Meningitis is an acute infectious disease with an aerosol transmission mechanism, occurring with various clinical signs from carriage to death. This disease occurs as a separate independent disease, and it may well be concomitant. This is a serious infection that needs proper and timely treatment. In long and proper rehabilitation after meningitis in children.
There are several types of the disease, usually the pia mater becomes inflamed, but there is a form of meningitis in which inflammation occurs in the dura mater. Common signs of the disease include photophobia, fever, fibrile temperature, severe headaches, neck muscle tone or stiffness.
To diagnose the disease, a puncture is taken from the spinal column with a special needle. The cerebrospinal fluid is then sent to a laboratory to identify the disease. Meningitis is divided into purulent and serous. Rehabilitation after such a serious illness plays an important role in a child’s health.
Clinical manifestations
In children and the elderly, meningeal symptoms may be absent or mild. This can also occur at the beginning of the disease.
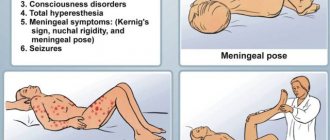
- General cerebral symptoms (nausea, vomiting, convulsions, impaired consciousness up to coma, psychomotor agitation, delirium, hallucinations).
- Symptoms of damage to the cranial nerves (hearing loss, visual disturbances).
- In severe cases of meningitis, patients take a characteristic position: lying on their side, legs bent and brought to the stomach, head thrown back.
Different types of meningitis have their own course and clinical features. Purulent inflammation of the meninges is characterized by a severe course with a rapid increase in symptoms, the presence of complications, and high mortality. Serous meningitis has a more benign course.
Therapeutic exercise for meningococcal infection
When assessing the therapeutic effect of exercise therapy on a patient, it should be taken into account that their therapeutic effect lies in the ability to stimulate physiological processes in the body. The stimulating effect is carried out through the nervous and humoral mechanisms. The nervous mechanism is characterized by the strengthening of those nerve connections that develop between the functioning muscular system, the cortex and subcortex and any internal organ.
The psychogenic influence in the action of exercise therapy is manifested by an increase in the mood of patients and the emergence of positive emotions, which is of great importance for the success of treatment. Exercise therapy products stimulate a feeling of vigor, distract the patient from “going into illness,” help eliminate anxiety and create a more balanced neuropsychic state.
Objectives of exercise therapy:
Exercise therapy products
Exercise therapy is contraindicated in the presence of purulent inflammation of the soft meninges and severe symptoms of intoxication.
Attention!
In the acute period, physical activity is contraindicated due to the fact that it can increase intracranial pressure, intensify headaches and other cerebral phenomena.
Exercise therapy drugs are prescribed after the patient’s general condition improves: the symptoms of intoxication and meningeal symptoms disappear, the intensity of headaches decreases. In the early period, classes use breathing exercises (of a dynamic nature), exercises aimed at relaxing muscles, and exercises for the distal parts of the limbs. In order to relax the muscles, massage is prescribed (stroking and light rubbing techniques). With the improvement of the general condition and stabilization of laboratory parameters, the patient’s motor mode expands.
During the period of reverse development, the main attention is paid to strengthening all body systems, improving the function of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. For this purpose, in classes, general strengthening exercises alternate with breathing exercises, which the patient performs in IP. lying and sitting.
During this period, low-intensity physical activity is advisable; the exercises are isotonic in nature, carried out effortlessly, at a calm pace. Sharp, jerking movements, especially with the head, are excluded. Exercises with changing the position of the head at the beginning of the period should be performed with a limitation of the amplitude of movement, which then gradually increases.
With a significant improvement in the patient's general condition, stabilization of blood circulation and liquor circulation, physical activity is increased, transferring the patient to an active training regimen (Duseinov K.D. et al., 1990).
Gradually increasing physical activity promotes adequate training of the heart muscle, normalizes central and peripheral vascular tone, and prepares the patient to perform household and professional activities.
