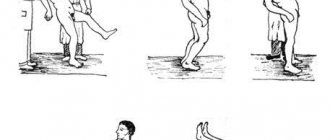
The most important diagnostic symptom, which indicates damage to the pyramidal system (the system of nervous structures that support the coordination of human movements), is Babinski's symptom. In medicine, it is described as an abnormal response to irritating stroking of the edge of the sole from the outside. In this case, normally the toes should bend, but if there is a pathology, they, on the contrary, slowly unbend and fan out to the sides.
In the article we will describe this reflex in more detail and talk about its manifestations.
Etiology
The structure of the central nervous system in humans involves a complex scheme of subordination of some structures - on the periphery, and others - the cerebral cortex and subcortical centers. To accomplish the task at hand - transmitting an electrical impulse, or command, so-called nerve tracts are provided. One of the most important is the pyramid path. Along it, impulses move from the brain to the muscle groups of the skeleton.
The mechanism of control over human movements involves performing not only voluntary contractions - on command, but also involuntary - unconscious ones, as well as a ban on motor activity. For example, in a situation where a sharp foreign object gets into a shoe, a pain signal is immediately sent to the cerebral cortex - but in order to prevent a person from falling, the leg muscles stop bending after the first involuntary contractions. The balance is not broken.
If damage to the pyramidal tract occurs, Babinski's sign will be positive. This means that the inhibitory function of the motor nerve pathway has been lost. Such disorders are possible both on one side and on both sides at once - bilateral damage.
Main reasons:
- neuroinfections – inflammation of the nerve fiber of a bacterial or viral nature;
- vascular accidents - strokes;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- autoimmune disorders – multiple sclerosis;
- neoplasms – benign/malignant tumors;
- intracranial hypertension.
The significance of the Babinski reflex can only be assessed by a specialized doctor - a neurologist. After all, there are periods in people’s lives when a failure in the pyramidal tract is a sign of a nervous system that has not yet fully matured. In some situations, the symptom accompanies injury to the tendons of the limbs.
Mechanism of occurrence
What Babinski's symptom is can be understood by studying the mechanism of its occurrence. An impulse entering the brain with information about the presence of a stimulus in the foot area is analyzed by cells of the cerebral cortex.
In Betz's pyramidal cells, a response, motor or inhibitory impulse is formed, transmitted along the descending pathway. As a result of this process, the muscles of the foot contract, indicating a positive or negative result.
The path that ensures the delivery of the response signal to the skeletal muscles is called the pyramidal nerve tract. When the impulse has passed through the ascending path to the brain and descending along this tract without obstruction, the toes bend down towards the foot. Such a reaction to an irritant is considered normal.
We can talk about a pathological Babinski symptom when the result is the opposite. Namely, the thumb is extended, the rest are spread wide to the sides, forming something like a fan in shape.
Features of manifestations in adults
If the Babinski reflex is detected in a person after he reaches the age of 18, this indicates a pathological process in the central nervous system. Such a symptom cannot be a physiological norm.
Normally, when applying line-like movements along the sole of the lower limb, the toes must be bent. In some people, they can maintain a neutral position - the required reaction is absent. However, in a situation where adult fingers diverge to the sides, this is only a pathology. It requires clarification and differential diagnosis.
The pathological Babinski reflex is characterized by a combination with other symptoms - disturbances in cerebellar coordination or muscle self-control over the limbs. People seek advice from a doctor because of difficulties with movement, frequent injuries, and paresis. Upon examination, they will find not only Babinsky’s symptoms, but also others - in direct dependence on the cause of the disorder and the level of damage to the pyramidal tract.
Provoking factors for Babinski's symptom can be:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – motor neuron disease;
- tumor in any area of the spinal cord/brain;
- Friedreich's ataxia;
- toxic encephalopathy;
- hemorrhagic type of stroke;
- demyelization of nerve fiber;
- consequences of meningitis;
- spinal injuries;
- Tuberculosis of the meninges.
If a neurological deficit is identified - a symptom of motor neuron damage, the study of the symptom in adults requires an integrated approach. Delaying differential diagnosis means exposing a person to additional danger. As the disease progresses, the prognosis is poor.
Therapy
Babinski's symptom is one of the pathological reflexes in which the therapeutic effect of treatment can occur only if the root cause of its occurrence is discovered.
Based on the results of a complete diagnosis, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. Treatment in this case will depend on the identified disease. The main direction of the fight is to prevent complete muscle paralysis due to the progression of the disease.
Depending on the disease, the following treatment methods can be used:
- immunotherapeutic (for mild degrees);
- medicinal (for mild and moderate severity);
- chemotherapy (malignant tumors);
- physical (massage, radio/UHF therapy, electrophoresis);
- surgical (if conservative treatment is ineffective).
The choice of method and treatment regimen are strictly individual for each patient. As a rule, in addition to the neurologist, other specialists in a narrow field of medicine participate in this process, depending on the disease.
