Clonus in various somatic disorders
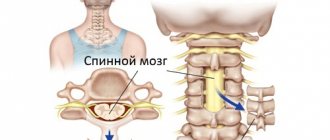
The pathophysiology of clonus in pyramidal chain dysfunction is manifested in the absence of an inhibitor coming from the cerebral cortex to the motor neurons of the spinal cord. Without an inhibitory impulse, reflex excitation lasts a long time, which is why involuntary muscle twitches are repeated.
In epilepsy, clonic convulsions manifest themselves in sequential contraction of the flexion and extension muscles, in rapid involuntary movements of the leg. The epileptic nature of clonus also occurs in infants, when in a dream the baby involuntarily twitches its legs for a minute or two. It is recommended to contact an experienced neurologist and begin a targeted examination.
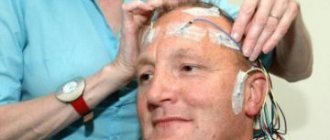
EEG monitoring is the most informative for a doctor when the baby is put on a special “hat” with sensors in which he must sleep. The sensors are connected to a computer, which records manifestations of knee clonus. If abnormalities in the functions of the central nervous system are confirmed, the doctor prescribes treatment for the child.
Knee Reflex Diagram
Foot clonus in an infant indicates muscle hypertonicity, which manifests itself due to intracranial hypertension. The tendon reflex increases in newborns with suspected cerebral palsy, porencephaly, microgyria, and gliomatosis. However, clonus of the knees and feet in children in the first days of life may manifest itself as a transient physiological phenomenon. In this case, it is not accompanied by other pathology.
Neurotic disorders are characterized by pseudoclonus: twitching of the cup or foot is not rhythmic and quickly fades away. True clonus is characterized by prolonged stereotypical twitching of the feet and legs, high general tone, which usually indicates central paralysis. A separate phenomenon is myoclonus - a single impulse startle. It occurs due to active muscle contraction, which occurs in many people at the moment of falling asleep.
Causes
The causes of the disease can be different, it all depends on how quickly the disease develops. Most often, pathology occurs due to damage to nerve endings in the brain.
There are a number of reasons that cause clonus:
- Multiple sclerosis occurs due to disruptions in the immune system, which leads to damage to the nerve endings in the head.
- A stroke can occur because hypoxia occurs due to a blood clot. Pathology can lead to clonus disease, because the part of the brain that is responsible for movement may be damaged.
- Severe injuries and bruises to the skull can damage the nerve cells in the head.
- If you use drugs or overdose on medications, this will lead to a large amount of serotonin.
- New growths in the head can provoke foot clonus.
Severe muscle spasms may occur, both in the foot and in the kneecap. The disease can occur abruptly or gradually. Diseases such as epilepsy, heredity, renal failure, and cerebral palsy can provoke pathology.
There may be foot clonus in newborns . This occurs due to muscle hypertonicity. If the disease is not treated, it can lead to serious consequences.
Methods for detecting pathology
The doctor can cause clonus of the patella in a patient who lies on his back with straight legs. The doctor takes the top of the patella with two fingers, pulls it up, then quickly releases it. A possible reaction of the body to such a motor test is rhythmic contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle, twitching of the patella. The test confirms the presence of disturbances in the pyramidal tract.
On the foot, the physician checks for clonus by supporting the patient's leg under the knee while the patient lies flat on his back. With one hand, the doctor lifts the leg so that it bends slightly at the knee, with the other hand he firmly grasps the foot and bends it to the back with a sharp movement. This action causes tension in the Achilles tendon. If, after stretching, a rhythmic twitching of the foot begins, this is clonus.
The doctor can cause clonus of the patella in a patient who lies on his back with straight legs. The doctor takes the top of the patella with two fingers, pulls it, then quickly releases it. A possible reaction of the body to such a motor test is rhythmic contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle, twitching of the patella. The test confirms the presence of disturbances in the pyramidal tract.
Forecast
Clonus has a different prognosis depending on the underlying cause. If a sudden injury or illness causes clonus muscle spasms, symptoms will likely subside over time or respond well to physical therapy.
Chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis, meningitis or stroke may require long-term management of symptoms. Clonus may worsen as the underlying condition progresses.
The article was written based on materials from the Medical News Today website.
Clonus has a different prognosis depending on the underlying cause. If a sudden injury or illness causes clonus muscle spasms, symptoms will likely subside over time or respond well to physical therapy.
Chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis, meningitis or stroke may require long-term management of symptoms. Clonus may worsen as the underlying condition progresses.
The article was written based on materials from the Medical News Today website.
Clonus: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis
Clonus is a neurological condition that occurs when the nerve cells that control muscles become damaged. This damage causes involuntary muscle contractions or spasms.
Symptoms are distributed in several different muscles, especially in the limbs. These include:
- ankles;
- knees;
- calves;
- wrists;
- jaw;
- biceps.
Damaged nerves can lead to muscle dysfunction, resulting in involuntary contractions, muscle tension and pain.
Clonus is a condition that can cause muscle spasms over a long period. This pulsation can lead to muscle fatigue.
Because of the constant strain, clonus can make daily life stressful and debilitating. In this article, you will learn more about the causes and treatment of this condition.
Medications
Sedatives and muscle relaxants help reduce symptoms. Doctors often recommend these drugs primarily for people experiencing cloning.
Medications that may help with clonus reduction include:
- Baclofen;
- Dantrolene;
- Tizanidine;
- Gabapentin;
- Diazepam;
- Clonazepam.
Sedatives and antispastic drugs may cause drowsiness. Patients taking these medications should not drive or operate heavy machinery.
Other side effects may include mental confusion, lightheadedness, or even trouble walking. You should discuss these side effects with your doctor, especially if they may interfere with daily activities.
Physiotherapy
Working with a physical therapist to train muscles can help increase range of motion in the injured area.
Botox injections
Some people respond well to clonus to Botox injections. Botox therapy involves the injection of certain toxins. The effects of Botox injections wear off over time, so a person will need repeat injections on a regular basis.
Surgery
Surgery is often the last resort. During a procedure to treat clonus, surgeons will cut off parts of the nerve that are causing the abnormal muscle movements, which should relieve symptoms.
Home Remedies
While medical treatments, home remedies may be helpful to support these efforts.
Using heat packs or using warm baths can relieve pain, and using cold packs can help reduce muscle pain. Stretching and yoga can help increase your range of motion.
You can use a magnesium supplement or a magnesium salt bath to help relax your muscles. You should consult your doctor before using magnesium as it may interact with other medications.
What is knee clonus
Detection of clonus by palpation and inspection
Involuntary muscle contractions in a certain rhythm occur due to the impact on the tendon ending. Most often, a person experiences clonus of the feet and kneecaps, caused by tension in the tendon. Such reactions indicate an excess of the knee and Achilles reflexes. They manifest themselves in any situation of hyperreflexia with dysfunctions of the central nervous system of an inorganic nature.
Clonus of an inorganic nature differ from reflexive disorders based on lesions of an organic type or arising against the background of neuroses. They are characterized by insufficient stability and uniform bilateral expression.
If the clonus are not uniform and symmetrical, this indicates an organic disease in the central nervous system. The uneven manifestation of reflexive responses to external stimulation is called anisoreflexia. It is caused by a unilateral decrease or increase in reflexes.
What can I recommend?
To prevent clonus, which in the most severe cases indicates paralysis, it is necessary to give up bad habits, carefully treat infectious diseases, and constantly measure and monitor blood pressure.
In addition, the state of the nervous system is well influenced by adherence to a healthy lifestyle, expressed in long walks, good sleep and regular exercise, as well as proper nutrition and a varied diet.
You should know that the nervous system is well strengthened by B vitamins, and do not forget to take them periodically.
So, clonus is the maximum possible reaction of the body to an external influence, expressed in rapid involuntary muscle contractions, which, under certain conditions, is characteristic of the kneecaps and feet. As a rule, this increase in reflex is a symptom of a serious pathology of the nervous system, so it is important to identify it as early as possible, and then begin to diagnose and treat the underlying disease.
Symptoms
If clonus occurs in epilepsy, it manifests itself during seizures and fainting. Muscle spasms begin to occur at a rapid pace in the arms, legs and body and the patient cannot keep it under control. The extrapyramidal system is responsible for abnormal movements.
Clonus occurs in neurosis, but it is false and the person quickly gets tired. Muscle tone and various problems of the musculoskeletal system occur. This manifests itself in the form of twitching on the face, neck, arms and legs.
Various paresis and paralysis may occur, and this also includes clonus of the patella. With this disease, there may be muscle spasms, the patient constantly feels tired.
Constant tension arises and a person feels eternally in some kind of discomfort. If symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. The sooner treatment is started, the sooner the patient will begin to experience a normal life.