The amount of physical activity during exercise during this period depends on the somatic condition of the patient and the neurological manifestations of the disease. It is not recommended to include exercises involving sudden tilting or turning of the head, or static exercises that can provoke an increase in cerebral symptoms.
According to a number of authors (Pokrovskaya N.Ya., Shaposhnikov L.M., 1975; Lobzin Yu.V., 1988; Duseinov K.D. et al., 1990), after suffering from the disease, post-infectious symptoms persist for a long time in patients asthenia, vegetative-vascular dystonia and hypertension syndrome. These phenomena can last from 3 months. up to a year.
Therefore, even after the patient is discharged from the hospital, it is recommended that he continue exercise therapy in outpatient and home settings. Systematic and regular use of exercise therapy helps to significantly reduce these periods and more quickly restore working capacity.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of meningitis is based on the patient’s typical complaints, medical history, examination data and objective examination by a doctor. Meningial symptoms must be checked. If inflammation of the meninges is suspected, a lumbar puncture and examination of the cerebrospinal fluid are performed. This study helps confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease. If necessary, computed tomography and electroencephalography are prescribed for differential diagnosis with other diseases.
Treatment
Treatment of meningitis is carried out in a hospital; all patients are prescribed rest and bed rest. Treatment tactics depend on the cause of the disease.
Main directions in treatment
- Eliminating the cause of the disease.
For bacterial meningitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics (cephalosporins) are prescribed, for viral meningitis, antiviral drugs (acyclovir, proteflazid, interferons), and for fungal meningitis, antifungal agents (amphotericin). If tuberculosis is suspected, anti-tuberculosis drugs (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide).
- Reducing intracranial pressure (mannitol, furosemide).
- Maintaining the normal functioning of the circulatory and respiratory systems.
- Anti-inflammatory and decongestant therapy (dexamethasone, prednisolone, diclofenac, nimesulide, ibuprofen).
- Infusion therapy, detoxification (hemodesis, reopolyglucin).
- Sedatives (diazepam, seduxen).
During the recovery period, patients are recommended to engage in physical therapy, treatment with physical factors, and sanatorium-resort treatment. If self-care is possible, patients can be sent for health improvement to the resorts of Crimea, Molokovka, Solnechnogorsk, Sochi, Pyatigorsk, etc.
Comprehensive rehabilitation after meningitis
After recovery, the patient needs rehabilitation after meningitis. Recovery from illness, especially after severe forms of the disease, can last for several months. For two years after the illness, the patient must be observed by a neurologist at intervals: in the first year, 1 examination every 3 months; subsequently, a specialist should be visited at least once every six months. This measure allows you to promptly identify possible complications of the disease and begin their treatment.
Rehabilitation after meningitis at the Yusupov Hospital has several components:
- physiotherapy is used to restore the functions of the central nervous system. When restoring patients, both classical and hardware techniques are used using European equipment;
- physical therapy at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out by experienced instructors who help patients gradually restore movement;
- The diet during the rehabilitation period is used to replenish vitamins, minerals and other important components. Experts recommend including lean meat and fish, vegetables and fruits after heat treatment, and dairy products in your diet. Baby food should be crushed, as large food particles can damage the mucous membrane;
- occupational therapy is a set of methods aimed at adapting the patient to everyday life. Specialists in this field help adapt the available opportunities to their lifestyle and habits, help the patient perceive himself as a full-fledged person, and enjoy life. Occupational therapists help patients cope with limitations that may arise during the course of their illness;
- Cognitive therapy includes exercises to restore attention, memory and logical thinking. At the Yusupov Hospital, experienced psychologists who know effective techniques interact with patients.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital develop a rehabilitation program taking into account the patient’s condition, physical capabilities and preferences. An individual approach allows you to achieve a positive result and relieve the patient from the following complications - weakness, low mood, fatigue, malaise, intellectual impairment, paralysis, convulsions.
