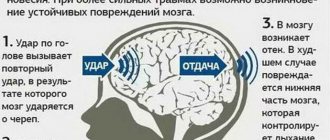
Why does the temperature change during VSD?
In medical practice, it is not customary to talk about vegetative-vascular dystonia as a disease. This is just a set of symptoms that combine disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which controls most processes in the body.
Changes in temperature during VSD occur due to disruption of body thermoregulation. A part of the brain called the hypothalamus is responsible for this function. If there are no provoking factors for an increase in temperature (illness, weather conditions, individual characteristics), then the norm on the thermometer is 36.6 degrees. In some cases, even a corridor of 36 to 37 degrees is considered normal temperature for both a child and an adult.
When a disease develops, for example, a viral infection, intoxication, inflammation, the human immune system reacts with an increase in temperature from 38 to 41 degrees. In addition to the high temperature on the thermometer, other symptoms will appear: headache, nausea, pounding in the temples, weakness, coughing, sneezing, runny nose. But temperature during VSD occurs for another reason, and this is not related to the reasons already mentioned.
The hypothalamus signals an increase in temperature (or decrease) in a stressful situation, when a person has fear, panic attacks, or depression does not end for a long time. Then a large amount of adrenaline is released into the blood, which is needed to activate self-defense, enhance performance, and endurance. If the hormone surges are frequent and keep the body in constant tension, a malfunction occurs in the thermoregulation system and the temperature on the thermometer at the moment of the adrenaline surge overcomes 37 degrees, but does not cross the line of risk with a temperature value of 38.
After calming down or resting in a horizontal position, the temperature during VSD returns to normal and no trace remains of the elevated temperature. In medicine, such a temperature during VSD is called subfebrile , because temperature jumps do not occur once, but over a long period of time.
Why does an increase in body temperature occur during VSD?
Maintaining a constant internal environment - the so-called homeostasis - is one of the most important functions of the autonomic nervous system.
The hypothalamus, part of the subcortical part of the brain, regulates the thermal regime. The so-called “temperature point” is established in it, which in a healthy person is about 36.6 degrees. If the receptors of the hypothalamus perceive an increase or decrease in body temperature, the corresponding compensatory mechanisms are launched - heat transfer or heat generation. In vegetative-vascular dystonia, due to a disorder of nerve connections, this mechanism is disrupted. The hypothalamus stops perceiving the normal 36.6 degrees and considers this figure to be too low. Naturally, it activates the process of heat production, thereby the body temperature begins to rise. Thus, this is primarily a neurological problem, which means it will not be treated with the usual antipyretics.
It should also be remembered that in some cases the reverse process occurs, then hypothermia (hypothermia) may occur.
Temperature during dystonia can also increase for other reasons. Often, VSD causes an increase in blood pressure and activation of cardiac activity. This, in turn, promotes blood flow to the surface of the body, and it seems that the patient is throwing a fever. This happens especially often after significant physical or psycho-emotional stress.
A general decrease in immunity also contributes, due to which inflammatory and infectious processes easily occur. Such conditions are accompanied by an increased release of biologically active substances into the blood, which can also cause the “temperature point” in the hypothalamus to shift.
The condition is also provoked by pregnancy, climate change, alcohol abuse and other bad habits.
An increase in body temperature with dystonia has its own characteristics. This condition is not accompanied by other signs of colds. Low-grade fever with VSD can last for a long time, weeks, and in some cases, months. However, there may be short-term changes during vegetative crises. Typically, the thermometer readings never exceed 38°C. The mark of 39°C indicates the addition of some other pathology.
Low-grade fever occurs during VSD in the evening, and at night it can drop to normal. This is primarily due to natural physiological cycles. In addition, during sleep the nervous system calms down, which also helps restore normal thermal conditions.
With VSD, one feels feverish even after physical exertion, even minor ones. The symptom is equally characteristic of adults and children.
In any case, if you notice a prolonged increase in temperature, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause.
How do you understand that an increase in temperature is a symptom of dystonia?
Low-grade body temperature, which ranges between 37.1 and 38, may indicate various changes in the body, from infection with worms to simple fatigue. But the temperature during VSD has special provoking moments, the disappearance of which normalizes the readings on the thermometer.
- The temperature rises during VSD only during physical activity of a different nature - fast walking, lifting weights, doing some kind of work that requires effort. At rest, the elevated temperature with VSD disappears.