Clonus stop - what is it?
Foot clonus occurs because there is damage to the nerves that control the muscles. Such a blow leads to a long muscle spasm.
This leads to constant muscle fatigue and pain. If this happens often, the person feels exhausted. First of all, it is necessary to understand why foot clonus occurs, and most importantly, to ensure that treatment is prescribed on time.
- 1. Reasons
- 2. Symptoms
- 3. Diagnostics
- 4. Treatment
Causes of the disease
If clonus occurs spontaneously, the doctor suspects epilepsy or a nervous tic. If clonus occurs due to external irritations, the causes may be: meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, tumors in brain structures, head injuries.
Clonus is caused by rare diseases:
- Huntington's chorea;
- hyperkinesis;
- hemiballismus;
- myoclonus;
- tremor;
- psychoneurological disorders.
According to some estimates, hyperexcitability in infants is diagnosed in more than 40% of children born. The attitude towards this phenomenon in different countries is ambiguous. Thus, in Europe, hyperexcitability is considered a borderline (temporary) condition that does not require special adjustment, while in the countries of the post-Soviet space it is considered a pathology that requires treatment.
Clonus and its causes
Extreme manifestations of hyperreflexia are expressed in the rhythmic alternation of tendon reflexes, and are called clonus. When using this term, they most often mean rapid, jerky contractions of the muscles of the foot or kneecap. In addition, clonus of the toes and hands, mandible, buttocks, or forearm may be observed.
The causes of this syndrome vary. So, if clonus occurs spontaneously, then, as a rule, we can talk about epilepsy, or diseases such as nervous tics or tremor.
Sometimes clonus occurs due to external irritants, accompanying diseases such as meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, brain tumors or traumatic brain injury. Having become a reaction to a single stretch of the tendon, clonus is expressed in multiple contractions of parallel muscles, and in this case it is difficult to predict the duration of this process.
If the twitching movements of the kneecap or feet are not characterized by rhythm or quickly fade away, this most likely indicates pseudoclonus, which is characteristic of neurosis.
On the contrary, long-term stereotypical muscle contractions, characteristic of true clonus, along with muscle spasticity, increased tone, tendon and periosteal reflexes, are symptomatic of such a pathological condition as central paralysis.
Diagnostic mechanism
Clonus of the patella is characterized by its sharp downward displacement, while it retains its position even if it is pulled back. In order to provoke this altered reflex, the patient is asked to assume a horizontal position and straighten his legs.
After this, the doctor grabs the kneecap with two fingers - the thumb and forefinger, moves it down and holds it in this position. The tendon is stretched, causing the muscles to involuntarily contract and the kneecap to twitch rhythmically.
To provoke foot clonus, the patient must also be placed on the couch and his leg should be bent at the knee and hip with one hand, and his foot should be grabbed with the other, sharply bent and straightened. Stretched, the Achilles tendon will provoke uncontrolled rhythmic movements of the foot, reminiscent of twitching.
It is worth emphasizing that both of the above examples of altered reflexes indicate disorders of the nervous system. But still, one of the most unfavorable situations is an uneven increase in reflexes (the so-called anisoreflexia), in which the left and right halves of the body react to the stimulus with different degrees of intensity.
Unlike a symmetrical increase in reflexes, which does not always mean that this is a sign of brain damage, their unevenness is an alarming symptom. As a rule, this is possible in two cases: inhibition of the reflex on one side, associated with damage to the reflex arc in the nerve, roots or gray matter of the spinal cord, or its activation on the other (which indicates damage to the pyramidal tract).
Treatment
Treatment for foot clonus depends on what exactly caused the pathology. Many specialists can use different therapy techniques. The doctor must find and select treatment individually for each patient separately.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain and relieve inflammation. The drugs have a number of side effects; for example, if you have a gastrointestinal disease, long-term use of the medicine is prohibited. Nervous system disorders and allergies may also occur.
- Sedative medications help relieve emotional stress and normalize the condition of nerve cells. If you use such drugs, it will help cope with irritability. It is not recommended to drive while taking such medications.
Physiotherapy also gives a positive result in treatment; it helps to train all muscles. A specialist may also prescribe surgery, but this is used only in extreme cases. Traditional methods of treatment can be used to help alleviate the condition.
Clonus of the feet and patella must be treated on time. The doctor will direct you to undergo a comprehensive examination in order to make an accurate diagnosis. If the disease becomes chronic, clonus of the feet and patella may worsen. Therefore, it is necessary for a specialist to select and prescribe therapy.