Exercise therapy for headaches
Headache is a very unpleasant condition that almost every person has encountered. In some cases, headaches can seriously impair a person's quality of life and affect their ability to work. For chronic headaches, you should consult a specialist to eliminate the underlying cause of the disease. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are treated by qualified doctors who will perform diagnostics and determine the source of headaches. For non-drug treatment, exercise therapy instructors at the Yusupov Hospital will prescribe the most effective exercises.
Types of headaches
Headaches indicate the development of problems in the body. They can occur periodically in rare cases or be chronic. In some situations, a headache is a sign of a pathological process: inflammation, injury, etc. Therefore, if you have severe or frequent headaches, you should consult a specialist to clarify the situation. For chronic headaches, a consultation with a therapist is initially necessary, who, after conducting an initial examination, will suspect the cause of the illness and refer you to the right specialist (neurologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, etc.).
Headache varies in location, duration and intensity. It can be observed in the forehead, temples, back of the head, eyes, or cover all areas. A headache can occur suddenly or gradually increase, pass quickly or last for several hours or even days. The following main types of headaches are distinguished:
- migraine. The pain usually occurs in one place and is pulsating. Accompanied by nausea, photophobia, odor intolerance, and significantly reduces performance. It can last from several hours to three days. This is a fairly common type of headache. More often observed in young women;
- headache from overexertion. Mild headache, which most often occurs in the frontal part (other localization is not excluded). The pain increases gradually and can last for several days or weeks. It is associated with chronic fatigue and long-term muscle tension. This type of pain occurs in people with a sedentary lifestyle who are forced to remain in an uncomfortable position for a long period. Also, tension headaches are the result of stress and lack of proper rest;
- post-traumatic headache. Occurs after a traumatic brain injury or neck injury. The location of the pain and its intensity will depend on the type of injury. Pain may appear immediately after the injury or after some period of time;
- pain due to infectious diseases. Almost always occurs with influenza or ARVI and goes away as the person recovers. In this case, the pain will be pressing, not very intense. With meningitis, the pain is acute and does not go away for a long time. The person also experiences low-grade fever, nausea and vomiting. In any case, a symptom of an infectious disease is not only a headache, but also other signs.
The prescription of therapy will directly depend on the type of pain, its nature and cause. Any infectious pain requires treatment of the underlying disease, sometimes in a hospital (for example, with meningitis). Other types of pain can be treated with medication, but this does not provide a lasting effect. Over time, tolerance to the pain medication may develop, requiring an increase in dose or the use of a stronger medicine. Therefore, to eliminate pain, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital recommend using physical therapy methods.
Exercise therapy for headaches
There are many exercises that are aimed at getting rid of headaches. Therefore, instructors at the Yusupov Hospital always use an individual approach when working with each patient. It is important to assess the patient’s condition, his capabilities and select the most effective therapy. Physical therapy with instructors from the Yusupov Hospital is prescribed as a course. Consistent daily exercise helps achieve the desired effect. Recurrence of headaches is possible if the source of the disease is not eliminated or the conditions that provoke the pain recur. Exercise therapy instructors at the Yusupov Hospital recommend that you reconsider your lifestyle and try to avoid unfavorable situations:
- treat infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- take care of your health;
- try to eliminate stress;
- take breaks from work, changing activities;
- have a full rest.
To eliminate headaches due to overexertion or in case of problems with the cervical spine, you can perform the following exercises:
- tilting the head down. Starting position: sitting, legs resting well on the floor, back straight. Gently tilt your head and press it to your chest, without effort. Fix the position for 30 seconds;
- tilting the head to the side. Starting position: as in the previous exercise. Gently tilt your head towards your right shoulder and hold for 30 seconds. Repeat to the left shoulder;
- turning the head to the sides. Starting position: as in exercise 1. Bring your right hand to your left cheekbone and lightly pull it to the right. Repeat in the opposite direction. The duration of each exercise is 30 seconds;
- circular movements of the head. Starting position: as in exercise 1. Slowly rotate your head, first clockwise 10 times, then counterclockwise.
