People who have been on the verge of life and death always tell about the same thing: a person slides through a dark tunnel to a bright light at the end, he is overcome by a feeling of absolute peace and happiness, he hears pleasant music, soft light envelops him from all sides. People often describe their out-of-body experiences as seeing themselves from the outside and experiencing a feeling of floating.
Those who have had a near-death experience (NDE) sincerely believe in the reality of their experiences and use them as evidence of the existence of the soul and life after death. However, neuroscientists suggest that all the effects of NDE are due to the functioning of the dying brain.
What happens to the brain after cardiac arrest
Using electrodes planted in the brains of patients, neurologists discovered Terminal spreading depolarization and electrical silence in death of human cerebral cortex that even after the heartbeat stops, nerve cells in the brain continue to function.
Death is marked by the last wave of electrical activity in the brain. This wave begins 2-5 minutes after the brain stops receiving oxygenated blood and reflects dangerous neural changes that lead to permanent damage.
A short burst of activity was also found in an earlier study, Surges of electroencephalogram activity at the time of death: a case series. . Scientists performed electroencephalography (EEG) on dying people and found that the loss of blood pressure was followed by a temporary peak in activity that was characteristic of consciousness. Scientists have suggested that it is associated with the depolarization of neurons due to hypoxia - lack of oxygen. It has also been suggested that people who have had near-death experiences could have had their mystical experiences at that very moment.
However, the effects of NDE are not only experienced in the run-up to death. Similar conditions can be felt without a threat to life.
How can you revitalize your brain?
How to turn on a dead brain? The subjects in our study suffered severe and widespread neuronal death, explains Pastor. The integrity of axons—the long projections that neurons use to communicate with each other—disintegrates, and normal signal processing no longer works.
Alternatively, you can try to salvage what's left, like fixing broken headphones, by tying up the remaining wires. But any attempt to restore a dead brain will likely require spare parts—regrown brain cells to replace those lost during the injury. Moreover, cells need favorable conditions to grow and integrate into existing brain circuits. Bioquark will do both.
The team's "secret sauce" is a combination of bioactive molecules and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs are found in almost all tissues and have been used in cell replacement therapy for ten years. Although no such trials have been conducted in humans, preliminary studies in rodents with traumatic brain injury have shown that transplanted MSCs integrate into the brain and help improve recovery of motor and cognitive systems.
By studying the extreme stages of brain death, Pastor and scientists hope to find unique insights into the functioning of the dying brain. Stem cell transplants are nothing new, but Bioquark wants to take it a step further: Armed with bioactive molecules, researchers hope to establish a microenvironment in the brain that will promote “epimorphic regeneration,” the process of growing back a missing body part.
Tissue healing is key to revitalizing the brain
When an adult suffers a physical injury, such as losing a finger, our body reacts by forming scar tissue. The default response is healing, not regeneration. But during early embryonic development, tissue damage triggers a massive and highly coordinated response that keeps the body from becoming inflamed and scarred. Rather than end up with a nasty scar, a human fetus can regenerate lost tissue, much like flatworms can regenerate severed heads (and maybe even retain memories from the previous head!).
Much of this process involves recruiting huge numbers of local cells to help the tissue repair itself. And not just stem cells. In many cases, the adult cells lose their identity and revert to a stem cell state. In this way, the body “recycles” these cells to support tissue regeneration.
This process occurs quite naturally in the fetus, says Pastor. Why not imitate this process by forcing the adult brain to abandon scarring in favor of regeneration? Previous Bioquark research found that this repair process depends on bioactive molecules that can be extracted from amphibian eggs.
The extracted bioactive components, mainly microRNAs and proteins, can reprogram damaged cells into a stem cell state, the scientists wrote in a 2014 patent.
Stem cells are even somewhat minor players. There are concerns that their role may be exaggerated. They also place greater emphasis on morphogenetic extracts. However, relatively little work has been published on the lead chemical extract, a mixture of bioactive molecules exotically named BQ-A, in animal models of brain death.
The problem is that there are few such models, and they are all far from each other, and some are even exotic, like poisoning pigs with carbon monoxide, explains Pastor. “We stay away from such models and instead focus on models of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury in preliminary studies.”