Reasons for development
Hyperexcitability in newborns is associated with mild damage to the central nervous system during childbirth or even during pregnancy. Often, pathology occurs due to a lack of oxygen.
The main reasons for the development of pathology include:
- intrauterine infections;
- toxicosis, especially in later stages (preeclampsia);
- alcoholism, smoking during pregnancy;
- taking certain medications;
- fetal hypoxia, fetoplacental insufficiency;
- premature or post-term pregnancy;
- maternal stress during pregnancy;
- anatomical narrowing of the pelvis, which creates difficulties when passing through the birth canal;
- rapid or, conversely, prolonged labor;
- birth injuries.
In addition, symptoms of hyperexcitability in babies under one year of age are characteristic of the period of teething (at this time babies are especially restless) as well as with intestinal colic
Diseases such as rickets, spasmophilia, and neuro-arthritic diathesis leave their “imprint” on the nervous system. And, of course, temperamental children (cholerics) are easily excited.
Myoclonus
Myoclonus (or myoclonus) is a symptom, not a disease, characterized by short-term rapid contractions of a muscle or group of muscles.
Myoclonic jerks or jerks are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions, called positive myoclonus, or muscle relaxations, called negative myoclonus.
Myoclonic jerks can occur singly or sequentially, with or without a pattern. They may occur infrequently or multiple times every minute.
Myoclonus sometimes occurs in response to an external event or when a person attempts to make a movement. The person experiencing the twitching cannot control it.
In its simplest form, myoclonus consists of muscle twitching followed by relaxation. An example is hiccups, which is also myoclonus.
Other familiar examples of the condition are the jerks that some people experience while falling asleep. These simple forms of myoclonus occur in normal, healthy people and are not problematic.
If more widespread, the condition can cause persistent shock-like contractions in a muscle group.
In some cases, myoclonus begins in one area of the body and spreads to muscles in other areas. More severe cases of the condition can distort movement and severely limit a person's ability to eat, speak, or walk. These types of myoclonus may indicate an underlying brain or nerve disorder.
The diagnosis is made based on symptoms and is sometimes confirmed by the results of an electromyographic study. Treatment includes correction of reversible diseases of the brain or nervous system and symptomatic therapy with medications.
Causes of myoclonus
Myoclonus may develop in response to:
Prolonged deprivation of oxygen to the brain, called hypoxia, can lead to posthypoxic myoclonus. The condition can occur on its own, but most often it is one of several symptoms associated with various nervous system disorders. For example, myoclonic jerk may develop in patients with:
Myoclonic jerks are also common in people with epilepsy, a disorder in which electrical activity in the brain becomes erratic, leading to seizures.
Types of myoclonus
Classifying the many different forms of myoclonus is difficult because the causes, consequences, and responses to therapy vary widely. The most commonly described types are listed below.
- Action myoclonus is characterized by muscle twitching caused or amplified by voluntary movement or even the intention to move. It can be worsened by attempts at precise, coordinated movements. This type is the most disabling form of myoclonus and can affect the arms, legs, face and even the throat. This type of myoclonus is often caused by brain damage that occurs due to a lack of oxygen and blood flow to the brain when breathing or heartbeat temporarily stops.
- Cortical reflex myoclonus is a type of epilepsy that occurs in the cerebral cortex, the outer layer or “gray matter” of the brain responsible for much of the information processing that occurs in the brain. During this type of myoclonus, jerking usually involves not only several muscles in one part of the body, but jerking may also occur that involves a group of muscles. The cortical shape can become stronger when people try to move in a certain way or feel a certain sensation.
- Essential myoclonus occurs in the absence of epilepsy or other obvious problems in the brain or nerves. It can occur randomly in people with no family history, but can also occur in members of the same family, indicating that it can sometimes be hereditary. Significant myoclonus tends to be stable without increasing in severity over time. In some families, there is an association with significant myoclonus, significant tremors, and even a form of dystonia called myoclonus-dystonia. Another form of significant myoclonus may be a type of epilepsy with no known cause.
- Palatal myoclonus is a regular, rhythmic contraction of one or both sides of the back of the mouth, called the soft palate. These contractions may be accompanied by myoclonus in other muscles, including the muscles of the face, tongue, throat, and diaphragm. The contractions are very rapid, occurring 150 times per minute, and can persist during sleep. The condition usually appears in adults and can last indefinitely. Some people with the palatal form view it as a minor problem, although some sometimes complain of a "clicking" sound in the ear, a noise produced when the muscles of the soft palate contract. The disorder can cause discomfort and severe pain in some people.