Physical therapy for headaches at the Yusupov Hospital
A specialist should prescribe physical therapy exercises. If you do it yourself, at best it will not give any results. At worst, it will only make the situation worse. This is especially true for headaches caused by infections. To seek help from the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, you just need to make an appointment at a time convenient for you. The doctor will examine the patient and, if necessary, prescribe an examination to clarify the condition.
Exercise therapy instructors at the Yusupov Hospital are certified specialists in the field of rehabilitation and have extensive experience working with diseases of varying severity. Based on the diagnosis made by a therapist or specialist, appropriate exercises are selected to help get rid of headaches. The course of exercises is carried out under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor, who will be able to adjust the classes if the need arises. The patient will then be able to repeat these exercises at home to prevent headaches or if they recur.
You can get information about the work of the clinic, diagnostic center, and also make an appointment with any specialist by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Effective recovery after meningitis at the Yusupov Hospital
Treatment and rehabilitation after meningitis is carried out at the Yusupov Hospital. At the first signs of this disease, emergency hospitalization is necessary, which will reduce the likelihood of complications and speed up recovery from meningitis. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital receive patients with signs of meningitis, 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Qualified psychologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide psycho-emotional rehabilitation after meningitis, which helps patients return to work life and normalize sleep. The daily work of the medical team at the Yusupov Hospital makes it possible to improve the quality of life of even seriously ill patients who were abandoned in other clinics.
Rehabilitation after meningitis allows patients to return to active life without unpleasant symptoms and complications. If you have signs of meningitis or need rehabilitation after an illness, make an appointment with neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital by phone or by filling out the feedback form on the website.
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges, which is infectious in nature, with a different clinical picture, including death. It can occur as a separate disease, but there are cases in which it is concomitant. With such a diagnosis, serious and correct treatment is simply necessary. This infection is especially dangerous for children; their rehabilitation will be long.
This disease can be transmitted by airborne droplets, food, household contact and water.
Exercise therapy complex for meningitis
Enter your username and password if you are already registered on feniks.help
Incorrect login or password.
Enter your email address and password.
Please provide the email address or phone number you used when registering. You will be sent an email with a link to a password change form or an SMS message with a new password.
Instructions for changing your password have been sent by email.
To register, enter your email and password
By clicking the “Register” button you consent to the processing of personal data in accordance with the privacy policy.
SEE ALSO: Cerebral edema meningitis Vaccine meningitis b Meningitis characteristic symptoms Meningitis in a newborn consequences of anyone who had it When to get vaccinated against meningitis
Classification and main types of meningitis
- By origin, primary and secondary are distinguished;
- by development – acute and chronic;
- according to the severity of the course - light, medium and severe;
- are serous and purulent in nature;
- by location - basal and spinal;
- by prevalence – generalized (everywhere) and limited;
The causes are classified as fungal, viral, bacterial and mixed. Bacterial meningitis occurs only when the immune system is very weakened, and neutrophils are increased in the blood.
The causative agent of meningitis is a spore-forming bacterium from the genus Neisseria.
Once on the mucous membranes, the pathogen enters the blood, infecting it. For a very long time it was believed that children were most susceptible to this type of disease, but the lack of vaccinations has led to the fact that now adults are also susceptible to the disease. The causative agent of the viral species is considered to be an enterovirus, which is resistant to external influences and even freezing. This disease is very common.
Therefore, it is important to follow certain rules during prevention and rehabilitation: strictly observe personal hygiene, use only boiled water, and thoroughly heat treat food before consumption.
But meningitis also happens in adults, which is much more difficult and can carry a serious form called “serous meningitis,” a moment when inflammation of the brain and spinal cord occurs at the same time, so the incubation period lasts about two weeks. The process is very aggressive, causing rapid intoxication of the body. You should immediately seek professional help, otherwise serious consequences cannot be avoided, such as hearing loss, blurred vision and even amputation, and death is possible.
