It is one of the most complex brain pathologies. Most often associated with age-related changes caused by cell death that occurs due to age-related changes.
Age-related changes in the body provoke the onset of many diseases. One of which is Pick's disease. With this variant of senile dementia, disturbances occur in areas localized in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. This acquired senile dementia is characterized by behavioral disturbances. The patient's instincts are disinhibited, and cognitive functions collapse.
This type of senile dementia was first described at the end of the 19th century, in 1892, by psychiatrist Arnold Pick. At the initial stages of studying the disease, it was recognized as one of the manifestations of senile dementia. As the study progresses, Pick's disease is identified as a separate pathology. Until now, the pathology has been little described. It is diagnosed in 1-2% of older patients. The diagnosis is not always established immediately. For a long time, its manifestations were attributed to another variant of senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease. The difference is the localization of areas of death in the brain. If in Alzheimer's disease they are not strictly localized, the entire brain is affected; in Pick's disease the temporal and frontal lobes are affected.
A significant difference between the diseases is the absence of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Symptoms of the formation of plaques that occur during inflammatory processes do not appear. Due to death, thinning of the cerebral cortex occurs. The size of the cerebral ventricles increases. The distance between them practically disappears.
Manifestations start with speech disorders. Pick's disease causes behavioral changes in the patient. At the third stage, total dementia is noted.
Pick's disease is treatable, but age-related changes in the brain cannot be completely cured. The process of cell death is not completely stopped by medications.
When was Pick's disease first identified?
Pick's disease occurs in older people and affects women more often than men, but this criterion is much less pronounced than with other diseases. Individual parts of the brain are affected, most often the parietal, frontal or temporal. Moreover, personal changes are noticeable almost from the first stages. The disease develops quickly. Life expectancy from the moment Pick's disease is diagnosed is 6 to 8 years.
Pick's disease is characterized by the same nature as other diseases caused by atrophic processes in the brain. If previously it was believed that it was genetically determined, this opinion has now been refuted. No genotype changes were found in those suffering from Pick's disease.
It is believed that the brain is affected by layers of slow viral infections, as well as vascular changes, which have not been studied at this stage.
The first description of the symptoms of this disease appeared in 1892 and was carried out by the Czech doctor Albert Pick, after whom the name of the disease was given. He proved that the presence of negative and degenerative changes in the brain is hereditary. Therefore, people whose relatives include people suffering from dementia need to monitor their health very carefully.
- Recommended articles to read:
- Social services for older people
- Diseases of old age
- Valuable tips on how to choose a boarding house
Worth knowing!
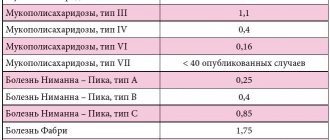
Quite often, Pick's disease is confused with Niemann-Pick's disease. The main difference between these two ailments is the age indicator. If the first is detected after fifty years, the second is diagnosed in childhood, and this illness is not a mental disorder.
Niemann Pick disease is hereditary. It occurs due to a violation of lipid metabolism, as a result of which these natural compounds accumulate in the brain, liver, spleen and lungs.
Depending on the form of the disease, the first manifestations of pathology can be detected in a child as early as several months or in adolescence. Pathologies in a child are not diagnosed at birth.
The mechanism of inheritance occurs through mutation of certain genes. The disease is caused by a deficiency of sphingomyelanin, which is responsible for the breakdown of lipids. As a result, the process is disrupted, and lipids accumulate in the cells, enlarging them.
Diagnosis of the disease reveals pathological enlargement of the spleen, adrenal glands, and liver. The color of the organs changes, becomes yellowish, and spots appear on the lungs.
Alzheimer's and Pick's disease: differences
The diseases progress in old age and are characterized by increasing dementia, therefore, they are not easy to diagnose. First of all, doctors examine the dynamics of development and structure of the disease. They evaluate the following changes:
1) Personality, memory and “instrumental” functions of intelligence
Pick's disease is characterized by personality changes already at the onset of the disease. Become noticeable:
- Childishness;
- Disinhibition;
- Decreased speech and motor activity;
- Lack of spontaneity;
- Unmotivated behavior.
People who begin to develop Pick's disease can, already at the initial stage, commit actions that harm their social status and financial situation: for example, they leave home and work, and begin to wander.
