Pain in the head area that occurs due to compression of the nerve roots or the occipital nerves themselves is called neuralgia. The pain is often shooting in nature and becomes constant as the disease progresses. Pathology of the peripheral nervous system does not threaten human life, however, it can significantly worsen its quality.
What is the disease?
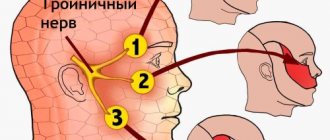
Occipital neuralgia is a symptom complex indicating damage to the nerve fibers of the cervical plexus. In most cases, the greater occipital nerve is involved in the pathological process (the greater auricular and lesser occipital nerves may also be affected).
Typically, neuralgia develops when the nerve roots located in the back of the head are irritated. It is divided into 2 types:
- primary (occurs without obvious prerequisites);
- secondary (occurs against the background of injuries, neoplasms, etc.).
Causes of occipital neuralgia can be:
- cervical spine injuries;
- infectious processes;
- overstrain of the cervical muscles due to a static position;
- diseases of the spine;
- osteochondrosis;
- connective tissue diseases;
- inflammatory processes in blood vessels;
- gout;
- diabetes.
In older people, the disease can develop due to various metabolic disorders.
Possible complications of occipital neuralgia include:
- persistent drug-dependent headache;
- torticollis;
- blindness;
- concomitant mental disorders associated with constant pain.
Causes of pinching and inflammation of the occipital nerve
Before studying the causes of inflammation of the occipital nerve, you need to familiarize yourself a little with the anatomy of this structural fiber. There is a division into the minor or major branch of the occipital nerve. The axons arise in part from the radicular nerve, which emerges between the first two cervical vertebrae. The second part arises from the radicular nerves emerging between the third and fourth cervical vertebrae. In the area of the acromial humeral joint, these two parts are connected and directed to the occipital region.
Pinching of the occipital nerve can be observed both at the level of the roots extending from the spinal cord in the region of the spinal column, and along the entire remaining length. Depending on the existing clinical symptoms, an experienced vertebrologist or neurologist will be able to accurately determine the location of the pinching. And after removing the obstacle to this nervous structure, you can quickly and effectively relieve pain, increased skin sensitivity and many other negative manifestations of pathology.
Now we can move on to the probable causes of this disease:
- neuralgia of the occipital nerve can be provoked by osteochondrosis with degeneration of the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral disc;
- pinching often results from a disc herniation;
- spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis and instability of the position of the vertebral bodies lead to compression of the radicular nerves;
- inflammatory processes in the area of the acromial and humeral joints prevent the normal passage of axons;
- tumor and infectious processes;
- injuries, bruises, blows, sprains and bone cracks.
There are risk factors that provoke the development of an inflammatory response. These are physical activity that is not typical for a given person, excess body weight, a sharp change in the usual lifestyle, violation of the rules for organizing one’s place for night rest and work. Compression of the collar area of the neck by tight collars, bulky scarves and ties can also cause pinching of the occipital nerve.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that headaches have a variety of etiologies, the patient needs to describe as accurately as possible to his doctor during the examination what he feels.
Only he will be able to compare the described symptoms with the concomitant condition and identify neuralgia.
After this, the necessary studies will be prescribed that will confirm or refute the proposed diagnosis, and most importantly, will allow us to identify the true cause of the pathology.
For these purposes, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- radiography.
A neurologist should examine the patient. If necessary, examinations by other specialists may be required.
Symptoms of inflammation and pinching of the occipital nerve
Inflammation of the occipital nerve is characterized by symptoms indicating a disruption of the innervation of a certain area of the head. An area of increased skin sensitivity may begin approximately at the level of palpation of the spinous process of the second cervical vertebra.
Clinically, the disease manifests itself as follows:
- the occurrence of acute or sharp shooting pain can be provoked by turning or tilting the head, uncomfortable posture during sleep, prolonged wearing of clothes with a tight collar area;
- gradual increase in intense pain and the area of its distribution;
- unpleasant sensations occur when touching the scalp in the occipital area;
- acute headache, migraine in nature (differs from true migraine by the absence of photophobia and irritation by loud sounds);
- dizziness can only be a consequence of spastic tension in the muscles of the collar zone, since the occipital nerve is not involved in the innervation of brain tissue and their membranes;
- disruption of the blood supply to the posterior structures of the brain due to tension in the neck muscles can cause increased blood pressure, dizziness, nausea, and decreased mental performance.
Clinical symptoms of occipital nerve pinching can vary in intensity. The less pressure on the fiber structures, the less pronounced the symptoms. Complete paralysis with loss of skin sensitivity is possible with serious injuries, for example, with a penetrating wound that damages the integrity of the nerve.
Please note that a decrease in the severity of pain with occipital neuralgia may be associated not only with recovery. Without timely treatment, the condition may worsen. Degradation of the nerve fiber occurs due to insufficient supply of nutrients. Trophic disturbances during compression entail deterioration of innervation. That part of the tissues for which the pinched branch of the occipital nerve is responsible for innervation loses sensitivity. At the same time, the acute headache subsides.
