Causes
The source of the disease is presumably a selective inflammatory process of the vestibular nerve (8th pair of cranial nerves). Selective, because other nerve fibers of the body remain undamaged, which remains unclear to date. What causes inflammation of the vestibular nerve? It can be:
- any viruses (especially herpes simplex virus type 1);
- food poisoning (toxicoinfections);
- infectious and allergic diseases;
- metabolic disorders.
The role of viruses in the occurrence of vestibular neuronitis is almost undeniable at present. The fact is that symptoms of the disease often appear a week or two after suffering an acute respiratory illness. In addition, vestibular neuronitis is characterized by an epidemic surge in the incidence rate at the end of spring. Cases of the disease occurring in members of the same family over a short period of time have been described. People started talking about the herpetic nature of the disease when descriptions of cases of herpetic encephalitis appeared after the onset of vestibular neuronitis.
Sometimes the cause of the development of the disease remains unknown, which indicates that the nature of vestibular neuronitis is not fully established.
Labyrinthine artery clogged
This cause of disturbance of the vestibular apparatus poses a particular threat. The fact is that the blockage interferes with the normal blood supply to the brain. The consequences can be critical: cerebellar stroke, heart attack, intracerebral hemorrhage. All of these lesions are life-threatening. If symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Signs of a blocked artery:
- severe dizziness;
- global loss of coordination;
- hearing loss in one ear.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment for disorders of the vestibular system is prescribed in accordance with the results of diagnostic procedures and is a complex process involving the use of medications and physiotherapy.
Drug therapy
Medicines are used for symptomatic treatment. This is due to the fact that it is almost impossible to eliminate the dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus that provokes the syndrome with the help of drugs. Despite this, taking medications can significantly improve the patient’s condition and reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks.
Groups of drugs for the treatment of vestibular syndrome:
- antihistamines (“Tavegil”, “Diphenhydramine”);
- anticholinergics (“Atrovent”, “Platifillin”);
- antiemetics (“Cerucal”, “Meterazine”);
- nootropic drugs (“Piracem”, “Cavinton”).
Antispasmodics, sedatives and analgesics are also used for therapeutic purposes. They are recommended to be taken directly during an attack. In the absence of contraindications, the patient can use No-Shpu, Bellaspon, and Cinnarizine.
If the pathology is of infectious origin, antibiotics or antiviral agents are prescribed for therapeutic purposes. Before taking it, be sure to study the instructions for contraindications. Taking medications is permissible only in accordance with the prescribed dosages.
Physiotherapy
During the treatment period, the patient undergoes various physiotherapeutic procedures. They are aimed at overall strengthening of the body, restoring the functions of the inner ear, improving local blood circulation, eliminating dizziness and other symptoms of vestibular syndrome.
The procedures used include:
- mud therapy;
- acupuncture;
- hirudotherapy;
- acupressure head massage;
- magnetotherapy.
The patient is also recommended to follow a diet and lead an active lifestyle. It is imperative to give up bad habits and follow a daily routine.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods are used for auxiliary purposes. Before using them, consultation with your doctor is required.
Effective recipes:
- Clover decoction. To prepare, pour 1 spoon of dried plant into a glass of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. The resulting product is drunk 1/4 cup before each meal.
- Tea with sage. Plant raw materials (4 spoons) are placed in a container with 0.5 liters of boiling water and stirred thoroughly. The product is infused and then drunk instead of tea, preferably before meals. It is recommended to add honey to the drink.
- Parsley infusion. Parsley seeds are used for medicinal purposes. They are crushed using a coffee grinder and then brewed (1 spoon of powder per glass of boiling water). The resulting drink is taken 50 ml 4 times a day.
- Carrot juice. Used to eliminate dizziness and strengthen the immune system. It is necessary to drink 3 glasses of freshly squeezed juice throughout the day.
- Kelp. Used dry. To eliminate the symptoms of vestibular syndrome, it is enough to take 1 teaspoon with water.
Numerous traditional methods are used to treat vestibular disorders
It is important to remember that alternative medicine, if used incorrectly, is harmful to health; it is less effective than drug treatment
Physiotherapy
Special gymnastics is one of the methods for treating vestibular disorders. With the help of exercises, the muscles of the cervical spine are strengthened, blood circulation is improved, and muscle spasm is relieved. Gymnastics also helps prevent the development of various diseases, including osteochondrosis, increased intracranial pressure, and migraines.
