03/30/2019 Alena Masheva Health
When some symptoms of diseases appear, they may disturb a person because they are unusual. For example, fever in the head. This feeling can arise completely accidentally and seemingly without reason - at work, while traveling by transport, while walking or relaxing. Why is it felt? Is this a dangerous manifestation? What can cause it? How to determine what happens to the body when you feel heat in your head? You will find answers to all these questions below.
What is this?
In fact, heat in the head is a rather subjective sensation. But, nevertheless, indicating the real presence of pathology. Depending on the specific case, it can be very different:
- The head feels hot, after which the burning sensation spreads to the neck, shoulders, back and spreads throughout the body.
- The feeling of discomfort is associated with a severe headache in the back of the head, crown, forehead or temporal area.
- The symptom of heat in the head can occur with or without elevated body temperature.
- Often a burning sensation is associated with increased sweating.
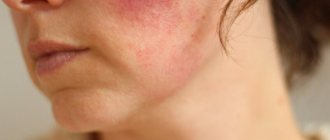
- In some cases, the skin of the face changes its color - it turns pink, or even becomes red and even purple.
- Along with the heat in the head, there is an increase in blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Of course, all these manifestations are of a different nature, although a person feels the same. Why does the feeling arise? There are a lot of reasons. From malfunction of blood vessels to overstrain of the nervous system. Doctors say the most common cause of heat in the head is the ebb and flow of blood to it. Due to the expansion and contraction of blood vessels. This process is accompanied by an unpleasant feeling - you feel as if this part of the body is burning or burning.
Let's take a look at the main causes of fever in the head. Let's start with the simplest, most common, harmless ones and end with serious, pathological conditions that are accompanied by a similar symptom.
Burning in the head: causes
If you feel a burning sensation in your head, the cause is usually well known to medicine. There are few diseases that cause this symptom.
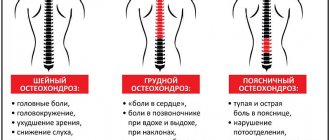
Cervical osteochondrosis
With cervical osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs in the cervical spine become deformed and undergo dystrophy. This type of osteochondrosis is the most dangerous because the disease disrupts the blood supply to the brain. The consequences of an advanced form of cervical osteochondrosis are very sad: from tinnitus and headaches to loss of vision and the ability to move independently.
The disease is rapidly spreading among people 25-40 years old, who spend more and more time in a physiologically incorrect position:
- sitting at the computer;
- talking on the phone, holding it with their shoulder;
- sit in the car for a long time.
There are many factors that provoke the disease.
A burning sensation in the head is one of the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. Other symptoms indicating the presence of the disease:
- aching pain in the back of the head and neck;
- the pain radiates to the shoulder or arm, sometimes the fingers go numb;
- crunch in the neck and pain when turning the head;
- pain and burning between the shoulder blades;
- numbness of the face, tongue, etc.
Sympatho-adrenaline crisis
With the sudden activation of the sympathetic nervous system, a sympatho-adrenaline crisis begins, which in Europe and the USA is called a panic attack. This disease affects about 2.5% of the world's population.
The attack lasts 6-8 hours and is accompanied by painful symptoms:
- fear of death;
- suffocation;
- unbearable headaches;
- a jump in blood pressure above 200 mm Hg;
- tachycardia, heart pain;
- chills.
There are many reasons why panic attacks occur:
- severe stress;
- tumor of the adrenal glands, spine, spinal cord;
- pathological processes in the hypothalamus of the brain.
Physical or emotional exhaustion
Depletion of the body's internal resources leads to many serious consequences that can become irreversible. With chronic fatigue, healthy vascular tone is disrupted and blood flow from the brain worsens. Retention of blood in the brain is manifested by a burning sensation in the head.
Severe fatigue often requires urgent hospitalization and subsequent inpatient treatment of the patient.