- The second indicative sign of VSD when the temperature rises is the time of day. Violation of body thermoregulation occurs in the morning after waking up with the start of activity or during the day. At night, the elevated body temperature with VSD returns to normal and does not have jumps while the person is sleeping.
- Increased sweating without reasons explaining this condition is also a sign of VSD, if the body temperature is elevated. The body tries to prevent overheating on its own by cooling it with the release of moisture.
Low-grade fever sometimes accompanies a person throughout the day, but is not felt in any way and does not change the daily rhythm of life. Physical or mental stress is perceived as a normal state, and an increase in temperature during VSD does not interfere with performance and the quality of the work performed.
Some patients learn about the temperature indicating VSD only when visiting a doctor for a regular medical examination or when undergoing a commission from a physician according to work orders. People usually don't notice changes
Evidence that elevated temperature is a sign of VSD, and not a specific disease, is considered to be a decrease in temperature to 36 degrees or lower, after a person lies down and before that a temperature of 37.2 or 37.5 was recorded.
To confirm the fact that low-grade fever is a symptom of VSD, you need to see a doctor and take tests that will show an accurate picture of the internal state of the body. This will avoid the development of a dangerous pathology.
Standard set of laboratory tests:
- Blood sampling for biochemistry, general analysis.
- Thyroid (thyroid) hormones.
- Glucose level.
- Tumor marker.
- HIV, RW (RW).
- Culture for tuberculosis.
- UAM (urinalysis).
- X-ray of the respiratory organs or fluorography.
If in the listed studies there are no signs of illness, in which there may be an elevated temperature day and night, then low-grade fever indicates malfunctions in the thermoregulatory system controlled by the hypothalamus.
Dangerous or not?
Low-grade fever for a long time can not only be a harmless symptom of VSD, but also indicate real problems in the organic system. The safety of elevated temperatures can be judged if the following factors are present:
- Indicators increase only during the day, and naturally decrease at night. This can be easily checked by setting an alarm, for example, for 2 am and taking a thermometer.
- After taking a horizontal position, the thermometer marks are back to normal.
- Physical activity tends to increase the degree.
- For a long time, the patient has no accompanying symptoms, and the condition does not get worse.
- A dystonic person has the gift of “telepathy” and can know for himself what types of actions/events will increase the degree.
When the temperature fluctuates during VSD, the patient may not even notice it until he accidentally measures it.
Slight changes on the thermometer are one of the mildest symptoms of dystonia compared to the same pressure surges, burning in the chest, adrenaline attacks and neuroses.
But if, nevertheless, the thermometer mark gets on your nerves, you can try to restore the situation with the help of a regular contrast shower, eliminating stress and overwork, good rest and sleep. Taking antipyretics is pointless; it is just an unnecessary blow to the liver. The same applies to anti-inflammatory drugs. To improve the functioning of the hypothalamus and smooth out the chaos in the nervous system is not an easy task. But anyone who overcomes their inner hypochondriac and begins to treat dystonia as an annoying misunderstanding has the best chance of changing the incorrigible.
We recommend that you read: Suicidal thoughts - how to get rid of them?
Reduced temperature
In some situations, a symptom of VSD may also be a low temperature, which is recorded on the thermometer below 36.6 degrees. A person notices that his hands and feet are always cold, despite the time of year outside and warm clothes. Some people are used to joke on this topic that cold hands are evidence of a warm heart, that is, of a person who always does only good.
We can agree with this if, in addition to cold hands and low temperature on the thermometer, there are no other symptoms confirming problems with the heart and blood vessels. Vascular dystonia can lead to complete or partial circulatory impairment, when blood and nutrients do not reach all cells of the body. The limbs where the vessels are thinnest are affected first. There is no blood flow, there is no heating of the hands and feet.
In addition to cold limbs and low temperature with VSD, trembling occurs, for example, during panic attacks. Until the attack ends, a person cannot warm up even under a warm blanket. It is necessary to relieve stress, give a sedative and hot tea, and distract with something so that a person with signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia comes to his senses. Can the temperature rise to normal levels if this is a sign of VSD? Of course, just like low-grade fever, low values can return to normal at rest.
Treatment of prolonged fever
How to get rid of such a symptom as low-grade fever with VSD? This condition does not require specific and long-term treatment. During this period, a person should be more attentive to his condition, as this is a harbinger of complex disorders in the functioning of the body.
