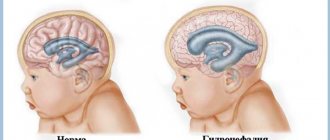
The present time is referred to as the age of brain research. One of the most interesting topics in scientific research on this organ has been the ability of the brain to change its structural and functional properties in response to a person's experiences throughout life. For most of history, neuroscientists believed that the basic structure of the brain was predetermined before birth, and the only changes that could occur were degenerative, the result of disease, injury (concussions, TBI). Modern scientists have directed research towards brain restoration. What conclusions did they come to? Is the brain recovering or not?
Research results
Two major discoveries were made by scientists involved in neural networks and human brain research. A study published in Cell Stem Cell reports that Japanese doctors have begun culturing human brains. The journal Science presented material on how chemical destruction was prevented by stimulating the regeneration (renewal) of the brain and spinal neural network.
A neuron is a structural unit of nervous tissue that, under a microscope, resembles a body with tentacles. The task of a neuron is to receive and process information.
The Japanese started from brain cells, which, through appropriate cultivation, were multiplied tenfold and enriched in accordance with the structure of the brain of a human embryo. It was also discovered that in the resulting particles of brain matter, the size of which is 1-2 mm, neural activity, measured in electromagnetic impulses, spontaneously arises. Scientists from the city of Kobe believe that in the future it will be possible to create structures of brain tissue that can be implanted in place of parts damaged by disease (ischemic stroke, multiple sclerosis, etc.) or injury.
Brain neurons are not able to regenerate like their counterparts in nerve endings. Another way to save damaged parts of the brain or spinal cord (damage often leads to serious consequences, including paralysis, coma) is to activate the possibility of regeneration in both main organs of the nervous system. In experiments on mice, a team led by Dr. Che Qiang at Harvard Medical School in Boston was able to answer the question of whether brain cells repair themselves by chemically influencing the process. In mice, scientists used genetic engineering to stimulate the release of a substance called mTOR, which responds to neuronal regeneration. It is present in the newborn, but is destroyed in the adult, especially after injury. Thanks to this process, scientists were able to restore almost half of the damaged optic nerve in a short time (2 weeks). Even the formation of new axons has been recorded.
Che Qian concluded: “We knew that after development ends, networks stop growing due to genetic mechanisms. We believe that one of these mechanisms may also restore regeneration and stop death after injury."
Advances in emergency medicine have ensured that more brain-injured patients survive. Today it is known that the adult brain is capable of rearranging its functional connections, creating new ones, and changing physiological parameters. This phenomenon is called neuroplasticity; it has become the basis for the treatment of central nervous system diseases of various origins.
Fewer cells die and more form in autistic people. It can be said that autism, paradoxically, is a disorder that has beneficial effects on the brain.
Hippocampus and brain recovery
According to recent data, the human brain contains about 85 billion nerve cells (neurons). It is known that throughout life there is a gradual loss of these cells (they begin to die around the age of 30).
One of the first studies to generate interest in brain plasticity among lay people was conducted by Eleanor Maguire of University College London. She found that London taxi drivers have much more developed hippocampi than bus drivers. The hippocampus is the part of the brain responsible, among other things, for the perception of space. Given the fact that taxi drivers must remember many street names, their placement and connections, it has been suggested that this change is caused by training in spatial orientation, which bus drivers lack.
The problem with this study is that it does not distinguish between innate and acquired function. In this context, interesting results were provided by studies of violinists, which established that these musicians have a much larger surface area of the motor cortex related to the fingers of the left hand. This corresponds to the fact that when playing the violin, each finger of the left hand must make an independent movement. In this case, on the right hand, all fingers work together. The objection to the possibility of a genetic predisposition is countered by the fact that the difference between the organization of the left and right hemispheres is directly proportional to the age at which musicians began to play the violin.
Reorganization of the cerebral cortex has also been observed in people with congenital visual or auditory defects. According to the “use it or loose it” principle, the unused cerebral cortex can be used by another function. Areas originally dedicated to processing visual or auditory stimuli are deprived of them, and their space is used for other functions, such as tactile. Reorganization is the result of the growth of long processes of neurons, axons. After a head injury that damages the brain, neural connections can be restored or replaced with new connections that compensate for the lost function in another part of the brain.
