The question of how much a human brain weighs and how an individual’s intellectual abilities depend on its mass has interested scientists since ancient times. For example, Archimedes, who lived in 300 BC, calculated this indicator by immersing his head in a container of water and using the liquid that spilled out, using mathematical calculations, he calculated the estimated weight of this organ. This method, of course, did not give the true result, but the very fact that they were interested in this back in those days is amazing.
At the moment, it is known that the mass of a person’s brain is approximately equal to 2% of the weight of the entire body, however, such a judgment is inaccurate, since the indicator changes throughout life and depends on many factors.
Energy consumption
The brain volume of any modern person exceeds that of any animal. The energy consumption of this organ will surprise most people to learn that about half of the glucose produced in the liver is consumed by the brain. The figure can be about 20 percent of the body's energy, or more clearly 10-15 W with a light load.
Active mental activity requires up to 25 W of power, and among scientific luminaries this figure sometimes reaches 30 W. In this case, a much larger number of electrical impulses are generated than all the computer technology on the planet produces. The mass of the brain is much smaller by orders of magnitude.
Evolution has created a more efficient mechanism for processing received information, compared to the technical solutions of people.
Functions
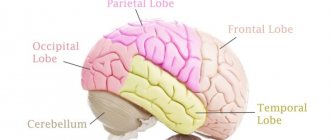
All parts of the brain stem are equally necessary. They provide people with the opportunity to smell, hear sound, understand speech, think about any serious things. If not for them, humanity could have remained in the Stone Age forever.
The functions of the brain stem are reduced to the distribution of information between the brain and the central nervous system. They are provided by nuclei and nerve endings. In this case, the trunk is a physiological connecting step between the spinal cord and the brain. If it is damaged, then signals from the brain will not be able to reach the end point, which will completely eliminate the normal functioning of the human body.
There are several groups of functions that are characteristic of the brain stem. Among them:
- Motor. This includes all actions associated with the muscles of the eyes and eyelids. The function is also responsible for the reflexes of the eyeballs and controls the chewing muscles.
- Sensitive. Ensures the functioning of taste buds, as well as all reflexes that affect the digestive system. Helps transmit signals for swallowing and many other actions, including even vomiting. Additionally responsible for sneezing.
- Parasympathetic. Affects movement and dilation of the pupils, controls the ciliary muscles. Managed by cores, ensuring the execution of a block function.
- Upper salivary. It affects the salivary glands, ensuring timely and necessary formation of saliva.
- Vestibular. Responsible for the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, which helps control body balance and stay on your feet.
- Swallowing. Ensures the swallowing reflex works. Complements the work of the sensitive function.
- Auditory. Transmits information to the cerebellum, is responsible for hearing, as well as recognizing heard sounds.
- Sensory. Gives sensitivity to the skin on the face, analyzes taste and sound, and recognizes vestibular stimuli.
The brain stem has the most important functions. It gives every person the opportunity to hear, feel, see, move, think. All of them are necessary for a full life.
If you distribute individual functions across parts of the brain stem, you get the following:
| Brainstem region | Functions |
| Midbrain | · Functioning of visual and auditory organs; · Management of relevant bodies; · Orientation in space. |
| Medulla | · Reflexes associated with coughing, vomiting, sneezing; · Breath control; · Cardiovascular system management; · Functioning of the digestive tract. |
| Pons | · Providing blood supply to the brain; · Fast transmission of signals between the brain and the central nervous system. |
| Cerebellum | · Coordination of movements, balance; · Muscle tissue tone. |
| Diencephalon | · Function of the thyroid gland; · Control of the adrenal glands. |
The importance of such functions makes us take the condition of the brain stem more seriously. He is no exception and may be susceptible to various life-threatening diseases.
If there are disturbances in one section of the trunk, failures may occur in others, because they are all closely interconnected.