First, scientists will test the power of these extracts to see if they can reboot the human brain. Pastor emphasizes that the study should show very basic brainstem function after treatment—an electrical whisper here, a cloud of neurotransmitter there.
In addition to cell-based therapies, Bioquark also plans to use brain stimulation techniques to turn on BQ-A. These techniques, including median nerve stimulation and transcranial laser stimulation, are often used to treat coma and other disorders of consciousness with varying degrees of success.
Why use so many different methods? Well, Bioquark wants to know right away what works and what doesn't.
The pastor sees two big flaws in current models of disease treatment and prevention. First, they focus more on treating late-stage symptoms rather than the original cause. Secondly, the approach of reducing any disease to one cause, and as a consequence, to one drug, is often used.
“Epimorphic regeneration is multifaceted in nature and involves many mechanisms working in synergy,” says Pastor. “To carry out such a complex initiative, it is obviously worth abandoning the concept of a “magic silver bullet” (which will never exist) in favor of the concept of a combination.”
When can you experience the effects of a near-death experience?
A recent study showed by DMT Models of the Near-Death Experience that near-death experiences can be experienced with the help of psychedelics.
The experiment was divided into two parts: in one, participants took the psychedelic drug dimethyltryptamine (DMT), and in the other, a placebo. After completing the trip, subjects filled out NDE Scale questionnaires, compiled with the help of people who had experienced near-death experiences.
It turned out that after taking DMT, study participants experienced the same effects as people on the verge of death: a feeling of dissolution, a mystical experience of unity with the environment and those who fill it.
According to another study Features of “near-death experience” in relation to whether or not patients were near death. , only 51.7% of patients experience NDE to the point of death. Of the 58 participants with near-death experiences, only 28 would actually have died without medical intervention. The remaining 30 people did not have a serious threat to life, but still survived all the effects of the near-death experience.
How long does the brain live without oxygen?
22.09. Exclusive No comments 10068 views, 36 — today Print article
Between 30-180 seconds of oxygen deprivation, you may lose consciousness.
At the one minute mark, brain cells begin to die.
After three minutes, neurons suffer more damage and long-term brain damage becomes more likely.
After five minutes, death becomes inevitable.
After 10 minutes, even if the brain remains alive, coma and long-term brain damage are almost inevitable.
What Causes NDE Effects?
Awareness of one's own death
One of the most common experiences is the awareness of one's own death. However, this feeling has also been experienced by living people with Cotard's syndrome (walking corpse syndrome).
A striking example is the case of Attributional style in a case of Cotard delusion. A 24-year-old female patient in a London hospital. She believed that she had died of a cold and was in heaven. After a few days, the mania began to subside and then disappeared completely.
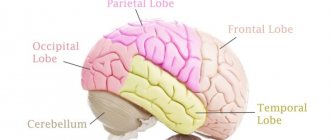
This syndrome is associated with dysfunction of the parietal lobe and prefrontal cortex of the brain. It is observed after head injuries, during the advanced stages of typhus and multiple sclerosis.
Light at the end of the tunnel
This experience is also often mentioned when describing near-death experiences. Living people experience similar sensations. During overload, pilots' blood pressure decreases greatly and hypotensive fainting may occur, which is accompanied by a temporary depression of Direct determination of man's blood pressure on the human centrifuge during positive acceleration. peripheral vision. For 5 to 8 seconds, pilots observe the same dark tunnel that humans experience during an NDE.
There is an assumption that the tunnel arises from Out-of-body experience and arousal. due to impaired blood supply to the retina. This state is characteristic of extreme fear and hypoxia, which, in principle, is close to dying.
Leaving the body
There is an assumption that the angular gyrus is responsible for this experience. In one experiment, Stimulating illusory own-body perceptions. found that stimulation of this area causes a sensation of transformation of the subjects' arms and legs (response of the somatosensory cortex) and movement of the entire body (response of the vestibular system).
Scientists have concluded that out-of-body experiences may occur due to distortion of information from the somatosensory cortex and vestibular system.
