Events and circumstances that lead to tension, fatigue and irritation happen to us many times during the day.
As a result, cephalgia develops. However, its occurrence is provoked not only by external factors. Headache is one of the main symptoms of sore throat, ARVI and other pathologies of the ENT organs, changes in blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, disorders of the digestive tract, intoxication, etc. If a headache develops without fever, first of all it is necessary to find out the reason for this condition.
Factors causing headaches without fever
When organs and systems malfunction, the brain sends signals to a person in the form of certain symptoms. They report that you need to pay attention to your health status, get examined and begin treatment. It is cephalgia that often becomes such a signal, indicating the presence of pathology.
During pregnancy, such discomfort without fever is a common symptom that worries a woman throughout the first trimester. Among the main reasons are the rapid restructuring of the body, changes in hormone levels, and an increase in blood volume for gestation. In this case, headache is not a pathology requiring treatment. Since a woman cannot take the pill during pregnancy, to improve her health, she needs to rest more, eat well, and breathe fresh air.
If a child has a headache but no fever, this may indicate overwork. After rest, the discomfort should go away. Sometimes such symptoms indicate the development of a cold. In this case, runny nose, cough and fatigue occur.
Before consulting a doctor with complaints of pain in the head, you need to reconsider your lifestyle. It is important to pay attention to the following points:
- duration and quality of sleep (at least seven hours a day);
- stay in the fresh air (about two hours daily);
- physical activity, walking, playing sports (at least 60 minutes a day);
- quality of nutrition (you need to adhere to a balanced diet);
- psycho-emotional state (exclude depression, disorders, overwork).
If the daily routine is not followed, sleep is short, nutrition is poor, there is stress and heavy loads (physical or psychological), it is necessary to change your lifestyle. Often it is the incorrect distribution of time and energy that provokes health problems.
Prevention
People suffering from headaches and wanting to forget about this problem need to follow simple rules:
- provide adequate rest to recuperate after a working day;
- exclude from the menu products that are harmful to health and contain E261;
- exercise in the gym without fanaticism, correctly distributing the load on all muscle groups;
- If you have a hereditary predisposition to migraine, consult a doctor and promptly stop the attack with effective medications.
A balanced diet, a healthy lifestyle, avoiding stressful situations, and playing sports are the best preventive remedies for headaches.
Svetlana Fomenko
Local therapist, freelance regional nephrologist, head of the day hospital of the Bogorodchansk Central District Hospital.
Education
Ivano-Frankivsk Medical Institute Faculty of Medicine, General Medicine, Ivano-Frankivsk Higher specialized, from 09.1984 to 06.1990
Colds without fever
A common cause of headache is ARVI. A similar illness is accompanied by classic symptoms: cough, weakness, cephalgia, but without fever. Associated symptoms are body aches, chills, snot, and dry cough. A cold can manifest itself in a similar way. This course of the disease is typical for adults. In children, in 80% of cases the temperature rises to 38 degrees. If it hurts to swallow, there is a loss of strength and nasal congestion, fever appears, bones ache, this signals the onset of a sore throat, which must be treated.
Diagnostics
General diagnostic methods, blood tests, and radiography do not give results. Electroencephalography during an attack and examination of the fundus are diagnostically valuable. There is vasoconstriction, swelling and dysrhythmia without convulsive readiness.
They are intermittent headaches; included in groups that lasted from several weeks to several months, but were separated by headache-free periods of several months or years. You may experience severe one-sided pain that is described as a burning or piercing quality that throbs. Pain behind the eye or in the eye area is common. Sometimes the affected eye may become inflamed and appear red and watery. Although it can last from 15 minutes to three hours. Burst headaches usually go away, only to reappear later in the day.
Angiography is indicated to exclude concomitant diseases. After severe attacks, small infarcts, atrophy and dilation of the medulla ventricles can be observed on MRI.
Cardiovascular diseases
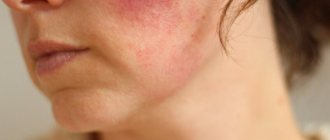
Changes in blood pressure negatively affect your overall well-being. Hypertension is accompanied by bursting pain in the back of the head. At the same time, dizziness, migraine and nausea appear, and the face burns. If you have high blood pressure, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary treatment. Normalizing blood pressure will relieve cephalgia. With low blood pressure, a deterioration in well-being is observed. Signs such as pain in the temples and frontal part of the head, drowsiness, loss of strength require taking the necessary measures for treatment. Therapy prescribed by a doctor normalizes the functioning of the cardiovascular system. When the pressure stabilizes, headaches will not bother you.
The appearance of a parotid fistula
A fistula is a hole in the skin
, located at the base of the tragus. It forms as an open wound in which there is an inflammatory process. The main cause of fistula is the presence of infection.
This could be advanced caries, stomatitis, purulent otitis media, etc.
Type of pain
Aching, dull, prolonged.
Localization
Area of the tragus and auricle.
Diagnosis
Identification of a fistula is possible during examination of the patient.
The otolaryngologist examines the auricle and also determines the length of the fistula tract. Treatment
The fistula must be removed.
Surgery is the most optimal treatment option.
How to get rid of headaches
Before taking an analgesic, you need to think about your lifestyle. When did you undergo the examination and tests? Do you get enough sleep, how do you eat, do you walk and rest enough? Are there any accompanying symptoms that can help make a diagnosis?
Since taking medications for headaches only temporarily relieves the symptom, without eliminating the underlying problem, it is recommended to consult a specialist to find out the causes of cephalgia. Correct diagnosis and timely treatment will help you quickly cope with the disease.
