Treatment of hematoma
The injury is classified depending on its location. You can hit:
- forehead;
- the back of the head;
- parietal region;
- temporal area of the head.
To establish a diagnosis, you need to determine the severity. Doctors use a special classification. It includes 3 degrees with distinctive features.
- Easy. It develops due to a minor injury that does not cause dangerous disorders in the brain. Characterized by short fainting, heaviness in the head, decreased sensitivity. Competent therapy allows you to restore health within 3 weeks.
- Average. The person loses consciousness for a long time. When he wakes up, he looks agitated and cannot adequately assess the situation. Amnesia, hand tremors, and changes in blood pressure often occur. Long-term treatment is necessary to stabilize the condition.
- Heavy. Diagnosed with significant brain damage. The integrity of the skull bones is often compromised. The victim is unconscious and may fall into a coma. He should be immediately connected to an intensive care unit and resuscitated. If the threat to life has passed, there will be a long recovery of reflex functions and brain activity, which is not always successful.
Most often, a hematoma on the head appears after injury to the soft tissues of the head: bruise, blow, pinching of the head during difficult childbirth.
The treatment method is selected depending on the intensity of damage to blood vessels, location and size of the formation.
Depending on the location, the following types of hematomas are distinguished:
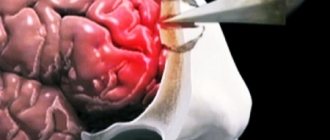
- Subdural - hematoma is located between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater. Hemorrhage occurs as a result of rupture of blood vessels located under the hard shell of the skull and the brain. When the hematoma grows, it compresses the brain tissue, and the person’s consciousness fades;
- Epidural - the hematoma is located above the dura mater. Hemorrhage occurs due to damage to the arteries of the brain. After this injury, the person may fall into a coma or remain conscious;
- Intracerebral - hematoma is located in the tissues of the brain. Blood from damaged vessels enters the brain and damages its nerve cells. As a result, the work of its departments is disrupted, and this can lead to serious complications.
Hematomas are also divided depending on their size:
- The volume of small blood tumors is 50 ml, they are treated with conservative methods, surgery is not necessary;
- The volume of secondary formations is from 60 to 100 ml, the treatment regimen depends on the location of the tumor;
- The volume of large formations is from 110 ml; the larger the formation, the more difficult it is to treat.
Any head injury requires medical examination. To determine the type and size of the blood tumor, the doctor must conduct a thorough examination using X-rays and CT scans.
Based on the results obtained, the specialist will determine a treatment regimen. Most often, conservative treatment is carried out, but in some cases surgery cannot be avoided.
The injury can be open, that is, damage to the skin is observed, and blood vessels are also affected. If the injury is penetrating, then the dura mater of the brain is affected, sometimes a fracture of the base of the skull is diagnosed - one of the most dangerous injuries.
With closed injuries, the skin is not injured. The following groups of brain damage have been identified:
- A concussion is a mild degree of traumatic brain injury, the manifestations of which disappear after a few days, there are no symptoms of vascular damage, and functional disorders are reversible. A bruise is a more severe injury and may cause brain damage. Manifested by such symptoms as nausea, vomiting, pale skin, tissue swelling, pain.
- compression of the affected area of the brain (foreign object, hematoma, air, bone fragment);
- hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space (the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater);
- diffuse damage.
A severe brain contusion can result from a combined injury.
With a head injury, there are 2 types of bruises:
- Brain contusion.
- Contusion of the soft tissues of the head.
Sometimes the injury is accompanied by hemorrhage. This is often accompanied by fractures of the bone tissue of the skull.
Types of damage are identified depending on location:
- contusion of the back of the head;
- damage to the temporal region;
- bruise of the frontal part of the head;
- damage to the parietal lobe.
Changes that occur in the brain as a result of a bruise are divided into primary and secondary. Primary ones are caused by the injury itself, and secondary ones are caused by deterioration of tissue nutrition and increased intracranial pressure, the appearance of edema, and hematomas.