Also, out-of-body experiences are characteristic of the state on the border of sleep and wakefulness - hypnagogia and sleep paralysis. The body unbound: vestibular-motor hallucinations and out-of-body experiences. . In this state, a person may hallucinate, be conscious, unable to move, and experience a sensation of floating next to their body.
Happiness and Prosperity
Near-death experiences are typically accompanied by a state of euphoria and calm. The same effect can be obtained from taking certain medications, such as ketamine. This drug binds to mu opioid receptors and causes euphoria, dissociation, spiritual experiences and hallucinations.
Scientists theorize that during NDE, the opioid reward system is activated to dull pain, and the released endorphins create all the positive experiences.
There is also a theory that norepinephrine is to thank for the euphoria. There is nothing paranormal about near-death experiences: how neuroscience can explain seeing bright lights, meeting the dead, or being convinced you are one of them. and the locus coeruleus is the part of the brain responsible for the release of this hormone.
Norepinephrine is involved in a person’s arousal from fear, stress and hypercapnia - an excessive amount of CO2 in the blood, so it may well be released in a near-death state.
The locus coeruleus is associated with brain structures responsible for emotion (amygdala) and memory (hippocampus), fear response and opioid pain relief (periaqueductal gray matter), and dopamine reward system (ventral tegmental area). Scientists believe that the norepinephrine system may be associated with positive emotions, hallucinations and other effects of near-death experiences.
Whole life before your eyes
In the near-death state, people often see a series of events in their own lives. In his book “We are our brain. From the Uterus to Alzheimer's" Dick Swaab argues that people experience past events by activating the medial temporal lobe. This structure is involved in storing episodic autobiographical memories and is very sensitive to oxygen deprivation, so it is easy to activate.
The 2004 Britton Near-Death Experiences and the Temporal Lobe study confirmed that people who have experienced a near-death experience have changes in activity in the temporal lobe.
Meeting with the Dead
Many scientists believe that a person's near-death experience takes place in an intermediate state between sleep and wakefulness, and that the REM sleep phase is responsible for all mystical images and hallucinations.
To test this hypothesis, scientists studied Does the arousal system contribute to near death experience? 55 people who had near-death experiences. It turned out that these people were more susceptible to sleep paralysis and associated visual and auditory hallucinations. Scientists have suggested that when in danger, such people are more likely to enter REM sleep, which is why they have vivid memories of their near-death experiences.
In addition, hallucinations are common in some brain injuries. For example, patients with Alzheimer's disease or advanced Parkinson's disease sometimes report ghosts or monsters, and after brain surgery, some patients see dead relatives.
Life after brain death: the body is alive, but the soul is alive?
6
Brain death does not always lead to the physical death of a person
Brain death and, as a consequence, clinical death, do not always lead to the physical death of a person, at least his body. Modern medical capabilities make it possible to maintain a person’s physiological functions for a very long time, and the body continues to live, albeit with artificial simulation of respiration (ventilation), cardiac activity, etc. Outwardly, a person continues to look alive, which gives hope to loved ones that he can recover from a coma - after all it is assumed that if the body is alive, then the soul is also alive.
There are many cases where patients were artificially kept alive for many years and the slightest manifestations of their independence only strengthened the faith of loved ones in the likelihood of recovery.
Recently, a book and film “The House Where The Mermaid Sleeps” was released in Japan, the main storyline of which was the parents’ struggle for the life of their daughter, who drowned in the pool. Artificial life, or can a soul live without a brain? The girl's name was Mizuho. At the hospital where she was taken, resuscitation measures did not help - she remained in a coma. Although her condition was stable, the question arose about disconnecting her from life support systems and transferring some of her organs for transplantation. To do this, it was necessary to obtain parental consent for examinations and recording of brain death. In Japan, and in other countries, this is the custom - if after the death of a minor, the relatives agree, then his internal organs can be used for transplantation.