Motherwort tincture helps normalize temperature during VSD
To bring the thermoregulation mechanism back to normal, there is no need to use antipyretics (if we are talking specifically about VSD). In this case, the autonomic nervous system needs to be helped with sedatives, for example, tincture of Valerian, Motherwort, and Peony. If low-grade fever due to VSD is combined with pressing pain in the sternum, tachycardia, the doctor prescribes Validol or drops of Corvalol, Valocordin.
An increase in temperature during VSD can be effectively treated with rest and recovery of the body after physical exertion. Cold compresses are used on the forehead to normalize the patient's condition. This symptom characterizes psycho-emotional pathology, so antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs will have no effect. In complex cases of VSD, antidepressants are prescribed.
Phytotherapy
Medicinal herbs have both tonic and sedative effects. In case of sleep disturbances or impaired thermoregulation due to vegetative-vascular dystonia, herbal-based sedatives are recommended to restore the body (we have listed them).
If the symptoms continue after rest, and the thermometer readings are still not encouraging, it is recommended to take a course of stimulating herbal medicines based on ginseng, Schisandra chinensis, eleutherococcus, and zamanikha. The course of treatment is from 3 to 4 weeks up to 5 times a year.
Who is diagnosed with VSD with a sign of elevated temperature
Jumps in body thermoregulation during VSD are observed in people of different ages and genders. Vegetovascular dystonia in children, especially adolescents, occupies a special place in medical practice. Reviews from many mothers on forums about children's health are full of descriptions of elevated temperature in a teenager over a period of time. Precisely increased during the day, decreased at night. Causes indicating pathology are not detected during examination. Mothers cannot understand why this happens and look for advice on the Internet.
Why does a child’s temperature rise during the day and drop at night? Experts point to the instability of the child’s body, especially during puberty. At this time, the body is growing rapidly, but organs and systems do not have time to rebuild, because their volume or performance is still focused on the baby. Children are always on the move, and the autonomic system does not have time to respond to this activity, because the body area has become larger. The temperature rises because the vegetative center receives a signal that the body is insufficiently heated. When the pace of activity decreases, temperature readings return to normal.
But for some teenagers, a condition where the temperature rises to 37.5 or 38 degrees and does not normalize during the day can bring problems:
- Decreased performance, especially in school.
- Headache.
- An anxious feeling in the morning after waking up.
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
Parents think about a cold, but this is only an imbalance in the autonomic system due to age-related changes in the body. But you need to see a doctor to rule out organic disorders that provoke serious pathology. In children, a violation of thermoregulation can be caused by a genetic or generic disorder in the functioning of the hypothalamus, when signals to neurons about an increase or decrease in temperature are chaotic. In this case, a diagnosis is required from specialists who study disorders in areas of the brain in order to exclude a discomforting condition in the child.
Among the adult population, low-grade fever with VSD is more often observed in women who are prone to suspiciousness, stress and emotional distress for various reasons. But do not confuse thermal problems in women during menopause. These are no longer manifestations of VSD, but hormonal changes in the female genital organs. The temperature does not decrease when you try to rest and sweating can be repeated many times, causing serious discomfort.
First aid for temperature fluctuations
How to get rid of low-grade fever and is it necessary to do it? In case of VSD, you can fight an elevated temperature on your own if it is provoked by some kind of physical activity. It is enough to lie in a horizontal position and relax so that the autonomic system returns to normal and the surge of adrenaline in the blood decreases.
- If low-grade fever during VSD does not cause discomfort, does not change the usual pace of life, does not force you to stay at home and cancel activities, then there is no need to take steps to reduce it. At night the temperature will return to normal.
- Excessive sweating is more difficult to control, especially in a public place. If a symptom appears during panic attacks or stress, you need to take a course of sedatives, having received a prescription from a doctor. A daily contrast shower will help prevent the development of other problems due to increased sweating during vvd. A cold compress on the forehead will distract the body from the provoking factor and normalize heat exchange.
- With a primary increase in temperature without obvious signs of a cold, inflammation, or intoxication, you need to go to the clinic to confirm VSD and choose the right treatment if the symptom of VSD interferes with normal life.
