The medication is a drug that affects the central nervous system. Mexidol has a membrane-stabilizing, antihypoxic effect. The medicine increases the body's resistance to stress, improves memory, prevents and suppresses seizures, and reduces the amount of individual lipid fractions in tissues. Acts as a nootropic and antioxidant.
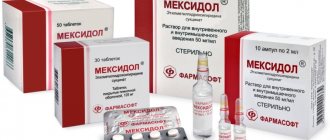
Mexidol: release form
The active ingredient that provides the antioxidant activity of the drug is ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate.
Release form: solution for parenteral administration with a concentration of the active substance of 50 g/l and tablets of 125 mg.
Release form: dark or light ampoules with a break point. Volume 2 ml of 5% solution. Ampoules are sold in contour plastic cells of 5 pcs.
Tablets – 10 tablets. In a blister, and 90 pcs. - in plastic jars.
Storage conditions
When stored properly (in a cool, dark place) it is good for 3 years.
(Visited 28,221 times, 298 visits today)
Mexidol is available in the form of tablets for oral administration, white with a slight beige tint. The tablets are packaged in blisters of 10 pieces, 3 or 5 blisters in a cardboard box.
Each tablet contains 125 mg of the active ingredient - Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, as well as auxiliary components, including lactose, which should be reported to patients with congenital lactose intolerance or malabsorption syndrome.
Mexidol: what helps?
The drug activates metabolic reactions, improves microcirculation, reduces blood viscosity and improves cerebral circulation. Protects the cell membranes of red blood cells and platelets from destruction, reduces cholesterol levels.
Normalizes redox processes in brain cells.
Mexidol relieves symptoms of alcohol intoxication during withdrawal syndrome. Restores cognitive functions, eliminates autonomic imbalance after long binges.
Strengthens the effect of other drugs: tranquilizers, antipsychotics and anticonvulsants.
Mexidol helps with depression, improves memory and increases learning ability.
Taking Mexidol for coronary heart disease helps preserve the myocardium by strengthening the myocardiocyte membrane, as well as protecting the vascular wall from cholesterol deposition.
Promotes the formation of collateral circulation in conditions of myocardial damage after a heart attack.
pharmachologic effect
Mexidol is an inhibitor of free radical processes, a membrane protector. It has a pronounced nootropic, anticonvulsant, antistress, and antihypoxic effect on the body.
Under the influence of the drug, the body's resistance to various negative environmental and internal factors increases - shock, stress, intoxication with alcohol and drugs, circulatory disorders, ischemia.
Mexidol increases the content of Dopamine in the brain, improves metabolic processes in brain tissue, its blood supply and oxygen supply to cells. Under the influence of the drug, the level of cholesterol in the blood decreases.
The active ingredient of the drug helps remove toxins from the body that accumulate due to alcohol poisoning, as a result of which the patient improves the functioning of internal organs and the nervous system.
Under the influence of the drug, the therapeutic effect of tranquilizers, antidepressants, antipsychotics, sleeping pills and anticonvulsants is enhanced, which makes it possible to significantly reduce their daily dose, as well as reduce the likelihood of developing side effects.
The drug improves the condition of the heart muscle against the background of ischemia, restores myocardial contractility and normalizes blood supply to the ventricles.
Features of the use of Mexidol in the treatment of alcoholic diseases
This drug is not compatible with alcohol, but it allows you to completely (in some cases partially) neutralize the negative consequences of excessive alcohol consumption.
The result of taking Mexidol will be the following changes:
- change in the pharmacological effect of alcohol,
- elimination of withdrawal symptoms,
- relieving cravings for alcohol,
- curing various mental disorders that have developed against the background of alcoholism,
- getting rid of concomitant mental disorders not caused by alcohol,
- cure somatic complications of alcoholism.
Only Mexidol does not treat alcohol addiction. Pharmacotherapy includes a whole range of drugs with different effects, such as: nootropics, vasoactive drugs, antioxidants, drugs with neuromodulatory and neurotransmitter effects. Mexidol is a highly effective drug of combined action with a minimum number of side effects. The drug has an effect on various stages of pathogenesis, eliminates polypharmacy, reduces the time and cost of treatment, and also makes the treatment of alcoholism more effective.
Mechanisms of the damaging effects of antioxidants
The drug reduces the formation of peroxide substances that destroy cell membranes, which leads to increased oxygen delivery to tissues and preservation of tissue structures.