These symptoms are also characteristic of Alzheimer's disease, but appear at a later stage of development.
Basic intellectual functions remain virtually unchanged, this applies to such indicators as:
- Orientation on site;
- Memory;
- Time;
- Events;
- Check.
Complex mental activity undergoes changes:
- Generalization;
- Abstraction;
- Criticism.
Alzheimer's disease begins with memory loss. The patient forgets the information he has just received, new facts. Mild cognitive impairment occurs. Personal changes remain invisible for a long time.
2) Disorders of speech, movement, reading and writing
The next symptom of the early stage of development of Pick's disease is speech impairment:
- Decreased speech activity;
- Poor vocabulary;
- Stereotypy.
In Alzheimer's disease, these functions may decline more slowly and less severely. Slowing of speech and limited vocabulary become noticeable. Patients forget words, but replace them with similar ones in meaning. Only the late stage of the disease is characterized by aphasia.
But reading and writing in Alzheimer's disease begin to suffer at the initial stage of the disease. With Pick's disease, there may be no obvious manifestation at all, or a similar symptom may be recorded at the final stage.
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by a disorder of complex motor actions - apraxia, which manifests itself only slightly in Pick's disease.
3) Mental disorders
In rare cases, with Pick's disease, mental disorders occur, such as rudimentary hallucinatory episodes, short periods of increased arousal, and delusional statements. In late stages of Alzheimer's disease, delusions of harm, false identification syndrome, occur. In 30 percent of patients, these syndromes manifest themselves in the middle stage of the disease.
4) Additional research data
Despite the differences above, differentiating the symptoms of these two diseases can be difficult. Additional studies in Pick's disease, such as MRI and CT, show symmetrical atrophy of the temporal or frontal regions of the brain. There are cases when changes are detected both there and there. In Alzheimer's disease, changes do not appear in the early stages, but in later stages diffuse atrophy of the cerebral cortex may be observed.
Read material on the topic: Caring for the elderly
Symptoms and signs
Manifestations of Pick's disease can be recognized by mandatory and additional signs (symptoms).
Mandatory ones include:
- inconspicuous, not bright initial stage and gradual progression of the disease (increased pathological manifestations);
- rapid manifestation of difficulties in observing socially acceptable behavior (social norms cease to be understood and recognized);
- difficulties in establishing control over one’s own behavior already in the initial stages of the disease;
- emotional flattening - emotions lose both in magnitude and in the brightness of manifestations already in the early stages of the disease;
- early reduction of criticism.
Additional symptoms of PD allow us to identify details of its clinical manifestation and are divided into several groups:
- Behavioral: loss of ability to maintain hygiene, sloppiness, inertia of thought processes, difficulty concentrating, stereotyped and impulsive actions.
- Speech: decreased verbal productivity (speech is not spontaneous, comes down to answers to questions asked, forced muteness); stereotypy and repetition in the construction of statements, echolalia and perseveration.
- Physical and neurological: reflexes appear primitively (grasping, oral automatism, spontaneous falls, etc.); spontaneous urination (incontinence) is observed; decreased muscle tone, lethargy and trembling; low blood pressure.
How does dementia manifest in Pick's disease?
Changes in the structure of the brain that are negative, progressive and irreversible are dementia. It leads to loss of memory, intelligence, ability to learn and spatial orientation, and loss of existing skills.
The listed signs develop over about six months, while the person’s consciousness initially remains completely clear. In rare cases, a more dramatic change in personality and character occurs.
Unfavorable life factors provoke the occurrence of dementia:
- Traumatic brain injury, bruise.
- Long-term use of the drug without medical supervision.
- Metabolic disorders in the body due to diseases of the internal organs, which are progressive in nature.
- Chronic lack of vitamin B in the body.
- Tumors.
- Infections.
- Alcoholism.
Pick's disease: 3 stages
Pick's disease has three stages of development, which gradually transform into one another. It is extremely rare for a person with this disease to live more than ten years.
First stage of the disease
At the first stage, the character becomes selfish, unmotivated actions appear, which are explained by the sick person by the fact that it is impossible not to carry them out.
- Speech changes: speech slows down, there is repeated repetition of the same words, standard expressions and jokes.
- Self-criticism decreases.