So, the parents practically agreed to the declaration of death, but then the child, when his mother was saying goodbye to him, moved his finger. This gave hope, and the grief-stricken parents changed their minds and began to fight for her life. The girl was taken home, her mother and grandmother began to look after her. The content possibilities were rich. Mizuha underwent surgery, installing a ventilator in her body, which saved her from the bed. Now she began to sit in a wheelchair, she could be taken out for walks and, outwardly, she had the appearance of a sleeping child. The girl was enrolled in school, and a teacher began to come to her home and read aloud to her. To keep her body in good shape, a special control system was connected to Misuho, and now she could smile, move her arms, legs, do exercises, etc. Metabolism was also maintained at an excellent level. Years passed, and the child still did not wake up, and the longer this happened, the more often the parents were visited by thoughts about whether she was really alive? One day, the father asked the doctor: “..who or what is he at home, a patient or a corpse?” The doctor answered philosophically that the official definition of death was introduced for one specific purpose - to make it possible to use the organs of the deceased for transplantation to another person. What it really is is difficult to answer.
Indeed, in Russia, as in Japan, a similar formulation is enshrined in law: “The moment of a person’s death is the moment of the death of his brain or his biological death (irreversible death of a person). Brain death occurs with the complete and irreversible cessation of all its functions, which is recorded with a beating heart and artificial ventilation of the lungs.” Article 66. Determination of the moment of death of a person and termination of resuscitation measures. Federal Law of November 21, 2011 N 323-FZ
It all ended with the fact that one night, the mother dreams that her daughter is saying goodbye to her.
The mother runs to the bed and sees that all the indicators on the monitors have sharply worsened. After a farewell conversation with her daughter, the mother believed in her death and gave permission to conduct standard medical examinations, which confirmed brain death. Surprisingly, despite the many years Misuho spent unconscious, her organs were declared fit and were transplanted into other people, thereby saving their lives. One of the final dialogues between the father and the doctor, when Misuho is no longer alive, is interesting:
Doctor: “When did your daughter die – three years ago, when she drowned or, now, when she died of her brain?” Father: “Now that her organs have been taken away and her heart has stopped beating.
“But the heart was transplanted into another girl,” the doctor objected, “So your daughter now lives in a different body.”
Trailer for the film “The House Where The Mermaid Sleeps” 2021: Epilogue A very sad and difficult story, at the end of which the question is raised, what is life, where does it go, what happens to the soul? How is life related to physiology, since organs transplanted from dead people continue to live in other bodies, although all the dead had total necrosis of the brain? The questions of where the soul lives and what happens to other people when they receive foreign organs are still open. Therefore, a link to a post dedicated to reincarnation will appear here soon. We believe that the soul is immortal and make every effort to prove this fact. We invite everyone who wants to take part in the “Immortality of Life” project to make contributions and participate in the development of the project with new posts, discussions, and voting to organize experiments.
How to cope with mental trauma
As with any injury, an emotionally damaged brain requires a period of recovery and rehabilitation. We don't return to our normal activities immediately after heart surgery, but we somehow hope to bounce back after the mental struggle of losing a loved one.
If you are interested in science and technology news, subscribe to us on Yandex.Zen so as not to miss new materials!
Research shows that these types of trauma can be managed through a variety of activities, from medication to psychotherapy and even massage . For example, in one case, participation in eight weeks of cognitive decision-making therapy improved a person's ability to carry out complex mental processes. Other studies show that it is enough for a person to simply suddenly change his occupation.
For some, that means cuddling up in a favorite T-shirt or blanket, journaling about positive memories, or creating a photo album or video about life with a loved one. For others, it means moving to another country, changing a job or changing their image. Ultimately, the brain still returns everything to its place. However, according to scientists, the consequences of loss still remain with a person for life. And there is no way to fix this.
Possible reasons
Brain death can occur for various reasons, but the pathophysiological processes are approximately the same. Brain death occurs due to persistent circulatory disorders, oxygen starvation, and stagnation of metabolic products. Diseases that lead to organ death can be varied: trauma, inflammatory diseases, heart disease, multiple organ failure and many others.
After cardiac arrest, the brain does not die immediately . This depends on many criteria: the general condition of the patient, concomitant diseases, the age of the patient, the disease that caused this condition, the ambient temperature. Irreversible tissue necrosis begins after 3 minutes, but in young healthy people this process is slower. At low air temperatures, the brain dies more slowly. If after 3 minutes or more the patient responds to resuscitation measures and returns to life, no one can predict the consequences; perhaps some neurons have died, and this will significantly affect the patient’s life in the future.