control emotions, someone writes down negative experiences in a diary and subsequently burns the pages.
- Exercise stress
Maintaining muscle tone and good physical fitness will improve blood circulation and reduce the likelihood of tension headaches.
One of the ways to prevent tension headaches is adequate physical activity.
- Mental condition
Don't be afraid to visit a psychologist or neurologist. By dealing with your emotional problems, you will get rid of headaches forever!
Keep records of the time and intensity of the headache. This will help with diagnosis if the nature of the ailments becomes such that you have to see a doctor.
What can a doctor do?
Official medicine offers several ways to treat headaches.
Drug treatment
The use of medications (analgesics, muscle relaxants and antidepressants) helps to quickly relieve pain and get rid of discomfort. However, it should be remembered that the abuse of painkillers will only lead to an increase in negative symptoms, since there is no therapeutic effect on the very cause of the pain. Sometimes antiepileptic drugs are prescribed, which helps normalize the functioning of the nervous system and relieve muscle tension.
Antidepressants are sometimes used to treat tension headaches
Systemic treatment for tension-type headaches sometimes includes antidepressants. They help cope with prolonged low mood, which often leads to chronic headaches. New generation antidepressants that do not cause drowsiness are used. It is especially important that the effect of taking antidepressants occurs quickly; they also help the patient cope with depression and help eliminate headaches. When selecting medications, the doctor must choose the appropriate type of antidepressants, since otherwise the opposite effect may occur - increased anxiety or the occurrence of panic attacks.
Massotherapy
Therapeutic massage helps to get rid of headaches. A physiotherapist or chiropractor who can advise you before the procedure will help you choose this or that type of massage.
The following types of massage will help relieve the disease:
- General head massage.
- Acupressure targeting specific muscles.
- Massage of the cervical-occipital area.
The massage should be carried out in a calm and pleasant environment. It is very important that during the massage there are no strong pain sensations, this indicates that the massage therapist has acted incorrectly! You should also not put pressure on the vessels. A mandatory step is to warm up the muscles. It is necessary to thoroughly stretch the muscles themselves, as well as the areas of their attachment to bone tissue.
Massage will help relieve headache attacks
The combination of massage with physical therapy exercises is more effective. The doctor may additionally prescribe a session of physical therapy, as this will relieve muscle spasms.
Massage is useful for improving blood flow and muscle tone. It relieves fatigue and has a positive effect on mood. This type of treatment is especially effective if your work is devoid of physical activity.
Folk remedies and grandma's recipes
If you do not want to take pills or you do not have time for a massage, the following folk remedies are suggested:
- Ointments with a distracting effect.
- Herbal teas (for example, with honey and mint).
- Breathing exercises.
Recipe for herbal tea with thyme.
For headaches, folk wisdom offers the following recipe. Crush 5 g of dried thyme in a mortar and pour 500 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for about an hour or two. You can drink several times a day for a week.
Tea with thyme has an analgesic and tonic effect
Valerian root has a calming effect.
In order to brew tea based on it, you need to pour in 2 tablespoons of crushed root, add 400 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 10 hours. With the help of the resulting decoction you can get rid of illness in a matter of hours!
Dried fruits, potato juice (50 ml several times a day), infusions of golden mustache and orange peels also have beneficial properties. An excellent remedy are lilac flowers. A fragrant sprig of a plant standing in the room will be an excellent prevention of relapses of the syndrome.
If you have a headache, there can be many options for this condition. The pain can be pressing, when it presses on the head, as if squeezing it in a vice, and it can be drilling, pulsating, shooting.
The pain unsettles you and deprives you of the ability to concentrate, do work—it even deprives you of rest and the ability to feel relaxed.
When a headache occurs, the feeling of discomfort becomes predominant. And all that a person does when experiencing a headache is one big resistance to the annoying annoying problem, because sometimes pressure on the eyes, nausea, spots in the eyes, and dizziness are added along the way.
With intense pressing pain, a person may even lose consciousness.
