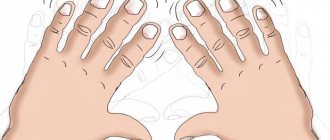
Hand tremors are rapid, involuntary, uniform movements of the upper limbs caused by muscle contraction. They are caused by a delay in corrective neural signals. Hand tremors most often occur in emotional people. With overwork, strong emotions, anxiety, pathologies of the nervous system, tremor increases significantly. But emotional tremor of the hands can also occur in a state of relaxation, when the hands move towards the target and are extended. The intensity and frequency of the shaking may increase or decrease.
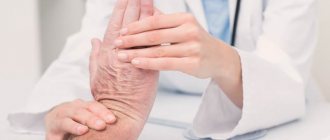
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital treat hand tremors on an individual basis. An effective therapy program is selected for each patient depending on the factors that provoked the onset of this disease.
Clinical picture
Hand tremors are the first and often the only symptom of the disease (can manifest from several months to several years). Trembling appears some time after the start of drug treatment (weeks, months). The tremor intensifies after the next dose increase or overdose of the drug. After discontinuation of the drug, trembling in the limbs decreases significantly, gradually disappears completely or can persist, but the amplitude decreases over time. Drugs most often increase the so-called physiological tremor. Trembling in the hands when trying to maintain a certain posture increases with purposeful movements in them (60–80%), less often trembling occurs at rest (20%). The tremor stops during sleep (90%), intensifies during physical and emotional stress (50%). In 10% of cases, head shaking is observed. An objective examination of the patient reveals symmetrical involvement of the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints in tremor. Postural tremor of the hands (80%), intention tremor in the hands (60%), resting tremor (25%), gross pathological postural-kinetic tremor (20%) are noted. Tremor characteristics: frequency 8–12 Hz, low amplitude. Head tremor (10%).
Symptoms and diagnosis
Tremor is a pronounced pathology, so it does not go unnoticed by the patient. The intensity of the tremors depends on numerous factors. In most cases, patients have shaking limbs and facial muscles. Trembling throughout the body is much less common, but may indicate more serious illnesses.
Signs of pathological tremor:
- the appearance of tremors at rest;
- inability to perform activities of daily living (eg, holding a spoon, tying shoelaces);
- the occurrence of intense tremors after taking alcohol or medications;
- impaired fine motor skills of the hands;
- paroxysmal nature of the pathology;
- increased vibrations when holding a certain position;
- violation of general coordination of movements.
To prescribe an effective medicine for tremor, its cause is first determined. For this purpose, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, which includes both laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
Diagnostic procedures include:
- study of anamnesis;
- MRI and CT scan of the brain;
- cardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- encephalography;
- general urine and blood tests;
- neurological examination and functional tests.
Treatment is prescribed based on the results of a diagnostic examination. This takes into account the individual characteristics of the clinical picture, the condition and age of the patient.
Treatment of drug-induced tremors
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist. Discontinuation of the drug that caused the tremor is indicated; β-blockers are prescribed to correct tremor.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Cyclodol (antiparkinsonian drug). Dosage regimen: orally, during or before meals at an initial dose of 0.5-1 mg/day, then it is gradually increased by 1-2 mg every 3-5 days until the optimal effect is achieved; frequency of administration is 3-4 times a day. Maximum doses for adults: single - 10 mg, daily - 16 mg.
- Amantadine (antiparkinsonian drug). Dosage regimen: orally, after meals at an initial dose of 100 mg/day, if necessary after 1 week. it is possible to increase the dose to 200 mg/day; the maximum daily dose is 400 mg.
- Anaprilin (non-selective beta-blocker). Dosage regimen: initial dose 40 mg 2-3 times a day; if necessary, the dose is gradually increased to 160 mg/day.
Why are your hands shaking?
The condition is called hyperkinesis. Accompanied by uncontrolled and unexpected movements of the body or its parts. It occurs due to alternating contraction and relaxation of muscle tissue. As a rule, alcoholic tremor involves only distal or distant parts. Pollen, facial and tongue muscles are mainly affected.
Hand trembling is observed in the following cases:
- Chronic dependence on alcohol.
- Acute intoxication due to alcohol consumption.
- Withdrawal syndrome.