Wrong lifestyle
If the body is exposed to the destructive effects of alcohol, nicotine, chronic stress for a long time or lives in an abnormal mode, its rapid destruction begins, which also affects the brain. A burning sensation in the head is one of the symptoms of impaired cerebral blood supply due to bad habits.
Arterial hypertension
With hypertension, tension occurs in the walls of the arteries and a decrease in their lumen. As a result, blood pressure increases in the narrowed vessels.
In addition to a burning sensation in the back of the head, hypertension is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain (pulsation) in the back of the head, temples and crown of the head - they intensify with any mental or physical effort;
- dizziness;
- visual impairment, etc.
Brain tumors
Demyelination of the brain When there is a lack of a substance such as myelin in the brain, the myelin sheaths of nerve fibers that insulate them are destroyed. Then the nerve fibers themselves are destroyed. This is a serious disease that requires urgent specialized treatment.
Emotional stress
Flushing can cause a variety of strong emotions and sensations—anger, fear, rage, frustration, shame, despair, and intense mental anguish. In some people, excessive intellectual stress, by the way, can also be accompanied by pain and heat in the head.
Additionally, symptoms such as facial redness are noted. The condition is not dangerous to life and health. But this is a signal for you to put things aside, calm down, and pull yourself together. Try to abstract yourself from the problem - both in thoughts and in space. Get out of the room and take a walk in the fresh air. Once you calm down, the headache and fever in the head will disappear on their own.
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
Before starting treatment, you must find out what caused the burning and heat in your head. You need to visit a therapist, neurologist and possibly other specialists, take general blood and urine tests, and also make an appointment with an ophthalmologist. This is an initial consultation with doctors.
In addition, an X-ray of the skull is taken, a CT scan or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is performed. In this case, a standard set of studies is used.
If an anomaly is suddenly discovered in the brain area, then to accurately determine the disease it is necessary to undergo a tomography. This is the best method for diagnosing diseases in the head area. The patient is placed in a tomograph.
Its principle is based on the effect of hydrogen protons on the human body. After this, encephalography (or ultrasound) is prescribed. The patient's head is lubricated with Vaseline and an ultrasonic sensor is passed over it. The received data is displayed on the monitor. They need to be recorded and decrypted.
The last stage of the examination is electroencephalography. This method is based on recording nerve impulses emanating from the brain.
Using electroencephalography, you can find out in which part of the head the disorder occurred. All of the above methods of examining the head are painless, but effective in identifying serious diseases.
In the process of general diagnostics, the following facts are revealed:
- frequency of pain in the form of burning and tingling;
- the connection between pain and the body’s response to pain;
- nature of pain, intensity, duration, localization.
Differential diagnosis is a method that allows you to identify a disease in a person by excluding possible diseases due to the patient’s lack of obvious symptoms of the suspected diseases.
As a result, the correct diagnosis is made and proper treatment is carried out. There are special computer programs that help to most accurately identify the disease based on the detected symptoms.
Before starting pain treatment, a number of tests are carried out, including laboratory tests - they can look for signs of infection and inflammation. A visit to an ophthalmologist is mandatory for the patient.
A visit to this doctor is indicated in almost all cases of headaches, since there may be changes in the fundus of the eye that can only be determined by an ophthalmologist using special equipment; The examination also establishes the true cause of the headache. Plus, the ophthalmologist will evaluate the state of refraction, visual acuity and visual fields of the patient.
Wrong diet
It may come as a surprise, but unhealthy food is also one of the common causes of this manifestation. In particular, too spicy food, products with an excess of monosodium glutamate can be a sufficient reason. The head feels hot for a short time.
This short-term feeling of high temperature, by the way, has its own name - “Chinese restaurant syndrome.” There is a lot of fast food there, literally oversaturated with monosodium glutamate. This substance excites brain cells so much that it feels like the head is heating up and heating up. It goes away on its own over time.
