About the reasons
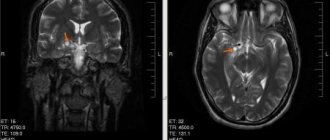
With cerebral palsy during intrauterine development, the mother's labor, or when the child is already born, his brain is damaged. The pathology is manifested by various forms of mental disorders, impaired speech function, and motor activity.
If a woman in labor has a pathology of an infectious nature, severe intoxication, or allergization, then there is a high risk that the child will be born with paralysis, in particular the astatic form of cerebral palsy. An infectious pathology that affects the brain provokes inflammatory processes in the meninges, which in turn will lead to cerebral palsy in the child.
Frequent infectious diseases cause the occurrence of other dangerous processes of the autoimmune type, leading to cerebral palsy. The following can have a destructive effect on the brain of an unborn child:
- Unbalanced, incorrect diet of the mother of the child.
- Intoxication manifestations.
- Extragenital nature of the pathology.
- Asphyxia, injuries during childbirth, during which the spinal column was damaged.
Types of cerebral palsy
There are types of cerebral palsy:
- Hemiplegic or hemiparetic type of cerebral palsy is common. It is expressed by paresis, paralysis, covering 50% of the child’s body. Muscle tone is selectively high. There are no problems with sensitivity. Most patients have mental disorders, decreased intelligence in the form of debility. But such a child is able to learn, adapt socially, and work.
- In the hyperkinetic form, hyperkinetic manifestations are expressed with impaired muscle tone, which can be reduced or normal in a calm state. But active physical activity increases it. This type of paralysis in children in rare cases leads to intellectual disability.
- When a child has a spastic type of diplegia, spastic paresis is observed, usually in the legs. Muscle hypertonicity is pronounced, the wrist joints are mobile. Due to damaged cranial nerve fibers, the child experiences strabismus. The deviation to the side of the tongue and smoothness of the nasolabial folds are also noticeable. There are no problems with sensitivity, the pelvic organs are normal. There are mental disorders, but not as severe as those present in other types of disease.
- The presence of double hemiplegia indicates damage to the upper and lower extremities. A sick person is unable to learn to sit, stand, or walk. Mentally, the child is severely retarded, imbecile, or has pronounced idiocy.
- The manifestation of cerebral palsy, expressed as an atonic-astatic form, is distinguished by the fact that the muscles are in hypotonicity, motor activity is preserved, but it is poorly coordinated. Such a person stands and walks late in life. Speech dysfunction is expressed in 58-61% of patients, mental disorders are identified in 53-57% of cases.
Complications
In the absence of rehabilitation measures during the course of the pathological process, the patient may be diagnosed with complications. Most often they manifest themselves in the form of:
- Cramps. The development of epilepsy is observed in 50 percent of patients. This complication negatively affects the development of the baby. With epilepsy, there is an increase in the severity of other symptoms, which reduces the effectiveness of rehabilitation techniques.
- Orthopedic disorders. The disease causes excessive muscle weakness, which leads to the development of various curvatures of the spine - scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis. With pathology, there is inconsistency in muscle function and disturbances in the blood supply. Progression of complications is diagnosed with age.
- Mental retardation. Complications are observed in almost all children, which negatively affects rehabilitation. Adult children have difficulty communicating with others, so they withdraw into themselves.
- Digestive disorders. Against the background of low physical activity, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system are diagnosed. The most common condition is chronic constipation. With pathology, patients are obese.
Complications manifest themselves in the form of drooling and enuresis. In patients with pathology, visual and auditory function is impaired.
About the atonic-astatic course
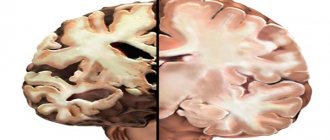
When there is a manifestation of the atonic form of existing cerebral palsy, this indicates cerebellar damage to the brain and its frontal lobes.
The patient has pronounced hypotonicity, manifested in impaired balance both when walking and in a quiet position. Motor activity is hypermetric, with impaired coordination, arms and legs tremble.
A person is not able to be in an upright position and hold his head calm. Sitting, standing, walking are difficult or not possible at all.
It is not only difficult for such a patient to coordinate his movements, this form of paralysis is expressed by the fact that mental activity and speech function take too long to develop.
In infants, it is not easy to distinguish the atonic astatic type of cerebral palsy from the ataxic type, since at this stage they are characterized by muscle hypotonicity, the rest of the symptoms appear later.
