Dementia is a dysfunction of the intellect, its defeat, as a result of which there is a decrease in the ability to comprehend the connections between surrounding realities, phenomena, and events. With dementia, cognitive processes deteriorate, and there is a depletion of emotional reactions and character traits, often to the point of their complete disappearance. In addition, the ability to separate the important (primary) from the insignificant (secondary) is lost, and criticality of one’s own behavior and speech is lost.
Dementia can be acquired or congenital. The second is called mental retardation. Acquired dementia is called dementia and manifests itself in weakening of memory, a decrease in the stock of ideas and knowledge.
Early signs
The first signs of the disease are concentrated in the emotional sphere of a woman, in contrast to men, where disturbances are noticeable in the mental sphere. The female nervous system is more labile and less resistant to stress, so the first symptoms of dementia in women differ little from the manifestations of neuroses, short-term disorders and everything that in everyday life is called “nerves.” Women feel physical and psychological fatigue, a reluctance to do usual things, housework, devote time to their hobbies, and communicate with loved ones. Sick people stop taking care of themselves. They explain their condition by overwork at work or menopause. At this stage, women still retain a critical attitude towards themselves and their condition; they can still be convinced to see a doctor. Over time, frequent mood swings, tearfulness, touchiness, a desire to sort things out and start quarrels, unmotivated aggressiveness, or, on the contrary, isolation, a desire for solitude, and apathy appear. Later, signs appear that directly indicate impending dementia - loss of a critical attitude towards oneself, memory lapses, disorientation in time and space, expressions of ideas of danger and damage. Grandmothers complain that “their neighbors are irradiating them with invisible rays through the walls,” and that bandits are watching them. More tragic options are when elderly women, going out to the store, cannot find their way home and become victims of criminals and scammers.
It is important to recognize the early symptoms of impending dementia in order to combat it and slow the progression of the disease. The timely choice of a qualified, friendly doctor is crucial for the fate of the patient and his loved ones.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital help diagnose the disease in the early stages. The presence of the disease is confirmed by the results of diagnostic measures, which not only indicate pathology, but also identify its causes. Each patient is developed a treatment program and rehabilitation measures that slow down the progression of the disease. In this process, neurologists are assisted by doctors from other hospital specialties to make their own adjustments to achieve the most effective result.
Neurodegenerative diseases are also a serious problem for the patient’s family and friends.
At the Yusupov Hospital, specializing in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia, attention is paid to communicating with patients' relatives, teaching them care skills, observation, and ways to solve medical and social problems.
Prevention of dementia
Preventing dementia is quite difficult, since its causes are often independent of preventive measures. But still, you should adhere to the recommendations described below in any case:
avoid head injuries and concussions;
- Monitor your health, get examined by specialists, and treat chronic diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid excessive psycho-emotional stress;
- follow a daily routine, get at least 8 hours of proper sleep;
- take regular walks in the fresh air;
- alternate intellectual loads with physical ones;
- eat healthy and balanced.
Dementia is a serious illness. When a loved one suffers from dementia, it affects the entire family
It is important to understand and accept the situation, and do everything possible to treat the patient and preserve his remaining skills. Despite the fact that personality decline is an irreversible process, quality care and proper treatment can significantly slow down dementia
Only you can improve the quality of life of a sick loved one and give him a chance for recovery.
For mild dementia, the help of neuropsychologists and speech therapists will be necessary. NEAPL center specialists are ready to provide it. Contact us!
Signs in old age
The causes of dementia in women are identified within all types of the disease:
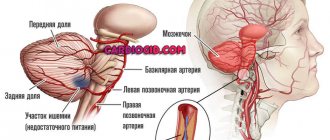
- Atrophic or degenerative form. It occurs with organic lesions of the brain, when cells of the nervous tissue die from various damage to the central nervous system: infectious, toxic, parasitic, trauma, inflammatory diseases of brain structures, the presence of oncological foci in them, etc. Atrophic and degenerative forms occur more acutely, with increasing symptoms of dementia. MRI studies reveal diffuse lesions of the cerebral cortex;
- Vascular form. The functions of the central nervous system change due to the pathological state of blood circulation, which is unable to ensure normal metabolic processes and trophism of the brain due to atherosclerosis and other lesions of the vascular network. The same reasons include heart disease: ischemia, valve insufficiency, and previous heart attacks. The largest percentage of causes of vascular dementia are strokes. It significantly aggravates the course of dementia and often becomes an independent cause of neurodegenerative degeneration of brain tissue. The vascular form is more typical for men.