Allergy
If you feel not only fever, but also itchy skin, rashes and sores appear, then this sign indicates the beginning of an allergic reaction. He deserves attention! But what to do if there is fever in the head in this case? You need to protect yourself from exposure to factors that irritate the immune system.
If you have already been diagnosed with an allergy, you must take an antihistamine prescribed by your doctor. If you encounter a reaction for the first time, this is a good reason to urgently contact an allergist.
Effective treatment
Treatment should begin with determining the cause of the disease. To do this, carefully observe the moment when pain appears. What precedes an attack? Maybe a conflict at work or an unpleasant conversation provokes pain, then it is necessary to treat with sedatives:
- valerian;
- motherwort;
- Novo – Passit.
Sedatives have been used for a long time, their effectiveness is undeniable. One of the most popular is valerian extract, available in the form of infusion, tablets, drops. Can be used by adults, during pregnancy and breastfeeding only after consulting a doctor. Only a doctor can prescribe sedatives to children 6-12 years old. When taking valerian, sleep improves, it becomes deeper, and falling asleep occurs faster.
Valerian can be used in courses of 14-21 days at intervals of 3 months. After sleep, a person wakes up rested, alert, and ready for the day ahead. Becomes less susceptible to stress and reacts more adequately to events occurring around him. The functioning of the nervous system is stabilized.
Motherwort preparations are also very common. These products are available in the form of infusion or tea bags. Motherwort has not only a sedative, but also a hypotensive effect. People with low blood pressure should pay attention to this. The drug can be used by adults; it is not recommended for children.
After taking motherwort, some patients noted the following side effects: nausea, vomiting, confusion, drowsiness. Quincke's edema is possible due to an allergic reaction.
Skin problems
Another reason is the presence of diseases affecting the scalp. Many of them are accompanied by an unpleasant burning sensation. In particular, dermatitis. You may also experience severe dandruff, rashes, and painful itching.
As for the causes of heat in the head in women, we can additionally highlight the incorrect selection of cosmetics - shampoos, hair masks, coloring and lightening preparations. By acting on the skin, they can irritate it so much that there is a feeling of a strong, incessant burning sensation, as if engulfing the entire head.
Features of first aid
If necessary, a burning sensation in the back of the head or other places can be eliminated on your own.
Actions in the absence of injuries and normal blood pressure:
- Apply a damp terry towel to your head for 15 minutes;
- taking water-salt procedures (bath with sea salt);
- relaxation of the shoulders and neck through massage;
- drinking tea, sage or mint infusion;
- elimination of irritating factors (bright light, unpleasant sounds);
- at least half an hour's rest.
Bad habits
Addiction to alcohol and tobacco products can also be a sufficient reason for the feeling of heat in your head. Why? As for nicotine, under its influence blood vessels narrow. Consequently, blood flow to the brain is hampered. This may feel like an unpleasant burning sensation. Also, for many people, for the same reason, smoking tobacco is accompanied by headaches.
People who abuse alcohol often experience this feeling of heat. Due to the fact that areas of the brain responsible for vascular tone, the autonomic and endocrine systems are affected. The brain, under the influence of alcohol, begins to behave like an incompetent worker. Suddenly and for no reason, the blood flow to the brain “turns on”, which is why the person feels a strange and incomprehensible sensation of heat.
Physiological failures
Most people who complain that they have a headache have acquired factors that are not a sign of malaise. Such cases can be eliminated by changing habits and lifestyle. Causes of unpleasant headaches include:
- Chronic fatigue. Significant mental and physical stress with a lack of sufficient rest leads to vegetative-vascular failures. There is stagnation of blood and disruption of brain nutrition. General and focal symptoms appear - headache, inability of the body, of course, to perceive irritations. In this situation, a night sleep of at least 8 hours and a work regime that is not harmful to health are recommended.
- Hypodynamic lifestyle. Sedentary work—as a driver or at a computer—and lack of physical activity slow down cerebral blood circulation.