Anthropometry
It is difficult to accurately determine the volume of the human brain in our time. Doctors mainly resort to empirical formulas to calculate the physical dimensions of an organ. So the overall dimensions of the skull in centimeters are taken, multiplied, a couple of coefficients are added and an approximate result is obtained. Moreover, the linear size of the skull of men and women is calculated using different formulas.
conclusions
The brainstem is the most important part of the brain, as well as the entire body. The general condition of a person depends on his health. The slightest damage can cause serious consequences: loss of hearing or vision, inability to taste food, or maintain balance. The most dangerous is damage to the respiratory center, which leads to respiratory arrest. Prevention of brain stem diseases consists of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding head injuries and timely elimination of factors that can trigger the pathological process.
The bigger, the better
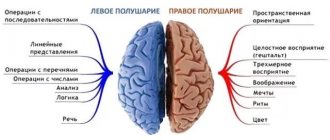
There is an opinion: the larger the brain, the smarter its owner, be it a person or an animal. Everything is correct. In terms of mental abilities, mammals are far superior to worms and insects, and apes are far superior to their less developed relatives. Well, depending on how you look at it: birds, worms and monkeys have enough brain size to survive in their familiar environment, but humans constantly adapt their habitat and lifestyle to suit themselves. And in the last century, this process has outpaced the lifespan of people: over the course of a generation, the world changes so much that a person needs to continuously learn in order to live in it, or go into the jungle.
Now about the interesting stuff.
- Research from the 19th century and modern times does not indicate that brain mass has increased.
- In insects, its role is replaced by nerve nodes and a chain.
- Anatole France's brain weighed half as much as Ivan Turgenev's.
- If after more than 20 years the adult brain begins to lose approximately 1 gram per year, and closer to 50-60 the figure grows to 2, and sometimes 3 grams, then after 60 years this figure of mass loss can exceed 4 grams per year. Interestingly, acquiring new skills and knowledge and engaging in intellectual activity do not have a positive effect on brain weight. It grows only in children and adolescents.
- The maximum weight of the organ was recorded in an idiot and an epileptic, and it did not function fully.
Conclusion: it doesn’t matter how much a human or animal brain weighs. More important here are the ratio of organ mass to body mass and the number of connections between neurons. It’s not for nothing that science has established that an active person (reading books) uses about 5% of his intellectual potential. For someone new to mental activity, 3% is enough, and it doesn’t matter whether it’s a woman or a man.
The number of neurons also says little about the capacity of the cranium: with equal numbers in different species of animals, some differ significantly in intellectual abilities, but only in solving problems proposed by humans.
Weight in society depends on brain weight
It seems that logically it turns out like this: the larger the brain, the smarter its lucky owner should be. And you don’t have to look far for examples: mice with one-gram brains run around the fields, monkeys with their measly 400 grams sit in the zoo, and homo sapiens pores in front of a computer monitor from morning to night. Where should he go? He needs to use his entire 1400 grams, enclosed in his skull, somehow. So he draws drawings of spaceships and proves Poincaré's theorem.
But here’s a paradox: why doesn’t other inhabitants of the Earth with a brain several times larger help him - the elephant (5 kg) or the sperm whale (7 kg)? It turns out that intelligence depends not so much on the size and weight of the brain, but on the ratio of its weight to the total weight of the whole body. And here man has no equal. For example: in humans, the ratio of body weight to brain weight is only 50 points (70 kg divided by 1.4 kg), while in a cow it is 1000, in a dog it is 500, and in a chimpanzee it is 120. Our weight competitors, sperm whales, generally have 3000 points. Among our smaller brothers, only dolphins are close to us “in mind”: with a brain mass of 1700 grams, they have a 135-kilogram carcass, that is, the ratio is 80. In general, in comparison with animals, we win. How does the difference in brain weight affect the human race? We addressed this question to the famous Russian scientist, Professor of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Biological Sciences, Head of the Embryology Department of the Research Institute of Human Morphology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Sergei SAVELIEV.
Professor of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Biological Sciences, Head of the Embryology Department of the Research Institute of Human Morphology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Sergei SAVELIEV.