Due to the rapid spread of infection, temperature surges occur, and intracranial pressure leads to severe headaches and repeated vomiting. The skin takes on a pale appearance and on the second day becomes covered with a star-shaped rash with necrosis, mainly in the abdomen, legs and buttocks. It constantly becomes denser, which leads to necrosis.
Then gastrointestinal hemorrhage occurs, the heart is affected, blood pressure drops and tachycardia occurs. The kidneys are exposed to enormous intoxication and the joints are destroyed. This form of progression leads to a rapid deterioration in laboratory parameters. With this development, death can occur within 10 hours.
Serous meningitis – All about massage..
Serous meningitis is an acute infectious inflammation of the meninges, which is caused by an enterovirus, characterized by seasonality, occurring in sporadic cases or epidemic outbreaks.
Most often, children and adolescents who are in organized groups get sick. Outbreaks of serous meningitis have been known since the mid-19th century in various countries around the world, but the viruses that cause it were discovered only a century later.
According to etiology, the following types of serous meningitis are distinguished: fungal, viral and bacterial (syphilitic, tuberculous) meningitis. In addition, primary and secondary forms are distinguished. Primary meningitis occurs due to primary damage to the meninges, which is not preceded by any infectious agents.
Secondary damage to the meninges occurs after an infection, as a complication. The mildest form of meningitis is considered to be that caused by viral infections.
The disease occurs without serious complications, and with timely treatment by highly qualified specialists, it goes away without a trace.
If treatment is late or not entirely adequate, then in the case of viral meningitis, the consequences for an adult or child can be very sad.
There are two routes of transmission of infection. The first is implemented by a person suffering from meningitis. The pathogen can also be transmitted by healthy individuals who are carriers of the infection.
The routes of infection with meningitis are quite varied. The virus can be transmitted through dirty vegetables, fruits, and hands.
Infection is possible in crowded places (airborne), reservoirs, and swimming pools.
Children aged three to six years are most susceptible to infection. In schoolchildren, it is significantly reduced; in adults, cases of this disease practically do not occur.
Clinical picture of serous meningitis
Serous meningitis of viral origin is characterized by an acute onset. Body temperature rises significantly. The patient complains of muscle pain and intense constant headaches. They are often accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting.
General anxiety, abdominal pain, cramps, delirium can also be called characteristic signs of this form of meningitis.
However, after four to seven days, body temperature decreases to normal levels, and the symptoms of meningitis disappear.
During this period, the patient should be under close medical supervision, as relapses with significant deterioration of the condition are often observed. In addition, signs of damage to the peripheral and central nervous system may develop.
Serous meningitis of bacterial (tuberculous) origin is characterized by a subacute course. In the initial period, the patient experiences general weakness, increased fatigue, headache, and anorexia develops.
A characteristic feature is a change in character.
The child becomes touchy, whiny, and his mental activity decreases. The duration of this period is two to three weeks, after which meningeal symptoms develop (Kernig's sign, stiff neck muscles, etc.). The outcome of the disease may be focal changes in the brain (paresis of the limbs, aphasia, etc.).
Manifestations and signs of serous meningitis
The causative agent of the disease, which has entered the brain, immediately begins to multiply, which contributes to changes in the hemodynamics of blood vessels. After the end of the incubation period, the disease begins to manifest itself.
The signs of meningitis in adults and children are almost identical:
- First of all, there is a significant increase in body temperature (up to 40 degrees). After a few days the temperature subsides.
- Intense headache that is similar to a migraine. The pain does not go away even after taking painkillers.
- Vomiting, which can occur several times a day and does not depend on food intake.
- Disruption of the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: development of diarrhea, pain in the abdominal area.
- Increased irritability, the patient may experience hallucinations.
- The disease is accompanied by clouding of consciousness, chills and fever.
- In severe cases, the patient may lose consciousness.
All the described symptoms manifest themselves to varying degrees, depending on the individual characteristics of the body. During the examination, an increased content of lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid is observed. Diagnosis is based on the results of laboratory parameters and lumbar puncture.
