What is this pathology?
Let's start with the definition of dizziness. This condition is commonly called vertigo. The feeling of involuntary rotation or movement of one’s own body in space or objects relative to one’s body is considered dizziness. At the same time, a person loses stability, balance, and a feeling appears as if the earth is disappearing from under his feet.
Dizziness is classified into the following groups:
- Central. The cause is brain disease or injury.
- Peripheral. The cause is damage to the vestibular nerve or inner ear.
- Systemic. The cause is a malfunction in any of the systems: visual, vestibular, muscular.
- Not systemic. The causes are neurogenic.
Psychogenic dizziness should be classified in the fourth group. Appears as a result of mental and neurotic disorders. This is especially observed during periods of strong excitement or after it. A synonym in medicine is considered to be “Phobic postural dizziness,” that is, depending on the vertical position of the body.
Diagnostics
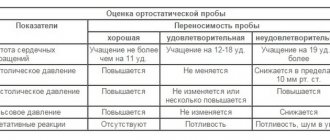
Diagnosis consists of excluding the most likely causes of dizziness, based on the complaints of a particular patient. It is also important to identify various traumatic factors that could lead to this condition. To exclude various organic (direct organ suffering) causes of dizziness, neurological and otorhinolaryngological examinations are used, with special attention paid to symptoms such as the Romberg test, finger-nose and other coordinating tests, namely the process of their implementation, and, if necessary, neuroimaging (MRI, MSCT brain and temporal bone), functional studies (EEG, REG, ultrasound, etc.). It is important to conduct a thorough interview with the patient and test him using psycho-emotional scales (HADS and others).
Features of the pathology
Psychogenic dizziness has its own characteristics:
- It has no system.
- Random and abnormal deviations may occur within a few seconds.
- Feeling of instability for 2-3 seconds.
- It occurs unexpectedly, but provoking factors may be present.
- All complaints are related to dizziness that occurs while walking or standing.
- May be combined with other types of disorders. Psychogenic dizziness will be secondary.
- There are no clinical or paraclinical signs of organic pathology.
- Feelings of anxiety or anxiety-depressive conditions accompany dizziness, but these factors may be absent.
Bibliography
- Zamergrad M.V., Parfenov V.A., Yakhno N.N. and others. Diagnosis of systemic dizziness in outpatient practice. // Neurological journal. 2014. 19. (2). 23-29.
- Levin O.S., Shtulman D.R. Neurology: a reference book for a practitioner. Moscow: Medpress-inform, 2013. 1016 p.
- Parfenov V.A., Zamergrad M.V., Melnikov O.A. Dizziness: diagnosis and treatment, common diagnostic errors: Textbook. // Moscow: MIA, 2009. 152 p.
- Romanova M.V., Isakova E.V., Kotov S.V. Complex treatment of patients with postural phobic dizziness. // Almanac of Clinical Medicine. —2013. (28). 3-8.
- Brandt T. Phobic postural vertigo. // Neurology. 1996. (6). 1515-1519.
- Bronstein AM Gresty MA et al. Phobic postural vertigo // Neurology. 1997. (46). P. 1480–1481.
Causes of psychogenic dizziness
As a rule, a greater likelihood of psychogenic dizziness is observed in people predisposed to panic attacks. Women are most prone to this. Also, a feeling of fear, anxious fears can be attributed to the causes of such dizziness.
Let's highlight a few more reasons:
- Stressful situations.
- Overwork at work.
- Lack of sleep, insomnia.
- Excessive mental stress.
- Sudden change of position.
- Climate change.
- Hyperventilation syndrome.
- High blood pressure.
- Neuritis.
- Menopause in women.
- Motion sickness in transport, when riding on a swing.
- Altitude intolerance.
As a rule, all these situations are associated with worries or anxiety. There is also an obvious fear of losing control over the position of the body, falling and possibly getting injured.
Symptoms
Psychogenic dizziness includes a wide and varied spectrum of symptoms and signs. The symptoms of the phenomenon are not tied to time, any human action, blood pressure or other manifestations. The disease does not have a specific time frame for the duration of symptoms.
Specific signs of psychogenic dizziness:
- sensations arise or intensify against the background of emotional excitement, increasing anxiety, tension or constriction;
- no systematicity was recorded;
- absence of noise in the head and ears.
Associated symptoms that may appear when the disease manifests itself:
- increased sweating;
- nystagmus - involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes of high frequency;
- rapid breathing due to a feeling of lack of oxygen;
- panic attacks;
- sleep disorders - insomnia, nightmares, intermittent sleep, difficulty falling asleep;
- feeling of a “lump in the throat” - inability to swallow;
- increased heart rate;
- irritable bowel;
- "restless" bladder;
- general weakness;
- increased fatigue.