A set of exercises is prescribed individually, in accordance with the physical capabilities of the patient
When performing exercises, basic safety precautions are required to avoid injury.
Types of VA lesions
Dizziness is recognized as the main accompanying factor of vestibular apparatus disorder. Experts identify several forms.
- Peripheral. The most popular type occurs with disease of the auditory nerve tubules in the vestibular apparatus.
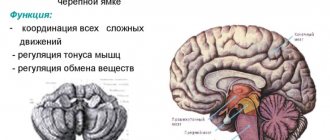
- Central. Diseases of the vestibular parts of the brain: brainstem, cerebellum, cortical parts.
- Afferentative. Dizziness occurs due to problems with vision, hearing, and dysfunction of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Causes of vestibular apparatus disorders
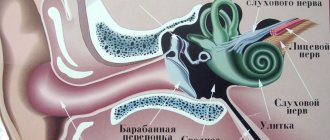
The main structures responsible for maintaining the balance of the body are the nuclei of the eighth nerve of the brain, the vestibular apparatus itself. These two structures are connected by the vestibular-cochlear nerve, which transmits signals in both directions: from the nuclei to the vestibular organ and vice versa.
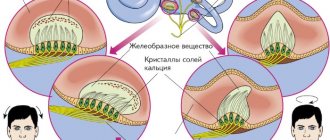
The organ is located in the inner ear. It consists of a system of semicircular canals and the cochlea, uterus, and saccule, through which calcium crystals (otoliths) move along with endolymph, a fluid. The cochlea contains sensitive hair (ciliated) cells that perceive signals.
These organs ensure that the body is maintained in space without losing balance and control over the body. Pathologies leading to a deterioration in their activity may be associated with circulatory disorders, innervation, and endocrine diseases.
The main causes of disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus:
- Head injuries.
- Otosclerosis.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Meniere's disease.
- Inflammation of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
- Diabetic neuropathy.
- Tumors.
Trauma and otosclerosis
Traumatic brain injuries: fractures, bruises, concussions can lead to damage to parts of the vestibular organ.
Otosclerosis is sclerosis (hardening) of the hearing aid. This disease can be caused by infections such as measles, as well as hormonal diseases. Otosclerosis often develops during pregnancy, as well as during the use of oral contraceptives. Problems in the functioning of the parathyroid glands also lead to the development of thickening of the organ of hearing and balance.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis, which is scarring of nerve tissue, can affect nuclei in the brain, the cerebellum, and the vestibulocochlear nerve. In this case, the person suffering from this disease experiences dizziness, in which the patient cannot maintain the balance of the body.
Arterial and intracranial hypertension
A strong and prolonged increase in blood pressure, which is observed in symptomatic hypertension and essential hypertension. Can lead to gradual damage to brain structures, as well as swelling of the semicircular canals and vestibulocochlear nerve.
An increase in intracranial pressure, i.e. the pressure of brain fluid in the system of brain cavities, can cause balance disorders and other symptoms of the disorder.
In inflammatory diseases of the brain and disruption of the secretion and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, the pressure in the ventricular system increases. This can lead to swelling of the vestibulocochlear nerve and its nuclei, semicircular canals, and cochlea. Dizziness and nausea appear, and sometimes myoclonic seizures and absence seizures, as in epilepsy.
Meniere's disease
The disease is associated with increased production of endolymphatic fluid, which circulates through the semicircular canal system, cochlea, uterus and sac. Its causes are unknown, but it is assumed that infectious diseases of the hearing aid, trauma, and vascular disorders are involved in the development of the pathology. Meniere's disease, along with vestibular disorders, is also characterized by vegetative manifestations: increased sweating, pale skin.
Neuritis, neuropathy, tumors
Inflammation of the eighth cranial nerve and diabetic neuropathy can also lead to poor balance control. Tumors of the hearing organs lead to loss of the ability to regulate the position of the body in space.