In case of serious injuries, contusion of several areas of the brain is sometimes diagnosed.
When a child bruises the soft tissues of the head, a lump appears. However, as a result of the blow, brain injuries are also possible, the consequences of which can appear in adulthood, after 40 years or later. Therefore, even if a lump simply appears after a blow, it is recommended to seek medical help.
The head has different lobes, which allows the injury to be classified:
- Bruised forehead.
- Contusion of the back of the head.
- Bruised temple.
- Damage to the parietal lobe, vault, or base of the skull.
In most cases, damage occurs to the occipital or frontal lobe. Injury to the parietal region is less common. Damage to the temporal part occurs least often. The most rare and at the same time complex cases are when there is extensive damage that covers several head lobes.
Depending on the severity of the injury, the bruise is classified as follows:
- Minor injury.
- Damage involving loss of skin integrity.
- Jaw injuries.
- Lesions of the skull and brain.
According to the international classification of diseases ICD 10, the classifier code is included in S00-S09. The specific classifier depends on the severity of the damage. Code S00 – superficial head injuries, which do not include contusions of the brain, damage to the orbits and eyes on the face.
An open head wound is classified as S01, a skull fracture is classified as S02. Other unspecified wounds of the scalp correspond to classification S09.
Medical professionals classify head contusions according to several main criteria. First of all, with a head injury, the degree of severity matters. According to this criterion, experts distinguish:
- First degree. Diagnosed with a minor impact. In this case, the victim may have a small abrasion or bump from the bruise. The following painful signs may appear: weakness, dizziness, absent-mindedness. A slight bruise is not dangerous to health, and its symptoms disappear within seven to ten days.
- Moderate severity. In such cases, the head injury is more serious. The person experiences alarming symptoms: the area of the injury is very painful, there are serious memory lapses, confusion, and impaired coordination of movement. In addition to the fact that a lump forms on the head, swelling or subcutaneous hematoma appears. In this case, the fallen person recovers for quite a long time - from several months to a year.
- Severe degree. A severe head injury leads to the fact that the victim’s condition sharply worsens – up to a prolonged loss of consciousness and subsequent fall into a coma. In this case, the normal functioning of internal organs may be disrupted, as well as the extinction of reflex activity. If immediate medical attention is not provided, death may occur.
In accordance with the ICD 10 reference book, injuries in the head area are assigned codes from S00 to S09 - the higher the serial number, the more severe the damage.
The child hit the back of his head, what to do?
06.07.2017
Hello, dear parents. We have already discussed the topic of head impacts during falls, for example, what to do if a child hits his ear, or a child hits his nose when falling. Today we will talk about what to do if a child falls and hits the back of his head.
In this article, you will learn what such a fall can lead to, what consequences can occur if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, and what symptoms indicate the seriousness of the toddler’s condition.
You will also learn how to provide first aid and what to do to try to prevent possible bruises on the back of the head.
Alarming symptoms
It is possible that a blow to the back of the head will pass with virtually no characteristic symptoms appearing. Or maybe the bruise will just hurt. But parents should know that if any signs and characteristics appear in the behavior and well-being of the baby, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, and sometimes call an ambulance immediately.
- The baby's limbs were numb.
- In the eyes of the little one, everything splits into two.
- Nausea occurs, which may be accompanied by severe vomiting.
- Detection of differences in pupil sizes, short-term eye twitching.
- The skin became pale. A blue tint may appear.
- The child cries a lot, do not calm down for more than 15 minutes.
- Convulsive attacks appeared.
- There was a nosebleed and hemorrhage in the eyes.
- Changes in coordination of movements, imbalance.
- Clear discharge appears from the ears, mouth or nose.
- It is difficult for the child to turn his head to the side.
- Speech retardation.
- The child hit the back of his head, the lump grew very large - be sure to see a doctor.