Mexidol activates the following enzymes: superoxide dismutase, calcium independent phosphodiesterase, acetylcholinesterase.
This improves the transmission of nerve impulses at synapses and binding to ligands. Mexidol increases the formation of neurotransmitters, in particular dopamine.
The drug triggers glycolytic reactions and ensures the oxidative processes of the Krebs cycle during tissue hypoxia, which supports the formation of ATP and creatine phosphate at the required level.
Tumor cells are poor in mitochondria (produce energy) and rich in lysosomes (contain a complex of highly active enzymes). These enzymes are capable of digesting proteins, and their uncontrolled release into the cytoplasm of cells leads to self-digestion and cell death.
Vitamin A in a cancer cell accumulates in lysosomes, and vitamin E in mitochondria. Without the protection of vitamin E, vitamin A quickly oxidizes and destroys lysosome membranes, releasing proteolytic enzymes that cause rapid death of the cancer cell.
Vitamin C is not involved in the metabolism of cancer cells, but together with vitamins A and E it serves as good protection for healthy cells (the mechanism of natural death of cancer cells in the presence of antioxidants is not considered in official oncology).
Cancer patients and doctors should know that the complex of vitamins A, E and C has a clear direct anti-cancer effect, which manifests itself within 7-10 days after the start of their use. In cancer patients, the amount of vitamins A and E is reduced by 70%, and vitamin C by 60%.
When using antioxidants after surgery, the relapse rate decreases from 80% to 5.7%. With a 15-day course of treatment with antioxidants, the condition of cancer patients, blood tests, and pain disappear significantly.
Former cancer patients, and healthy people as well, should take antioxidants constantly and throughout their lives.
Patented antioxidant complexes produced in the form of dietary supplements are noteworthy.
Composition of antioxidant complex No. 1 (take 1-2 liters of freshly squeezed juices per day)
- Vitamin B15 (Puritans pride, USA)
- B50 (NowFoods, USA)
- E-400 (NowFoods, USA)
- S-500 (NowFoods, USA)
- Zinc NowFoods, USA)
- Superantioxidants NowFoods, USA)
- Selenium NowFoods, USA)
- Chlorophyll NowFoods, USA)
- Omega 3-6-9 (NowFoods, USA)
- Glutathione (NowFoods, USA)
- ANSS (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin A (NowFoods, USA)
The drugs are used with meals, at the same time.
Composition of antioxidant complex No. 2 (drink 1-2 liters of freshly squeezed juices per day)
- Novomin (Siberian Health)
- Zinc (NowFoods, USA)
- Selenium (NowFoods, USA)
- Indole-3-carbinol (for hormone-dependent tumors) (NowFoods, USA)
- Grape seed extract (NowFoods, USA)
- Resveratol (NowFoods, USA)
- Quercetin (NowFoods, USA)
Composition of antioxidant complex No. 3 (drink 1-2 liters of freshly squeezed juices per day)
- Vitamin C-500 (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin A (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin E-400 (NowFoods, USA)
- Pine bark extract (NowFoods, USA)
- Coenzyme Q10 (NowFoods, USA)
- Alpha lipoic acid (NowFoods, USA) or berlithion (Berlin Hemi)
- Pycnogenol 100 mg (NowFoods, USA)
- Hemp oil (Russia)
Mechanism of action of Mexidol
This drug has an original mechanism of action. Unlike the mechanism of traditional neuropsychotropic drugs, it is distinguished by the absence of specific binding to a number of receptors. Mexidol promotes:
- lipid peroxidation,
- activation of superoxide dismutase,
- increasing the polar fractions of lipids in the membrane,
- reducing the ratio of cholesterol to phospholipids,
- reducing the viscosity of the lipid layer,
- increasing membrane fluidity,
- improving energy exchange in the cell,
- activation of the energy-synthesizing functions of mitochondria,
- protection of the apparatus and structure of cell membranes.
The drug leads to a change in the functional activity of the membrane. The consequence of this is conformational changes, which result in a modulating effect on the activity of membrane-bound enzymes, receptor complexes and ion channels.
The drug "Mexidol" is characterized by a pronounced lipid-lowering effect. The drug helps reduce the level of low-density lipoproteins and total cholesterol, and helps increase the level of high-density lipoproteins.