Sign of vertebrobasilar insufficiency
The disease most often affects people over 60 years of age. To treat vestibular disorders, it is necessary to treat cardiovascular diseases. The main causes of this type of disease are cerebellar stroke, damage to the vestibular nerve, and vascular diseases of the inner ear. The main symptoms of the disease include the following:
- unexpected dizziness for no specific reason;
- balance problems;
- accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Possible accompanying symptoms:
- deviations in visual understanding, may double;
- speech impairment, nasal voice;
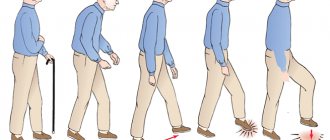
- Falls may occur due to loss of balance.
The sign of vertebrobasilar insufficiency may not manifest itself for several months. Therefore, if such signs appear for a long time, this diagnosis is excluded. It is necessary to undergo a complete examination of the body.
Causes of problems with the vestibular apparatus
Positional vertigo. This problem is especially common in women over the age of sixty, and sometimes in men of the same age. Symptoms of this problem are: the appearance of a feeling of rotation in a circle when the head position changes, a feeling of nausea, vomiting, and sometimes sharp stomach pain.
Vestibular neuritis. Usually happens due to infections, lichens. One of the most common problems of the vestibular system. Vestibular neuritis can be judged by the following symptoms: dizziness with the illusion of spinning in a circle, nausea, vomiting.
Vestibular neuritis
Typically, symptoms of extreme severity last for three to four days, after which they disappear, but complete recovery should not be expected earlier than in a month. In older people, this condition may last for a couple of months.
Symptom of vertebrobasilar insufficiency. Violation of the vestibular apparatus manifests itself together with diseases of the cardiovascular system. It is especially common in people over sixty years of age. Insufficiency may appear after a stroke, problems of the inner ear, or vestibular nerve. Nausea, vomiting occurs, balance is disturbed, which is why a person constantly falls, and coordination and visual perception do not work correctly - the image often doubles. Speech becomes incoherent.
The syndrome described above is short-lived, and if signs of the disease continue to appear for a long time, the patient should be admitted to the hospital for a more detailed examination and identification of all problems.
- Blockage of the internal auditory artery. This problem is very dangerous; it occurs in conjunction with a violation of the blood supply to the brain, which can lead to a cerebellar stroke or heart attack. Acute dizziness, loss of coordination and balance, one-sided deafness - these are the main signs of fatal and dangerous disorders of the vestibular system. If symptoms are detected in a patient, you must urgently call an ambulance.
- Bilateral chronic vestibulopathy. Appears due to drug intoxication. Moderate dizziness, nausea, and loss of stability appear.
chronic vestibulopathy
- Maniere's syndrome is one of the most common inner ear problems. In the presence of this syndrome, dizziness increases quickly and subsides much more slowly, hearing decreases at different periods of time, which ultimately can lead to complete deafness, as well as a feeling of noise in the ear and stuffiness.
- Ear diseases: otosclerosis (damage to the bone capsule of the inner ear), cerumen plug, dysfunction of the auditory tube. Otitis appears in acute form or purulent otitis.
- Various types of injuries
- Basilar migraine. Signs include the appearance of prolonged dizziness, which occurs in attacks; the problem is especially common among teenage girls - they are more prone to motion sickness in transport.
- Epilepsy. Dizziness, nausea, disturbances of consciousness and hallucinations are the main signs of the appearance of disorders.
Epilepsy
- Tumor of the cerebellopontine angle. Hearing decreases gradually, which can ultimately lead to complete loss. Dizziness is not typical for this type of tumor, but there is a lack of coordination of movement.
- Craniovertebral pathology. Almost the most common cause of vestibular apparatus disorders, accompanied by speech and swallowing disorders.
- Multiple sclerosis. Accompanied by extreme dizziness and nausea.
Before you begin to treat the organs of the vestibular apparatus, it is necessary to identify all the causes of the pathology.
Exercises for vestibular disorders
In the acute period of vestibulopathy, this makes no sense. But to more quickly restore the function of the vestibular analyzer, it is necessary to carry out exercise therapy.
Set of classes
Exercises are performed for no more than 15 minutes several times a day. They can be done even while lying in bed. The pace needs to be gradually increased.