Possible results of the impact
Parents should know what injuries, other than a minor bruise, their child may suffer as a result of a blow to the back of the head:
- Brain contusion. This can happen if the child hits the back of his head on the floor. Since small children have not yet fully formed and strong enough skeletal system, and in particular the bones of the skull, a brain contusion may occur after a fall. If the form of such an injury is mild, the doctor will prescribe medication; in the case of severe injury, surgery.
- Concussion. Occurs quite often with blows to the back of the head. As a rule, treatment takes place without complications, with the help of medications.
- Fracture. Often accompanied by discharge from the child’s ears or nose. They can be presented as clear liquid or blood. Treatment is conservative.
- Traumatic brain injury. Can be closed or open. The treatment process is the longest. Symptoms of this pathology are severe drowsiness, fainting, vomiting, and convulsions.
One day my son fell on the street and hit the back of his head. At the same time, there was even an abrasion with slight bleeding, which was successfully stopped. Everything worked out without drug treatment.
Once, when my friend and her daughter were returning home from kindergarten (in winter), they slipped, fell and hit the back of their heads. Everything turned out okay for the mother, but the girl was diagnosed with a concussion and appropriate treatment was prescribed.
There was also a case with a neighbor boy. He was visiting his grandmother and one day she washed the floor in the hallway and told him not to leave the room until it was dry. But then the cat Vaska jumped out from under the sofa and ran into the corridor. Sashenka, who had been trying to get the cat for a long time, ran after him, forgetting about his grandmother’s warning.
He slipped, fell and hit the back of his head hard. At that moment a big lump jumped out, he cried for about five minutes without stopping, either from pain, or from resentment that Vaska managed to escape again. Mom took Sasha to an appointment at the clinic, where, on the doctor’s recommendation, they underwent x-rays. Fortunately, everything worked out fine.
They were prescribed medications to resolve the lump.
The child hit the back of his head, consequences
It is important to know that as a result of the blow, the child may develop certain consequences. Depending on how serious the injury was or the delay with which the parents went to the hospital (that is, assistance was not provided in a timely manner), the following consequences may be distinguished:
- The child has problems perceiving the environment. What is typical: if the blow was struck on the left side of the back of the head, then problems will also be observed on the left side.
- The child may become absent-minded and have problems concentrating. Which will adversely affect the learning process in kindergarten and school.
- Problems may arise with both short-term and long-term memory.
- The child’s sleep is disturbed, he constantly sleeps poorly, often wakes up, and may even cry or be hysterical.
- The child suffers from constant headaches and possibly problems with blood pressure.
As a rule, if help was provided in a timely manner, almost all possible consequences can be avoided. Of course, if we are talking about a traumatic brain injury, then the child cannot do without tangible consequences; the injury is too severe.
First aid
- The first thing you need to do is calm down and not panic.
- It is important that the baby is at rest after the impact.
- Inspect the site of the injury, check for abrasions and bruises.
- If a hematoma appears, it is necessary to apply a cold or ice object to the site of the bruise, but do not forget to wrap it with cloth first.
- If the bruise is bleeding, you need to disinfect it, for example, with hydrogen peroxide. Use cotton swabs.
- If visual damage is not noticeable, explain to the child that he now needs peace and only quiet games. And monitor his well-being for several days.
- If you identify any symptoms that characterize a complication of the baby’s condition, you need to call an ambulance. This should also be done in case of severe bleeding, fainting and other alarming symptoms.
- It is important to know that if the baby loses consciousness, he must be placed on his side. It is also important to do this if there is vomiting, so that it does not accidentally enter the respiratory system.
- Even if, at first glance, everything is fine with the child, sometimes it is better to play it safe and go to see a doctor.
Prevention
Try to do everything possible to make your baby’s time as safe as possible:
- Take care of special pads on the corners of furniture.
- Wash the floors when the child is not at home or is sleeping.