Conclusion: the effect of Mexidol is determined by its powerful antioxidant properties, the ability to activate the energy-synthesizing functions of mitochondria and stabilize cellular biomembranes, modulate the passage of ionic currents and the functioning of receptor complexes, promote synaptic transmission, the binding of endogenous substances and the relationship of brain structure. This mechanism of action allows the drug to influence the main links in the pathogenesis of various diseases.
Mexidol has a wide range of effects, low toxicity and fairly minor side effects. The drug increases the effect of other centrally active substances.
Indications for use
Due to the lack of evidence of the safety of the drug for pregnant and nursing mothers, it is recommended to refrain from taking it during pregnancy and feeding a baby.
special instructions
Combined with pharmaceuticals used in therapeutic practice. In pediatrics, it is not used for special indications, since there is no evidence of safety.
While taking it, you should not drive a car or other vehicles that require quick reactions.
Available in pharmacies with a prescription.
Mexidol tablets are prescribed to patients for the treatment and prevention of the following conditions:
- The period of rehabilitation of the patient after an ischemic stroke or with frequent transient ischemic attacks;
- Traumatic brain injuries or consequences after them;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia with frequent attacks of panic attacks;
- Brain dysfunctions of various origins - after injuries associated with metabolic processes;
- Impaired functioning of the brain and coronary vessels caused by the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques;
- Coronary heart disease as part of complex treatment;
- Neuroses and various psycho-emotional disorders;
- Withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism with severe disturbances in the psycho-emotional state;
- The rehabilitation period after poisoning with tranquilizers or antipsychotic drugs;
- Prevention of the development of heart and vascular disease in patients at risk or with excessive physical exertion;
- Chronic stress.
The tablets have some restrictions for use, so before starting therapy you should carefully read the accompanying instructions. The following conditions are contraindications:
- Severe liver failure;
- Acute liver dysfunction;
- Individual intolerance to the components included in the tablets;
During pregnancy, lactation and patients under 12 years of age, treatment with the drug is not carried out or is prescribed with special caution, which is due to the insufficiently studied safety of the drug on the body.
Since there are no clinical data on the effect of the drug Mexidol on the intrauterine development of the fetus, treatment with this drug is contraindicated in pregnant women.
It is not known whether the drug is excreted in breast milk and how this can affect the child’s body, therefore, due to the lack of information, treatment with the drug is not carried out among nursing mothers. If a course of therapy is necessary, a woman should think about ending the lactation process.
Mental disorders in brain tumors
Brain tumors are relatively common in the general population, with an annual incidence of 9 per 100,000 for primary brain tumors and 8.3 per 100,000 for brain metastases. Traditionally, brain tumors are classified based on their histopathological characteristics or anatomical location. There are two types of tumors: primary ones, which originate directly from brain tissue, and those that metastasize throughout the brain (metastatic tumors often present with more neuropsychiatric symptoms).
The most common primary brain tumors are gliomas, which are divided into several types: astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. Groups of brain tumors that do not belong to glial tissue include meningiomas, schwannomas, craniopharyngiomas, germ cell tumors, pituitary adenomas, and tumors of peripheral regions. Most brain tumors are gliomas, 40%-55%. Tumors that metastasize to the brain account for 15-25% of all brain tumors.
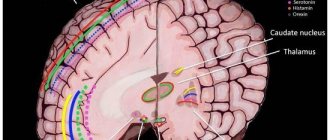
Most brain tumors manifest themselves with fairly specific neurological signs. However, in rare cases they may manifest primarily as psychopathological symptoms. In a study by M. Keschner et al. (1938) reported that 78% of 530 patients with brain tumors had symptoms of mental disorders, with 18% having only psychopathological symptoms as the first clinical manifestation of a brain tumor. Because of the brain's neural connections, a lesion in one area can present with a variety of symptoms depending on the functional activity of a particular network of neurons. In other words, the symptoms of brain damage depend on the function of the networks of neurons underlying the affected areas. For example, significant associations have been found between anorexia symptoms and hypothalamic tumors, between psychotic symptoms and pituitary tumors, memory symptoms and thalamic tumors, and affective disorders and frontal lobe tumors.
As is known, treatment of brain tumors includes: surgical resection of the tumor, stereotactic radiosurgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Often, psychopathological symptoms may be the only manifestation of brain tumors; the latter can be expressed in affective and anxiety disorders, psychosis, cognitive disorders, for example, memory problems, personality changes or anorexia. Symptoms that necessarily require neuroimaging include: atypical psychosis, mood/memory changes, new or atypical psychopathological symptoms, personality changes, and anorexia without body dysmorphic disorder. Unfortunately, psychopathological symptoms in brain tumors are of little value in determining the location of the tumor.
