Today, various oncological diseases are increasingly becoming a threat to human health. Their emergence is due to the spread of various factors that are considered integral elements of the modern world.
Not all tumors are malignant, many are benign in nature, which makes them less dangerous, but they still cannot be simply ignored. Among such neoplasms one can distinguish brain lipoma.
Definition
Lipoma is a benign tumor that forms from adipose tissue. In most cases, it is asymptomatic . In rare situations, complications may occur that may ultimately lead to disability. Therefore, if symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.
What is a brain lipoma?
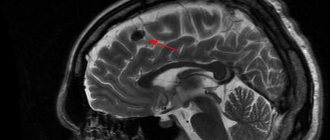
Some tumors can develop asymptomatically for a long time and are discovered accidentally during preventive examinations or diagnostic procedures for another disease. Such neoplasias include brain lipoma. This is a very rare, benign formation, most often located under the cortex of the organ. A lipoma consists of a capsule, the volume of which is filled with adipose tissue. The tumor grows extremely slowly, gradually squeezing nearby sections and disrupting their blood supply. The diameter of the neoplasm ranges from 2-3 mm to 5 cm. Most often, lipomas are found supratentorially, they are adjacent to the corpus corpus callosum or located in the region of the pineal gland and in the third ventricle. Much less commonly, a tumor of fat cells is located at the base of the hemispheres. Lipomas in other parts of the brain are incidentally rare. Intracranial formations of this type are characterized by extremely slow progression, latent course, and an extremely low risk of malignancy (malignancy).
Causes
Factors contributing to the occurrence and development of lipoma can be divided into two categories: congenital and acquired.
The first group is characterized by genetic predisposition . Moreover, the type of cancer that one of the relatives suffered does not matter. The mere presence of any neoplasm is enough to increase the likelihood of a lipoma.
As for the group of acquired factors, the following elements can be distinguished:
- The effect of various chemicals on the body. In everyday life in a modern city, it is difficult to avoid exposure to chemicals. They are present everywhere: in food, in clothing, even in the air. This situation significantly increases the risk of cancer.
- Emission of radiation . A person is exposed to radioactive radiation every day, but in minimal doses that do not have any effect on human health. But at some enterprises, hazardous elements are used in production, and people working with them are at risk.
- Disturbances in the metabolic process of fats . Such pathological disorders can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and excessive accumulation of fat in the subcutaneous layer.
- Lack of proper nutrition and proper sleep patterns - all this contributes to the occurrence of disturbances in metabolic processes and, as a result, an increase in the likelihood of developing the disease.
- Bad habits : use of nicotine, alcohol, drugs.
- Demodecosis. The tumor can form due to blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands. Activation of the corresponding microorganisms is carried out in connection with reduced immunity.
Etiology, pathogenesis, localization
The human brain is affected by various types of neoplasms, but neoplasms of a lipoid nature are very rare: only 0.5% of registered cases of oncopathology in the cranial cavity.
Usually a woman or man lives quietly, raises children, goes to work and does not know about the lump growing in the head. Thanks to its slow growth, the disease remains hidden. It is discovered by chance, for example, during an examination for another disease.
If the tumor reaches a significant size, the first symptoms appear. They force a person to make an appointment with a doctor and undergo an examination.
Lipomas found in the central nervous system are considered congenital by doctors and are explained by a failure of fetal development with the migration of primary lipocytes into the embryonic nervous system. Since it occupies an axial position closer to the dorsal side of the embryo, lipomas are usually detected in the middle position and on the dorsal side of the brain.
According to the place of development, experts distinguish the following types of tumor:
- interhemispheric lipoma (corpus callosum);
- lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure.
Occasionally, a tumor is recorded in the quadrigeminal cistern.
The corpus callosum, as the largest commissure connecting the anterior hemispheres, often becomes the site of formation of pericallosal lipoma of the brain.
Falx lipoma, or falx cerebri, is isolated (falx is a part of the leaf of the outermost meninges, shaped like a sickle and extending into the gap between the cerebral hemispheres).
The causes of lipomatosis occurring in the central nervous system have not been fully elucidated. The formation and increase in the volume of wen can be caused by:
- Congenital factors:
- a tendency to develop cancer pathology, transmitted at the genetic level,
- disturbance of embryogenesis and developmental anomalies.
- Acquired factors:
- lipid metabolism disorder due to poor nutrition;
- influence on the body of chemical agents and radio radiation;
- heavy smoking, alcohol abuse, drug addiction;
- dysfunction of endocrine organs;
- suppression of the body's immune system, insulin-dependent diabetes;
- trauma, inflammation (meningitis, encephalitis), neuroinfections.
Classification and symptoms
In the first stages of development, lipoma passes without symptoms.
With further development, the tumor grows and some nonspecific signs appear. For this reason, the disease in question is difficult to diagnose . In particular, the patient is characterized by the following general manifestations:
- Severe and frequent headaches.
- Vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of consciousness due to circulatory problems.
Interhemispheric
This variety is characterized by positive symptoms, which are expressed by:
- Uncontrolled movements of arms and legs.