- Changes in the hormonal system. Women experience such changes during pregnancy or menopause. The production of estrogen decreases, this leads to disruption of the functioning of the organs that provide blood circulation in the body, which provokes headaches. In men, testosterone decreases, which can also cause discomfort in the head area.
- Having bad habits. Alcohol and nicotine, which contain toxic substances, affect the destruction of vessel walls and promote the growth of blood clots and blood clots. As a result, the capillaries located in the head, due to the influence of various toxic substances on them, become less elastic and durable. Brain tissues do not receive enough oxygen and blood, which is the source of headaches. After completely giving up the bad habit, the unpleasant sensation goes away on its own after two weeks.
Heatstroke
A fairly serious cause of fever. This symptom may indicate both heatstroke and sunstroke. They lead to a rush of blood to the head, since in these conditions the vessels dilate.
Sunstroke and heatstroke can also be recognized by additional symptoms:
- Vomit.
- Nausea.
- Strong headache.
- Cloudiness or loss of consciousness.
Be sure to take the victim to a cool, shaded place. Give him enough water and offer cold compresses until qualified medical help arrives.
Hormonal disorders
We also note that such a symptom may also indicate a period of hormonal changes in the body. For example, about menopause, premenstrual syndrome. During these periods, the proportion of the female hormone called estrogen in the body, which is responsible for vascular tone, decreases. Why its deficiency can lead to disruption of their regulation, which is reflected by periodic ebbs and flows of blood to and from the head. This is felt by a person as heat, burning. A woman may also complain of increased sweating and a feeling of lack of air.
This problem is also typical for men. Only if the level of the male hormone testosterone decreases. This is observed during menopause, any pathologies, diseases, injuries affecting the testicles. The lack of sex hormone is reflected in the tone of blood vessels. Their systematic expansion and spasms occur. As a result, it seems that your head is burning, your ears and face turn red.
Problems with the vascular system
If the rush of blood to the head is not associated with menopause or menopause, we can talk about the presence of problems with the vascular system itself. In particular, the development of atherosclerosis and subsequent hypertension.
The heat in the head itself may indicate a hypertensive crisis. Since it is in this case that the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. Along with the fever, you may feel a headache.
However, the danger of a hypertensive crisis is that it cannot manifest itself with symptoms. You continue to feel well while this serious condition develops. You can notice it in time with regular blood pressure measurements with a tonometer. If your blood pressure rises above your “working” level, you must urgently take the medicine prescribed by your doctor.
How to diagnose the disease
A timely comprehensive examination by a neurologist is of great importance. This will allow you to avoid complications, identify the causes and begin treatment. When it starts to “burn in your head,” a number of diagnostic measures are indicated:
- blood test (general, biochemical) - will reveal a range of chronic somatic pathologies;
- ophthalmological examination - will help to detect changes in the fundus using special equipment, check the quality of vision, the state of refraction;
- echoencephalography is a method for identifying large tumors based on the Doppler effect;
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring – 24-hour monitoring of blood pressure levels with average readings;
- Electroencephalography – captures and records in graph form electrical discharges occurring in the brain. Using this technique, you can exclude epilepsy, find out the state of the functioning of parts of the brain;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a safe method due to the absence of x-ray radiation. Detects the smallest neoplasms and vascular pathologies.
VSD
This symptom can be felt by people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia. In particular, it indicates the onset of a vagoinsular crisis (an attack during VSD). The reason for this is the “imbalance” of the body, a violation of both its thermoregulation and control over vascular tone.
A vagoinsular attack, in addition to baking in the head, can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Weakness or, conversely, strange excitement.
- Dizziness.
- Panic mood.
- Nausea.
- Dry mouth.
- Unreasonable rumbling in the stomach.
- Pre-fainting state.
Hyperthyroidism
Heat in the head also indicates endocrine problems. In particular, about hyperthyroidism - increased function of the thyroid gland. With this pathological condition, it produces slightly more thyroid hormones than the body needs. They, in turn, speed up metabolism.