One of the great surprises of recent times is the discovery that the adult brain can, in some areas, create entirely new neurons from stem cells, a process influenced by human experience.
How to restore brain cells
Dying occurs due to weakening of the connection between them (thinning of the dendrites). In order to stop this process, doctors recommend the following:
- Healthy food. It is necessary to enrich your diet with vitamins and beneficial microelements that improve reaction and concentration;
- actively engage in sports. Light physical exercise helps improve blood circulation in the body, improve coordination of movements and activate areas of the brain;
- do brain exercises. In this case, it is recommended to solve crossword puzzles more often, solve puzzles or play games that help train nerve cells (chess, cards, etc.);
- load the brain more with new information;
- avoid stress and nervous disorders.
It is imperative to ensure that periods of rest and activity alternate correctly (sleep at least 8-9 hours) and always have a positive attitude.
Neurogenesis
Information not known to the general public is that the brain creates new cells throughout life. This phenomenon is called neurogenesis.
The human brain is made up of many parts (but not all of them undergo cellular renewal). Neurogenesis occurs in the area responsible for the sense of smell and in the hippocampus, which plays an important role in memory quality.
Experts have also discovered that damaged brains also produce new cells. Evidence of higher neurogenesis during illness was presented by New Zealand's University of Auckland, which studied people with Huntington's disease, in which a person's mental abilities decrease and uncoordinated movements appear. The creation of new neurons was most intense in the most affected tissues. Unfortunately, this is not enough to suppress the disease. Identifying the conditions under which this process occurs and stimulating it could lead to treatments for Huntington's or Parkinson's disease by transplanting stem cells into the affected areas of the brain.
Medical science is taking its first steps in studying brain neuroplasticity. The next step is a precise description of the conditions under which its changes occur, determining the specific impact on individual functions in human life. Understanding and using knowledge of neuroplasticity also requires analysis of genes associated with the growth of axons or neurons from stem cells.
Some useful information about neurons
Neurons, unlike all other cells in our body, “do not know how” to divide, so until recently scientists were convinced that a person lives his entire life with the limited supply of nerve cells that he received at birth. The results of numerous modern studies have shown that this statement is not true, since neurons are still created throughout our lives. This happens thanks to stem cells, which have the ability to transform into cells of almost any type.
Our brain has its own supply of stem cells. Scientists cannot yet determine the exact number of departments involved in the formation of new nerve cells. What the scientific community knows is that new neurons are formed in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory and emotion, and a thin layer of cells located along the ventricles of the brain (subventicular zone).
Many newly formed neurons die almost immediately due to the active work of neurotransmitters, the negative influence of the microenvironment, certain proteins and other chemistry occurring in our brain.
In order for a newly formed nerve cell to continue to exist, it needs to form a neural connection (synapse) with other nerve cells. Since the brain does not need lonely floating neurons at all, it simply destroys them, because they do not bring it any benefit and will not be able to bring it in the future. The same neurons that were able to establish connections with other nerve cells are successfully integrated into the structure of our brain.
Every day, about 700–800 neurons can be integrated into the structure of the brain, which managed to survive and form new neural connections.
Brain-programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is a completely normal process that should not be feared. With the help of apoptosis, the brain restores order and gets rid of unnecessary neurons.
The average adult brain consists of approximately 85–88 million nerve cells.
The brain of a newborn contains many more neurons, but by the end of the first year of life their number is almost halved. Psychophysiologist and employee of the Psychological Institute of the Russian Academy of Education Ilya Zakharov explains this by the fact that the human brain develops most actively in the first three years after birth.
Why is this happening? The fact is that it is during this period of time that the child actively explores the world around him: he constantly touches something new, smells it, sees it, tastes it or touches it, etc. All new knowledge is recorded in the baby’s brain in the form of new neural connections, thanks to which all formed and already consolidated skills, all acquired emotional and intellectual experience are preserved.
Although the human brain develops in this way throughout life, it makes its “main breakthrough” in early childhood.