A benign tremor is present. It has a hereditary predisposition and develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, Parkinson's disease and various endocrine disorders. Therefore, when a symptom occurs, it is extremely important to conduct a full diagnosis to find out the causes of the symptom.
The mechanism for the development of tremors is as follows. When an alcoholic drink is regularly introduced into the body, it no longer has time to break down into safe compounds. As a result, toxins accumulate, negatively affecting the condition of the brain , the cerebellum especially suffers. As a result, the gait is disrupted, it is more difficult to keep the body in an even position, and the hands shake. Long-term alcohol consumption can cause cerebellar degeneration. This leads to disruption of connections between the lobes of the brain, which leads to changes in motor coordination.
It is noteworthy that disruption of connections between the frontal lobes and the cerebellum is typical for middle-aged men. Therefore, when drinking alcohol, they most often experience hand tremors. Degeneration is provoked by regular intoxication of the body. It progresses slowly, so the symptom is observed more often in those who have a long history of alcoholism. At the same time, tremor can develop due to alcoholic encephalopathy. Characterized by damage to the brain body.
Recommendations
Consultation with a neurologist and electroneuromyography are recommended.
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in Russia: |
| Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Russian State Medical University, Professor, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Gusev E.I. | |
| • | Leading specialists and institutions for the treatment of this disease in the world: |
| G. AVANZINI, Italy. |
Tremors - how to get rid of it after binge drinking
When deciding how to relieve tremors after binge drinking in a particular patient, doctors set as their goal the prevention of the development of more dangerous manifestations of withdrawal syndrome. The patient’s motivation to treat alcoholism is increased and they are convinced that they need to give up further drinking. Afterwards, a diagnosis is carried out and it is determined which of the available medications can be used.
Non-drug methods of dealing with the problem
To reduce tremor, you need to eliminate all irritating factors that affect a person. This refers to sound stimuli, bright light, unpleasant tactile contacts, etc. It is also important to restore a healthy water-salt balance, stop dehydration, and normalize blood sugar levels.
It is more likely to achieve positive dynamics if you include B vitamins in the therapeutic regimen. They stabilize the activity of the central nervous system.
Medicines that help combat tremors
Under no circumstances should an alcohol addict self-prescribe medications. Only an experienced doctor can determine which remedies are suitable for a particular patient. Self-medication for shaking is fraught with serious complications.
More often than others, the following are used to relieve negative symptoms:
- Benzodiazepine tranquilizers. Scientists have found that drugs from this group help in the treatment of alcohol addicts. They activate the activity of GABA-A receptors, due to which nervous and muscle excitability quickly decreases. At the same time, they treat insomnia and calm you down.
- α-2-agonists and β-blockers. With the help of drugs from these pharmacological groups, it is possible to relieve the patient from tachycardia, arterial hypertension, and tremor.
- Anticonvulsants. Some of the drugs in this group effectively block NMDA receptors. Thanks to this, the problem of shaking becomes less pronounced. True, you cannot take strong anticonvulsants for a very long time - disturbances in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract will occur.
- GABA-B receptor antagonists. Indicated for involuntary muscle spasms and shaking. They reduce the excitability of nerve and muscle fibers, having a stimulating effect on GABA-B receptors. Compensate for NMDA receptor dysfunction caused by withdrawal symptoms.
- Medicines whose structure of active ingredients is similar to GABA. They help with epileptic seizures, normalize nerve conduction and the activity of the ANS.
- Anticonvulsants, working in several directions at once. This refers to drugs that inhibit the activity of the nervous system, block AMPA and NDMA receptors, reducing the production of dopamine. With such a complex effect on the body, medications for seizure syndrome help well with ANS hyperactivity.
After the examination, the doctor will select the medications that are indicated for the patient and determine their dosages. An alcohol addict will only have to strictly follow all medical prescriptions.
But you need to understand that overcoming tremors is not yet a victory over alcohol addiction. In order for the problem to remain in the past forever, coding should be carried out. Only then can the patient be sure that he will never again encounter the unpleasant symptom of trembling of the hands, legs, face, and whole body.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 2.7 | 3.5 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 3.5 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.8 |
Hand tremors - causes and treatment + medications and recommendations
In the practice of a therapist of almost any specialization (pulmonologist, cardiologist, gastroenterologist) there are patients who either complain of trembling in their hands, or it is detected during an examination. And then the doctor needs to figure out whether this trembling is a symptom of the disease with which the patient came in, or whether it is a concomitant symptom and is not associated with the underlying pathology.