In this condition, there is an increase in body temperature and a sensation of heat and burning in the head. Moreover, the patient is in an excited state, he has a rapid heartbeat, trembling limbs, and increased sweating.
Feeling hot
Menopause
Diabetes
84532 August 24
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. The feeling of heat that a person experiences occurs due to a sharp expansion and blood filling of small subcutaneous vessels. This condition is called arterial hyperemia. At the same time, the skin turns red and becomes hot.
The lumen of blood vessels is regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Its changes depend on signals from the vasomotor (vasomotor) center of the central nervous system, hormones, pyrogenic (heat-causing) substances entering the blood, and a number of other factors.
Types of sensations of heat
The vessels are constantly influenced by factors that have a vasoconstrictor or vasodilator effect. For example, under stress, blood vessels narrow under the influence of the hormone adrenaline, and the skin turns pale. At the end of the stressful situation, the vessels relax and fill with blood.
Pathological arterial hyperemia, which is accompanied by a feeling of heat, develops either under the influence of irritants (infections, toxins, tissue breakdown products from burns, pyrogenic substances), or due to a violation of nervous regulation.
There are
neurogenic
arterial hyperemia (occurring in response to irritation of nerve endings) and
metabolic
(caused by the action of local chemical factors). An example of neurogenic arterial hyperemia is redness of the face and neck during hypertension, menopausal syndrome, and also during strong emotions.
Blood electrolytes have a metabolic effect on vascular tension: calcium and sodium constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure, while potassium and magnesium, on the contrary, dilate them. Metabolic regulators include carbon dioxide, organic acids, and hormones.
Possible causes of feeling hot
Hot, hot and spicy foods can cause a rush of blood to the skin and a feeling of heat.
Alcohol has the same effect on the body.
, which promotes the dilation of blood vessels.
Taking certain medications
can also cause a feeling of heat spreading throughout the body. These include vasodilators, hormonal agents, antidepressants, etc.
The causes of arterial hyperemia and, as a result, feelings of heat can be different. If the regulation of vascular tone is disturbed, arterial hypertension may develop, accompanied by a sudden increase in blood pressure - a hypertensive crisis. The most common cause of this condition is hypertension. However, in a third of cases, arterial hypertension is caused by diseases of the internal organs: acute glomerulonephritis and other kidney damage, adrenal tumors and other diseases of the endocrine system. The magnitude of the rise in blood pressure during a hypertensive crisis depends on the age and individual characteristics of the person. At a young age, symptoms of a crisis may occur at a lower level of blood pressure, and at an older age – at a higher level.
A sharp increase in blood pressure is accompanied by headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, visual disturbances (“floaters”, double vision). Possible numbness of the limbs, a feeling of pins and needles, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath.
Due to a violation of nervous regulation, chills occur, followed by fever, and increased sweating. The end of the crisis is accompanied by frequent urination.
Increased blood pressure and the symptoms accompanying this condition also occur with an adrenal tumor - pheochromocytoma
and other hormone-producing tumors. The tumor secretes large amounts of catecholamines (adrenaline and norepinephrine).
Clinical signs of pheochromocytoma may include headache, sweating, increased heart rate, irritability, weight loss, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, weakness, and fatigue. In some cases, patients may experience fever, shortness of breath, hot flashes, increased thirst, increased urination, dizziness, and tinnitus.
Many women complain of hot flashes during menopause
. Changes in hormonal levels occur even before the cessation of menstruation, during premenopause (menopausal transition). At first, its manifestations are insignificant, and most often they are not given importance or are attributed to the consequences of fatigue and mental stress. Hormonal and metabolic changes, in particular, a decrease in the level of estrogen, progesterone and an increase in the production of GnRH, are accompanied by hot flashes, which can be repeated several times a day.
Women describe them as a periodic short-term feeling of heat followed by chills, increased sweating, and rapid heartbeat.
In most cases, hot flashes only slightly affect your well-being.