The importance of neurogenesis
Recent estimates indicate that the hippocampus produces about 700 new brain cells every day. At first glance, this number does not seem large, but the creation of each new neuron is very important, especially for the psychological state of a person. If the formation of new cells stops, depression and psychosis begin to appear. Restoration of brain neurons is important for learning, memory, intelligence (study of certain places, orientation in space, quality of memories).
Recent scientific research has shown that it is possible to improve the production of new brain cells on your own, i.e. at home. What types of activities have a positive effect on the formation of neurons?
Neuron production increases:
- education;
- sex;
- training of cognitive functions;
- mnemonics;
- physical activity (significant help);
- nutrition (regular meals, longer pauses between meals)
- vitamin P (flavonoids);
- omega-3 (also a good antidepressant).
Neuron production decreases:
- stress;
- depression;
- lack of sleep;
- diets rich in saturated fats;
- anesthesia used during surgery;
- alcohol;
- drugs (especially Amphetamine);
- smoking;
- age (with age, neurogenesis continues, but slows down).
Neurons can die in a number of diseases:
- epilepsy – cell death occurs during an attack;
- cervical osteochondrosis – neurons die due to poor circulation;
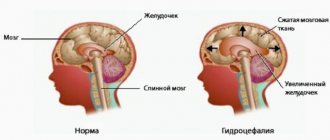
- hydrocephalus;
- encephalopathy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- Parkinson's disease is a disease characterized by impaired mobility of the legs, arms, and cerebellar signs (due to damage to the amygdala);
- Alzheimer's disease is a disease that leads to dementia, a disorder of speech functions (due to damage to speech receptors).
Neurons may temporarily stop renewing when you take certain cancer drugs. Therefore, after treating cancer with pharmaceutical drugs, people suffer from depression. After restoration of neurogenesis, depression disappears.
It is safe to say that the formation of new brain cells occurs naturally in healthy people. However, whether the process will speed up or slow down largely depends on the person himself.
Gage and Erickson: Brain nerve cells appear in the hippocampus
Research by Fred Gage from the Salk Institute for Biological Research (California) and Peter Erickson from Sahlgrenska University (Sweden) confirmed the possibility of new nerve cells appearing in the hippocampus of adult primates, including humans.
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system of the brain. Participates in the mechanisms of emotion formation, memory consolidation (that is, the transition of short-term memory to long-term memory)
Scientists removed hippocampal tissue from five patients who died of cancer. At one time, these patients were injected with BrdU to find cancer cells. Gage and Erickson found a large number of neurons labeled with BrdU in the hippocampal tissue in all the deceased. It is important that the age of these people before death was between 57-72 years. This proves not only that nerve cells are restored, but also that they are formed in the hippocampus throughout a person's life.
What supports the creation of new neurons?
In addition to the ability to renew itself, the brain is constantly changing, adapting to the external environment, optimizing its activity in accordance with human living conditions. In case of injury, severe intoxication with poisons, medications, or micro-stroke, circulatory disturbance occurs (blood flow to the brain decreases), hypoxia (oxygen starvation) develops, and functions from the affected areas can be transferred to undamaged segments, from one hemisphere to the other. This way a person is able to learn new things and create new habits at any age.
The brain is affected by everyday life, ways of acting, and constant habits. To maximize the manifestation of his wonderful abilities, activity is required, stimulating brain activity in all possible ways.
Electrical stimulation
Targeted electrical stimulation supports the cooperation of neurons in a specific center. This is a non-invasive, drug-free therapy performed by passing a low current through electrodes placed on the scalp. Electrical stimulation can restore brain activity and restore neurons, selectively activating protective mechanisms in the brain, causing an increased release of endorphins and serotonin.
Physical activity
Physical activity and the process of neurogenesis are closely related. As heart rate and vascular blood flow increase during exercise, the levels of factors that stimulate neurogenesis increase. Physical activity also helps release endorphins, reducing stress hormones (especially cortisol). At the same time, testosterone levels increase, which also promotes neurogenesis.
To prevent the negative effects of aging on both the body and brain, physical activity is an excellent choice. It combines both of these goals. You don't have to lift dumbbells or do exercises at the fitness center. Regular vigorous walking, swimming, dancing, cycling is enough. These actions strengthen weakened muscles, improve blood circulation and mental abilities.