The onset of psychogenic dizziness is often preceded by a vasomotor disorder, which manifests itself in unpleasant sensations in the head - pulsation, hot flashes, heaviness, etc.
Signs and symptoms of pathology
Dizziness of a psychogenic nature at the developmental stage has several signs:
- Performance decreases and fatigue increases.
- Mood worsens, irritability increases.
- Appetite either disappears or increases sharply.
- Sexual activity may decrease or increase sharply.
For those who have experienced psychogenic dizziness, patients describe the symptoms as follows:
- Tinnitus appears, but hearing is not lost.
- Fog in the head.
- There is a feeling of instability, but this does not affect the gait.
- Attention is completely focused on the noise and dizziness.
- There is increased anxiety.
- There is a feeling of lack of air.
- Cold sweat.
- Thinking is unclear, confused.
These symptoms are also typical for panic attacks. You can also add a few characteristic symptoms:
- Cardiopalmus.
- Possible trembling of limbs, chills.
- "Formication.
- Irrational fear of impending disaster.
- "Cotton" legs.
This condition can also be caused by memories of a traumatic situation.
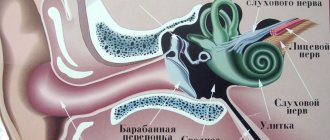
Psychogenic dizziness is not caused by a disorder of the vestibular system, although the symptoms are very similar.
It is worth noting that manifestations of these disorders can be called psychogenic only if the patient recognizes the connection with the cause.
Causes
The cause of the development of the postural phobic form may be an episode of idiopathic vestibular vertigo, which is accompanied by loss of the ability to navigate in space, restlessness, a feeling of panic, anxiety, autonomic disorders (increased sweating, rapid heartbeat, rapid, shallow breathing). Borderline personality disorders lead to the development of a condition known as mental maladjustment.
This condition reflects a dysfunction in the individual’s adaptation to changing environmental conditions, which negatively affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Pathogenesis involves disorganization of systems that regulate adaptive activity. Not every event becomes a factor provoking the development of an episode of impaired motor coordination. Perceptual stimuli that are often associated with an episode of motor incoordination include:
- Stay on the bridge.
- Climbing stairs.
- Being within a spacious, empty space.
Individual situations are identified that serve as factors provoking the episode for the patient. Postural phobic disorder develops as a consequence of excessive demands on oneself, increased anxiety, and strict, continuous self-control.
False symptoms of psychogenic dizziness
There are symptoms that patients mistakenly confuse with dizziness.
Here are some of them:
- Flickering of objects in the eyes.
- Double vision.
- The appearance of a “mesh” before the eyes.
- The appearance of nausea.
- Pre-fainting state.
- Feeling unsteady.
- Feeling of "emptiness" in the head.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you have a question about how to treat psychogenic dizziness, you need to contact a therapist, who will then refer you to specialized specialists:
- Otorhinolaryngologist.
- Neuropathologist.
- Cardiologist.
- To a psychiatrist.
To find out the reasons, specialists may prescribe the following types of examination:
- Computed tomography of the brain. Allows you to recognize abnormalities in the structure of the brain.
- Ultrasound of large arteries and vessels that supply blood to the brain.
- X-ray examination of the skull and cervical spine.
- General and biochemical blood test. Determination of blood glucose levels.
- Balance tests are required.
- Audiography.
- Definition of nystagmus.
At the initial stage of diagnosing psychogenic dizziness, the doctor must exclude all possible causes that are associated with loss of balance.
These include:
- Damage to the vestibular apparatus.
- Diseases in which one of the symptoms is loss of consciousness, fainting.
- Diseases of a neurological nature, which are accompanied by impaired walking and balance.
The above examinations will help find the true cause.
At the second stage, neurotic disorders that arise as a result of stress are diagnosed. As we found out earlier, the most common cause is panic attacks and anxiety-depressive disorder. Let's look at how to get rid of psychogenic dizziness below.
Psychosomatics of dizziness according to V. Sinelnikov
According to V. Sinelnikov, the causes of dizziness are in accumulated problems, the inability to solve them, caused by “flying thoughts,” i.e., the inability to concentrate.
Solution: Discipline, focusing on a specific problem until it is solved. Determining your life goal.