Brainy Lazy People
— Sergey Vyacheslavovich, the encyclopedias say that the heaviest brain among Caucasians is 1375 grams, and the lightest among indigenous Australians is 1185 grams. Why did God deprive them?
“God has nothing to do with it, it’s a matter of geographic isolation,” explained Professor Savelyev. — Even tens of thousands of years ago, people were distributed across various regions of the globe, and their brains began to form depending on the complexity of the environment. The constant search for different options for survival in a changing climate is what developed the brains of Caucasians to a certain size. The lucky ones who populated the warm regions did not need to strain their brains too much, which is why it apparently slowed down with the masses. Negroids, by the way, have a brain mass higher than that of Australoids, by only 59 grams.
— It turns out that if Australians move to places with a harsher climate, their brains will increase?
— Perhaps, but not right away. The brains of homo sapiens took tens of thousands of years to form, and to radically enlarge them, it will take about the same amount of time.
— Do Russian brains by any chance win in the weight category?
— No, we don’t take prizes. The brain mass of Russian people, according to the most average data, is 1399 grams. And we are in fourth position after the Belarusians (1429), Germans (1425) and Ukrainians (1414). Our brains are followed by Korean (1376), Czech (1368), English (1346) brains. The list is completed by the Americans (1323), Japanese (1313) and French (1280).
- Such advanced peoples have such small brains?!
- Who told you that big brains are much better? The ordinary modern sybarite, who no longer needs to strain himself in search of all sorts of ways to obtain food and clothing, inherited big brains from his ancestors as a free application. He can achieve success only if he himself wants it and is active. However, a paradox arises here: among people with big brains there are more lazy people.
- No wonder: a large mechanism is always clumsy...
-...and requires large energy costs. Judge for yourself. In a “mindless” state, the brain spends 9 percent of all energy and 20 percent of oxygen, but as soon as a person thinks about something serious, his gray matter immediately absorbs up to 25 percent of the nutrients entering the body. The body doesn’t like this, it gets tired quickly, and therefore a person intuitively strives for an easier life. He has no equal in finding different ways to be lazy. But if the owner of a heavy brain overcomes his laziness, he can move mountains.
The most mysterious human organ, which sometimes puzzles even Dr. House.
A BIG DIFFERENCE
— As you know, the male brain is heavier than the female brain by an average of 130 grams. Why did we also not get enough during the distribution there, “above”?
— 130 grams is the average value typical for Europeans. The smallest difference in the mass of male and female brains between Buryats and Africans is approximately 85 grams. The difference between the British and Swedes is about 150 grams. And Japanese women are inferior to their spouses in terms of brain mass by as much as 168 grams.
— Does such a big difference prevent them from understanding each other?
- It interferes. It is not for nothing that men and women are compared to the inhabitants of different planets. The cerebral cortex of a man contains about 11 billion nerve cells, and that of a woman - about 9, that is, 2 billion less. And women have very few neurons in the associative areas: a man has about a billion neurons there, and a woman has 300,000. And these are very important areas, they are involved in the processes of remembering, learning and thinking, and the results of their activity make up what is usually called intelligence. And there is no way to compensate for this shortcoming. Even if you hire a hundred teachers, the woman will not become smarter. If there is no substrate, then there is nothing to learn.
- How many brains do you need to have to proudly bear the name “man”?
— The minimum brain mass that does not affect social behavior is close to 850 grams. That is, this mass is enough to be called a “reasonable person.” I will say more, it was widely believed that in order to develop speech, a person must have a brain mass of at least 1000 grams. But recent special observations of people with normal(!) intelligence and a brain mass of less than 900 grams have refuted this point of view. In addition to this case, several other people were known in the world with a brain mass of 870 to 700 grams, who also - oddly enough - did not experience speech and social difficulties.
- Those who are born with a very small brain of 200-300 grams - microcephalics - live long?