- When there is ice outside, put on special shoes for your child and yourself that will resist falls.
- Get rid of paths in the apartment that can “ride” across the floor, thereby putting your child in danger.
- If your toddler moves around the apartment with the help of a walker, monitor his movements.
- Do not leave your baby unattended on the bed. If you leave the room, it is better to sit him on the floor. At the same time, you need to be absolutely sure that all corners in the room are safe and nothing poses a threat to the child’s health.
- If your child is learning to skate, roller skate or bike, make sure to purchase special equipment, including a helmet.
You already know that you can’t be completely sure that nothing will ever happen to your baby. Children are very active, love to run, jump, and are not always attentive.
Therefore, no one is safe from a possible fall or hitting the back of the head on a hard surface.
Remember how to behave in the event of such a bruise in order to alleviate the baby’s condition and prevent consequences from developing.
Source: https://zdorovyemalisha.ru/pervaya-pomosch/rebyonok-udarilsya-zatylkom-chto-delat.html
Symptoms and manifestations
A hematoma can appear immediately after a head injury or after a few hours. Therefore, the patient needs to be examined twice: immediately after the impact and after 2-5 hours.
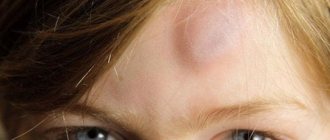
A blood tumor can be detected using a routine visual examination. The area of skin where the bruise formed is higher than other areas.
It looks like a burgundy or red lump, the shade of which changes over time due to the transformation of hemoglobin. The bruise first turns yellow-green and then light yellow.
When pressing on a hematoma, a person experiences painful sensations. The tumor has a dense consistency that does not move when pressed.
Blood accumulates in the soft tissues and puts pressure on the brain, causing the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Dizziness;
- Desire to sleep;
- Confusion (confused speech, long pauses);
- Movement coordination disorders;
- One pupil is larger than the other;
- Weakness in an arm or leg.
With severe internal hemorrhage, lethargic sleep, muscle spasms, or a coma may occur. That is why the patient must be monitored regularly. To rule out more serious injuries, an X-ray or computer diagnostics of the head is performed.
Consequences of injury
There are 3 main forms of trauma to the occipital part of the skull.
- Brain concussion. This injury is characterized by the development of reversible damage. The most common symptom of a concussion is loss of consciousness, which lasts from a few seconds to 30 minutes. In addition, patients experience nausea, vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Possible short-term memory loss, negative reaction to light and noise.
- Brain contusion. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms of a concussion and local symptoms. With a mild injury, loss of consciousness lasts from several minutes to several hours. Short-term speech impairment and paralysis of facial muscles are often observed. With a moderate injury, the above symptoms may be accompanied by a decrease in the reaction of the pupils to light and involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes (nystagmus). A severe brain injury is characterized by the victim falling into a coma, which can last for several days.
- Compression of the brain. This injury often occurs against the background of severe brain contusion. Most often, compression of the brain results in the development of an intracranial hematoma. Sometimes the cause may be swelling of the brain, fragments of the bones of the cranial vault, or a combination of all these reasons. Compression of the brain most often requires immediate surgical intervention.
In case of injury in the back of the head, a medical examination and a calm regime are necessary. According to the dynamics of subjective symptoms and objective neurological results, a CT scan is sometimes performed, an examination that can detect increases in brain depression, subdural or epidural hematoma. In this case, neurosurgical intervention is necessary - elimination of the hematoma.
- symptomatic analgesics;
- weak opioids;
- NSAIDs;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
Rehabilitation treatment is added later.
If you hit the back of your head and there is a suspicion of damage to the cervical spine, you need to be careful in your actions to prevent deterioration of your general condition during manipulation.
It is advisable to relieve increasing pain from the very beginning with medications from the NSAID group (Brufen, Ibalgin, Ibuprofen). If pain persists, consult a doctor.