Most of the major studies on brain tumors and psychopathological symptoms date back to the 30s of the 20th century.
Depression can occur at different stages of development (before, during, or after diagnosis/treatment) of brain tumors. Depression has been reported in 2.5%-15.4% of primary brain tumors. According to A. Manio et.al. (2011), depression was found in 44% of all brain tumors, both primary and metastatic, and was associated with functional impairment, cognitive dysfunction, decreased quality of life, and anticipation of death. It has also been noted that depression is more common in frontal lobe tumors. More specifically, left-sided frontal lobe tumors were more often associated with depression and hypokinesia.
It is worth reminding the reader that apathy should be distinguished from major depressive disorder and chronic fatigue syndrome. Patients with apathy, when talking about their mood, state that they are not depressed, but have constant fatigue and lack of motivation. Apathy may be due to “functional shutdown” of the frontal lobe and paralimbic areas or damage in these areas. At the same time, research shows that apathy is common in neurodegenerative disorders and is independent of depression. Diagnostic criteria for apathy proposed by S. Starkstein et al (2001) include: lack of motivation, decreased goal-directed behavior (lack of effort or dependence on others to structure activities), decreased goal-directed cognitive activity (lack of interest in learning new skills or new experiences, or lack of concern about one's personal problem) or weakened expression of emotion (flattened affect or lack of emotional sensitivity to positive or negative events).
In addition to depression, patients with brain tumors may exhibit other symptoms of mood changes, such as mania. There are reports in the literature that depression is associated with left-sided frontal tumors, and mania is more common in right-sided frontal tumors with characteristics such as euphoria and underestimation of the significance of one's illness.
Other common mental disorders associated with brain tumors include hallucinations and psychosis. S. Madhusoodanan et al. (2010) reported that although symptoms of mood changes are most common in brain tumors (36% of cases), psychotic symptoms are found in 22% of patients. Usually the latter are detected with tumors in the cortical and pituitary regions, as well as in the pineal gland and “posterior brain structures”. Among these regions, pituitary tumors were the most common in psychosis. However, in another study, temporal lobe tumors were strongly associated with psychotic disorders.
Frontal lobe and ventricular cysts may present with personality changes. These changes may include disinhibition, hypersexuality, and aggressive behavior.
Weight loss and decreased appetite are associated with various types of malignancies, and in patients with brain tumors they may be among the first prognostic signs of neoplasms. This can lead to misdiagnosis of anorexia nervosa, especially in young girls. Although anorexic symptoms can result from tumors in different locations in the brain, hypothalamic tumors most often present as symptoms of anorexia.
Brain tumors are a rare occurrence as a primary cause of psychopathological symptoms. The rarity of this condition is reflected in the late recognition of a brain tumor, manifested in the insidious course of the disease process, atypical symptoms, and a variety of signs indicating several cause-and-effect factors that complicate the diagnosis of the disease. Small clues that a psychiatrist can look for include neurological signs: apraxia, visual field deficits and other mild neurological symptoms. The first manifestations of the disease here may be personality changes, sleep disturbances, apathy, weight loss, and anorexia. Some indicators that suggest the presence of brain tumors may include psychopathological symptoms that do not fit into specific diagnostic categories or atypical symptoms, symptoms that are refractory to treatment, and frequent relapses of previously controlled symptoms when other factors contribute to disease progression (eg, noncompliance with treatment , frequent acute stressors, chronic stress situations, or changes in medication regimen or dosage) by the physician were excluded.
Neuroimaging is the primary diagnostic technique used to visualize the presence of brain tumors. In this case, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used for relatively rough anatomical assessments. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is used to relative quantify metabolic processes at different locations in the brain. Studies of neuronal activity related to local cerebral blood flow are carried out using functional MRI (fMRI). Positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography provide imaging using radionuclides. We remind the reader that CT remains the modality of choice for suspected brain injury and acute hemorrhage (other advantages include greater availability, fewer contraindications, and lower costs). MRI offers higher resolution and is useful in assessing necrosis, hemorrhage, cysts, tumors, and white matter changes. Diffusion tensor imaging (tractography) can monitor damage to connections between different brain structures. Functional studies are mainly used for research purposes and currently appear to have little advantage over CT and MRI in routine clinical practice. Neuropsychological testing is useful in assessing cognitive function. and neuropsychological dysfunction, in documenting changes before and after treatment, and in monitoring the effectiveness of rehabilitation interventions.