Perhaps, neurologists find themselves in a more advantageous position, since tremor, or trembling, is studied in detail in the course of neurological diseases. Consider such a common symptom as trembling hands.
Hand tremors - what is it?
Hand tremor is a state of trembling of the hands, which can be either short-term or permanent, symmetrical and one-sided, pronounced and erased, with a high amplitude and frequency of trembling and with a low one, dependent on volitional effort and not subject to it.
As you can see, hand tremors have many characteristics that the doctor needs to understand together with the patient, since it is the methods of questioning and examination that are of primary importance in the diagnosis of tremor of all types.
There is nothing easier than checking your own body for tremors. To do this, you need to stretch your arms forward, spread your fingers and hold them in this position for at least a minute. Most often, if trembling is noticeable from the first seconds, it will gradually intensify as fatigue in the hands increases.
Sometimes trembling in the hands can be observed in a completely healthy person, but only for a short time, and only when exposed to strong emotional stimuli (excitement, strong fear).
There are many causes of tremor and treatment directly depends on them. Obviously, alcohol tremors or hand tremors in a child are completely different things.
Polyneuropathy, what it is, its causes and how it is treated: https://medknsltant.com/polinejropatiya/
Causes of hand tremors
The causes of hand tremors can be divided into two large groups. The first group includes physiological tremor, which is a functional disorder, may be temporary and does not indicate any disease.
Its reasons are:
- Increased emotionality. Asthenic, neurotic individuals and artists may experience hand tremors during excitement;
- Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, traces of emotional stress;
- Character accents. Thus, with hysterical psychopathy, a person may experience tremor of the head and hands at certain intervals;
- Drug reaction. Some drugs increase the convulsive readiness of the nervous system: some antidepressants, adaptogens (Rhodiola rosea, golden root, extracts of ginseng, Schisandra, Eleutherococcus), lithium preparations, aminophylline, some antipsychotics;
- Trembling in the hands can be caused by drinking strong coffee, tea, or strong cigarettes;
- The use of drugs such as amphetamines causes tremors in the hands;
- A pronounced example of tremor in a healthy person can be chills during hypothermia, after heavy physical work (for example, working as a loader);
It is important that all these types of physiological tremors have an external factor, upon the exclusion of which the condition should disappear. You should consult a doctor if the tremor does not disappear 15 days after normalizing your lifestyle.
Pathological tremor can, as a rule, indicate either poisoning (chronic), or a nervous disease, or other causes, for example, endocrine. Frequent causes of pathological trembling in the hands, which is a symptom of the disease, are:
- Poisoning, for example, lead, carbon monoxide, strychnine;
- Chronic alcoholism and withdrawal syndrome are a separate line;
- Severe tremors in the hands are caused by hypoglycemia, which occurs with type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin-dependent);
- Thyrotoxicosis and pathology of the adrenal glands also provoke prolonged tremor;
- Chronic liver failure, with severe jaundice in fulminant forms of viral hepatitis. In this case, a “popping” tremor occurs - the hands tremble even if the person is lying in bed;
- Damage to individual brain structures: brain stem, cerebellum, extrapyramidal nuclei causes persistent tremor, as in other extrapyramidal disorders. Trembling of the hands when the cerebellum is damaged is called intentional: the swing of the hands increases when trying to reach any object;
- Familial forms caused by hereditary predisposition;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease;
- Hepatocerebral dystrophy, or Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases (acute disseminated encephalomyelitis);
- Progressive forms of tick-borne encephalitis, encephalitis and chronic encephalomyelitis;
- Anemia, including hereditary, conditions associated with chronic blood hypoxemia: helminthic infestations, habitual blood loss due to hemorrhoids, ulcerative colitis and chronic gastric ulcers;
A separate nosological form is essential tremor, which can be familial in nature, but there are no disorders of other systems. Hence the name - “essential”, which can be replaced with something else: “trembling for unknown reasons”.
Based on the description of some of the reasons, it becomes clear that the problem of tremor is very complex, and doctors cannot approach its explanation “carelessly.”
There is an unhealthy practice, without understanding it, to immediately diagnose a patient, especially after 60 years, with “Parkinson’s disease”, and send such a person to the center of extrapyramidal pathology.