- Visual and auditory hallucinations.
- Disinhibited behavior.
How does melanoma manifest: the initial stage of the disease. This article lists the symptoms of liver cirrhosis in male alcoholics.
Follow the link https://stoprak.info/vidy/golovy-i-shei/shhitovidnaya-zheleza/kakie-simptomy-u-zhenshhin.html clinical picture of thyroid cancer in women: symptoms and treatment.
Interhemispheric fissure
Manifestations of this type are caused by the effect of mutated tissues on certain brain centers:
- The field of vision is impaired.
- The pituitary hormone is actively produced.
- Constant and severe headache.
Spinal cord
Such a benign tumor is distinguished by the following manifestations:
- The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted.
- There is a disorder in the motor function of the human body.
Such manifestations are associated with the pressure of a growing tumor on certain centers of the nervous system.
Consequences
It is safe to say that the localization of lipoma in the brain is one of the most dangerous. This can lead to:
- To disruptions in the functioning of the human psyche.
- Various disorders in the functioning of the body.
- Stroke.
- Brain edema.
- Impaired blood circulation.
In addition, depending on the type of lipoma, the consequences may be as follows:
- The interhemispheric variety can lead to partial or complete loss of vision and hearing.
- Lipoma of the interhemispheric fissure can cause pituitary adenoma.
- If a spinal cord tumor is allowed to develop, the person can be paralyzed.
In some complicated variations of the neoplasm, it is possible that it will become malignant. These include: deep lipomas, pathological angilipomas, cell spindle lipomas.
In this video, experts explain how a brain lipoma leads to irreversible consequences:
Is treatment possible with folk remedies or without surgery?
Practicing neurologists and surgeons most often choose observational tactics and advise paying attention to the cause of symptoms in the brain.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
It is necessary to differentiate the symptoms; other concomitant diseases may be involved in their occurrence.
Traditional medicine resorts to folk methods and lifestyle adjustments. It is recommended to eliminate harmful factors and lead a healthy lifestyle. Traditional medicine offers several ways to combat lipomas with brain localization.
Burdock tincture. The roots need to be crushed and 1.5 cups of vodka added to 1 glass. Infuse for a month in a dark place. The tincture is taken 2 hours before meals, 1 tablespoon.
The most common and proven remedy for lipomas of any location is cinnamon. Daily dose 1-2 spoons.
The juice of beets, carrots, garlic and black radish are mixed and poured into a bottle. The mixture should be taken 2 dessert spoons after meals.
Chopped fresh celandine in a gauze bag with 200 g of sugar is placed at the bottom of a 3-liter jar, filled with warm whey. Leave for about 30 days in a dark and cool place. For consumption, filter and take 25 ml 30 minutes before meals. Be careful and follow the dosage.
Diagnostics
Today, the following methods are used to diagnose the disease in question:
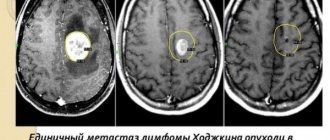
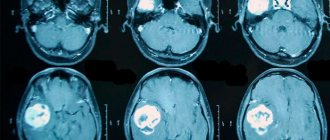
- CT scan . The essence of this procedure is layer-by-layer X-ray scanning of brain tissue. It allows you to accurately determine the size, shape and location of a benign neoplasm. In addition, this diagnostic method helps to collect information about the state of the circulatory system in the affected area.
- Magnetic resonance imaging . Examinations of this kind are carried out using an electromagnetic field - the brain is scanned with its participation. This makes it possible to detect minute changes in brain tissue.
What are the first symptoms of liver cirrhosis in women that you should definitely pay attention to? Testicular tumor in men: here is a list of causes and types of treatment.
Treatment of adrenal adenoma in women: https://stoprak.info/vidy/kory-nadpochechnikov/kak-proyavlyaet-sebya-adenoma-u-zhenshhin.html indications for removal.
Treatment
When the first signs of the disease appear, you first need to visit an oncologist. Unfortunately, this specialist may not be available at the medical facility. In this case, you can consult a surgeon.
With deep lesions of lipoma, patients complain of the described symptomatic manifestations. Then you can contact your local doctor, therapist, hepatologist, nephrologist or gastrologist with your problems.
Initial treatment for a benign tumor is based on watchful waiting. This technique involves systematic monitoring of the tumor without surgical intervention.
The specialist’s actions depend on the size of the tumor - such therapy is reasonable only for small lipomas and without dangerous symptoms , when the surgical route is not recommended.
But still, the surgeon often has to take up a scalpel to rid the patient of the tumor. This option is necessary when is large and has the possibility of its transformation into malignant .
Before the operation, the doctor determines the appropriate method of pain relief in accordance with the individual characteristics of the client and the location of the lipoma.
Removal occurs on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting. The latter option is mandatory for large tumors.
There are three surgical options:
- Removal of the tumor along with the capsule . Eliminates the recurrence of lipoma, since the tumor is completely removed. The main danger of this technique is the need to trepanate the skull , that is, it will be necessary to remove part of the skull to fully access the lesion.