In the long term, pinched and chronic inflammation of the occipital nerve leads to local hair loss. This is due to the fact that when the innervation of the subcutaneous layer and epidermis is disturbed, the hair follicles lose blood supply and nutrition. They atrophy and baldness of the occipital region occurs. Another negative consequence is pain in the mastoid area and decreased sensitivity in some of the posterior parts of the auricle.
Headaches in the later stages are associated with impaired blood supply to the soft tissues of the scalp.
Treatment
Help for patients with occipital neuralgia is divided into two stages: relief of a painful attack and prevention of the onset of a new one. The basis of pain treatment is medications.
Drug treatment
All medications have contraindications and possible side effects. Before taking the pill, especially when self-medicating, be sure to read the instructions for the drug.
During an attack, various groups of medications can be used. The most commonly used drugs are NSAIDs – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They influence the mechanisms of inflammation, slowing down the process, which leads to a reduction in all symptoms. Some NSAIDs have a greater analgesic effect and are more often recommended for neuralgia: diclofenac, ibuprofen, meloxicam and their commercial preparations.
Anti-inflammatory steroids (glucocorticosteroids), anticonvulsants, and sedatives can also be used. Their action can also be aimed at the inflammatory process (GCS) or influence neuralgia indirectly.
Sometimes doctors prescribe medications whose effects have not been proven. For neuralgia, there is no reason to use muscle relaxants and vitamins unless there is a diagnosis of vitamin deficiency.
Surgery
Surgical methods are used extremely rarely. With frequent relapses (repeats) of painful attacks and identification of an organic (“real”) cause of occipital neuralgia, surgical elimination of the cause may be recommended.
It is used outside of attacks and for secondary occipital neuralgia caused by: muscle compression, spinal deformities, pinching by tumors.
More complex techniques can also be used that change the functioning of nerves and the conduction of impulses by them. Using neurostimulation, a neurosurgeon can activate or turn off certain receptors and nerve fibers, removing the pain component. This surgical option is suitable for the primary form of occipital neuralgia.
Physiotherapy
Treatment and rehabilitation physiotherapeutic techniques are widely used. Electrophoresis, laser exposure, magnetic stimulation, infrared irradiation for heating, and local heat compresses are usually used.
Helpful information
The effectiveness of physiotherapy has not been proven in the treatment of any disease. Most of them are safe for the patient and can only improve the condition in combination with other treatment methods.
But some methods cannot be prescribed: for example, heating is contraindicated in case of obvious inflammatory process.
Massage
Visiting massage therapists, vertebrologists, and chiropractors is a significant increase in the effectiveness of general therapy. Massage of the head, neck, and “collar area” can help relieve hypertonicity and spasm of the neck muscles, improve blood circulation, and improve posture. Massage is contraindicated in the acute period (during attacks), as it often only causes increased pain.
Self-massage can also be used: stroking the skin of the back of the head, followed by gentle rubbing. Afterwards – soft pressure. It is advisable to do all movements in the direction from top to bottom.
Manual therapy can also be helpful, but it should be used with caution and only quality therapists should use it. You can do without “spinal traction” and “reduction of intervertebral discs” - these procedures have no scientific basis and often lead to additional damage.
Folk remedies
The variety of folk methods for treating occipital neuralgia allows everyone to choose the appropriate method. Although none of the methods are traditional medical treatments, most often provide temporary relief. It is better if folk remedies are used not on their own, but in combination with methods from traditional medicine.
- Bath with herbs. Both dried plants and essential oils are suitable. Dried herbs (chamomile, oregano, mint or other relaxing herbs) are brewed in a small volume of water (1-2 cups) and then added to a bath of warm water. A few drops of essential oil can be added instead of tincture. Helps you relax in general, relax your neck muscles and take your mind off things. Use with caution during inflammation.
- Compress on the neck. It is used as a distraction therapy (when applying mustard plasters and cupping) and local heating (mustard plasters or warming compresses). To avoid thermal and chemical burns, you need to monitor the duration of application, wrap hot compresses in several layers of fabric. Use with caution during inflammation.
- Teas, tinctures. There are many recipes for brewing tea or creating a suitable tincture. For example, a spoonful of dried St. John's wort is brewed in a glass of boiling water. The drink should be divided into three doses per day.
Before treating inflammation of the occipital nerve
Diagnosis is necessary primarily to exclude diseases with similar symptoms. Before treating inflammation of the occipital nerve, you need to conduct a full diagnosis. To do this, you need to see an experienced doctor.
In our manual therapy clinic you can get a completely free consultation. vertebrologist, neurologist or orthopedist. These specialists have extensive experience in the treatment of vertebrogenic neuralgia. They will conduct an examination. They will make an accurate diagnosis. They will provide comprehensive information about the possibilities and prospects of treatment using manual therapy methods. You will receive information on how to properly treat such a disease.
For additional diagnostics, an x-ray of the cervical spine is used. with osteochondrosis, its complications and some other diseases of the spinal column, characteristic changes are visible in the image. The site of compression of the occipital nerve can be detected.
Prevention
To prevent this disease, it is important to follow preventive recommendations:
- protect the neck as much as possible from cold exposure, avoid hypothermia;
- provide the body with necessary vitamins;
- avoid injury to the neck, back and back of the head;
- include the right amount of physical activity in your daily life.
By following all recommendations and precautions, you can try to avoid pathology. And when the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately seek help from specialists.