Arterial hyperemia and a feeling of heat can be a sign of dysfunction of the thyroid gland, for example, with thyrotoxicosis
. Patients with thyrotoxicosis complain of general weakness, fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbance, sweating, trembling fingers, palpitations, and sometimes pain in the heart area.
Despite the increased appetite, patients with thyrotoxicosis lose weight.
Violation of thermoregulation, which occurs due to accelerated metabolism, leads to an increase in body temperature and causes a constant feeling of heat. The skin becomes warm and moist, the skin vessels dilate, which is accompanied by redness of the face. Sweating increases, nails become brittle, and hair falls out.
Sometimes hot flashes and a feeling of heat in combination with high blood pressure occur with diabetes mellitus
. These symptoms are accompanied by general malaise, sweating, thirst, and an increase in the volume of urine produced.
Which doctors should I contact?
If symptoms such as fever and hot flashes appear regularly, you need to contact, who, based on the complaints and tests, will refer you to or.
Diagnostics and examinations
The appearance of periodic hot flashes, accompanied by a feeling of heat, sweating, and redness of the facial skin, requires mandatory diagnosis.
The doctor evaluates the patient's complaints, taking into account age, gender and concomitant diseases. When blood pressure increases, turning into crises, it is necessary to determine the nature of the pathology - primary (associated with a violation of nervous regulation) or secondary (due to diseases of the internal organs). For this purpose, a clinical blood test and a general urine test, a urine test according to Nechiporenko, a blood test for glucose, cholesterol, and creatinine are prescribed.
Hydrocephalus
A common “folk” name is “dropsy of the brain.” This disease is accompanied by increased intracranial pressure. Because of this, patients may feel fever, an unpleasant burning sensation in the head, and pain.
Most often, these unpleasant sensations haunt a person in the morning. However, in the case of an advanced disease, the symptoms continue to torment throughout the day. In addition to these, the following is noted:
- Vomit.
- Nausea.
- Visual dysfunction.
- Labored breathing.
- Drowsiness.
Causes
Thanks to modern medical technology, neurologists can trace discomfort to nerve cells in the brain. For this purpose, positron, digital tomography or MRI is used.
There are many causes of burning and tingling in the head. Hunger, harsh light, excessive noise, prolonged viewing of TV or working at a computer - due to these factors, not only a headache, but also other sensations appear, including a burning sensation (in the occipital region of the head, in the temples, in the frontal , parietal part, etc.).
Diseases accompanied by a burning sensation in the head:
- infections (CNS diseases, viral, bacterial infections);
- elevated temperature (infection, sunburn);
- hypertension;
- mental illness (depression, stress, chronic fatigue);
- intoxication (any poisoning - exposure to toxic substances on the body: microbial toxins, metals, food, drugs...);
- vaccination;
- allergy;
- cancer with metastases to the brain (burning from excess pressure or stimulation of sensory nerves);
- sinusitis;
- menstruation;
- diseases of the spine, muscle spasms;
- cerebral artery atherosclerosis;
- ear diseases;
- eye diseases;
- dental disease;
- nose diseases;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- tumors of brain tissue;
- nervous irritation;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- eating habits: excessive acidification, chemical ingredients in food.
Overwork and stress
Excessive mental stress, fatigue, overwork usually cause increased body tension, overload of the muscles of the neck and face. As a result, the nerves are depressed and irritated, causing a burning sensation, most often in the back of the head.
A common cause of a burning sensation at the top or back of the head is fatigue. Most people cannot imagine a working day without a computer. This type of work involves significant eye strain, especially for people over 40 years of age. With prolonged sedentary work, these problems cannot be avoided. As a result of increased overvoltage, a burning sensation occurs in the back of the head, frontal and eye areas.
Gastrointestinal surgery
It would seem, what is the connection here? But everything is explained simply: digestion is largely regulated by the intestinal hormonal system. The substances it produces, among other things, dilate blood vessels and activate the vagus nerve.