— Scientists have studied more than 60 cases of microcephalic survival. They live 25-30 years. There was only one case when a woman with a brain mass of 277 grams lived to be 74 years old, although in a psychiatric clinic. Studies have shown that with a brain mass of 232 to 622 grams, microcephalics could pronounce individual words and lead an extremely simplified social life. These were mostly shepherds, wood gatherers, village fools, and inmates of almshouses or psychiatric clinics. It is interesting that in such people one part of the brain remains the most intact - the olfactory one.
BYRON IS “HEAVIER” TURGENEV
- It was always believed that Turgenev had the largest brain mass - 2012 grams. But then suddenly our genius was “outweighed” by Byron with a brain of 2230 grams?
— The data on Byron’s brain is not entirely correct, since there is information about a number of pathological processes in his brain. In general, it is very significant that a large brain mass is usually the result of unhealthy processes. Thus, the maximum brain mass of 2850 grams was found in a 21-year-old idiot who suffered from epilepsy. Therefore, experts today are of the opinion that the species limit for the maximum mass of a healthy human brain is 2200-2300 grams. The only exception to this rule so far is a black African who had a brain mass of 2480 grams and was completely healthy.
— Do people with big brains have high intelligence?
- Not always. Let's put it this way: they have a greater chance of becoming geniuses. With an average human brain weight of 1400 grams, in gifted individuals the brain in 72% of cases exceeds the average weight. Calculations show that a person with a brain mass above average is about 6 times more likely to have special abilities than someone with a small brain. This pattern does not mean that all people with small brains are obviously mediocre. It’s just that the likelihood of developing above-average abilities is significantly reduced.
- Can ordinary people without special talents have big brains?
- Certainly. There were cases when the brain of ordinary workers even exceeded the mass of the brain of the most outstanding personalities. The size of a headdress cannot be a criterion for the intellectual abilities of its owner. To confirm this conclusion, an example is usually given with two famous writers: the same Ivan Tergenev and Anatole France. Against Turgenev's 2012 grams, France had only 1017 grams. The twofold difference in brain mass with similar literary talents refutes the assumption of a connection between people's abilities and a large brain.
Weighing the brains of gifted people has been done for more than 700 years. The main focus was on the brains of representatives of art, science, literature, politics and crime. The researchers hoped to find a link between brain size and talent or criminal tendencies. The connection between big brains and talent and small brains and criminal activity seemed clear. Numerous measurements of brain mass of people of various social groups, inclinations and realized abilities have shown that there are no obvious connections between brain mass and giftedness. Most likely, as recent studies have shown, giftedness does not depend on the mass of the brain, but on the mass of its specific parts. For example, the visual field can have a volume from 3 to 6 thousand cubic millimeters, respectively, a person with a small brain, but a maximum visual field will be a great connoisseur of painting, and a person with a large brain, but a small visual field will most likely not understand why people painting canvases with paints.
— How often are gifted people born?
- One in a thousand.
AFTER 50 YEARS, YOUR HEAD BECOMES LIGHTER
— Has the brain changed over time? Were the convolutions of our ancestors different from ours?
— Measuring the capacity of the cranium of peoples living for a long time in the same territory showed that the brain mass of cultural peoples slowly increases over time. These conclusions are based on measurements of skulls discovered in France and Egypt. For example, the capacity of a Parisian's skull 700 years ago was 35.5 cubic cm less than 100 years ago. And the Egyptians had 44.5 cubic cm more during the heyday of ancient Egyptian culture in the 16th-11th centuries BC than during the period of long decline in the 21st-18th centuries BC. This change is associated with both cultural and biological progress of humanity. Or maybe the reasons for the brain changes are related to the mixing of several ethnic groups. There has been a trend of increasing average brain mass across all races and ethnicities over the past 100 years. Thus, the mass of the male brain increased by an average of 42 grams, and that of the female brain by 41 grams. In Japan, for example, over 60-70 years of economic development, the average brain mass of Japanese people increased by 30 grams in men and by 15 grams in women.
- Does this mean that we are getting smarter?
