Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern diagnostic method that visualizes the organ under study and all surrounding tissues. Today this is the most effective method that visualizes all types of tissues, and for a more accurate result, contrast is sometimes prescribed. What does an MRI show? Using this study, you can diagnose various diseases, neoplasms, and injuries. The effectiveness of the study has long been proven, but despite this, there are doctors who do not use it.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for various diseases of internal organs, such as:
- brain;
- kidneys;
- liver;
- pancreas;
- prostate;
- ovaries;
- uterus;
- spleen.
Benefits of MRI
Magnetic tomography allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the areas under study in three projections. During the procedure, the device takes many slices, the thickness of which can be set individually and is usually 2-4 mm.
Images taken using a tomograph
Obtaining a large number of sections allows you to examine the entire organ and detect even the slightest abnormalities and pathologies.
What types of tomographs are there?
Modern magnetic tomographs are available in various variations with a wide variety of characteristics.
All tomographic devices are divided into:
- open;
- closed.
Despite the fact that conducting a study in an open tomograph is usually considered more comfortable for the patient, closed devices have greater power and detail. If the patient does not have a strong fear of closed spaces and does not have weight restrictions, it is recommended to conduct the study in a closed-type apparatus.
Tomographs are also divided according to the strength of the magnetic field radiation, the unit of measurement of which is called Tesla. Magnetic tomographs can be:
- low-floor – power up to 1.0 T;
- high-field – radiation intensity above 1.0 T.
Low-field tomographs do not provide a clear and detailed picture. A study using a high-field tomograph will allow you to examine the diagnosed area with the highest accuracy.
Modern high-field tomograph
The DiMagnit clinic has a closed-type tomograph from Philips, whose power is 1.5 Tesla. Using the device, it is possible to obtain images of the highest quality and detail.
How to register for RT?
In 2021, online registration for the Republic of Tatarstan was launched through a personal account on the RIKZ website. Through this service you can select the date and time, subject, region and testing location. Here you can reschedule the PT test to another date if you suddenly cannot attend the trial exam on the appointed day. Test results and consultation on the academic subject are also sent to your personal account.
Should you be afraid of the procedure?
Some patients are worried before the test. But their fears are in vain - magnetic resonance imaging is absolutely painless, and the effect of magnetic radiation on the body is safe.
Unlike other types of radiation diagnostics, MRI does not use ionizing radiation. The magnetic field does not have a carcinogenic or mutagenic effect on the cells of the body. Magnetic resonance scanning can be performed as often as needed.
The difference between MRI and CT and ultrasound
Magnetic resonance diagnostics has a number of advantages compared to ultrasound and computed tomography.
Ultrasound examination allows you to obtain a two-dimensional image of the area under study, but does not allow you to see a three-dimensional image of soft structures.
Computed tomography can be compared to MRI in terms of image clarity, but has a number of serious contraindications. CT is more often used to visualize hollow organs and bone structures, while MRI is much more effective at visualizing soft tissue.
Can other tests be performed after an MRI?
Diagnosis of a patient consists not only of instrumental but also laboratory tests. Typically, tests are taken before an MRI, but after the procedure this is also possible if the MRI was performed without sedatives, contrast agents or anesthesia. When using medications, you can donate blood for analysis no less than 24 hours later.
You can donate blood as a donor under the same conditions, but if there is no serious need for this, it is better to postpone the procedure for another day. Instrumental methods can be performed additionally both before and after MRI.
To summarize, it should be noted that the results of MRI may differ from the results of CT, ultrasound, or x-ray, which is due to the special effect of the tomograph on the tissue. But you shouldn’t worry too much about the diagnosis; it’s better to trust professionals who can correctly decipher the examination results. The patient’s main task is to help collect an accurate history and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
What does an MRI show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is successfully used to diagnose diseases:
- thyroid gland;
- liver;
- gallbladder and ducts;
- pancreas;
- kidney;
- spleen;
- joints;
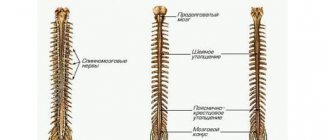
- spinal cord;
- vessels of the head, neck, abdominal region;
- pelvic organs;
- soft tissues;
- etc.
All of the above anatomical structures are perfectly visualized on MRI images. The diagnostic results make it possible to accurately identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organs being examined.