- To begin with, eye movements are used with a motionless, fixed head. First, move the pupils in the horizontal, then in the vertical plane.
- Then rotate the eyeballs clockwise and counterclockwise.
- Tilts and turns of the head should be done slowly at first, so as not to provoke recurrence of vertigo attacks.
At first you can close your eyes. Subsequently, the exercises are performed with open eyes and at a faster pace. To make it more difficult, they throw the ball from hand to hand or shrug their shoulders. When the vestibular apparatus is dysfunctional, it reduces the quality of life, up to the formation of permanent disability.
The symptoms of vestibulopathy are varied, and it is important to pay attention to them, even when the cause is already known (arterial hypertension). If the course of existing vestibulopathy worsens or if symptoms arise for the first time, it is important to seek qualified medical help.
Diagnostics
Since vestibular syndrome has many causes, its diagnosis is quite difficult. Patients are examined by a neurologist and an ENT doctor. They listen to complaints, collect anamnesis, examine patients and study symptoms in detail. Then specialists conduct a direct standard examination of the hearing organ and determine the neurological status of the patients. Using cold and warm water, diagnostic tests are carried out, the essence of which is to influence the middle ear and determine the difference in nystagmus.
Special medical techniques include:
- Audiometry allows you to accurately determine disorders in the perception of sounds,
- Electronystagmography is a graphical recording of changes in the biopotentials of the eyeball,
- Ophthalmoscopic examination - examination of the fundus using special instruments,
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography,
- Vestibulometry is carried out to determine the causes of dizziness and assess the severity of disorders.
How the organ works
The human vestibular apparatus produces signals of two types: statistical (often they are associated with the position and coordination of the human body in space, the location of its individual parts) and dynamic (movements associated with acceleration). The whole work looks like this: mechanical irritation of the hairs occurs, as a result of which a certain type of signal is sent to the human brain, and after analysis, the brain sends the corresponding command to the muscles. And all this in a fraction of seconds. In other words, coordination of human muscles occurs, which makes it possible for the body to navigate in space. If we make a rather rough comparison with human technology, then the gyroscope is the most suitable tool for this.
Causes of vestibular dysfunction
- Benign positional vertigo. People over 50 years of age are at risk. The cause of the disease is considered to be the deposition of calcium salts in the canals of the inner ear.
- Neuritis of the vestibulocochlear nerve. Most often, the pathology develops against the background of previous viral infections, including herpes, chickenpox, and influenza. The disease is accompanied by dizziness, decreased hearing acuity, and increased sweating.
- Vertebro-basilar syndrome. The reason for the development of this condition is poor blood circulation and insufficient blood flow to the brain caused by pathologies of the soft tissues and blood vessels of the cervical spine. Most often found in older people.
- Vestibulopathy. The disease is provoked by exposure to toxic drugs. In most cases - antibiotics. Among the features of the course of the disease, it is worth noting rapidly developing hearing loss, constant nausea and dizziness.
- Meniere's syndrome. Pathology of the inner ear, accompanied by noise and crackling in the ears.
- Chronic diseases (otitis, eustachitis, otosclerosis).
- Migraine.
- Brain tumors with manifestations of epilepsy.
Treatment
Treatment of the vestibular apparatus is a difficult task, as it depends on the causes of organ damage, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Pills
Anticholinergics – prevent the development of dizziness. Have a lot of side effects
Elderly people are prescribed with caution, as they can provoke psychosomatic disorders. "Relanium", "Vestibo". Antihistamines – relieve dizziness and related symptoms
Representatives of this group are “Betaserc”, “Betagistin”. Benzodiazepines – eliminate dizziness and associated nausea. They have side effects and can cause addiction. These include Lorazepam and Diazepam. Antiemetics - relieve acute attacks, but are prescribed for a single dose, as they can cause muscle dystonia. Vasodilators - have a weak antihistamine effect, reduce the excitability of the vestibular apparatus. Cinnarizine is often prescribed.
In acute cases, vestibular dizziness is subject to drug therapy prescribed by a specialist.