As a result, it turns out that the person does not have Parkinson’s disease, but he turns out to be unnecessary to any of the doctors. Therefore, the problem of timely diagnosis of symptomatic tremors is acute for clinicians.
Causes of Parkinson's disease and the role of hereditary factors: https://medknsltant.com/bolezn-parkinsona-simptomy-i-priznaki-lechenie/
Tremor degrees
All manifestations of trembling in the hands must be classified according to the degree of severity, since sometimes this serves as a reason for transferring the patient to disability, due to persistent disability. Tremor is divided into:
1) Slightly expressed, or appearing at certain periods of time, which are significantly shorter than the normal state. Tremor does not affect the patient’s lifestyle or quality of life in any way;
2) Moderate tremor. The patient is sometimes forced to change jobs, since he cannot control subtle and small movements. Some social functions suffer: for example, in a restaurant or at a party a person may break a crystal glass, etc.;
3) Significantly pronounced tremor. With it, the patient cannot serve himself: with a glass of water he can break his face and teeth, he is forbidden to use a fork, as he can gouge out his eye, such a person cannot hold a book, he is forced to put it on the table, but at the same time turning the pages will be difficult.
Writing and typing text on a computer is also extremely difficult. Such persistent hand tremors occur with multiple sclerosis with damage to the cerebellum, as well as with hepatocerebral dystrophy and encephalitis.
Tremor in a child
Previously, we looked at the types of hand tremor in adult patients and this assumed that they have a fully mature and functional nervous system. If you are considering hand tremor in a child, you need to keep in mind that this symptom may be temporary.
It may simply arise due to the unpreparedness and underdevelopment of the nervous system to receive and transmit impulses due to incomplete maturation of the peripheral nerves.
As a rule, this type of disorder occurs against the background of emotional stress and the release of norepinephrine into the blood. This is usually a signal for active muscle contraction and increased utilization of oxygen and glucose by the muscles, but the muscles react with trembling.
It is important for the pediatrician to know that the baby overcame the critical periods of intrauterine development without “adventures”, and during pregnancy there were no diseases, intrauterine fetal hypoxia, or phenomena of fetoplacental insufficiency.
Other causes of tremor may include intrapartum (perinatal) birth trauma, threatened miscarriage, prematurity, rapid labor, congenital diabetes mellitus (diabetic fetopathy), or congenital syphilis.
Under normal conditions , with the correct development of the child, most often after reaching the age of one year, hand tremors in babies disappear. Otherwise, observation by a pediatric neurologist and subsequent treatment are required.
Alcohol tremors
Tremor of the fingers of drunkards became part of folk proverbs and sayings, and became the subject of theatrical miniatures. In fact, the toxic effect of ethanol on the nervous system is to blame, which results in the development of toxic polyneuropathy.
As a rule, the tremors are worse in the morning. In the initial periods of alcoholism, tremor is expressed inconsistently, but over time it becomes constant.
- It can be treated only with the condition of complete abstinence from alcohol, otherwise all detoxification methods will be ineffective.
Essential hand tremor
A few words have already been said above about essential tremor. To complete the picture a little, it should be said that this disease is common in 2% of the young population, under the age of 40, and much more often in old age.
Hand tremors occur with a frequency of 8-10 times per second, sometimes tremors of the head, legs, and voice join the movements.
Essential tremor should not be confused with Parkinson's disease: Parkinson's sufferers experience “freezing of posture,” muscle rigidity, propulsion, and “jagged” hypertonicity. In addition, with essential tremor, unlike Parkinson's disease, there is no progression, and patients retain memory, intelligence and the ability to self-care for a long time.
This disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, from parents to offspring.
"Atarax": instructions for use
"Atarax" is a tranquilizer, quite often used as tablets for hand tremors. The main active ingredient is hydroxyzine hydrochloride. Doctors prescribe Atarax as a sedative for children aged three years and older. Atarax can also be used as part of a complex treatment for hand tremors in older people. You can purchase the drug at any pharmacy if you have a prescription from a doctor.
Reviews from patients report that sleep improves while taking it. Anxiety and suspiciousness become less or disappear completely. As a rule, Atarax is rarely prescribed as an independent remedy; it is usually used as part of a complex treatment of psychosomatic disorders or neurological diseases.