- There is a slowdown, less often hyperkinesis of actions.
- There is a loss of former moral principles - instinctive emancipation: a person can relieve himself in public, for example. Sexual promiscuity is noted.
- Psycho-emotional changes occur occasionally: hallucinations, delusions of inferiority, jealousy.
Second stage
The transition of all symptoms to a focal form and progression occurs in the next stage of Pick's disease.
The following symptoms are more pronounced:
- State of amnesia.
- Agnosia is a violation of visual, auditory, and tactile functions.
- Aphasia is a speech pathology, when the speech reserve decreases, the patient loses the ability to express his thoughts. Understanding the speech of others also becomes difficult; the patient cannot grasp its meaning.
- Apraxia – the ability to perform actions is impaired or the sequence of execution changes. So, having received candy, a person can unwrap it, throw out the sweet itself, and put the candy wrapper in his mouth.
- Acalculia is a violation of the ability to perform computational operations, even the simplest.
Third stage
The third stage leads to irreversible profound dementia. The patient needs constant monitoring and psychological assistance.
Read material on the topic: Senile insanity: signs, treatment and patient care
Our boarding houses
Golitsyno
Minsky
At the last stage of Pick's disease, any medical intervention loses its meaning. The only thing that remains is to try to make the patient’s life as comfortable and convenient as possible. That is why doctors recommend that family and friends resort to professional nursing care.
Pick's disease: photo
Below is a photo essay of ten years in the life of Australian Jackie Heath, who was diagnosed with Pick's disease in 2007. Photos and story provided by the woman's son.
The first photo is from 2005. The first changes were misdiagnosed as consequences of a menopausal condition.
According to Jack's recollections, his parents then lived in Canada, and he and his sister lived in Australia. One day my father called and said a phrase that shocked the young people: that my mother would die soon.
Second photo. On the beach, approximately 2010 .
Jack did not believe what was said, his sister cried, his mother reassured him that everything was God’s will and everything would be fine. Soon my mother began to become paranoid, she began to forget names, and lost the ability to eat on her own.
Third photo. Walk by the sea.
Mom loved to ride a motorcycle with her father, but in 2011, due to paranoia, they abandoned such trips, since one of them almost led to a serious accident. The woman could wander aimlessly around the house all day, and after six months she stopped getting up. At the same time, she stopped eating solid food and switched to baby food. Development turned backwards - back to helpless childhood.
Fourth photo.
By then the woman had stopped talking. Her father looked after her around the clock, and the state helped a lot. Jack visits his parents every month, talking about how difficult it is for his pregnant sister without his mother's advice during this time.
Fifth photo. Birth of first-born grandson.
A long-awaited event for the whole family, especially mom. The father heroically endures life's hardships, providing round-the-clock care for his wife and telling her to do everything possible and accept life as it was given by God.
Sixth photo. Despite Pick's illness, Jack's parents maintained a social circle and even went out to parties. This at least somehow diversified life.
Jack says that the common misfortune has brought the family together very much. Even as children, they were not as close to their father as they are now. Sister Zoë was very upset that the baby would not know what his grandmother was like and wanted to tell him a lot about her.
Seventh photo. With the baby, who at that time was in his second year. The child is very wary; he understands that the grandmother is not like everyone else.
Everyone regrets that the baby will never know what his grandmother was like before. Everyone dreams that Jackie will regain consciousness at least for a moment, to tell her about his love, about what is happening in the family at the present time.
Eighth photo. Jackie has lost a lot of weight and walks very little.
The entire life of the family over the past seven years has turned into a protracted farewell. Everyone watches as a loved one loses life skills one by one. There is no opportunity to talk, discuss what is happening. The woman has long lost the ability to communicate meaningfully.
Ninth photo. Another walk along the beach. Jackie is 58 years old, she hardly opens her eyes, and when she does, she stares blankly into the unknown.
Everyone is already tired. Thoughts come that it would be better if everything happened faster.
Tenth photo. It may be terrible, but everyone is praying for a speedy end and peace for both Jackie and the family.
Eleventh photo. Sometimes Jackie smiles, laughs for some reason.
Jack says that in this whole terrible story there is still a positive moment: my mother’s illness brought the family together very much and gave them the opportunity to take care of her the way she used to take care of them.