- Mixed form. Combines many diverse causes of senile dementia from the field of endocrinology, psychiatry, narcology and other medical areas. Disorders of the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and reproductive organs in combination with vascular and cerebral pathologies often become the cause of dementia in women.
Foci of brain damage can be located in different areas and levels of the central nervous system:
- Cortical lesions;
- Subcortical lesions (pathology of the substantia nigra with muscle rigidity, stiffness, tremor);
- Cortical-subcortical lesions. Most often occur due to vascular causes;
- Multifocal lesions. Pathological multiple foci occur in the spinal cord and other parts of the central nervous system.
The patches spread over time, causing the severity of age-related dementia in women to worsen along with a variety of neurological symptoms.
Signs of Alzheimer's disease in the elderly depend on the severity of the pathological process and the duration of its impact. The main symptoms characteristic of various forms of the disease are noted:
- Loss of a critical attitude towards one’s condition;
- Memory problems;
- Decreased intellectual abilities, changes in speech, handwriting;
- Persistent depression;
- Anxiety, phobias, insomnia;
- Paranoid suspicion;
- Feeling of irritability, rudeness, dissatisfaction;
- Problems with choosing words and forming complete phrases;
- Difficulty communicating even with loved ones;
- Loss of moral and spiritual values.
Gradually, in the later stages of the disease, phenomena of confusion, loss of basic self-care skills, complete apathy, and personality disintegration develop.
Diagnosis and identification of the stages of Alzheimer's disease and subsequent total dementia, even for experienced neurologists, presents certain difficulties due to the diversity of individual manifestations. Modern diagnostic equipment comes to the aid of doctors, which allows them to differentiate the forms and stages of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The material and technical base of the Yusupov Hospital has a constantly updated fleet of diagnostic and therapeutic equipment produced by the world's leading companies for making accurate diagnoses.
Symptoms of the disease in young people
In the modern world, Alzheimer's disease is no longer considered a disease of old age. Every year, out of every 100,000 thousand, 90 people under 40 years of age fall ill. In studies of genetically predisposed patients, only 4.5% were found among young people. For others, the disease is considered acquired. For what reasons? Scientists all over the world are struggling with this mystery. It has been found that early Alzheimer's disease is caused by mutational processes in intracellular components that contribute to the death of nerve cells. Often these changes are triggered by the presence in the pedigree of a person with Down syndrome and other genetic disorders. The clinical picture of Alzheimer's in the young is extremely difficult to identify. The symptoms have long been similar to the manifestations of neuroses, chronic fatigue, and prolonged depression. But when characteristic signs appear: loss of short-term and then long-term memory, problems with assimilation of new information, difficult orientation in time and space, difficulties with speech, sudden weight loss, then the diagnosis of a neurodegenerative disease becomes obvious. Young people with Alzheimer's need intensive treatment and regular rehabilitation courses in order to delay the development of severe consequences for as long as possible.
Main factors in the development of cerebral pathologies
Brain diseases in older people do not arise out of nowhere.
Some vascular pathologies, in particular stroke, can take a person by surprise, but their development is preceded by invisible processes. The scourge of modern people - high blood pressure - is one of the main causes of cognitive impairment after dyscircular encephalopathy and stroke. Other factors:
- Atherosclerosis, as a result of which blood vessels narrow and cholesterol plaques appear on their walls;
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- Chronic cerebral ischemia;
- Mental and neurotic disorders, depression.
All these reasons obviously reduce the level of health and worsen cognitive abilities.
Stages of the disease in women
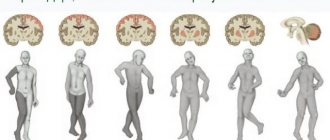
Forms of dementia go through their successive stages:
- Predementia. Occurs 7-8 years before the full clinical picture develops. It is expressed by weak negative cognitive manifestations, minor impairments in memory of recent events.
- Moderate stage. There is increased irritability, a tendency to attacks of headaches and dizziness. It is difficult to assimilate new information. Memory fails significantly, especially short-term memory.
- Difficult stage. It occurs individually for everyone. There are patients who progress from the first to the last stage in 3-4 years (mostly young or middle-aged women). There are also many who live with moderate dementia for another 18-20 years and manage to raise children and care for grandchildren. Age-related dementia in women, the rate of its progression may vary depending on genetic burden, the stability of the nervous system and the plasticity of the brain.
In the severe stage, the process of personality disintegration continues, the entire range of cognitive abilities is lost. There is physical and mental exhaustion, difficulty moving even within one’s apartment, simple everyday activities are performed with tension, and patients prefer to stay in bed all day. Due to congestion, infections of the urinary tract, bronchopulmonary system, bedsores and trophic ulcers develop. At this stage, the patient needs constant care.