Any action aimed at reducing tension and stress promotes neurogenesis. Choose an activity that suits your preferences.
Freshness of mind
There are many ways to regenerate neurons while maintaining a fresh, sharp mind. Various actions can help with this:
- reading - read every day; reading makes you think, seek connections, supports the imagination, arouses interest in everything, including other possible types of mental activity;
- learning or developing knowledge of a foreign language;
- playing a musical instrument, listening to music, singing;
- critical perception of reality, study and search for truth;
- openness to everything new, sensitivity to the environment, communication with people, travel, discovery of nature and the world, new interests and hobbies.
An underrated yet effective method of supporting brain activity is handwriting. It supports memory, develops imagination, activates brain centers, coordinating the movement of muscles involved in the writing process (up to 500). Another advantage of handwriting is maintaining elasticity, mobility of joints, hand muscles, and coordination of fine motor skills.
Nutrition
In connection with the topic at hand, it must be said that the human brain is 70% fat. Fat is a part of every cell in the body, incl. brain tissue, where in the form of myelin it is the insulation surrounding nerve endings. Brain cells create it from sugar, i.e. do not wait for fat to come from food. But it is important to eat healthy fats that do not contribute to the occurrence and development of inflammation. Health benefits come primarily from fats containing omega-3.
Many people, hearing the word “fat,” involuntarily shudder. In an attempt to maintain a slim waist, they buy low-fat products. These foods are unhealthy, often even harmful, because fat is replaced with sugar or other ingredients.
Eliminating fat from your diet is a mistake. Its restriction must be strictly selective. Hydrogenated fats found in margarines and industrially processed foods are harmful to the body. Unsaturated fatty acids, on the contrary, are beneficial. Without fat, the body is unable to absorb vitamins A, D, E, K. They are soluble only in fat, which are of great importance for brain activity. But you also need saturated fats found in animal sources (eggs, butter, cheese).
Low-calorie nutrition is good, but it should be varied and balanced. It is known that the brain consumes a lot of energy. Provide it in the morning. Oatmeal with yogurt and a spoon of honey is an ideal breakfast option.
How to restore the brain with the help of products and folk remedies:
- Turmeric. Curcumin affects neurogenesis and increases the expression of the neuropathic factor, which is necessary for a number of neurological functions.
- Blueberry. The flavonoids contained in blueberries stimulate the growth of new neurons and improve the recognition functions of the brain.
- Green tea. This drink contains EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate), which promotes the growth of new brain neurons.
- Brahmi. Clinical studies examining the effects of the brahmi plant (bacopa monnieri) on brain function showed that after 12 weeks of use, volunteers significantly improved verbal learning, memory, and the speed of processing received information.
Three C's:
- Sun. Healthy exposure to sunlight on the body is 10-15 minutes a day. This promotes the formation of vitamin D, affects the secretion of serotonin, the growth of brain factors that directly affect neurogenesis.
- Dream. Its abundance or deficiency significantly affects brain activity. Lack of sleep causes inhibition of neurogenesis in the hippocampus, disrupts the balance of hormones, and reduces the degree of mental activity.
- Sex. Sexual activity increases the secretion of happiness hormones, endorphins, reduces anxiety, tension, stress, and promotes neurogenesis.
Meditation
The positive effects of meditation on the human brain and overall health have been scientifically documented. Regular meditation has been shown time and again to increase gray matter growth in several areas of the brain, including the hippocampus.
- Meditation stimulates the development of certain cognitive abilities, especially attention, memory, and concentration.
- Meditation improves understanding of reality, focus on the present, and prevents the mind from burdening the mind with fears of the past or future.
- During meditation, the brain works in a different rhythm. In the first phases, increased activity occurs, which is manifested by a higher amplitude of α-waves. During the process of meditation (during the following phases), δ-waves arise, associated with the regeneration of the body and rehabilitation after illness.
- Meditation done in the evening stimulates the brain, increasing the production of melatonin, which is part of the process of neurogenesis. The body relaxes.