In most cases, even with effective treatment, the patient requires long-term rehabilitation to restore lost functions. In severe illnesses, the recovery process is impossible, and the damage may be irreversible.
That is why preventive examinations by a neurologist and other specialists are necessary. A timely detected Babinski symptom for a person is an opportunity to prevent harmful consequences for the body.
Manifestations in children
The situation with the Babinski reflex in children is far from ambiguous - the symptom up to a certain age can be attributed to a variant of immaturity of the nervous structures. It will definitely be checked in babies who have just been born. Normally it is positive, on both sides. A negative result from Babinsky's study may indirectly indicate pathologies of the nervous system such as cerebral palsy or a congenital tumor.
As the connections between nerve cells and fibers strengthen, the reflexes in newborns change - some of them weaken, while others strengthen. Up to two to three years, the system is constantly rebuilt and adapts to changes inside and outside the body.
Later manifestations of the Babinski reflex after 3-4 years should cause natural anxiety - by this age the symptom gradually fades away. However, its presence may indicate either underdevelopment of parts of the nervous system, or a hidden pathology. It is often caused by brain injury in children.
The prognosis will depend on the timing of diagnosis - identification of Babinsky's symptom, as well as treatment measures followed by rehabilitation. The child's body is flexible and has great potential for recovery. Therefore, with appropriate therapy, the child will develop according to age.
Diagnostics
As a rule, a positive Babinsky test is the result of a special examination performed by a neurologist. After all, people themselves without medical education may not even be aware of the presence in their body of a failure of the impulse to the skeletal muscles.
In order to clarify what was the root cause of the pathological symptom, it will be necessary to carry out a number of clarifying diagnostic procedures:
- various blood tests - general, biochemical, for autoimmune processes;
- angiography of cerebral vessels - previous headaches may indicate vascular lesions, for example, atherosclerosis with foci of ischemia;
- magnetic resonance imaging - changes in the nerve impulse due to compression of the fiber by a tumor, traumatic tissue edema, intracranial hematoma;
- spinal puncture to take cerebrospinal fluid for examination - to rule out an infectious lesion of the system;
- according to individual indications - tissue biopsy, more precisely the motor roots of the spinal cord, for the purpose of differential diagnosis with cancer.
Only after careful comparison of information and analysis of research results, a neurologist will make an accurate diagnosis and select effective therapy.
Bilateral Babinski sign
Evidence of severe damage to the nervous system, both in adults and children, will be the appearance of Babinski's symptom on both sides. Most often, it is based on the course of the infectious process. For example, this may be a sign of meningitis - a severe pathology of the membranes of the brain as a result of damage by bacteria.
Whereas a pathological focus in the spinal cord often occurs due to tuberculosis of the bones with transition to the meninges. As a result of a functional malfunction in the pyramidal tract, the motility of nerve endings on both sides will be impaired, and not just on the right, as, for example, with a direct blow to the back.
Spinal infantile paralysis is another common cause of the Babinski reflex. If it first appears on the left, the symptom coincides with a feverish state. However, over time, the muscles will become paralyzed on both sides. They involuntarily contract and provoke severe pain.
Less commonly, severe anemia - a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the bloodstream, also contributes to the development of bilateral Babinski's symptom. Especially with B12 deficiency form of the disease. In such a situation, the symptom will not appear on only one side. The final diagnosis will be established after laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Types of reflexes
Healthy people will have physiological and pathological reflexes from the moment they are born. Only a doctor should evaluate them.
In the field of neurology, reflexes and symptoms, including Babinsky’s, are usually divided into congenital - they are also unconditioned, and acquired - developed over a number of years. Their loss or re-development can tell a specialist a lot about the state of the central nervous system.
Thus, in the absence of congenital reflexes, it is necessary to immediately carry out in-depth diagnostics of the brain - its anatomical underdevelopment is often revealed. If children's reflexes were suddenly detected in adults, it is necessary to exclude infectious, post-traumatic, and oncological lesions in the brain structures.
Whereas the loss of acquired reflexes is a common result of demyelization of nerve fibers, for example, in multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease. By identifying the Babinski symptom, the doctor will begin a neurological examination of the patient. Subsequent diagnostic studies will allow you to put everything in its place and select a treatment regimen.
The achievements of modern medicine make it possible to fight even severe neurological diseases, a sign of which is the Babinski reflex, and achieve positive results.
Special role
Babinski's sign on the right or left is classified as pathological reflexes. That is, those that manifest themselves with structural or functional damage to different parts of the central nervous system. They, as you already understood, are used to diagnose nervous diseases.
When the intensity of manifestations of such reflexes is high, we talk about hyperreflexia, but if it is reduced to the point of loss, then we are talking about hyporeflexia, and if the manifestation of the reflex is uneven, then about anisoreflexia. But, by the way, if the decrease or increase in reflexes is symmetrical, then often this is not a sign of central nervous system diseases.