Pick's disease: causes
Experts cannot say unequivocally about the causes of Pick’s disease. Only the most likely factors provoking the development of the disease are noted:
- Heredity. It has been noted that the symptoms of the disease are most likely to appear in those people who have ever had relatives with similar health conditions.
- Severe traumatic brain injuries, which subsequently led to the death of neurons.
- Poisoning with salts of heavy metals, chemicals, alcohol. The likelihood of brain cell death increases with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors on the body. An example is the state of anesthesia used repeatedly.
- Severe mental disorders that were suffered by a person in previous periods of life.
Pick's disease: symptoms
An examination of patients with Pick's disease made it possible to identify several of the most characteristic symptoms: difficulty speaking and writing, changes in behavior.
Relatives talk about personality changes already at the initial stages of the disease.
The characteristic features for such patients are:
- With atrophic changes in the frontal parts of the brain, sudden mood swings occur, irresponsibility to household and work responsibilities, absent-mindedness, and sexual promiscuity are characteristic.
- With atrophy of the temporal regions, a state opposite to the first occurs: suspiciousness, a feeling of uselessness, loss, inferiority.
All those suffering from Pick's disease experience speech changes, such as simplification, reduction of active vocabulary, repeated repetition of words, use of simple speech patterns, and distortion of the grammatical structure of sentences.
Patients cease to understand speech addressed to them, lose self-care skills and personal hygiene, and periodically they experience sudden outbursts of agitation.
The middle stage of development of Pick's disease is characterized by obesity and the development of cachexia. Strong changes in personal qualities occur. The patient needs constant supervision.
As a result of the disease, a highly educated person with a rich vocabulary, who takes care of his appearance, in a few months can become a sloppy, tactless creature, unable to speak coherently.
Read material on the topic: Secrets of longevity - how to live healthy to 100 years
Pick's disease: diagnosis
The patient undergoes the first examination by a psychiatrist, who draws conclusions about the extent to which the neuropsychic sphere is impaired. A doctor's examination reveals speech disorders, inappropriate actions, and behavioral disorders. To determine changes occurring in the brain, additional examinations are carried out:
- Computed tomography, abbreviated CT. The result is a layer-by-layer study of the brain, which allows us to draw a conclusion about the size of the lesions in its lobes and the degree of progression of the disease.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can perform the same type of diagnosis as CT.
- Electroencephalography is based on the equipment capturing electrical impulses that occur in the brain during the transmission of signals. Data is displayed on paper in the form of a large number of curved lines. In Pick's disease, the cerebral cortex becomes thinner and, as a result, less sensitive, conducting fewer impulses, which is expressed on paper.
In case of Pick's disease, it is necessary to differentiate symptoms from Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's syndrome, brain cancer, mental disorders, and diffuse atherosclerosis.
How to help a patient and what are his chances
To date, there is no general method for treating Pick's disease. All a doctor can do is prescribe medication to delay progressive changes and improve a person’s condition.
However, modern medicine has discovered five areas of treatment that can achieve the greatest effect in slowing the progression of dementia. These include:
- Replacement therapy - acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, antidepressants. The action of these drugs is aimed at replenishing the deficiency in the human brain of certain substances that are no longer produced in the required quantities due to atrophy.
- Neuroprotectors – neurotrophic substances, calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, growth factors. These drugs help stimulate brain cells. As a result, metabolic processes are significantly improved, and this helps slow down the death of neurons and atrophy of the cerebral cortex.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are also used .
- Pharmacological correction of existing mental disorders in humans. In this case, antidepressants and drugs that suppress aggression are prescribed.
- Psychological professional assistance . This therapy includes various trainings. This technique is very effective in slowing the progression of the disease.
Psychological help from relatives plays an important role in therapy.
It is very dangerous to leave patients alone, because a person in the later stages of the disease is completely unable to account for his actions. There are cases when patients started fires, left gas open, and committed other destructive actions. Thus, it becomes clear that they simply begin to pose a danger to others and to themselves in the first place.
When this disease is diagnosed, the prognosis for life is unfavorable. A person becomes helpless, incapable of self-care, so he needs round-the-clock supervision, he loses social and communication skills, becoming asocial.
Within five years, the disease leads to moral personal decay and a state of complete decline in psychophysical activity sets in.