Removal of the tumor can completely eliminate psychopathological symptoms or behavioral disorders; even reducing the size of the tumor or stopping its growth leads to a weakening of the severity of mental disorders. In addition, treatment of some, in some cases, acute neurological syndromes, such as increased intracranial pressure or hydrocephalus, can improve cognitive functioning and reduce the severity of psychopathological symptoms.
Patients with brain tumors may exhibit increased susceptibility to delirium, seizures, drug side effects, and unpredictable drug interactions.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) have a favorable side effect profile and are less likely to cause delirium. Maprotiline and bupropion have a higher risk of seizures. Methylphenidate has been shown to be effective in patients with secondary depression. It has also been found to be effective in patients with apathy syndrome.
Mood stabilizers are useful in treating manic symptoms. Lithium may increase delirium and lower the seizure threshold. In contrast, valproate, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, benzodiazepines and gabapentin, which have anticonvulsant properties, may be preferable alternatives in this case. A recent review examined the possible neuroprotective effects of lithium in patients with brain cancer, especially during radiation treatment. Possible targets for lithium therapy may include: excitotoxicity, severe apoptosis, decreased neurogenesis and slowed aging, as well as accelerated regeneration processes.
Mexidol: when is it used?
The drug is used as an antioxidant in neurology, cardiology and psychiatry.
Indications for the use of Mexidol are as follows:
- Residual effects after strokes, as well as during transient cerebral ischemia to prevent exacerbation;
- Concussion, consequences of head injuries;
- Acute and chronic encephalopathies;
- Autonomic dysfunction;
- Neurosis-like conditions;
- Panic attacks;
- Cognitive impairment due to cerebrosclerosis;
- Acute coronary circulatory disorders, as an additional therapy;
- In surgery after surgical interventions, purulent inflammation of the peritoneum and pancreatitis;
- Psychopathy, withdrawal syndrome;
- Acute intoxication with psychotropic drugs;
- Neurasthenic conditions after strong physical exertion;
- For prevention before extreme stress.
Contraindications for Mexidol
- End-stage liver failure;
- Anuria;
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance.
The drug is non-toxic. Does not affect coordination, blood pressure and breathing.
Side effects of Mexidol
Possible side effects from the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
An allergic reaction such as urticaria or Quincke's edema is possible.
Mexidol: side effects
The medication is well tolerated; non-standard reactions occur in exceptional cases. When using the solution, the following may occur:
- nausea;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- constant drowsiness;
- clinical manifestations of allergies, with rashes, itching, redness.
When using tablets, the following is observed:
- discomfort in the epigastric region;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- attacks of nausea, heartburn;
- flatulence;
- loss of appetite, lethargy;
- general weakness, allergies.
In some cases, blood pressure increases or decreases, and coordination of movements is impaired. Patients complain of excessive sweating, problems falling asleep, and emotional reactivity.
Daily dose and method of administration
Tablet form
Mexidol tablets are prescribed at 375-750 mg/day.
First day – 1-2 tablets (125-250 mg).
Then the dose is increased to the maximum effective, but not more than 800 mg/day.
For cardiac patients, treatment is prescribed in courses of 1.5-2 months. Preventive treatment is carried out in the spring-summer off-season.
Symptoms of overdose include increased drowsiness.
Mexidol in ampoules
The drug is prescribed for intravenous jet, slow (5-7 min) administration, and drip – 60 drops/min. Before jet administration, dilute in an isotonic solution.
Intramuscular injection is made deep into the tissue of the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle.
The dosage regimen is prescribed individually: 1-2 ampoules 1-3 r/day. The maximum daily dose is 0.8 g.
- For the treatment of dementia - 0.1-0.3 g/day is administered intramuscularly.
- For alcohol withdrawal – intravenous drip – 0.5 g/day.
- Poisoning with neuroleptics – 0.3 g/day.
- In surgical practice, for the treatment of peritonitis, pancreatitis - 0.2 g 3 times / day.
- For severe necrotizing pancreatitis - 0.8 g twice the first two days, then 0.5 2 times a day by drip.