If no serious damage is found during the inspection, the following measures may help:
- Massage. After determining the location of the injury, massage of a specific group of muscles in the back of the head effectively eliminates the consequences of the injury. The correct technique of the procedure is important, so massage is performed only by a professional.
- Physiotherapy. The physiotherapist creates a combination of suitable exercises designed to involve all injured muscles and ligaments in the back of the head. Therapeutic exercise improves blood circulation, which provides good results in eliminating and preventing the consequences of injury.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapeutic methods include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound or laser treatment.
- Chiropractic. Carrying out this method belongs only to the hands of a specialist!
- Acupuncture. This therapeutic method is advisable when signs of neuralgia appear.
- Regime measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of treating the consequences of neck injuries.
Prescribing treatment without proper examination, determining the causes and localization of damage is unacceptable!
Pharmacotherapy
In recent years, pharmacotherapy has been overused and often inappropriately. Without careful clinical evaluation, drug treatment is useless. In addition, drug treatment primarily does not affect the underlying cause of the disease, but only its consequences. Therefore, proper rehabilitation is a much better solution.
Muscle relaxants help relax muscle spasms and relax skeletal muscles. Depending on the mechanism of action, they are divided into 2 groups:
- peripheral;
- central.
Peripheral muscle relaxants block the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. They are used in anesthesia or when short muscle relaxation is necessary. In contrast, central muscle relaxants are active in the brain stem and spinal cord, where they dampen reflexes. They are often used to treat acute painful muscle spasms after injuries to the back of the head or when spinal problems occur.
To prevent the victim’s condition from worsening, it is necessary to provide him with first aid. First of all, bandage the head tightly, place the patient in a horizontal position, and place a pillow under the head. Open a window to bring fresh air into the room.
To stop bleeding and relieve pain, apply Riciniol emulsion to the bruise site. Apply a bottle of ice water or an ice compress to the hematoma for 20 minutes. Apply cold every 30 minutes. If the victim feels normal, then treatment can be carried out at home. You will be interested in…
Treatment of hematoma on the leg after a bruise or other injuries
Apply cold during the first 24 hours to stop internal bleeding and ease pain. After 48 hours, apply alcohol compresses to the injury site.
To do this, mix vodka and alcohol in a 1:1 ratio, apply to gauze or bandage and apply to the injury for 10 minutes. Repetition frequency – 3 times a day.
You can speed up healing by applying dry heat to the injury site for 40 minutes. To make the hematoma resolve faster, use heparin ointment, bodyagu or iodine.
Consult your doctor before using any product. To strengthen blood vessels, use Troxevasin, Troxerutin. You can speed up healing using castor emulsion. Immediately after the blow, treat the damaged area with Ricinol, and the blood tumor may not appear at all.
If the victim loses consciousness, then it is necessary to go to the hospital. Consult a doctor if you have severe headaches, nausea, or vomiting. Bleeding from the nose or ears, decreased blood pressure, severe incoordination, and convulsions are dangerous symptoms that require medical attention.
A hematoma with a volume of 110 ml or more is a serious reason to consult a traumatologist. It may be necessary to open the tumor and drain the blood.
Take a closer look at the hematoma: if it pulsates, then the artery may be damaged, and this is very dangerous. Do not hesitate to call an ambulance, only a qualified specialist will prevent dangerous complications!
- Brain concussion. This injury is characterized by the development of reversible damage. The most common symptom of a concussion is loss of consciousness, which lasts from a few seconds to 30 minutes. In addition, patients experience nausea, vomiting, headache, and dizziness. Possible short-term memory loss, negative reaction to light and noise.
- Brain contusion. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms of a concussion and local symptoms. With a mild injury, loss of consciousness lasts from several minutes to several hours. Short-term speech impairment and paralysis of facial muscles are often observed. With a moderate injury, the above symptoms may be accompanied by a decrease in the reaction of the pupils to light and involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes (nystagmus). A severe brain injury is characterized by the victim falling into a coma, which can last for several days.