Indications for the diagnostic method
Why are scans done? MRI diagnostics, since its inception, has become the main method of examination for neurological, neurosurgical, orthopedic diseases, as well as a necessary procedure for diagnosing other diseases. Available at the clinic:
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord;
- MRI of the pituitary gland;
- MRI of cerebral vessels;
- MRI myelogram;
- MRI of different parts of the spine: cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral;
- MRI of the adrenal glands;
- MRI of joints;
- MRI of the abdomen and pelvis.
In case of injury to any organ, it is necessary to do an MRI.
Examination of the head allows one to distinguish between the gray and white matter of the brain, examine the state of the ventricular system, subarachnoid space, identify the presence of pathological processes, zones of demyelination, foci of inflammation, manifestations of cerebral circulation disorders of the ischemic and hemorrhagic type, and edema. Interpretation of MRI of the spine indicates the first signs of osteochondrosis, helps to assess the condition of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs and their prolapse, the spinal cord.
An MRI of the abdominal cavity can show pathological processes in the kidneys, liver, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder, blood vessels, lymph nodes and nerves.
In what cases is MRI prescribed?
The wide capabilities of magnetic resonance diagnostics make its use indispensable in the following cases:
- the need for a primary diagnosis;
- conducting a comprehensive survey;
- preparation for surgery;
- monitoring the effectiveness of the therapy and treatment methods used.
In each individual case, the choice of diagnostic technique is made by the attending physician. Magnetic resonance imaging is more often used than other methods to detect diseases and injuries of soft tissues.
The MRI technique is indispensable for diagnosis:
- Neoplasms.
Magnetic resonance scanning can clearly identify the boundaries and size of the tumor and the extent of its invasion into soft tissue. No other radiation diagnostic technique is capable of providing such a clear and detailed picture of diseases.
MRI also makes it possible to determine the nature of the tumor with a high degree of probability. Malignant neoplasms have unclear boundaries and grow into surrounding tissues. Benign neoplasms, as a rule, are clearly differentiated from healthy tissues.
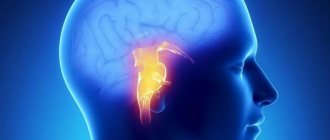
- Brain diseases.
The greater accuracy of magnetic resonance diagnostics makes it possible to visualize such small anatomical structures as the pituitary gland and the sella turcica. Also, MRI with contrast of the brain shows high efficiency for diagnosing demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, etc.), as it allows one to clearly see the structure of altered nerve tissues.
Brain images obtained with contrast-enhanced MRI of the brain are particularly clear because magnetic waves are difficult to image solid anatomical structures and there are no artifacts from the skull in the brain images.
- Diseases of the intervertebral discs.
MRI images of the spine
Magnetic resonance imaging is the only diagnostic method that allows you to see intervertebral discs. Even modern diagnostic methods, such as computed tomography, allow you to see only the space between the vertebrae, while MRI gives a complete picture of the condition of the discs, the possible presence of hernias and protrusions.
The use of MRI is not limited only to the above diseases, but is used when it is necessary to identify and monitor a wide range of pathologies, congenital developmental anomalies, consequences of injuries and previous surgical interventions.
Subject of examination
What organs can be checked by MRI? Resonance imaging is done to check all organs of the body. The following are examined:
- vessels of different parts of the body;
- brain and cervical spine;
- spinal column and skeletal system;
- cardiovascular system;
- hollow abdominal organs.
MRI shows all organs in a three-dimensional image, that is, it gives a three-dimensional picture. Unlike ultrasound diagnostics, resonance tomography can be used to check in which organs small neoplasms have appeared. Ultrasound cannot distinguish them.
Resonance tomography can distinguish even micro strokes and hemorrhages, which will provide prompt and timely therapy. The device detects vascular deformation, aneurysms, and multiple sclerosis that are invisible to other types of scanning.
When diagnosing the spinal column, a tomograph can detect a herniated disc that other scanning devices cannot detect. All this makes magnetic tomography irreplaceable and unique.
Let's consider what information about individual systems and organs can be obtained using MRI.
Brain scan
An appointment for tomography is given if the patient complains of frequent headaches of unknown origin, dizziness, or noise in the ears. The referral is prescribed for ischemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia and strokes. After the examination, you can obtain an objective clinical picture of the disease and prescribe a course of therapy adequate to the patient’s condition.