- Endoscopic removal. The operation is carried out through small hole in the skull, which reduces the likelihood of brain damage as a result of the surgeon's actions. In this case, the essence of the specialist’s activity is to insert an endoscope with a miniature video camera into the skull.
With its help, a detailed overview of the lipoma and surrounding tissue is performed. After this, taking into account the information obtained, the tumor is removed using special instruments.
- Puncture-aspiration method. It is the least invasive of all methods. A tube is inserted into the tumor through a small hole in the skull. Next, the lipoma cells are removed using an electric suction.
This operation does not eliminate the risk of recurrence of the disease, since the capsule remains in place. The postoperative period passes without any complications, the sutures are removed after a week.
To successfully remove a tumor of this type, a highly qualified cardiac or neurosurgeon , since the location of the tumor in the brain can cause many complications.
The structure of the tumor can also complicate the specialist’s actions: if it has a lobular structure , it is intertwined with vessels or nerves . Then removing the tumor can be quite difficult. With the slightest inaccurate movement of the scalpel, the surgeon can cross a nerve or vessel, and this causes serious and dangerous consequences.
Treatment of benign brain tumor: basic principles and choice of method
In some cases, the doctor may choose active surveillance. This applies to patients with arachnoid cysts and meningiomas, as well as lipomas, which do not cause significant health problems and, as a rule, are detected by chance or during preventive cancer screening.
If a patient is diagnosed with a benign brain tumor that is “unfortunately” located, interferes with the quality of life for other reasons, or has a high risk of malignancy, treatment is aimed at removing the tumor (surgery) or destroying it using modern radiosurgical methods.
For example, some meningiomas can be removed by traditional surgery, while others are inoperable. In the latter case, the tumor can be destroyed using CyberKnife, Gamma Knife, TrueBeam installations. Depending on the characteristics of the tumor, tomotherapy or proton therapy may also be the optimal treatment method.
Operable colloid, epidermoid and dermoid cysts are most often removed in the traditional way or using endoscopic or microsurgical technologies. If indicated, additional antibacterial drug therapy may be prescribed. Sometimes cyst removal is complicated, impossible, or only partially possible.
Radical removal of chondroma, choroidal papilloma, ependyoma, pituitary adenoma can be carried out surgically or radiosurgically.
When treating patients with schwannomas, microsurgical methods or stereotactic radiosurgery are usually used. According to indications, medication, hormonal and radiation therapy are additionally prescribed.
Leading neurosurgeons have high hopes for intraoperative fluorescent control for the purpose of total resection of tumors, in particular pituitary adenomas, since incomplete removal of neoplasm leads to relapses in 20% of patients. But although pituitary adenomas are rarely malignant, they can cause serious problems by compressing nearby areas of the brain, which can lead to Cushing's disease, gigantism, blindness and death.
At the medical school. Perelman University of Pennsylvania developed the first organ-specific marker OTL38, which consists of two parts: folate and an infrared-luminescent dye. Since folic acid is actively used for the development and growth of neoplasms, they are characterized by a high content of folate receptors on the cell surface (which is sometimes more than 20 times higher than the normal level). By binding to receptors, OTL38 causes luminescence of the affected tissues, making it possible to accurately identify the boundaries of the tumor and completely remove it.
As noted by Yu.K. Lee, MD, PhD, professor in the Department of Neurosurgery at the University of Pennsylvania, said, “This study heralds a new era in personalized tumor surgery. Surgeons can now see the molecular characteristics of a patient’s tumors, not just light absorption or reflectivity.”
If you need a second opinion to clarify your diagnosis or treatment plan, send us an application and documents for consultation, or schedule an in-person consultation by phone.
+7 499 490-24-13
Expert opinion
Forecast
Brain lipoma, due to its benign nature, in most cases has a favorable outcome. At an early stage of development, surgical measures make it possible to get rid of the tumor with almost 100% probability.
But with intensive growth, the tumor can have a detrimental effect on the optimal functioning of the entire body and the central nervous system, in particular. In such situations, surgery can get rid of the tumor in 70-95% of cases.
If the wen capsule was removed during surgery, then the likelihood of relapse is minimal.
Also, to reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to exclude from your life factors that contribute to the development of the tumor.
Causes of lipomas
Experts identify a set of prerequisites that can provoke the formation of lipomas. Among the most common:
- genetic factors, hereditary predisposition;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body and fatty tissues;
- insufficient level of personal hygiene;
- malfunctions of the thyroid and pancreas;
- chronic pathologies that significantly affect the body’s immune forces (diabetes, hepatitis, HIV, etc.);
- dependence on alcohol, tobacco, drugs;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity, excess fatty tissue;
- injuries, damage;
- sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity.
Despite the fact that lipoma is a benign formation, there is always a risk of developing its malignant form. This probability is especially high for people who are included in the relevant risk groups: they have precancerous diseases (polyps, dysplasia), have already suffered from oncological pathologies, have a hereditary predisposition to the formation of tumors, and are under the constant influence of carcinogens, radiation and other harmful environmental factors.