— There is no solution to this phenomenon yet. This small but significant increase has been observed more than once in earlier human history. I am inclined to believe that the cultural development of society does not affect the shape and structure of the brain. If the brain changes slightly in mass, then only within the limits of metabolic variability (the process by which the body produces and expends energy for its vital functions), determined by the quality of nutrition of the mother during pregnancy and the child during the period from birth to 12-14 years. However, this increase or decrease in brain mass is the same in all ethnic groups and does not exceed approximately 20-40 grams. A permanent increase in brain size does not occur under any ideal social conditions.
— How does brain mass change with age?
— With age, a change in brain size occurs due to an increase in the size of the cells themselves and due to hydration, that is, water supply. The human brain increases in size until about 26-27 years of age. Then it enters a stability phase. Until the age of 50, no changes occur. But this does not mean that nerve cells do not die. Neurons die from starvation throughout our lives: due to the fact that the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. After 50 years, the death of neurons becomes more intense. This leads to the fact that the brain decreases by 30 grams for every subsequent 10 years. And if a person lives to be 90 years old, his brain will shrink by 120 grams. It's a lot. And not everyone remains completely adequate. However, this lack of brain weight is compensated by rich life experience and skills.
Table. How brain mass changes with age without taking into account gender and ethnic differences.
Correlations
Many people think that the modern human brain is slightly larger than that of an ape, but this is not true. Human intelligence truly surpasses the mental abilities of any animal; the dolphin comes second in intelligence, not the chimpanzee. The human brain can weigh up to 2% of body weight, that is, it is 50 or slightly more times lighter than the entire body; for dolphins the figure is about 80 times, and for chimpanzees it is about 120. But even this calculation does not provide high accuracy, after all, it has been established that in different mammals, intelligence largely depends on the area of the cortex (neocortex), which is increased due to the gyri.
Descending Paths
Descending projection pathways are a group of tracts that send neural information from the telencephalon cortex and subcortical formations to brainstem structures. These include:
- Pyramid path. This tract connects the motor gyrus with the motor nuclei of the brainstem. So, with the help of this path, a person manages to control the muscles of the neck, head, eyes, face and torso.
- Extrapyramidal pathway. Thanks to this tract, people maintain their balance in space.
Mass indicators
It is no secret that the female and male centers of the nervous system differ in weight. This was established in 1882 by Francis Gatton and has been repeatedly confirmed by scientists from various research institutes and centers around the globe.
This difference is 100-150 grams on average.
Weight
Finally, we come to the most interesting thing: how much a human brain weighs, and what is its average size. An organ with the following dimensions is considered normal:
- length (from the frontal lobes to the back of the head) – 160-175 mm;
- width – 135-145 mm;
- height (vertical section) 105-125 mm.
This is for an adult. For the elderly, children and adolescents, these numbers will be lower, as well as for those whose brains are influenced by environmental factors harmful to it (alcohol, drugs).
What is the average mass
The average value is considered to be 1.38 kg for the stronger sex and 1.24 kg for the fairer sex. Individual correlations can be 900 – 2000 grams. Highly intelligent people, professionals in any field of activity and creative individuals do not have increased brain mass. Its density is 1.038-1.04.
In children
Newborns and infants are distinguished by brain mass, which reaches 10% (350-450 grams is considered the norm) of body weight and decreases noticeably in the first years of its life and development. At two years old, for example, the weight fluctuates around 900 grams, and at six – 1.2 kg. Over the next 10-16 years, the brain gains only about 0.2 kg in weight.
High and low weight
The lightest brain that was recorded was a 46-year-old man. The weight was only 680 grams, and such a tiny organ did not have any effect on a person’s behavior and social skills. Although back in 1873, K. Focht established that the threshold for brain mass is in the range of 750-800 grams. Those who had a lighter organ were distinguished by the presence of microcephaly, simplified behavior, could have simplified speech, their development did not often differ from the mental abilities of children 3-6 years old. Such people led an almost asocial lifestyle, herding sheep, collecting firewood and berries.