The tomograph shows the localization of blood clots, deformed vessel walls, hemorrhages, cholesterol plaques and other pathological abnormalities. Where can I get an MRI of the head? In any medical institution that has a tomograph.
Spine scan
This examination is prescribed for complaints of pain in the back and legs. What does the tomograph see? Using tomography you can detect:
- pathology of intervertebral discs;
- neoplasms of bone and nervous tissue;
- osteoporosis in the initial stage;
- deformation of the spinal canal;
- pathology of nerve fibers;
- infectious lesion.
The tomograph can also show the intensity of pressure of the intervertebral disc on the nerve processes, disruption of blood supply to any part of the spinal column, localization of metastases or tumors, and identify other pathological abnormalities.
The cervical spine is a complex interweaving of nerve endings and blood vessels with muscle fibers. The pathology of this part of the body leads to diseases of various body systems.
Diagnosis of the cervical spine is prescribed for complaints of osteochondrosis, after an injury, for congenital anomalies of the structure of the cervical spine, for pathology of cerebral circulation, before surgery and detection of metastases.
Pathological changes in the cervical spine provoke hearing/vision impairment, pressure instability, headaches, tinnitus and pain in the upper extremities. Vascular tomography allows you to find out the true causes of ailments.
Heart scan
Examination of the main organ of the body allows us to identify pathologies of the coronary system, atria, chambers, valves, myocardium, defects of any nature, and cholesterol deposits. The scan reveals disturbances in blood flow and arterial capacity. MRI is also used to monitor the condition of the heart and blood vessels in the postoperative period.
Since the heart muscle is in constant motion, scanning of the organ is carried out with a high-power tomograph and using contrast agents.
Peritoneal scanning
The peculiarity of an MR tomograph is that it qualitatively scans the soft tissues of organs. In this, no diagnostic device can surpass it. However, due to the high cost of the procedure, the diagnosis of abdominal organs is carried out using other methods, and MRI is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Scanning of the knee joints and blood vessels of the extremities
Injuries to the knee joints can lead to a person's incapacitation. Invasive diagnostic methods are very painful; it is difficult for pediatric patients to undergo joint arthroscopy. Therefore, diagnostics using the resonance method is the only painless and safe examination method.
Diagnostic appointment:
- rupture and damage to the meniscus;
- ligament/tendon injury.
The tomograph shows not only the condition of the kneecap and meniscus, but also the changes occurring in the tissues.
Diagnosis of veins and vessels of the lower extremities is a popular procedure in modern times. An appointment for examination is given in case of venous insufficiency, thrombosis, aneurysms, damage to the walls of blood vessels and other pathologies.
When to Apply Contrast
Magnetic resonance diagnostics can provide a very high degree of clarity of the resulting images. In most cases, the use of contrast is not required.
But when it comes to diagnosing tumors and small anatomical structures, a contrast agent can still be used.
The staining agents are made from the rare earth metal gadolinium and are injected intravenously into the patient during an MRI.
MRI contrast agents are much better tolerated than CT contrast agents. This makes the use of the dye safe even for patients with kidney pathology and does not require a preliminary test for creatinine, which is necessary for CT diagnostics with contrast.
MRI with contrast is used in the following cases:
- suspicion of a neoplasm;
- the need for differential diagnosis of a malignant tumor;
- study of the pituitary gland;
- the need to diagnose demyelinating diseases.
The use of contrast allows one to obtain a comprehensive picture of the disease, its course and the effectiveness of the therapy used.
Preparation
Mandatory MRI preparation activities include:
- checking for an allergic reaction to contrast in the body;
- informing the doctor about the presence of foreign metal bodies (cardiac, dental or cosmetic);
- information about recent operations and chronic diseases (for this, in case of renal failure, it is necessary to additionally take a biochemical blood test);
- a doctor’s warning that you are nervous in unfamiliar or difficult places;
- message about the presence/absence of a medical plaster (causes a burn).
Do I need to take a referral for a scan? Anyone can have an MRI done on a commercial basis, without a doctor's referral. But the referral provides detailed information about the condition of that part of the body that is important for diagnosis, as well as the mode in which the specialist should conduct the scan. All this information is collected after studying the anamnesis and conducting a laboratory examination (general blood test, biochemical), therefore, without a referral, diagnosis, in most cases, will not be advisable.