Methods of treatment and rehabilitation
Treatment of this form of cerebral palsy is usually ineffective; only rehabilitation measures are carried out, including acupuncture, physiotherapy, massage courses, physical exercises and speech therapy classes are also indicated.
All these methods have a small positive effect: the child becomes more active, moves better and speaks more clearly.
Taking medications also does not significantly improve the condition. Medicines are prescribed to eliminate some symptoms: diuretics and vasodilators to reduce intracranial pressure, nootropics to improve metabolic processes in the brain, and drugs with a sedative effect to reduce aggressiveness.
In rare cases, surgical intervention is indicated, but in this form of cerebral palsy, even surgical treatment is not able to improve brain function.
One of the specific methods of rehabilitation is hippotherapy. Interaction with a horse improves a child's emotional, mental and physical well-being, increasing his chances of social adaptation in the future.
Despite the fact that this form of cerebral palsy is practically incurable, regular rehabilitation measures contribute to the partial restoration of motor functions and reduce the severity of complications.
If your child has been diagnosed with cerebral palsy, there is no need to despair. Comprehensive treatment of cerebral palsy in most cases helps the child develop and even acquire communication skills.
We will look at the signs of cerebral palsy in a child depending on age on this page.
How it manifests itself
The horizontal arrangement characterizes a sharp decrease in muscle tone, and it is more pronounced on the arms than on the legs. The baby examines his brushes, but he is not interested in children's toys due to his inhibited psyche. Holding the head and resting on the hands is difficult, therefore, crawling will appear later. The child will move by jumping, with emphasis on his arms and legs.
The baby will be able to grab and manipulate toys much later than ordinary children, and his upper limbs tremble and his movements are poorly coordinated. The child is poorly motivated, he is afraid because his stability is reduced, and the activity of his hands can only increase over time.
When a child is 2 years old, he can sit on a chair, with his lower limbs spread to the sides. Kyphotic changes are evident in the thoracic vertebral segment. Such a child manages to sit normally and steadily only at the age of four to six; before this time it is difficult for him to sit due to the lack of protective functions of the upper limbs.
When a child is 4-8 years old, he can stand on his feet for a short time, if there is something to lean on, and his legs are very tense. If the baby has nothing to hold on to, he will fall, his upper limbs do not protect him, and stability is not maintained.
A small person is capable of falling if he is easily pushed. Independent walking is available only at the age of seven to nine, or is not available at all, and the lower limbs are widely spaced, the gait is weakly stable, and arrhythmic. Falls are quite common; the upper limbs are not involved at all in maintaining stability. Walking many kilometers is not possible for such children; they often cannot walk around themselves due to trembling of the upper limbs.
Almost all children with the atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy have low intellectual development, are prone to negativism, are little emotional, and are highly aggressive. Half of these patients are bothered by convulsive seizures, involuntary oscillatory motor activity of the eyes with strabismus. The nerve fibers responsible for vision are in an atrophied state, and speech function is weak.
How to treat
In fact, treatment for this type of paralysis does not bring visible results; only rehabilitation measures can be carried out. The therapy includes a course of classical massage, acupressure, and acupuncture will not be superfluous. Treatment with special physical training and physiotherapeutic procedures can have a positive effect on the patient’s condition, but the result is minimal. Drug treatment is also ineffective.
The prognosis for mastering motor skills is unfavorable. Severe mental disorders are clearly expressed, the children are intellectually retarded and are studying for further adaptation in special institutions.
Features treatment
Treatment of the atonic form of the disease does not bring the desired results. During the course of the pathology, rehabilitation measures are recommended. Patients are prescribed:
Patients should perform therapeutic exercises daily. He is advised to have regular sessions with a speech therapist. All of the above methods are characterized by a small positive effect. They help increase the baby's activity.
Medicines do not bring the desired therapeutic effect, so they are used to eliminate unpleasant symptoms. In order to reduce intracranial pressure, the patient is recommended to take vasodilator drugs and diuretics. Improvement of metabolic processes in the brain is achieved thanks to nootropic drugs.
Sedative medications can help reduce a child's aggressiveness. The selection of certain medications should be carried out only by a doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the pathology and the age of the patient.
Sometimes children are prescribed surgery. A specific rehabilitation method is hippotherapy. Thanks to interaction with the horse, the baby’s mood improves and the mental as well as physical state is stabilized. This ensures an increase in the chances of social adaptation in the future.
Rehabilitation techniques should be selected by the doctor after examining the child, which will ensure an improvement in his condition.