Treatment of serous meningitis
Treatment of a disease such as serous meningitis should always be carried out only in a hospital, with the patient isolated and under the constant supervision of medical workers.
At the first suspicion of the development of this disease, it is necessary to call an ambulance for hospitalization.
After the examination and before receiving test results, a qualified specialist, first of all, prescribes a course of antibacterial drugs to eradicate harmful microorganisms throughout the body.
To ensure that the effect is carried out throughout the entire circulatory system, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. Also, when determining the viral nature of the disease, the mandatory use of antiviral drugs is usually added to the course of antibiotics.
All basic medications are administered intravenously or into the spinal canal for the fastest and most effective effect. Also, antihistamines, dehydrating, and antipyretic drugs can be prescribed as part of the course of medications for internal use.
They are used to mitigate and eliminate the symptoms of the disease - serous meningitis.
Meningitis and folk remedies
It is important to know that it is impossible to cure meningitis at home! Treatment of meningitis should take place in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor.
If the patient does not receive antibiotic therapy on time, the disease can be fatal. Treatment of meningitis with folk remedies is intended only to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Unfortunately, many folk remedies can only alleviate the suffering of the patient, and not fight the cause of the disease.
- Thistle grass. An infusion of the herb is a good remedy for cramps.
- Chamomile tea. The drink is considered to be quite effective in calming the patient and relieving general tension.
- Lavender infusion. It is an excellent anticonvulsant and diuretic. The infusion is prepared from 3 tsp. dried flowers and 2 glasses of boiled water. The mixture is infused for at least half an hour.
- Collection for irritability and headaches. You should take 20 g of lavender flowers, primrose root, rosemary leaves, and peppermint, as well as valerian root. The mixture must be poured with a glass of boiling water. The filtered infusion is taken in an amount of at least 2 glasses per day.
- Poppy infusion with milk. An excellent sedative is an infusion of ground poppy seeds and hot milk at the rate of 1 tbsp. per glass. It should be taken half a glass 1 hour before meals. You need to create twilight in the room. It is advisable to ensure complete silence for the patient; arms and legs should be wrapped in a damp cloth. Place a cold object, such as an ice pack, on your head. Give drinks as often as possible.
To relieve headaches, fasting is recommended (minimum 1 day, maximum 3 days). Tibetan acupressure also helps well to eliminate this problem. In this case, you need to do a cleansing enema 2 times a day.
In case of convulsive movements, the patient should be wrapped in a cloth previously soaked in salt water and vinegar and wrapped in a blanket. After 1 hour, change the patient’s clothes.
A bath with chamomile gives a relaxing and analgesic effect. You can also take a bath with pine needles.
Prevention of meningitis
The most effective prevention of meningitis is vaccination. It is done for young children. However, adults can also receive the vaccine if they wish. It is especially recommended for students living in a dormitory, people with certain diseases of the immune system, military recruits, and tourists.
Also, as a preventive measure for meningitis, chemoprophylaxis is recommended for everyone who was in close contact with the patient. It is advisable to avoid contact with the patient.
If this is not possible, then use personal protective equipment - respirators and gauze bandages. Wash your hands with soap after contact with a sick person. Use only boiled water for drinking.
Wash berries, fruits and vegetables thoroughly and pour boiling water over them before eating. Maintain personal hygiene.
Source: https://fine-massage.ru/seroznyj-meningit/
How to detect the disease
The first thing the doctor does is carefully examine and interview the patient. If there is even the slightest suspicion of meningitis, then additional examinations are prescribed:
- a detailed medical history is collected;
- general cerebral and meningeal symptoms are detected;
- laboratory tests (blood and urine) are prescribed to detect inflammation of organs;
- performing a spinal tap;
- Bacteriological culture of mucous membranes is examined for the presence of pneumococcus and meningococcus.
After identifying the form of meningitis, a number of specific examinations are carried out.