- The practice of treating VSD shows that it is not worthwhile to reduce the temperature with VSD above 37 degrees with tablets, because the body copes with hyperthermia on its own if you give it a rest. Sometimes parents confuse fever with VSD with a cold and try to prevent the development of complications by giving antipyretics. But the temperature at all times up to 38 degrees in a child and 38.5 in an adult is the immune system’s response to a failure in the systems. If you start lowering the temperature during VSD and do not give the body the opportunity to fight the problem on its own, the immune system will weaken and will not be able to withstand a serious threat. It is better to monitor your general well-being during the day, drink more water and go to bed if you have mild hyperthermia. At night, symptoms indicating VSD will completely disappear, and normal temperature will remain until the morning or be completely restored.
If jumps on the thermometer are recorded after walking, especially fast or when climbing a mountain, you need to check the vascular system and heart. It is possible that these are the first symptoms of cardiovascular changes that require specialized treatment, and not temperature stabilization during VSD.
Warning symptoms of VSD
Temperature during vegetative-vascular dystonia does not always indicate only the presence of this disease. Often patients do not attach much importance to an increase in temperature if they know about the presence of VSD. But it is important to distinguish in time the manifestation of serious diseases of internal organs and vegetative-vascular dystonia. Only a doctor can determine whether there can be a temperature with VSD, and whether it is a manifestation of other diseases.
The following symptoms should alert the patient:
- Pain and discomfort in the heart.
- Bloating.
- Disorder of stool, belching of air.
- Feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath.
- Sexual dysfunctions.
- Hormonal imbalances, painful menstruation.
- Violation of thermoregulation in the human body.
All these symptoms together characterize vegetative-vascular dystonia. But also the simultaneous manifestation of several of them indicates the development of other pathologies.
Can the temperature rise to 39 degrees with VSD? It is worth noting that even if thermoregulation is impaired due to failures in the autonomic nervous system, the patient’s body temperature will not rise above 38 degrees. Moreover, during sleep it decreases to normal. Why do such fluctuations bother most patients?
Prevention of thermoregulation failures
To prevent VSD from changing your daily plans by increasing your temperature under any load, you need to train your body and eliminate a number of bad habits:
- Daily walks in the fresh air during VSD accustom the body to light physical activity, so that when walking quickly, the autonomic system does not react with a temperature failure during VSD. Fresh air saturates the circulatory system and normalizes the psychological state during vvd.
- Herbal teas for VSD instead of the usual coffee and black tea will calm the nerves, strengthen the immune system, and give strength. Mint, linden, raspberry, lemon, strawberry are an excellent alternative to industrial drinks for all types of illness, especially for panic attacks, depression, overwork and signs of vitamin deficiency.
- Adequate and timely sleep (at least 8 hours a day and no later than 10 p.m. lights out). Even when the temperature rises during the day, sleep helps to restore strength and normalize the temperature during the night. Neglecting this recommendation can lead to overwork and greater exhaustion, both physical and psychological.
Sometimes the cause of hyperthermia during VSD is a person’s psychosomatic state, when the problem is exacerbated in the head and no amount of VSD prevention will help. Here, a consultation with a psychiatrist is needed to rule out the root cause of the increase in temperature during VSD.
Prevention
Preventive measures will help not only normalize the temperature, but also eliminate other manifestations of VSD:
- walks in the open air;
- general hardening;
- adequate physical activity;
- eliminating the source of disturbance;
- physiotherapy and massage;
- correct diet.
Despite the fact that low-grade fever does not pose a danger to the body, it should be constantly monitored and surges should not be allowed.
Reviews
What temperature is comfortable for a person diagnosed with VSD and whether low-grade fever interferes with their life can be found out from the reviews:
Maria, 37 years old
I encountered the problem of temperature fluctuations during VSD when my daughter turned 14 years old. The teenage stage began, the body was rebuilt, and incomprehensible complaints appeared, mainly in the mornings before school. I thought that my daughter was being cunning and just wanted to skip school. I took her to the doctor and received a verdict of adolescent form of VSD. We were advised to exercise in the pool, take a course of multivitamins and go for walks. After some time, the temperature actually disappeared. The daughter successfully graduated from school. Now we don’t remember about everything.
Anna Vitalievna, psychiatrist, 10 years of experience.
I often work with patients who have been diagnosed with VSD and have had fluctuations in temperature. These are mainly clients with low self-esteem, who have experienced negative events, and who are dissatisfied with their social status. Several psychological trainings and people forget about elevated temperature with VSD. Not only the temperature is normalized, but also the general standard of living. Feel free to talk about the problem with a psychiatrist. Then life will cease to be gloomy and uninteresting. Panic, depression, negative thoughts will be a thing of the past.