Monoatomic gold
Ormus, monoatomic (monatomic) gold is often associated with increased intelligence and overall brain health. David Hudson, who discovered ormus and began analyzing it, said that the substance is capable of restoring the body at the genetic level. Ormus professionals also claim that monoatomic gold can correct DNA errors and even activate dormant DNA.
How to restore the brain of a patient with schizophrenia using neurobiomodulation
What to do if connections between brain structures are damaged?
Despite the fact that old psychiatrists never cease to claim that MRI shows nothing in schizophrenia, we observe a completely opposite picture. Diffusion tensor imaging (tractography) shows us that in schizophrenia, connections between the temporal and frontal lobes, in particular, the orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate ligament fibers, are often disrupted. Connections destroyed by a pathological process (disease) can be restored by stimulating the growth of fibers, restoring their membrane and stopping the course of the autoimmune process, which we most often observe from neuroglia, primarily astrocytes. To restore connections, we combine in our clinic: medication, physiotherapy and neuropsychological treatment. In the future, we are also focusing on deep brain stimulation by implanting stimulators (sensors, pacemakers) into certain brain structures that send impulses in a certain direction.
Neurobiomodulation
To restore damaged brain connections and, consequently, improve the psychological and social aspects of the quality of life of a patient with schizophrenia, it is necessary to begin and consolidate the changes achieved by the doctor and neuropsychologist after a certain period, giving priority to improving selective attention, planning and organization of working time. In our clinic, such trainings include physiotherapeutic stimulation of damaged brain ligaments. We call this treatment method neurobiomodulation. In other words, here we have both cognitive training and physiotherapeutic effects, often with weak currents (0.5-1 milliamperes). The average duration of such a procedure is 20-30 minutes, the number of sessions is 15. The number of such courses of neurobiomodulation during the year is 4.
Where do we start?
Tasks for the patient should be divided into several, relatively simple stages, each of which has its own characteristics (for example, taking a shower in less than 20 minutes, getting dressed in less than 5 minutes). The performance of each stage is distributed according to a points schedule; Each improvement achieved is rewarded at the end of each month. These points can lead to a large reward chosen by the person with schizophrenia, such as a trip home or an excursion. Such rehabilitation transforms the routine environment of the clinic into a system that promotes continuous learning and facilitates change in the usual environment. From the point of view of optimizing time and improving already learned actions, these types of strategies have shown good results, but when a patient with schizophrenia has to independently plan and develop a sequence of goal-oriented tasks, working with prospective memory appears, from our point of view, to be more effective.
Communication training
Communication impairments in a person with schizophrenia may be related to their executive functioning disorders. Here the skills needed to understand non-literal information in discourse, speech acts, metaphorical sentences and words are lacking and impaired. It is possible to offer the patient a model of supported conversation that shares responsibility for the success of the dialogue between the person with a communication deficit and the listener. The videos illustrate the difference between a conversation with two people without mental disorders and another with a person with schizophrenia. This allows the latter and the neuropsychologist to discuss the communication skills or abilities of the characters in the frame - for example, gestures and topics of conversation. In addition, patients participate in complex role-play and, finally, assessment exercises. Such trainings help teach a patient with schizophrenia verbal and non-verbal communication, allowing him to achieve the goals that he has set for himself in the process of conversation.
Cognitive training programs
We are developing various cognitive training programs to improve the cognitive abilities of patients with schizophrenia, especially those with social and professional maladjustment.
Neurocognitive therapy (NET) is part of one of these programs. Work with the patient is initially carried out in a hospital and then continues in an outpatient setting. The outpatient version of NET consists of a support group with cognitive exercises lasting up to 5 hours each week for 26 weeks and a weekly group of social processing of the achieved results of these trainings. Cognitive exercises include repetition of computer-based exercises on attention, memory and executive functions. Such a program may be associated with occupational therapy (WT) - a flexible work schedule, paid work during employment in a clinic, usually for a period of 1 to 3 months (fixed-term employment contract) - which is aimed at restoring or forming new professional skills. After 5 months of follow-up, those patients who received NET + WT showed significant improvements on pre- and post-test variables of executive function, working memory, and affect recognition.