Gymnastics
A fairly effective way to restore the proper functioning of the vestibular apparatus is special physical exercise. They not only give long-lasting results, but can also completely eliminate the disease. The main condition is that the set of exercises must be developed by the attending physician, since independent gymnastics can have the opposite effect.
ethnoscience
Homemade remedies can be used to prevent pathology and also complement traditional medicine. The most effective are tinctures made from ginger, meadow clover, and propolis. Stimulation of puncture points on the hands gives good results. If you feel dizzy, just rub a round object (stone, walnut, massage ball) in your palms.
Self-therapy for an unspecified disease can provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Diseases of the vestibular apparatus reduce a person’s performance and disrupt his orientation in space. To prevent the development of pathology, doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle, moving more, doing yoga, avoiding loud sounds and frequent flights. When the first symptoms appear and their progression, you should immediately contact a neurologist.
Dizziness: general concepts
There are situations when your head feels dizzy as a result of stress, fatigue, exhaustion, taking medications or intoxication.
A state of dizziness sometimes accompanies women during pregnancy, during certain phases of the cycle, and during menopause.
When strength is restored or the effect of the drug stops and the condition returns to normal, in this case you just need to avoid specific circumstances and try to take care of yourself.
Sometimes we can talk about so-called physiological dizziness as a person’s reaction to unusual conditions:
- water or air transport;
- attractions and extreme sports;
- climbing mountains, confined space;
- overheating, lack of air;
- changing the position of the body (for example, inverted poses in yoga), etc.
But at the same time, constant motion sickness in a car with nausea, weakness, panic, and tinnitus is not the norm. These phenomena often accompany dizziness, creating a lot of problems in everyday life.
In addition to the fact that a person with such a pathology has to limit himself in many ways, it poses a danger to life: falls “out of the blue,” incoordination of movement, collision with objects—the risk increases on city streets.
Why do you feel dizzy? At least 5% of people in the world consulted doctors with complaints of dizziness - not much less than with migraines. Attention is not always paid to finding the cause; the patient is simply forced to cope with individual symptoms: tinnitus, nausea, lack of coordination.
There are two types of dizziness: systemic and non-systemic. The first is directly related to defects in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. This causes a feeling of classic dizziness, in which the ability to adequately assess oneself and surrounding objects in space is lost, and the head seems to live its own life.
Non-systemic dizziness does not affect the vestibular system and is associated with other factors, including endocrine disorders, heart pathologies, anemia, etc.
Osteopathic science is based on the idea of the integrity of the whole organism. By restoring a unified balance, it is possible to bring individual systems back to normal and eliminate alarming symptoms.
Treatment
Complex treatment of vestibular disorder syndrome is aimed at eliminating the causes and clinical manifestations of the disease. The scheme of therapeutic measures is determined by the pathogenesis of vestibular dysfunctions.
With Meniere's disease, patients are advised to reduce the consumption of salty foods, limit alcohol, and quit smoking. Antibacterial drugs or steroid hormones are injected into the tympanic cavity. In severe cases, surgery is indicated. For the treatment of otitis media, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs are prescribed.
For all types of pathology, regardless of the cause, symptomatic therapy is carried out. Patients are prescribed:
- anticholinergic drugs - “Platifillin”, “Atrovent”,
- antihistamines – “Diphenhydramine”, “Suprastin”, “Tavegil”,
- benzodiazepines - Relanium, Lorazepam,
- antiemetic drugs - “Meterazin”, “Cerucal”, “Motilium”,
- vascular agents – “Cavinton”, “Piracetam”,
- medications with vasodilating, antiplatelet and neurometabolic effects - Betaserc, Betaver, Tagista.
During an attack, you need to apply cold to your head and a heating pad to your feet, take Bellaspon, Cinnarizine or No-shpu. During the interictal period, patients are prescribed proper nutrition and an active lifestyle, treatment with medicinal herbs and herbal infusions, head massage, acupuncture, exercise therapy, acupuncture, hirudotherapy, and magnetotherapy.
These general therapeutic measures restore the functioning of the statokinetic analyzer and eliminate dizziness. Patients become more confident in their gait, the functioning of the nervous system improves, and anxiety, restlessness, and panic disappear. The structures of the vestibular apparatus begin to work much better, the immune defense and general resistance of the body increases, pain and discomfort disappear, the severity of dizziness and dyspeptic symptoms decreases, the heart rhythm and blood pressure are restored, the movements of patients become coordinated, and the body position is stable. The body's condition noticeably improves, performance is restored, and the quality of life increases.