- Compression of the brain. This injury often occurs against the background of severe brain contusion. Most often, compression of the brain results in the development of an intracranial hematoma. Sometimes the cause may be swelling of the brain, fragments of the bones of the cranial vault, or a combination of all these reasons. Compression of the brain most often requires immediate surgical intervention.
Bruises of the forehead, temples, and back of the head are dangerous to health. To avoid complications, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and adhere to a gentle regimen until complete recovery.
Serious injury often causes consequences that make it difficult to return to normal life:
- impairment of motor activity;
- high intracranial pressure;
- the formation of purulent sacs in the affected area;
- meningitis;
- epilepsy attacks;
- frequent migraines;
- hallucinations;
- blurred vision.
Sometimes unpleasant consequences begin to occur several months or years after the injury has healed. To prevent such a scenario, you need to regularly undergo preventive medical examinations after the rehabilitation course.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment are prescribed by a neurologist. If head contusions are observed, the diagnosis is made based on the following methods:
- X-ray – the presence of skull fractures is determined;
- spinal puncture;
- computed tomography - the localization of damage, the presence of hematoma, and edema are revealed.
After receiving accurate results, adequate therapy is prescribed.
A severe head injury suggests that you definitely need to make an appointment with a specialist to undergo an examination. It is important for damage to the temporal, parietal, frontal and occipital lobes. The result is confirmation or refutation of serious diagnoses, for example, concussion. Many people are concerned about which doctor to contact with such injuries. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a traumatologist; a consultation with a neurologist may also be necessary.
The main diagnostic methods include:
- Radiography. It allows you to see if there is a violation of the integrity of the cranial bones
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which allows us to evaluate changes in brain structure and the depth of the hematoma.
- X-ray of the cervical spine. It is necessary in cases where there is a risk of vertebral displacement.
Treatment is usually carried out by two methods - conservative and surgical. The doctor selects the specific one. Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where the internal diameter of the hematoma exceeds 4 cm, as well as in cases of pronounced intracranial hypertension, if the displacement of brain structures exceeds 5 mm.
Bruised toenail
The following medications may be prescribed:
- Drugs that normalize the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
- Analgesics.
- Sleeping pills.
- Nootropic drugs that normalize brain function. They are usually prescribed as prophylactics.
To increase the rate of hematoma resorption, doctors recommend using gels, creams, and ointments for bruises. At the same time, if you are interested in how to remove a hematoma on the forehead, you should proceed as follows: on the first day, apply cold for up to 10 minutes every few hours, on the second day, warm it up, and also begin to lubricate the damaged area with special ointments.
When wondering how to treat a head injury, it is important to understand that the process depends on the severity of the injury. Treating a head injury at home is quite possible if it is a minor injury. Often it comes down to the following:
- For the first few days, the victim is recommended to rest in bed. You should only get out of bed when necessary.
- If the injury is localized to the right, you should rest on your left side and vice versa.
- It is important to completely avoid physical activity for the next few weeks. If this is not possible, you should limit them.
- During the recovery period, you should minimize watching TV and working on the computer.
- It is necessary to spend more time in the fresh air 2-3 days after the injury.
- You should strictly follow your doctor's recommendations.
Additionally, you can use folk remedies, which usually help speed up the healing process. Among the recipes are the following:
- Saline 3% solution. Natural fabric is soaked in the liquid and placed in the freezer for 4-5 hours. Before applying the compress, the fabric is soaked in water to soften it. The procedure lasts up to 10 minutes.
- Composition with iodine and alcohol. Alcohol can be replaced with vodka. The ingredients are mixed in equal proportions. The fabric is dipped into the resulting composition and applied to the damaged area.
- Crystalline camphor and water. The composition includes 10 grams of camphor and half a liter of water. The solution is infused at room temperature, and it is recommended to shake the product periodically. Application is possible only after complete dissolution. The mixture is moistened with a cloth and applied to the bruise site for up to 60 minutes.