- Progressive myoclonic epilepsy (PME) is a group of diseases characterized by myoclonus, epileptic seizures and other severe symptoms such as problems walking or speaking. These rare disorders often worsen over time and are sometimes fatal. Research has identified many forms of PME.
- Lafora disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive disorder, meaning that the disease occurs only when a child inherits two copies of the defective gene, one from each parent. Lafora's disease is characterized by myoclonus, epileptic seizures, and dementia (progressive loss of memory and other intellectual functions).
- The second group of PME diseases belongs to the class of lysosomal storage diseases , usually including myoclonus, vision problems, dementia and dystonia (prolonged muscle contractions that cause twisting movements or abnormal postures).
- Another group of PME disorders in the class of systemic degenerations is often accompanied by action myoclonus, seizures, and problems with balance and walking. Many of these diseases begin in childhood or adolescence.
- Reticular reflex myoclonus is a type of generalized epilepsy that occurs in the brain stem, the part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord and controls vital functions such as breathing and heartbeat. Myoclonic jerks usually affect the entire body, simultaneously affecting muscles on both sides of the body. In some people, myoclonic spasms occur only in a part of the body, such as the legs, and all the muscles in that part are used with each thrust. The reticular reflex form of the disorder can be caused by voluntary movement or an external stimulus.
- The stimulus is sensory myoclonus , triggered by a number of external stimuli, including noise, movement and light.
- Sleep myoclonus occurs in the initial stages of sleep, especially when falling asleep. Some forms appear to be sensitive to stimuli. Some people with this form of the disorder rarely experience anxiety or need treatment. However, it can be a symptom of more complex and bothersome sleep disorders, such as restless legs syndrome, and may require treatment.
Symptoms of myoclonus
Myoclonus may be mild or severe. Muscles can contract quickly or slowly, rhythmically or irregularly. Myoclonic jerks may be infrequent or frequent.
They can occur spontaneously or under the influence of sudden noise, light or movement. For example, they can be triggered by reaching for an object or taking a step.
In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (a rare degenerative brain disease), myoclonus worsens with sudden fear.
Myoclonus, which develops as a result of metabolic disorders, can be long-lasting and affect different muscle groups, sometimes leading to cramps.
Treatment of myoclonus
Treatment for myoclonus focuses on medications that can help reduce symptoms. The first choice drug for treatment, especially of certain types of myoclonus, is clonazepam, a type of tranquilizer.
Dosages of clonazepam are usually increased gradually until the patient feels improvement or side effects appear. Drowsiness and loss of coordination are common side effects.
The beneficial effects of clonazepam may decrease over time if a person develops tolerance to the drug.
Many medications used to treat myoclonus, such as barbiturates, levetiracetam, phenytoin, and primidone, are also used to treat epilepsy. Barbiturates slow down the central nervous system and cause a tranquilizing or antiseptic effect.
Phenytoin, levetiracetam, and primidone are effective antiepileptic drugs, although phenytoin may cause liver failure or other harmful long-term effects. Sodium valproate is an alternative therapy for myoclonus and can be used alone or in combination with clonazepam.
Although clonazepam and/or sodium valproate are effective for most people with the disorder, some people experience adverse reactions to these drugs.
Some studies have shown that doses of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), a building block of serotonin, lead to improvement in people with certain types of myoclonus and PME.
However, other studies suggest that 5-HTP therapy is not effective for all people, and, in fact, may make the condition worse in some people.
These differences in the effect of 5-HTP on people with myoclonus have not yet been explained, but they may offer important clues to underlying abnormalities in serotonin receptors.
The complex origins of the disorder may require the use of multiple medications for effective treatment. Although some medications have limited effect when used alone, they may have greater effect when used with medications that act on different pathways or mechanisms in the brain.
By combining some of these drugs, scientists hope to achieve greater control over myoclonic symptoms. Some drugs that are currently being studied in various combinations include clonazepam, sodium valproate, levetiracetam and primidone.
Hormone therapy may also improve response to antimyoclonic drugs in some people.
Prevention
Protect yourself from brain injury by wearing a helmet or headgear during activities such as riding a bicycle or motorcycle.
Contact your doctor if you start having seizures after starting a new medicine so changes can be made.