During surgery, the hormonal system may be affected or damaged, which results in disruption of its functioning. One of the consequences is a rush of blood to the head due to dilation of blood vessels, which is felt by a person as heat.
Musculoskeletal problems
Here we need to talk about cervical osteochondrosis and spinal injury. In such conditions, excessive irritation of the nerve endings occurs. Consequences of which:
- Feeling of heat in the head.
- Dizziness.
- Headache.
- Unpleasant sensations in the muscles.
If the cause of neuralgia lies precisely in osteochondrosis, a burning, burning sensation appears in the crown of the head, and then spreads towards the back of the head.
Why does pathology develop?
Experts believe that burning of the scalp with the further development of alopecia are a consequence of physiological, psychogenic or pathological aspects.
These sensations can manifest themselves in people of different genders or age categories. Most often they are concomitant symptoms of certain diseases.
But if the situation is left unattended and the underlying ailment is not treated, then you can get a bunch of serious complications and persistent alopecia. Therefore, let’s look at some of the causes of unpleasant sensations in the form of burning of the scalp.
Poor hair care
This is one of the possible causes of a burning sensation in the scalp. It may occur due to:
- Tight hairstyles, usually with various salon weaves such as afro braid or zizi.
- Hair styling with a hairdryer or curling iron after washing your hair.
- Hair coloring, where ammonia components are used as dyes, and hydrogen peroxide is used for bleaching.
- Women wearing hats or wigs that are inappropriate in size and fit tightly.
- Ignoring protection of your head from the sun, cold, snow or rain.
Wrong lifestyle
Usually, unpleasant pain symptoms, burning, itching of the skin on the crown or frontal area of the head are the result of serious overwork of the human body. The reason for this may be:
- Insufficient rest;
- Intense pace of the working day;
- Physical inactivity;
- Poor nutrition.
At the same time, bad habits such as smoking or alcohol abuse, a disorderly lifestyle worsen the functioning of a person’s vascular system, causing spasms of his small capillaries that feed the hair follicles or bulbs.
In addition, diseases such as atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia or arterial hypertension can only increase discomfort.
And due to circulatory disorders and deterioration of metabolic processes, blood begins to accumulate in certain areas of the head, appearing on the skin:
- Burning;
- Hair loss;
- Painful sensations;
- Unpleasant itching.
Allergy
Typically, the nature of the sensation of pain and burning of the skin on the head with allergies is temporary and episodic. Since it is related to:
- The use of low-quality cosmetics such as shampoos, balms, hair care styling products.
- By consuming certain foods in your diet such as eggs, citrus fruits, chocolate or fish.
- Using certain medications.
- Hair coloring, after which the scalp may look like it is burned, accompanied by burning and itching.
And now, regarding the last judgment, I want to warn some women that before the next hair coloring and applying a new dye, you do not forget to do a wrist test in order to avoid negative consequences.
Diseases of the body
A burning sensation on the scalp and associated hair loss can be caused by:
- Hormonal imbalance in the body of women during menopause or pregnancy;
- Constant stress or nervous breakdowns;
- Malignant neoplasm in the head;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- High blood pressure;
- Dermatitis or staphylococcal lesions of the skin of the scalp.
What to do?
If you feel an unreasonable heat in your head, if the symptom torments you periodically, you need to make an urgent visit to a therapist! To find out the cause of this manifestation, you will be prescribed diagnostic procedures:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Hormonal blood test.
- Drawing up a schedule of blood pressure changes.
- MRI.
- Cardiogram.
- Electroencephalogram.
- Radiography.
- Echoencephaloscopy.
Based on this, the doctor will make a presumptive diagnosis and redirect you to a more specialized specialist - a neurologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, and others. Based on the diagnostic results, based on an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will already draw up an individual treatment regimen, which, among other things, will relieve you of the fever in the head.