The mass of the largest brain is 2850 grams, and its owner, as mentioned above, was an idiot and schizophrenic. In the same 19th century, the largest brain of a normal person was recorded. It was 2222 grams.
Brain Development
The human brain is part of the central nervous system, which controls the vital functions of the body. A large number of psychologists, doctors and other specialists are working on the study of this organ, studying the structure and connection of its integrity with the functioning of the physiological systems of the body.
The usual dimensions of the brain are 20x20x15 cm, and it has a complex structure, and each section includes several types of neurons.
As already written earlier, the average weight of the human brain ranges from 1100-2200 g, but generally falls within the range of 1100-1500 g, and reaches its maximum weight by the age of 27, and then gradually begins to decrease, losing an average of 1 year for 3 years
Prenatal development
The formation of the central nervous system during the intrauterine period of a child’s life begins in the 3rd week after fertilization of the egg. In this case, the neural plate first develops from the outer germ layer, which bends over time to form the neural groove. The edges of this gyrus fuse to create the fetal neural tube, from the front of which the child's brain is formed. In this case, the end of the tube is first divided into 3 sections or 3 primary brain vesicles. From the first, the cerebral hemispheres and the intermediate section are formed, from the second - the middle, and from the last - the cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
The development of the brain in the prenatal period occurs in parallel with the maturation of other structures, and the most ancient parts are formed faster and more actively, therefore, in a healthy newborn child, when born, unconditioned reflexes such as breathing, swallowing, etc. are fully functioning, and the weight of this organ at the time of birth is approximately 300-500g.
Natal state
Further development of the functions of the central nervous system continues after birth, and at the end of the first year of a child’s life, the mass of the brain located in the cranial cavity is approximately 1000 g. In an adult, this figure fluctuates around 1300 g. Based on this, it becomes obvious that the largest the rate of increase occurs in the first year of life.
By this time, the subcortical structures are almost completely formed, and the mass of the organ grows due to the division of glial cells and an increase in the number of dendritic branches, while the number of neurons remains the same, since they stop dividing during intrauterine development.
During this period, the final maturation of the projection areas originating from the receptors of the sensory organs and motor pathways occurs, while the greatest development occurs in the structures responsible for the regulation of the motor system and the activity of brain activity.
Period from 2 to 5 years
During this period, the weight of the brain increases due to the development of areas responsible for spatial orientation and purposeful movement, as well as complex psychological processes such as thinking, memory, and the assimilation of information received from the outside world.
Period from 5 to 7 years
The fields of the human brain responsible for the ability to learn and remember are the last to mature. Moreover, all mental processes occurring in the child’s brain (perception, attention, memory, thinking and imagination) are associated primarily with the development of speech, which in turn is formed under the influence of these functions.
Thus, the development of the brain occurs in several stages, and a failure in the formation of one of the levels entails a disruption in the maturation of the structures of the next stage and, as a result, mental and behavioral deviations.
Racial and national differences
Haplogroup also affects brain weight. Holders of R1A, which are the majority or a significant part of Russians, Ukrainians, Belarusians, Poles, Serbs, Indian Brahmins and a less significant percentage of representatives of other nations, are endowed with the most massive brain. Among Western Europeans and Asian peoples it is slightly less. African Americans have the lightest brain weight - it weighs approximately 100 grams less than that of white-skinned Americans.
Brain size doesn't always matter, at least not decisively. A man is not always smarter than a woman; their nervous systems are sharpened to solve various problems. But among various peoples it has been noticed that among the Slavs and their descendants, who carry the Y-chromosome R1A, there are more creators and inventors, which is no different for the Negroid population.
Vitamin complexes to support memory and attention for children
Among the popular vitamin complexes for memory for children are the following:
- Supradin for children - average price per pack is 400 rubles*. Vitamins come in the form of gummies, which is a big plus for children.
- Complivit - vitamins have interesting colorful packaging and shape. The average price per package is 300 rubles.
- Multitabs is a large complex for normalizing the emotional state. The average price per package is 700 rubles.