- Potato starch. It is mixed with water until it becomes a paste. After this, it is applied to the injured area.
Some also use more unconventional methods of treatment, for example, leeches. Before starting to use folk remedies, it is best to consult with a specialist so as not to cause harm.
The patient is first tested using the Glasgow system. These are special tests that can be used to determine the degree of impairment of consciousness, motor and speech reactions. Upon admission to the hospital, doctors stabilize the victim’s condition and conduct emergency diagnostics.
- X-rays are taken to detect closed fractures and cracks.
- Computed tomography is used to determine the degree of injury and localization of inflammation.
If necessary, a spinal tap is taken from the person to check the level of red blood cells. A general blood test and coagulogram are required.
The doctor interviews the patient, listens to complaints and assesses the location and area of damage. He also pays attention to the color of the hematoma and performs palpation. This makes it possible to determine the presence of fluctuations, pain in the area of damage and the tension of the subcutaneous hematoma.
If damage to the skull bones is suspected, radiography is performed in two projections. The patient is also prescribed a general blood test and, if indicated, other studies.
Effective treatment of any disease is impossible without correct diagnosis. To confirm or deny the presence of a head contusion in a patient after a fall, the doctor will first conduct an initial examination and interview. If the injury was local, it may not receive the status of a head injury. The following basic diagnostic procedures will help to definitively establish the patient’s health status:
- Radiography. Several photographs of the head are taken to assess the condition of the entire surface of the skull.
- CTG - a study is necessary to determine whether there is an internal hematoma.
- Spinal cord puncture. Allows you to detect the level of red blood cells.
If health care workers have any doubts about the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed additional research methods.
Head contusion
Even the most minor head injuries can lead to irreversible consequences. A head injury is the most common type of injury to this area of the body. It is characterized by damage to tissues that, as a result of a fall, are pressed against the bones.
Head injury - symptoms
The manifestation of the injury will depend on the extent and location of the injury:
- A slight bruise of the soft tissues of the head occurs with internal hemorrhage and pain. After a couple of hours, the pain subsides, and a hematoma forms on the affected area. The patient feels drowsy, double vision and sometimes loses consciousness.
- If a bruise causes damage to the bones of the skull, the patient may experience vomiting, dizziness, and nosebleeds. These signs indicate the severity of the injury, but do not allow a final diagnosis to be made.
- If the back of the head is damaged as a result of the blow, the victim’s visual acuity may deteriorate. Symptoms of such a bruise include loss of consciousness and weakness in the legs and arms, indicating a concussion.
Contusion of the occipital part of the head - consequences
Trauma to this area of the head can lead to negative consequences. In case of any minor fall, you should consult a doctor and undergo an appropriate examination. In the absence of treatment, the patient suffers the following consequences:
- traumatic asthenia, characterized by deterioration in performance, difficulty concentrating;
- depression, insomnia. memory impairment, irritability;
- clouding of consciousness, the occurrence of hallucinations;
- dizziness,
- weather dependence.
What to do if you have a head injury?
Anyone nearby can help the victim. Help may include the following:
- For mild bruises, apply a cold compress to the patient. However, you should not keep ice for more than fifteen minutes on one area of the head; you need to take breaks.
- The victim must be taken home, ensure his peace and monitor his condition. Since dizziness and muscle weakness are possible, it is better not to go outside.
- It is necessary to avoid taking analgesics, as they may further complicate the diagnosis of injury.
- If the victim has suffered a severe bruise, then the first thing to do is contact a traumatologist, since the possibility of a skull fracture cannot be ruled out.
Head injury from a fall - treatment
For minor injuries that do not cause a concussion, you can lubricate the affected area with the following drugs:
- comfrey ointment;
- Heparin ointment;
- Traumeel gel;
- Troxevasin ointment;
- Dolobene-gel.