Associated symptoms
A common cause of the condition when there is pressure on the head from above is physical stress, effort, coughing. In this case, the compressive pain in the head is often bilateral, of moderate intensity, and can be combined with symptoms - photophobia, increased sensitivity to noise, nausea. Tension pain is often monotonous and dull, localized in the forehead, occipital or temporal part of the skull. Symptoms that may accompany a feeling of fullness in the head:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
- Soreness in the muscle area.
- Lacrimation, conjunctival hyperemia (redness of the membrane of the eye), swelling in the eyelid area.
- Hyperemia of the skin of the face.
- Rhinorrhea (copious discharge from the nasal cavity).
- Anxiety, restlessness.
With neurasthenia, the head hurts, as if it were squeezing the skull, and other symptoms of the disease appear - emotional lability (mood swings), obsessions, sleep disorders, inability to concentrate. Other signs of neurasthenia: paresthesia (sensitivity disorder - numbness, feeling of heat or chills, crawling in the limbs and body).
Movement disorders include muscle weakness and increased fatigue. With migraine, a feeling of constriction in the head is combined with symptoms such as nausea; after attacks, signs are observed - drowsiness, lethargy. The pain is often one-sided, throbbing, and is characterized by repeated attacks.
In the cluster form, painful sensations shoot, drill, and are localized in the orbital and temporal zones. The attack is often accompanied by psychomotor agitation, nasal congestion, lacrimation, and heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia - decreased heart rate).
In the vertebrogenic compression-irritative form of cephalalgia, the head is compressed and pressed when the neck is turned or when the patient bends over. The condition is characterized by a decrease in the volume of cerebral blood flow, which is manifested by nausea, photopsia (the appearance of moving, often luminous dots, lightning, spots in the field of view), blurred vision. The patient becomes dizzy, hearing acuity deteriorates, noise, hum, and whistling appear in the ears.
With forced head tilts, loss of balance and unsteady gait are observed. With the vertebrogenic reflex-angiospastic form of cephalgia, the skull bursts from the inside, causing painful sensations in the neck, shoulders, and upper vertebrae. Typically, symptoms worsen with rapid turns of the neck or as a result of prolonged stay in a static position (sitting at a table, playing the piano).
Why does it compress your head?
Pressing pain in the head is often pronounced, which negatively affects performance and sleep. The causes of pain can be different; it is not always caused by factors hazardous to health. But in order to understand exactly why discomfort occurs regularly or periodically, it is better to undergo diagnostics and consult with a specialist.
Pressing pain in the head appears for various reasons
Causes of pressure in the head
Most often, the head compresses against the background of vascular pathologies - problems with arterial and intracranial pressure, spasms, circulatory disorders, oxygen starvation of brain tissue. Less often, unpleasant symptoms arise due to back diseases, lifestyle, errors in the body’s thermoregulation, and intoxication.
Squeezing his head - what does it mean:
- hormonal imbalance - occurs in women during pregnancy and PMS, during menopause, against the background of long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- increased meteosensitivity - any changes in atmospheric pressure can provoke the appearance of pressing sensations inside the skull, headache and dizziness, weakness, weakness, pain and aching in the joints;
- trauma, brain tumors, damage to the skull bones;
- frequent stress;
- overwork, physical stress, chronic lack of sleep;
- pinched occipital or trigeminal nerve;
- exhaustion due to long-term diets:
- if, with squeezing sensations, the head shoots and bursts, then these are clear signs of a psychosensory disorder;
- with osteochondrosis, strong and constant tension in the neck muscles, pain from the back of the head rises to the top of the head.
Pressing pain appears due to osteochondrosis
Often the head is compressed in people who smoke and abuse alcohol, are addicted to fatty, spicy, fried foods - this lifestyle reduces the tone of blood vessels due to the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on their walls, the brain begins to suffer from oxygen deficiency, a feeling of vacuum and heaviness arises in the head
An unpleasant sensation, as if something is moving in the area of the back of the head or the top of the head, occurs with encephalopathy, against a background of severe anxiety, fear, advanced forms of VSD, the head becomes heavy, a gait appears like a drunk, the person may lose consciousness.