Vestibular rehabilitation is a set of measures that are carried out with the aim of quickly normalizing the functions of the vestibular apparatus. It includes gymnastics and gait training. At first, patients experience discomfort when performing exercises, and then get used to it. Vestibular gymnastics together with pharmaceuticals has a positive therapeutic effect. Surgical intervention is indicated for injuries and hemorrhages that pose a danger to the lives of patients.
an example of a universal vestibular gymnastics complex
Complex treatment improves the innervation and blood supply to the elements of the inner ear and has a positive effect on the entire body.
Treatment of dizziness with various techniques
The sensitive hands of an osteopath note the slightest deviations from the norm in the skeletal, muscle, and tissue structure.
skeletal
muscular
fabric
1. It is this doctor who is able to catch the rhythms of cerebral breathing, which, according to the craniosacral direction, is essentially the source of life of any organism.
“Breathing” is carried out due to the micromobility of the cranial sutures connecting the ossified plates. This occurs in time with the production of cerebrospinal fluid circulating between the skull and sacrum. Nature arranges it in such a way that when the next portion of cerebrospinal fluid is released, an “inhalation” occurs - the skull expands, avoiding pressure changes.
If the number of such cycles per minute becomes less than 6 or more than 12, a disorder occurs in the functioning of the self-regulation system; the corresponding parts of the brain are not able to send adequate signals to parts of the body, including the balance organs.
Problems in any part of the craniosacral system can cause dizziness, so the osteopath pays attention not only to the head and neck, but also to the pelvic area.
If a patient has ever injured his tailbone, especially with a sharp fall, he has already received a concussion, which may result in dizziness and other symptoms. The tailbone changes position, a pathological bend occurs, putting pressure on the skull through the spine.
Craniosacral techniques allow the doctor to restore the rhythm of the cerebrospinal fluid:
- he removes the clamps along the entire path of its flow;
- adjusts the mobility of cranial structures;
- eliminates dysfunctions between the skull and cervical spine;
- rules the pelvic area;
2. Treatment of dizziness is also carried out with visceral techniques. This direction of osteopathy involves manual manipulation of internal organs.
Despite the clear position of the insides, they do not exist statically, but make minor movements within the permissible amplitude.
Under the influence of unfavorable factors - physical or emotional stress, muscle weakness, painful condition of certain areas of the spinal column - the organs descend.
In women, the causes of prolapse often lie in difficult childbirth.
The sunken organs put pressure on neighboring ones, the nervous connection with the spinal cord is distorted, and here it’s not far from the head.
Moreover, the insides, in addition to their usual functions, have a lot of additional ones - after all, they are part of one organism.
If an organ is deformed or pinched, the heart has to work harder to supply blood to it. And, for example, kidney disease reduces the volume of red blood cells, causing anemia.
The right kidney supports and stimulates the gallbladder, and when it is deprived of this proximity, the risk of cholelithiasis increases, the symptoms of which officially include dizziness.
The main filter, the liver, eliminates toxins and metabolic products. Under the influence of bad habits or an unfavorable environment, as well as due to other disruptions in the body, it wears out.
The liver is affected by cirrhosis, hepatitis, it can no longer cope with the load, and toxic substances do not leave the bloodstream. The result of intoxication is dizziness. To prevent serious illnesses, it is necessary to restore the blood supply to the organ, remove the clamps, and early contact with an osteopath will avoid irreversible consequences.
The next danger to the brain and internal organs is oxygen starvation.
Deep breathing is hampered by decreased lung capacity. This occurs either due to deformation of the chest, or coarsening of the inner and outer pleural membrane as a result of pneumonia, etc.
This is only a small fraction of the connections between internal organs and dizziness. But how does an osteopath treat?
- Without disturbing the skin, the doctor makes gentle movements, smoothly pushing the organ to its rightful place.
- Eliminates interference with the movements it needs in the cavity space;
- Evaluates its position relative to other organs and tissues.
3. Structural therapy is aimed at working with bone and muscle structures.
Many people associate this direction with manual help. However, osteopathic techniques are distinguished by greater softness and jewelry.