Traumatic brain injury
Damage to the skull bones
, soft tissues and nerves is called a traumatic brain injury. A severe headache is the first sign of a traumatic brain injury, followed by nausea, vomiting and dizziness. Injuries, depending on the location of occurrence and symptoms manifested, can be of two types:
- Open - develops when the bones of the skull are strongly compressed or punctured by sharp objects, resulting in damage to the skin of the head, bones and brain body. The chances of survival are minimal, and the prognosis depends entirely on the depth of the lesion and the speed of medical care.
- Closed – the integrity of the aponeurosis is noted, in which damage to the skin is allowed.
Closed craniocerebral injuries are extremely dangerous because they may not appear for quite a long time.
The increase in clinical symptoms indicates the maximum danger, as well as the need and importance of early diagnosis. Closed TBIs are divided into the following subgroups:
- brain contusion;
- shake;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- damage to brain axons.
Type of pain
With a traumatic brain injury, types of pain may develop such as:
- dull, aching, squeezing;
- bursting, sharp, pulsating;
- paroxysmal.
Headache in the presence of TBI increases gradually, and is also accompanied by other symptoms indicating the presence of injury.
The intensity of the clinical picture directly depends on the area of damage to the skull and brain, as well as the speed of medical care. Localization
The source of pain is in the brain, mainly in the occipital part.
However, the pain can radiate to the neck and temples. Diagnosis
Primary diagnosis is based on the clinical manifestations of TBI. However, with a visual inspection it is impossible to determine the severity of the damage and its location, which can be helped by diagnostic methods such as:
- X-ray of the skull and cervical spine.
- Angiography.
- Lumbar puncture.
- Assessment of intracranial pressure.
You may need to consult specialists such as:
- neurosurgeon;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- surgeon.
When diagnosing a traumatic brain injury, it is important to assess the general condition of the body, as well as the damage that occurred due to the skull injury.
For these purposes, hardware research is supported by laboratory tests of blood and urine, as well as puncture of brain fluid. Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends entirely on the severity of the injury. First aid is to ensure vital functions: breathing and heartbeat. It is important to transport the patient as quickly as possible to the traumatology department, where, after a comprehensive examination, competent treatment will be selected.
The first 10-12 days of treatment require bed rest, after which, if the patient’s condition improves, he is transferred to the general ward.
Self-medication in this case is not recommended, since there is a high probability of death.
Nausea at different pressures
Almost every person in a situation where a headache and nausea occurs first of all measures blood pressure, and only after that makes a decision on the use of any medications or an urgent call for an ambulance.
Provoking factors for blood pressure surges are:
- stress,
- obesity,
- alcohol,
- nicotine,
- drugs,
- age over 65 years.
If blood pressure levels are reduced for a long time, then headaches and nausea may occur due to pathologies of the urinary system arising from water retention in the body.
Physiological causes of pain
The most difficult group of factors to identify that cause a headache, but the pressure remains normal, are physiological processes:
- violation of the texture of blood vessels - when the system cannot expand or contract normally, blood circulation deteriorates;
- muscle spasms – in the areas of the front and back of the neck, head, there are muscles that sometimes spasm pathologically;
- disruption of intercellular metabolism in the brain - an imbalance causes headaches without other causes.
Diagnosis of these conditions requires extensive MRI, CT, x-rays and other examinations.
Caffeine
This is not a pathological reason due to which a headache may occur at normal pressure. Tea, coffee, chocolate, lemonades and other tonics with added caffeine, when consumed regularly, cause an unpleasant symptom.
Constant intake of caffeine leads to the dilation of blood vessels, and when its supply stops, they begin to narrow. This is “caffeine withdrawal”, which affects people who drink 2-3 or more cups of coffee per day. Symptoms of withdrawal include:
- arrhythmia;
- decreased brain activity and lethargy;
- high pressure;
- depressed mood;
- nausea.
All this is dangerous to health: narrowing of the arteries and vessels supplying the heart can lead to problems with blood circulation and hypoxia.
Smoking
Another harmful substance that causes headaches is nicotine in combination with thousands of carcinogenic tars and substances. Smoking leads to vascular spasms, which cause pain.
Treatment
Patients are subject to intensive treatment during an attack and observation during the interictal period for preventive purposes. Effective treatment is carried out with vasoconstrictor ergot preparations:
- Ergotamine is taken sublingually, one tablet at a time. every 20 minutes until the pain symptom stops, maximum dose three tablets. per day.
- 0.2% solution of dihydroergotamine - 15 drops. appointment.
- 0.1% solution of dihydroergotoxin - also 15-20 drops. inside.
- Redergin - one tablet each. per day.
- Ditamine - one tablet each. twice or in ampoules of 1 ml during an attack IM, in solution taken orally 25 drops. three times a day.
Complex preparations Cafergot, containing ergotamine, belladonna, phenobarbital and caffeine, take two tablets at the beginning of an attack. No more than six tablets per day. Analogues - Ankofen, rigetamine, caffeamine.
Painkillers
Caffetine consists of paracetamol, ergotamine and codeine. The drug is especially effective at the beginning of the aura. Serotonin analogues Sumatriptan is the most modern remedy. It is taken in a single dose of 100 mg and is equally effective in injections and tablets. The maximum dose is 200 mg per day.
Adjuvant therapy
To prevent nausea and vomiting, Raglan and Cerucal are used. A severe, intractable attack is treated with hormonal and diuretic drugs, antipsychotics. Therapy is carried out in the neurological department.