You must lie still during the procedure.
Contraindications for MRI
Despite the fact that magnetic resonance diagnostics is a safe technique, the study has a number of absolute contraindications, in the presence of which diagnostics are prohibited:
- presence of a pacemaker, neurostimulator, insulin pump;
- vascular clips on the arteries of the brain;
- the patient’s inability to maintain a stationary position for various reasons;
- early childhood up to 5 years;
- the patient’s weight is more than 130 kg and body girth is more than 150 cm;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
There are also a number of conditions in which MRI examination is carried out with caution:
- severe pain syndrome, in which it is difficult for patients to remain in a motionless position for a long time;
- fear of confined spaces;
- psychical deviations;
- second and third trimester of pregnancy.
The presence of various prostheses and implants in the patient's body may be a contraindication to MRI if they are made of metals sensitive to magnetic radiation. Modern medical devices are most often made of titanium and other materials that are inert to the effects of magnetic fields. Their presence in the body does not interfere with MRI.
Before and after
Before we find out how an MRI study is performed, let’s pay attention to the preparatory stage: what you should know and consider if you are scheduled for the procedure.
The magnetic field of the tomograph is about 4 orders of magnitude higher than the strength of the natural earth's field. Doctors studied the influence of the process and proved that short-term radiation does not affect a person’s physical condition in any way, at least no noticeable harm was detected.
The effect of such powerful irradiation on the structure of atoms and molecules is not considered.
Despite this, the MRI technique requires compliance with a whole set of rules, recommendations and safety requirements. All of them must be brought to the attention of the patient.
- We fill out the proposed questionnaire, where we indicate our state of health, recent operations and illnesses, so that the doctor can identify contraindications, if any.
- After appearing in a booth or other changing room, we remove all metal objects (chains, earrings and other jewelry), clothes with such elements: a shirt with metal buttons, a belt, a jacket with a zipper. We remove from our pockets all metal-containing objects (keys, money) and those that use a magnetic field (phones and other gadgets, magnetic digital storage media, credit and other cards, headphones).
Before the procedure, make sure that your cosmetics do not contain metal molecules, the presence of which will distort the magnetic field and, as a result, the overall picture of the study.
- During a clinical study, it is imperative to protect your hearing from mechanical vibrations (the device is very noisy) using special headphones.
- Before going to bed, you should definitely find out the following things: what are the advantages of the procedure and how its implementation will help in treating or identifying the disease, how the MRI study will be carried out, whether you have any individual contraindications for its implementation, whether contrast is used, if so , then for what purpose.
- There are no restrictions on the intake of food and drink, except for the intake of psychotropic and narcotic substances, which include alcohol.
- When conducting an examination with contrast, the doctor may recommend not eating anything for 3-4 hours before visiting the tomograph.
If you have a fear of small and confined spaces, be sure to notify your doctor. He may decide to administer a sedative before the procedure.
How is an MRI performed?
Before the procedure, the radiologist questions the patient about the presence of contraindications to the study. The patient is asked to remove any metal accessories, including clothing with metal fittings, and lie down on a couch, which is then placed in the CT scanner tube.
During the diagnosis, it is strictly forbidden to move, as this may affect the clarity of the resulting images.
Scanning procedure
High-field tomographs produce a fairly high level of noise, which can cause some discomfort to patients. The medical department will provide you with headphones that will play pleasant music, drowning out the sounds of the operating device.
The tomograph scans the patient’s body in different projections and instantly transmits the images to the computer screen. The interpretation of the results by the research physician begins even before the procedure is completed.
Getting Results
Scan results are available immediately after the end of the study. Many of the images obtained are carefully examined by a radiologist, and a detailed report is drawn up describing both the normal anatomy of the area under study and possible abnormalities and pathologies.
15-30 minutes after the procedure, the patient is given a written report and a computer disk with the resulting images.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern, safe type of radiation diagnostics that allows you to obtain accurate and quick results and thoroughly examine the area under study. MRI helps to identify many diseases and abnormalities even at the initial stages of their development.
| MRI of the pancreas in Rostov-on-Don |
| How to do an MRI of the brain |
| MRI of the abdomen with contrast |
| MRI of the spine, what does it show? |
| MRI of ureters |
| MRI of the abdominal cavity, which organs are checked? |