When physical problems arise, a person’s greatest desire is to get rid of them. However, when looking at difficulties from a broader perspective, new space opens up. It’s not just about getting rid of a symptom, but also about understanding it, finding out why it appears, what it means. The body is perceived as a guide. And illness often arises in a situation when you need to stop, rethink the current situation, change it or your views on it, and move on. The healing journey can be an adventurous path of self-discovery and self-development. Illness can lead to perceptions of the body, mind and soul, context and meaning as a whole.
Treatment methods for psychogenic dizziness
For a disease such as psychogenic dizziness, treatment includes non-drug and medicinal methods.
Non-drug treatment is a priority. It includes:
- Psychotherapy.
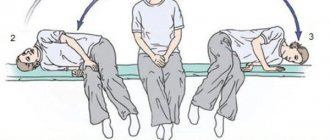
- Gymnastic exercises to improve the vestibular apparatus.
- Breathing exercises. Helps cope with increased vascular tone.
Treatment of psychogenic dizziness consists of changing the internal attitude towards traumatic situations so that dizziness and other disturbing symptoms do not occur. This is very difficult psychologically, although it costs nothing financially. The most difficult thing is to work on yourself, on your fears and beliefs. Treatment comes down to normalizing the psycho-emotional state.
It is also necessary to reconsider the patient's diet. Vitamins of groups A and C are necessary. They are found in the following foods, fruits and vegetables:
- Lemon.
- Orange.
- Beef liver.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Fish fat.
- Carrot.
- Persimmon.
- Strawberry.
- Sprouted grain crops.
- Rose hip.
- Black currant.
It is necessary to follow the correct diet, which should contain all the necessary microelements and vitamins for the body. It is advisable to eat at the same time, smaller portions are better, but more often.
Drug treatment
Medicines used to treat psychogenic dizziness:
- Antidepressants: Fevarin, Paxil.
- Anxiolytics: Phenazepam, Clonazepam, Atarax.
- Neuroleptics: Tiapride, Sulpirida.
- Nootropic drugs.
The drug "Betaserc" has proven itself to be excellent in the treatment of a disease such as psychogenic dizziness. Reviews about this drug are only good. Patients note an improvement in their condition. The dizziness goes away and there is no tinnitus. But the drug is recommended to be taken in long courses for a lasting effect and as an additional therapy.
Folk remedies
As we know, the priority is therapy without the use of drugs, including such diseases as psychogenic dizziness. Treatment with folk remedies in such cases has always been popular. Let's name some of them.
- Aromatherapy. Juniper and orange oils are useful.
- Oregano infusion. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water into 2 tablespoons of herbs. Let it brew.
- Lavender infusion. 1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water.
- Ginger tea.
- Eat pomegranate more often.
It is recommended to drink infusions half an hour before meals and throughout the day. Folk remedies do not give quick results, so therapy must be long-term.
How to help
If an attack of dizziness occurs at home, you must:
- Lie down so that your head, neck and shoulders are on the pillow.
- Avoid turning your head.
- Release clothing pressure.
- It is necessary to ensure good air access.
- You can apply a cold towel moistened with a light vinegar solution to your forehead.
If you feel dizzy on the street:
- You need to calm down and not panic.
- Sit down and focus your gaze, but do not close your eyes.
- Do not move or turn your head.
- If at the same time there is severe pain in the chest, abdomen, or numbness in the arms and legs, or speech impairment, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
Prevention of psychogenic dizziness
In order to reduce the amount of dizziness, you must not only try to remain calm in all situations and learn to control yourself, but also follow some recommendations:
- Move more and do exercises, especially when working sedentarily.
- Observe the work and rest schedule.
- Don't overwork, get enough sleep.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Do not make sudden movements of the head and neck, and do not suddenly change the position of the body.
- Relax more in the fresh air.
- Limit the consumption of salt, strong tea and coffee.
- Learn relaxation techniques.
If you experience frequent attacks of dizziness, you should consult a doctor. If serious pathologies are detected in the early stages, therapy will be more effective. Much more often, dizziness is associated with overwork and improper work and rest schedule, but it is still better to play it safe and visit a specialist.
Prevention
Dizziness from stress can be prevented and even cured if you take simple preventive measures:
- Vestibular gymnastics. Improves a person’s ability to maintain balance and navigate the surrounding space, and helps control attacks of vertigo.
- Active and healthy lifestyle. Mobility is a great workout for the vestibular system.
- Proper nutrition and special diet.
- Compliance with the work and rest regime. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day, as lack of sleep can cause attacks of vertigo.
- Minimizing stress in order to eliminate neurosis, neurasthenia and depressive disorder.
Visits: 16,783