If a dangerous diagnosis has been confirmed, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis for the first degree of concussion; for the rest, inpatient treatment is prescribed.
You can cope with a bump resulting from a head injury using traditional methods of treatment:
- In the first hours, cold is applied to the damaged area.
- The next day, they proceed to warming up the cone, applying warm compresses. This could be a boiled egg or heated salt.
- Thyme leaves have good healing properties. They are applied to the affected area.
- You can get rid of the bump with the help of pharmaceutical drugs such as troxevasin and heparin ointment.
It is important to follow all recommendations of a specialist. To speed up healing, it is advised to walk in the fresh air, follow a routine, give up intense physical exercise for at least a month, and spend time at the computer and TV screen as little as possible.
Rehabilitation
After the acute phase has been eliminated, physiotherapy is recommended. Magnetic therapy and iontophoresis stimulate brain function well. Acupuncture is useful to restore lost reflexes. If speech functions are impaired, consultation with a speech therapist is needed. Psychological disorders and depression can be eliminated with the help of a psychologist.
It is easy to improve your general condition and increase your energy potential with water procedures. Classes in the pool must be carried out with an instructor and the load must be increased gradually.
The rehabilitation process lasts from 1 month to 2 years. The duration depends on the established diagnosis.
For soft tissue injuries that do not affect brain function, treatment at home is allowed.
To relieve pain, cold is regularly applied to the affected area on the first day. To quickly resolve bruises and bumps, external agents are used:
- Troxevasin;
- Dolobene;
- Traumeel;
- Heparin ointment.
They need to be applied to the bump several times a day, without rubbing, and wait until completely absorbed.
First aid
If a person hits the back of their head, it is recommended to apply a cold compress to the affected area. You can use ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle filled with cold water. You need to keep the compress for 15-20 minutes, then take a half-hour break and repeat the procedure. It is extremely important to monitor your pulse and breathing. If blood appears, the wound should be disinfected and bandaged.
A severe concussion is accompanied by poor circulation and severe hematomas around the eyes. The injured person should be kept at rest. The victim may feel sick, so it is necessary to turn him on his right side so that the vomit can come out freely and air can enter the lungs. It is recommended to tilt your head back slightly and tilt your face closer to the floor. Limbs should be placed at an angle of 90 degrees to prevent fractures during convulsions. It is necessary to call an ambulance and not take any action until the doctor arrives.
It is not recommended to give painkillers, as they interfere with the diagnosis of the injury.
Consequences and complications
Each hematoma can provoke dangerous complications. A blood tumor can occur as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skull or intracranial bleeding. If a person has a headache after a blow, loses consciousness, speech, vision, or motor function are impaired, then it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Sometimes after a bruise the lump does not appear. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition: if the above-described symptoms occur, he must be taken to the hospital.
It is necessary to conduct a full examination using computed tomography, this is the only way to identify the internal tumor that is compressing the brain.
An intracerebral hematoma, which occurs as a result of rupture of brain vessels, affects its tissue and can be fatal.
An intracerebral tumor compresses brain tissue, causing the victim to experience disturbances of consciousness. A complication is possible in the form of infection entering the site of the bruise and the formation of an abscess (purulent inflammation of tissue).
At the same time, the person’s temperature rises, the tumor enlarges and changes color, and the pain increases. This type of hematoma disrupts the functioning of the brain centers, and therefore the consequences of the injury can be the most severe.
Almost never a head injury goes away without a trace. Even after completing a course of treatment, a person is periodically bothered by the following pathological symptoms:
- Decreased performance, lethargy, reluctance to do anything.
- Changeable mood, tearfulness.
- Absent-mindedness, inability to concentrate on one thing for a long time.
- Problems falling asleep.
- Memory loss, lapses.
- Meteor dependence.
- Migraine attacks.
These painful signs are especially acute if an old person has suffered a head injury.