Prognosis and prevention
With constant medical supervision, the prognosis for dementia in most cases is favorable: slow progress is observed, in some cases stable remission is achieved - the patient attends a regular school and copes with stress. It is worth remembering that the recovery process is very long and requires daily care and treatment. Prevention of organic dementia in children is difficult, since the disorder is a consequence of another disease. Supportive measures include careful attention to the child’s well-being, timely treatment of infectious and other diseases, and the creation of conditions to minimize the risk of injury. The development of psycho-emotional disorders is prevented by creating a favorable, friendly family environment and active time spent together.
www.krasotaimedicina.ru
Treatment of the disease in women
Dementia and Alzheimer's disease have no cure yet. But modern medicine and pharmacology have learned to eliminate painful symptoms, soften their manifestations, which can and should be fought, and delay the appearance of more severe forms. There are remedies that help normalize sleep, improve mood, correct behavior, and stop psychosis. For these purposes, a whole arsenal of medications is used: anti-dementia drugs that correct cognitive disorders. They compensate for biochemical disorders that lead to the death of brain neurons, without affecting the pathological process itself, but only mitigating its symptoms. At the same time, the toxic effect of glutamate, released by neurons during degeneration, is weakened. Cholinesterase inhibitors partially restore the loss of acetylcholine that occurs when nerve cells die. Not without success, doctors prescribe courses of hormonal and anti-inflammatory therapy, injections of extracts of animal brain tissue. Non-drug treatment methods have proven themselves well: classes in groups of cognitive stimulation, cognitive training, where patients restore lost functions of self-care and communication. Special physical exercises are of great benefit.
Do not neglect the means and methods of alternative medicine. For senile dementia, doctors prescribed increased consumption of vegetable and animal fats. The Indian medical treatise “Ayurveda”, which is 5 thousand years old, advised that in case of damage to the nervous system, eat only ghee - high-quality melted butter - 1 day a week. It has been noticed that in places where residents eat a lot of coconut oil, the incidence of dementia is 3-4 times lower than global indicators. The legendary medieval physician Paracelsus drank a fresh chicken egg every morning, explaining that this would prevent a person from getting “shaky” (Parkinson’s disease).
Alternative medicine knew that the brain is virtually entirely composed of fatty tissue and needs to be replenished regularly. It was noted that the sharp increase in Alzheimer's disease in Europe and America in the 1960s coincided with the introduction and hype of low-fat food products. After 50 years, it became clear that this had undermined people's health. A negative role was played by the total war on cholesterol, taken to the point of absurdity, when people did not allow themselves a single gram of fat and kept their brains on a starvation diet. Today, based on knowledge of brain biochemistry, nutritionists recommend short courses of the ketone diet.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use in their practice all possible means to alleviate the condition of patients, including rational, balanced diet therapy. This opportunity is provided by the material, technical and scientific base of the hospital.
Age-related features of brain function
This does not happen, old age comes suddenly, but before that the person felt young and healthy.
Doctors consider the age after 70 years to be “senile”. At this time, irreversible changes of a degenerative nature begin to clearly appear. But aging processes begin much earlier, after about 35 years. Each person has his own path in life. But there are also general laws of development of the human body. Even healthy people, at a certain point in time, notice what experts call cognitive impairment. First of all, this concerns intelligence, attention and memory. Such changes are defined as cognitive-mnestic. When people age, neural connections are disrupted: new ones are not formed, and old ones die off. All this leads to deterioration of cognitive functions. Read the material on the topic: Attention of an elderly person: reasons for its weakening and tips for developing its stability
Prognosis of the disease in women
Alzheimer's disease and dementia are defined as steadily progressive neurodegenerative diseases. Everything is individual: for some women it is 5-8 years, others with this diagnosis can live to a ripe old age. It all depends on the resistance of the nervous system, its stability, living conditions, and family environment.
All over the world, scientists are working hard to create a means to combat the disease. Humanity needs a medicine for a long and full life of the brain. Much has already been achieved: the biochemistry of dementia, which develops due to mutations in pathological protein compounds that destroy brain neurons, has been worked out. It was found out where these proteins are formed and undergo mutations. Scientific laboratories around the world are searching for a substance that can break down amyloid proteins and remove them from the brain. At the same time, methods are being studied to recreate new healthy neurons and replace damaged nerve tissue with them. Researchers from different countries predict that these funds will be found.