Similarly, other computer-based cognitive remediation programs that train attention, memory, language, and problem solving have been shown to improve neurocognitive function.
What did neuroimaging of the brain show?
Comparing two groups of patients with schizophrenia using neuroimaging, we can say that those patients (the first group) who underwent cognitive enhancement therapy (which is a comprehensive approach to correcting cognitive impairment using computer neurocognitive training and group social-cognitive exercises) demonstrated significantly greater preservation of gray matter volume in the left hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus, and fusiform gyrus, not to mention significantly greater increases in gray matter volume in the left amygdala, compared with those who received enhanced supportive care (group 2), including psychoeducation and applied coping strategies training .
Cognitive rehabilitation therapy
Cognitive rehabilitation therapy consists of three separate modules dedicated to: 1) mood monitoring and treatment of residual depressive symptoms; 2) organization, planning and time management, and 3) attention and memory. The first module includes problem solving, increasing awareness of negative automatic thoughts and their cognitive restructuring; the second and third focus on organization, planning, and time management so that patients can use schedules and notebooks to keep daily task lists, and are taught how to prioritize activities.
What not to do?
Mental health (according to experts) is more important than the physical condition itself. So how do you support brain function? First of all, you need to know what harms him.
Contaminated air
The brain consumes a significant amount of oxygen, which is necessary for it to function properly. But modern people are constantly exposed to polluted air (vehicle exhaust, dust from industrial production). People from larger cities experience frequent headaches and short-term memory disorders. Longer exposure to polluted air causes permanent changes in the brain.
Alcohol and cigarettes
In addition to causing cancer, heart disease and a range of other health problems, alcohol and nicotine can impair brain function, new research shows.
Unlike alcohol, nicotine compounds do not damage brain cells directly, but lead to other neurological disorders, including. to multiple sclerosis. Long-term consumption of alcohol, prolonged binges, in addition to delirium tremens, cause a chemical imbalance leading to structural disorders. Alcoholics have been shown to have decreased cranial volume.
Lack of sleep
The body, including the brain, recovers most during sleep. Long-term sleep deprivation can cause damage to a vital organ. The body does not have time to create new neurons, and old ones lose the ability to interact with nerve cells. For insomnia caused by overexertion, it is better to take a sleeping pill.
Relaxation for neurons
There are several points on the head that stimulate the overstressed nervous system. Place the fingers of both hands just above your ears and gently massage the skin, creating light pressure. Do the same on the top of the head. Finally, massage your temples and masseter muscles on your cheeks.
Don't cover your head
And one interesting thing. The fact that the brain needs sufficient oxygen is explained above. But did you know that children can have problems with this? They like to hide under the covers, often falling asleep this way. During sleep, the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled increases. This reduces oxygen levels, which interferes with the proper functioning of the brain.
This also applies to adults. Provide sufficient fresh air while sleeping.
Change your brain
The scientists' findings are significant for everyone. Research shows that people of any age can learn new things and form new habits. What we learn in life, who we surround ourselves with, what and how we decide to do, how we think, determines who we are, what our vision of the world is. The more a person is open to new stimuli and knowledge, the more he develops his brain.
Thanks to a proactive approach, habitual but disadvantageous stereotypes can be eliminated. Using various psychological methods, it is possible to replace “trampled” pathways in the brain with new ones. You can transform anxious thought patterns into realistic ones, and replace a negative attitude towards the world with a positive one. It all depends on the restoration of the brain and on the person himself.
Brain nerve cells do not recover: first refutation
Nerve cells of the brain
became hostages of scientific authority.
Today, many people perceive the Spanish scientist’s statement as a truth since childhood, which has already become popular. And why? As a Nobel laureate in 1906, Santiago Ramon I Halem
was highly respected by his contemporaries.
Therefore, for a long time no one dared to refute his assumption that nerve cells were not restored. And only towards the end of the last century (only by 1999), employees of the Department of Psychology at Princeton University, Elizabeth Gould
and
Charles Gross
, proved through an experiment that a mature brain can produce new neurons in the amount of several thousand per day, and this process, called neurogenesis, occurs in throughout life.
Scientists published the research results in the authoritative journal Science
.
designua / bigstock.com