How to determine the cause of its occurrence based on the nature of the pressing pain
The head can be pressed and pulled over the entire plane, or the pain is localized in a specific area, radiating to the temple, eyes, bridge of the nose, ear or neck. Some specific manifestations of discomfort allow us to draw a preliminary conclusion about the possible cause of its occurrence.
Characteristics and features of pressing pain:
- with very high blood pressure, unpleasant sensations are localized in the parietal part, the pain syndrome is severe, patients characterize it as a hoop on the head, often accompanied by nausea, increased heart rate, dizziness, and tinnitus;
- increased intracranial pressure causes pain that presses on the forehead and eyes, accompanied by severe loss of strength and blurred vision;
- glaucoma - intraocular pressure increases, vision deteriorates, puts pressure on the temples and above the eyebrows;
- meningitis - severe constant pain, there is a feeling that the head is burning from the inside, unpleasant sensations cover the eyes, accompanied by an increase in temperature to critical levels, confusion and loss of consciousness;
- long-term or chronic diseases of the nasopharynx - with sinusitis, sinusitis, pain occurs, which is localized in the upper center, or in the forehead and bridge of the nose;
- migraine - before an acute attack of pain, black or luminous spots begin to flash in the eyes, discomfort is accompanied by vomiting, nausea, a person cannot tolerate strong odors, light, stuffiness, unpleasant sensations cover one side of the head, temple and eyes;
- if you are overcooled, in a draft, or if you are constantly in a room in the summer with the air conditioner running, your head will become stiff in the forehead area, a burning sensation will appear in your eyes, and a lot of mucus will come out of your nose.
Prolonged sinusitis may cause a squeezing headache.
Oxygen starvation against the background of iron deficiency anemia - the head hurts from above, but can cover the temples, forehead and back of the head, the person complains of frequent attacks of dizziness, weakness, decreased attention, flickering of spots before the eyes. With this pathology, the hands and feet are constantly cold, the quality of sleep deteriorates, and the skin becomes pale.
If the head is compressed from the front, this is one of the first signs of the flu, unpleasant sensations arise against the background of intoxication with toxins of pathogenic microorganisms, the vessels begin to increase in diameter, and the surrounding edematous tissues burst.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your head hurts frequently and is accompanied by other negative symptoms, you need to visit a therapist and describe in detail the nature of the discomfort and the location of the discomfort. After examination and initial diagnosis, treatment by a cardiologist, endocrinologist, surgeon, psychotherapist or neurologist, ENT specialist, or oncologist may be required.
What to do with pressing pain in the head?
Since headache is not an independent disease, but a sign of various pathologies, the method of treatment and the choice of medications depends on the cause that caused the discomfort.
To reduce the intensity of the pain syndrome, you can massage the collar area, apply Zvezdochka balm to your temples or apply lemon peel, drink tea with mint or chamomile.
Important! Self-medication with coffee or cognac can lead to serious consequences, especially if a headache attack occurs against the background of hypertension.
Medicines
In case of a severe attack of headache, as first aid you can take antispasmodics or analgesics - Analgin, Spazmalgon, Citramon, Paracetamol. If the causes of squeezing sensations in the head are established, it is necessary to take symptomatic medications.
How to treat pressing cephalgia:
- for migraines, triptans and ergotamines are prescribed - Naramig, Naratriptan, Ergomar;
- for hypertension, antihypertensive drugs and diuretics - Concor, Minoxidil, Verapamil, Losartan, Furosemide, Indapamide;
- for tension pain, mild sedatives will help - Negrustin, Persen, therapy is supplemented with physical therapy;
- in the treatment of osteochondrosis, anti-inflammatory ointments and chondroprotectors are used - Diclofenac, Movalis, Teraflex; exercise therapy and massage will help to strengthen drug therapy;
- muscle relaxants - Mydocalm, Sirdalud, eliminate muscle spasms;
- drugs to improve the nutrition of nerve endings in the brain - Trental, Eufillin;
- antiviral agents - Amizon, Remantadine, necessary for influenza and other viral infections;
- tablets for raising hemoglobin - Hemofer, Sorbifer Durules.