The symptom we have become familiar with is quite universal. Can talk about a wide variety of conditions, diseases, and serious pathologies. Its true cause can only be determined by a specialist based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Source: fb.ru
What provokes manifestations
Often, “burning heads” occur in older people, but the younger generation is not immune from this.
The most common causes of burning in the head:
| Cause | Pathological process |
| Cervical osteochondrosis | Thinning of the intervertebral cartilaginous tissue occurs and, as a result, irreversible changes in the skeleton. The formation of salt deposits leads to compression of blood vessels and nerves in the cervical region. Blood flows poorly to the brain, and this can lead to hypoxia. Elimination of manifestations (burning of the shoulder blades, dizziness, headache and neck, back of the head, back of the head “burning”) requires treatment of the key pathology. The left side is more likely to bother you, i.e. there is discomfort on the left side of the head, but a burning sensation in many other parts of the head is also possible. |
| Increased fatigue | Continuous stress, combined with chronic illness, impairs the functioning of blood vessels, thereby complicating the proper outflow of blood from the brain. Therefore, a person feels a burning sensation and heaviness in his head. To make an accurate diagnosis and get rid of these symptoms, you need to consult a doctor - a reflexologist, a neurologist, who will prescribe an examination: MRI, CT, etc. |
| Unhealthy Lifestyle | Overexertion (physical or mental), tobacco addiction, and lack of mobility provoke deterioration in vascular function, which destabilizes blood flow. It accumulates in the head, causing pain and burning. A balanced rhythm of life will lead to the disappearance of symptoms within 2 weeks. |
| Allergic reactions | There is a burning sensation of the scalp, the reason for which is the consumption of allergenic products or the use of bad cosmetics. This dermatitis is expressed in redness of the scalp, itching, dandruff, and rash. |
| Eye diseases | Pain occurs due to systematic eye fatigue and decreased vision. The eyes “bake”, the sensations in the temples and frontal lobes are tingling, burning. |
| Hormonal imbalance | An error in choosing hormonal contraceptives, the onset of menopause, and malfunction of the thyroid gland are factors of paroxysmal activity. Diagnosis requires an EEG and blood tests for hormone levels. |
| Neuralgia | Inflammation of the nerve fibers has clear signs: sensitivity is impaired, the back of the head and the crown “burn.” Therapy can last up to a year. |
| VSD, or vegetative-vascular dystonia | Vascular and central nervous system dysfunction causes disorientation, pain, and a burning sensation in the head. |
| Arterial hypertension | An increase in blood pressure is indicated by heaviness, pain in the back of the head, pulsation, heat in the occipital area, and tinnitus. Such symptoms progress with sudden movements. The cause of discomfort is the expansion of peripheral vessels. Here it is important to urgently begin pharmacological treatment to avoid the formation of blood clots that lead to strokes. |
| Sympatho-adrenal crisis | Panic attacks, being one of the manifestations of VSD of the hypertensive type, occur in 2.5 million people. Attacks last 6-8 hours. In addition to the fact that the back of the head is “on fire,” there are surges in blood pressure, lack of air, chills, and fear of death. |
| Neoplasms | Tumor formations of the brain cause compression of its tissue, compression of blood vessels and continuous burning pain in the head, against which analgesics are powerless. The problem can be identified by a feeling of nausea, severe fatigue, reflex disorders, and decreased vision. X-rays and EEG will help diagnose the tumor. A visit to an ophthalmologist and an MRI of the brain would be a good idea. |
Why does my head burn unbearably and hurt in the frontal area? The patient may have migraine or eye pathology. Also, discomfort in the forehead may indicate pharyngitis or sinusitis.
The left or right half of the head “burns” from the inside due to increased blood pressure. In addition, the localization of a burning sensation on the left or right can warn of the course of severe viral infections (meningitis, encephalitis).
A burning sensation in the head is possible with cervical osteochondrosis due to pinched nerve endings. This is characterized by localization of discomfort in the occipital region.