To eliminate the cause of dizziness, it is necessary to work with the musculoskeletal system. Abnormalities of the spinal column are the obvious culprits of the problem, but it is worth looking deeper.
The spine takes on the load of the entire body, and it reflects the condition of the joints, muscles, and ligaments.
As a result of injuries, stress, incorrect body position for a long time and physical inactivity, muscles spasm or lose their elasticity, and joints lose mobility.
A weakened muscle corset is unable to support the organs, and the clamps exert pressure and interfere with their free vibration. It was already discussed above how this provokes dizziness.
Having laid out the functional chains, you can be surprised to find direct connections between dizziness and a bruised elbow or dislocated hip. The client himself will not remember the injury, but the body retains echoes.
Self-rehabilitating, the body pulls all forces to the site of injury, and a distortion is formed at the level of the musculoskeletal structure.
Tensions in the neck, shoulders and back interfere with blood supply to the head, and gait disturbances can lead to loss of stability.
Structural treatment of vertigo involves targeting the systems described above with several goals:
- Ensuring a balance of muscle tone;
- Restoration of skeletal symmetry;
- Creating the necessary conditions for the functioning of organs;
- Release of blood vessels and nerve endings.
What to do if the vestibular system is damaged
When the balance organs fail and signal this in every possible way, a person should first undergo an examination and visit an ENT doctor’s office. Mandatory diagnostics include:
- special hardware tests for audiometry and electronystagmography;
- CT or MRI of the brain;
- blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination of blood flow;
- vestibular tests.
Training
If the dizziness is minor and only bothers you when traveling on a boat, going up in an elevator, or making sudden turns of the body, your balance apparatus needs to be trained. Exercises for the vestibular apparatus can be mastered by anyone if desired:
- Sit on a chair or armchair. Extend your index finger forward and fix your gaze on it. Start turning your head in different directions, gradually increasing the pace.
- Next exercise: take two cards in your hands, straighten your elbows. It is necessary to alternately focus your gaze on one of the cards, while your head must remain motionless.
- Stand up, spread your legs, and focus your gaze straight ahead. Start making circular movements with your body. First with a small amplitude, then with a large circle diameter.
- All exercises for training the vestibular system should be performed daily with several approaches.
Treatment
If imbalances progress and other symptoms are added to the momentary dizziness, gymnastics will not help. Urgent medical treatment of vestibular vertigo is necessary. The choice of drug and method of therapy will depend on the reasons that caused this:
- If damage to the balance apparatus is caused by peripheral polyneuropathy, then diabetes must be treated.
- For paroxysmal vertigo, the ENT specialist chooses a special technique: he turns the patient in a certain sequence, the crystals change location, after which an improvement in well-being occurs.
- Treatment of dizziness with Meniere's syndrome cannot be done without effective antihistamines and antiemetic drugs. In addition, the patient necessarily needs nutritional correction and a special diet.
- Migraines in children can be treated with aspirin, ergotamine, beta blockers and antidepressants.
- If disorders appear at retirement age, the doctor may suggest implanting implants that will restore the lost balance.
Folk remedies for dizziness
Along with drug therapy and preventive gymnastics, it is possible to treat the vestibular apparatus with folk remedies. For example, make ginger tincture:
- Take 4 tsp. grated ginger root, mix with a pinch of dried mint, fennel seeds, pumpkin seeds, chamomile flowers and orange zest.
- Pour hot water over the herbal mixture, let it brew for 15 minutes and drink if you feel dizzy, lose balance, or other signs of systemic disorders.
In case of persistent dysfunction of the balance apparatus, a balm made from three tinctures helps strengthen a weak body at home:
- For half a liter of alcohol, take 4 tablespoons of clover inflorescences. Wrap the container with foil and leave for 2 weeks.
- For the same amount of alcohol, take 5 tbsp. l. Dioscorea root. Insist as in the previous recipe.
- Fill the propolis with alcohol and put it in a dark place. After 10 days, strain the tincture.
- Mix all three components and take 1 tbsp three times after meals. l.