Physiotherapy effectively helps with pressing headaches - paraffin applications, mud therapy, hydrotherapy, effects on muscles with current, ultrasound, magnetic therapy.
The drug Mydocalm belongs to the group of muscle relaxants
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of a pressing headache, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, get rid of bad habits, walk more - all these activities help maintain the health of the vascular system and keep muscles toned.
Preventive measures:
- exercise regularly - swimming, yoga, breathing exercises;
- control posture, avoid excessive stress on the spine;
- take vitamins, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- eliminate all junk food from the diet;
- while working, do a short warm-up for the eyes and neck every hour;
- if you are prone to hypertension, even if your blood pressure is normal, you need to measure the indicators every day and enter them in a special diary in order to notice any deviations in time.
During the working day it is useful to do a neck warm-up
Maintaining a daily routine, proper rest and sleep, absence of stress - all these factors have a beneficial effect on health.
Pressing pain in the head appears suddenly and may be accompanied by nausea, convulsions, blurred vision or coordination of movement - all these symptoms are a good reason to consult a specialist. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid the development of ischemia, heart attack, stroke, and irreversible changes in brain tissue.
Loading…
Source: https://MedBoli.ru/zabolevaniya/pochemu-sdavlivaet-golovu
Diagnostics
Due to the many possible causes of head compression, correct diagnosis is important. In 35% of cases, it is not possible to establish the exact causes of pain. If the patient complains of bursting pain in the head area, the doctor collects an anamnesis and prescribes instrumental and laboratory examinations to identify etiological factors.
During the consultation, the nature, intensity, exact localization of pain, and factors provoking the development of an attack of cephalgia are clarified. A blood test shows the presence of an inflammatory process, metabolic and endocrine disorders (hemoglobin deficiency, changes in the concentration of hormones, glucose, lipids), which makes it possible to suspect the disease that provoked the symptom - cephalgia. During an ophthalmological examination, the following characteristics are revealed:
- Condition of the fundus and blood vessels.
- Visual acuity.
- The presence of a spasm of accommodation.
- Signs of visual dysfunction (loss of visual fields, appearance of foreign objects within the boundaries of vision - dots, spots).
A neuroimaging examination (CT, MRI) shows the presence of space-occupying formations in the medulla. Angiography and Doppler ultrasound are performed to identify the condition of the elements of the circulatory system of the brain, including to detect abnormalities in the development of blood vessels - arteriovenous malformations, aneurysms.
Using electroencephalography, features of the bioelectrical activity of the brain and the presence of convulsive foci are revealed. If the compressive pain in the head is severe, acute, a lumbar puncture is prescribed to rule out infectious brain damage (meningitis, encephalitis) and subarachnoid (in the space between the meninges - soft and arachnoid) hemorrhage.
Treatment
Treatment of conditions where there is constant pressure on the head and dizziness is prescribed based on the results of a diagnostic examination, taking into account the type of primary disease and other reasons that provoked cephalalgia. In case of arterial hypotension, it is necessary to establish a daily routine, observing the frequency of work and rest. Procedures indicated: morning exercises, good nutrition, hardening. The main groups of drugs for the treatment of circulatory disorders and pain relief:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Non-narcotic analgesics, ergotamine-based drugs.
- Anticonvulsants, muscle relaxants.
- Correctors of cerebral blood flow, vasodilators.
- Nootropic, neuroprotective.
Surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of space-occupying formations (tumor, hemorrhage, abscess) in the brain tissue. Treatment for infectious diseases involves the prescription of antibacterial and antiviral agents. Therapy for arterial hypertension includes taking medications - beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers. Corticosteroids are used in complex therapy of giant cell arteritis.
If there is a constant feeling of pressure in the head, it is better not to draw conclusions on your own and not to self-medicate, which can negatively affect your health. Careful diagnosis and correct therapy will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.