Features of taking Phenazepam for tremor
"Phenazepam" has bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine as its main active ingredient. With prolonged use, it can cause drug dependence even stronger than Phenibut. Before purchasing, you should get a prescription from your doctor. Phenazepam is not sold without a prescription, as the substance is classified as psychotropic.
The drug has the following effects:
- sedative;
- hypnotic;
- muscle relaxant;
- anticonvulsant;
- amnestic.
A prescription for Phenazepam can be obtained from a doctor if the patient suffers from insomnia, nervous tics, alcohol or drug withdrawal. Also, this drug is often prescribed to patients if they have started taking antidepressants. Then the duration of use of Phenazepam should not exceed two weeks. In psychiatry, Phenazepam is prescribed as part of complex therapy to patients with hallucinations of various etiologies.
If at the initial stages of using the drug a person experiences drowsiness and positive emotions, then after about a few months (with continuous use of Phenazepam) a “rollback” occurs. The person becomes irritable and angry. If drug dependence has developed, the drug should be discontinued gradually. In some cases, it may be necessary to cover it with other tranquilizers or even antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptics). Therefore, it is better not to experiment with taking Phenazepam on your own.
"Grandaxin": instructions and patient reviews
The main active ingredient is tofisopam. The drug belongs to the class of anxiolytic drugs, i.e., it has a pronounced anti-anxiety and sedative effect, and its use has a beneficial effect on sleep. Neurologists often prescribe this drug for hand tremors at a young age, but many older people have also benefited from this medicine.
Indications for use:
- anxiety disorders;
- insomnia;
- abstinence period in chemically dependent people;
- depressive disorders.
"Grandaxin" for tremor helps if the condition is provoked by the conditions mentioned above. During treatment, patients improve their sleep and psycho-emotional state. Nervous tics and tremors disappear. Reviews from patients also report that it improves performance, gives them energy for hobbies and sports.
General characteristics of the condition
Tremor is an involuntary rhythmic contraction of muscles that a person cannot control. The process involves one or more parts of the body (most often it occurs in the limbs, less often in the head, vocal cords, and torso). Patients in the older age category are most susceptible to chaotic muscle contractions. This is due to weakening of the body and concomitant diseases. In general, tremor does not pose a serious threat to life, but it does significantly reduce the quality of life. The shaking can be so severe that it prevents a person from lifting small objects or sleeping peacefully.
Possible reasons for development
Content:
- General characteristics of the condition
- Classification of involuntary contractions
- Features of therapy
In most cases, tremors are caused by injuries or pathological processes in the deep layers of the brain responsible for movement. Involuntary contractions can be a symptom of multiple sclerosis, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases (for example, Parkinson's disease). They may also indicate kidney/liver failure or a malfunction of the thyroid gland. In medical practice, a predisposition to tremor due to genetic factors is often encountered.
Sometimes trembling does not indicate a disease, but is a protective reaction of the body to external stimuli. Among them are mercury poisoning, alcohol intoxication, and severe emotional stress. In this case, the tremor is short-term and disappears along with the stimulus.
Trembling never occurs for no reason. If you cannot explain the origin of the tremor or its intensity seems frightening, consult a doctor.
"Pantogam": a nootropic drug with a long-term effect
Taking Pantogam for tremor is advisable if the condition is triggered by stress. There are two forms of release of the drug - syrup and tablets. The syrup is usually prescribed to children aged six months and older. while taking Pantogam, the ability to learn increases, memory improves, and a person becomes more positive. Irritability, suspiciousness, and anxiety go away.
The main active ingredient is hopantenic acid. This substance began to be used back in the Soviet years, and it has established itself as a relatively safe remedy for a number of neurological pathologies. Hopanthenic acid exhibits moderate anticonvulsant and nootropic activity, increases the brain's resistance to toxic effects during hypoxia of various origins. The drug is prescribed to both elderly people and young children for various types of neurological disorders, decreased learning ability, and developmental delays.
"Pantogam" is relatively rarely used as a drug for hand tremors. However, in complex therapy it is prescribed for many neurological disorders. Pantogam has a significant advantage: the effect lasts for about a month from the moment of discontinuation. This is one of the few drugs with a truly prolonged effect. In addition, Pantogam can be purchased at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.