Treatment with folk remedies
Only in combination with the main course of treatment does this make sense. Therefore, before using a folk recipe, it is better to consult a doctor. Using ginger as a decoction helps relieve nausea and dizziness. To do this, grind the ginger, add mint and chamomile flowers.
You can also use fennel and orange zest. 15 minutes after infusion in boiling water, you can take the drink up to 3 times a day, 4 tsp.
A balm is known that is prepared by mixing three tinctures: propolis, clover and dioscorea. After preparing the mixture, it is left for 10 days in a dark place. Then, three times a day after meals, 1 spoon of the resulting balm can be taken in the absence of allergic reactions.
Symptoms
Dizziness and a feeling of spinning are the main clinical manifestations of the disease, which patients with the syndrome most often complain about when visiting a doctor. With systemic vertigo, patients complain of rotation of objects in the environment in front of them, with non-systemic vertigo - unsteadiness of gait, swaying of the body from side to side. Such sensations arise suddenly and have a strong impact on the psyche of patients. They begin to grab onto the bed or chair to avoid falling.
Dizziness, depending on the damage to the structures of the vestibular system, is of three types:
- proprioceptive dizziness is perceived by patients as a change in the position of their own body,
- tactile - the feeling that “the ground is disappearing from under your feet”,
- visual - rotation of surrounding objects around the patient.
Symptoms of vestibular syndrome also include the following clinical signs:
- unstable body position,
- the feeling that “everything around is moving and spinning”
- nausea and vomiting, diarrhea,
- spots and dark circles before the eyes, decreased visual acuity,
- inability to fixate gaze on a specific object,
- blurry look,
- change in heart rate,
- fluctuations in blood pressure,
- disturbance of the rhythm of breathing and pulse,
- decrease in body temperature,
- change in pupil size,
- general weakness, malaise, depression,
- confusion,
- disturbance of orientation in time and space,
- fast fatiguability,
- headache of varying intensity,
- impaired concentration,
- nystagmus,
- unsteadiness of gait,
- tremor and myoclonus,
- muscle hypotension,
- speech disorders,
- anxiety, concern, panic,
- ringing or noise in the ears, hearing loss,
- pale skin on the face and neck,
- profuse sweating,
- blurred vision.
Forms of vestibulopathy:
- Vertebrogenic vestibulopathy develops as a result of pathological processes in the cervical spine - osteochondrosis, protrusion, hernia. Patients experience characteristic clinical signs: prolonged dizziness, headache, inability to fix their gaze.
- Vestibular neuronitis is an acute infectious inflammation of the nerve fibers of the inner ear and vestibular ganglion, manifested by imbalance, eye nystagmus, paroxysmal dizziness, fear, nausea, vomiting, congestion and tinnitus, and autonomic disorders. Patients note that the appearance of these symptoms was preceded by ARVI. A complication of the disease is encephalopathy.
- Post-traumatic vestibulopathy is the result of traumatic damage to the labyrinth, perforation of the eardrum and hemorrhage into the middle ear cavity. The causes of such processes are: concussion, bruise, compression of the brain, barotrauma, fractures of the base and vault of the skull, epidural and intracerebral hematomas. Dizziness in patients is persistent with nausea, vomiting, nystagmus, ataxia, and hearing impairment.
Any disease, including vestibular syndrome, should be treated in the early stages, when it has not yet developed to its maximum and has not caused irreversible changes. If the syndrome is started and left to chance, the body's resources will not withstand it. The body itself may not cope with the disease. All patients with signs of pathology should consult a specialist and undergo a thorough examination to make an accurate diagnosis and receive recommendations for rapid recovery. For therapy to be effective, the cause of the disease must be determined. It is necessary to treat not the symptoms, but to eliminate all etiopathogenetic factors that provoked the disease.
Symptoms of VA disease
Signs of violation appear in two forms: direct and concomitant.
Direct manifestations:
- dizziness;
- nystagmus (involuntary movement of the eyes horizontally or in a circle).
Associated manifestations:
- nausea of varying degrees, vomiting;
- pallor or redness of the face and neck;
- problems with balance, coordination;
- sweating;
- problems with the heart and breathing;
- change in pressure indicators.
Signs of vestibular dysfunction occur in attacks and can have varying degrees of impact. Symptoms may be caused by smell, food, or weather changes.