How to cure and not cause harm
The most correct decision is immediate hospitalization as soon as the first signs of infection appear. In the hospital, the patient’s temperature must be brought down with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If there are signs of bacterial meningitis, an antibiotic is prescribed. If your child gets meningitis, you need to make every effort to completely eliminate this disease so that you don’t have to return to it in the future.
Immediate hospitalization is a mandatory measure as soon as the first signs of infection appear
An anticonvulsant drug is used only when the patient has severe seizures, and anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out with dexamethasone. To completely cure this disease, it is necessary to undergo proper rehabilitation after meningitis, because it is a full recovery after meningitis that will prevent the likelihood of getting it again.
Proper rehabilitation and diet therapy
The main rule after treatment of meningitis is observation by a neurologist. During the first year, monitoring is carried out every 3 months, and then at the discretion of the doctor.
- One of the components of rehabilitation is a diet that allows you to restore strength. It is preferable to boil, stew and steam food. Meat and fish products can be eaten only of the low-fat variety, and children can be given in the form of cutlets and pates. Any vegetables need heat treatment. Porridge is useful, but in boiled form. It is necessary to include proteins from dairy products in your diet.
- The use of physiotherapy is mandatory: massage, electrophoresis, electrosleep, magnetic laser therapy and magnetotherapy. But the procedures must be prescribed by a qualified specialist, taking into account the patient’s condition and his characteristics.
- Occupational therapy procedures are aimed at adapting the patient to living conditions, helping to restore amplitude in movements and coordination. This helps patients overcome psychological problems associated with their physical disability.
- Cognitive therapy will help restore attention, logical thinking and memory.
If you have meningitis, you must follow the minimum rules of proper nutrition.
Rules for proper nutrition:
- Be sure to eat food 5-6 times in small portions the size of your palm;
- It is worth excluding some foods (whole milk, beans, buckwheat, spicy foods such as pepper, mustard);
- Carbonated drinks and large amounts of sweets should be reduced;
If you follow these few tips, you will be able to overcome the disease and recover faster without any consequences for your body.
Recovery from meningitis is very long and difficult; it is necessary to use all the strength and capabilities of the body. But with the support of loved ones and proper supervision by specialists, you can achieve excellent results and live a full life, forgetting about this terrible disease.
It is always necessary to clearly control your health, which is completely in our hands, then it will be easier for you to live, due to the fact that all diseases will be treated at the very initial stage. Always be healthy, love and take care of yourself.
Olya
Living deliciously is a whole science!
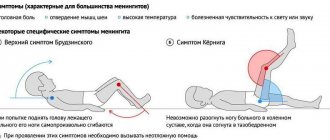
Symptoms
Meningitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms. The first symptoms of the disease in adults are as follows:
- Specific headache – constant, unbearable, aching. Any head tilt enhances this feeling.
- Severe tension in the muscles of the back of the head. The sick person is unable to lie in a relaxed position; he involuntarily throws his head back, since its natural position causes severe pain.
- Chills and fever. This is the dominant symptom and one of the first to appear.
- Painful sensitivity to light and sound. Bright light and even not very loud sounds have an irritating effect on the patient.
- Lethargy and drowsiness. The patient is not always able to quickly and accurately formulate a thought or answer the question posed.
- Vomit. Moreover, it is repeated and often not accompanied by a feeling of nausea. Vomiting with meningitis is distinguished by the fact that it is not associated with eating, and therefore does not bring relief and often leads to dehydration.
These are the main and most characteristic signs of the disease. However, certain forms of meningitis may also cause:
- Rash. These rashes are always irregular in shape and often form extensive hemorrhages.
- Cramps. They are observed less frequently in adults than in children.
- Mental disorders. They can manifest themselves both at the initial stage of the disease and in a later period.
Important! The first symptoms of meningitis appear unexpectedly, and the disease develops rapidly.
If the disease is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started immediately, the consequences of meningitis can be tragic for an adult patient.
All of the above-described manifestations of the disease in question are not considered specific, as they may indicate other possible pathologies.