- For acute strokes and dyscirculatory encephalopathies - 500 g drip 4 times a day for two weeks.
- The drug is discontinued gradually after achieving positive clinical and laboratory results.
- For preventive purposes – 200 mg 2 times a day, course – 14 days.
- In hospital settings, Mexidol is prescribed to children for the treatment of neuroinfection at a dose of 0.1 mg. intramuscularly.
- A 5% Mexidol solution is used to rinse the mouth for stomatitis, gingivitis and purulent inflammation in the periodontal pocket. Apply 3 times a day.
Mexidol is broken down in the liver and excreted in the urine. Action time – 4 hours.
Interaction with other drugs
Meskidol potentiates the effect of anticonvulsants, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants. Reduces the toxicity of ethyl alcohols.
Tablets of 125-250 mg are prescribed orally 3 times a day. The dose of Mexidol should be increased gradually. The course of treatment ranges from 14 days to 6 weeks and depends on the type and severity of the disease.
The drug solution is intended for intramuscular, jet or drip administration. It is necessary to administer 200-500 mg 1-3 times a day per day, the method of administration is determined depending on the type of disease. The course of treatment is 5-30 days.
After collecting tests and determining a sustainable positive effect, Mexidol is gradually discontinued. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated after 1-3 months.
Important: Mexidol and instructions
Mexidol enhances the effect of anxiolytics, benzodiazepine derivatives, levodol and anticonvulsants, and reduces the toxic effect of ethyl alcohol.
Often, to enhance the therapeutic effect, as prescribed by a doctor, the drug is prescribed together with nootropics, herbs with a sedative effect, tranquilizers, Actovegin, Piracetam and their analogues. Such therapy can only be prescribed by the attending physician, because It is he who determines the benefits and harms of complex treatment, the degree of its effectiveness.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter
The tablets are intended to be taken orally, without chewing, with water or any other liquid. Treatment begins with 1 tablet 3 times a day, if necessary increasing the single dose to 2 tablets. The duration of drug therapy depends on the diagnosis, but is at least 2 weeks.
To eliminate and prevent signs of ischemia, patients with coronary heart disease are recommended to take this drug for at least 6 weeks. During periods of probable exacerbations (autumn and spring), the course is repeated.
If the dose recommended in the instructions is exceeded, the patient may experience drowsiness, lethargy, and dizziness.
As a rule, these phenomena disappear after discontinuation of the drug, but if lethargy increases and there is no response to stimuli, the patient should be immediately taken to a doctor for symptomatic treatment.
The drug Mexidol, when used simultaneously with ethanol, reduces the toxic effect of the latter.
When tablets are used simultaneously with nootropics, antipsychotics, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, their therapeutic effect is enhanced, so patients require dose adjustment.
Mexidol for oncology is possible or not
The active ingredient that provides the antioxidant activity of the drug is ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate.
Release form: solution for parenteral administration with a concentration of the active substance of 50 g/l and tablets of 125 mg.
Release form: dark or light ampoules with a break point. Volume 2 ml of 5% solution. Ampoules are sold in contour plastic cells of 5 pcs.
Storage conditions
When stored properly (in a cool, dark place) it is good for 3 years.
(Visited 28,221 times, 298 visits today)
Each tablet contains 125 mg of the active ingredient - Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, as well as auxiliary components, including lactose, which should be reported to patients with congenital lactose intolerance or malabsorption syndrome.
Mexidol: what helps?
The drug activates metabolic reactions, improves microcirculation, reduces blood viscosity and improves cerebral circulation. Protects the cell membranes of red blood cells and platelets from destruction, reduces cholesterol levels.
Normalizes redox processes in brain cells.
Mexidol relieves symptoms of alcohol intoxication during withdrawal syndrome. Restores cognitive functions, eliminates autonomic imbalance after long binges.
Mexidol helps with depression, improves memory and increases learning ability.
Taking Mexidol for coronary heart disease helps preserve the myocardium by strengthening the myocardiocyte membrane, as well as protecting the vascular wall from cholesterol deposition.
pharmachologic effect
Mexidol is an inhibitor of free radical processes, a membrane protector. It has a pronounced nootropic, anticonvulsant, antistress, and antihypoxic effect on the body.
Under the influence of the drug, the body's resistance to various negative environmental and internal factors increases - shock, stress, intoxication with alcohol and drugs, circulatory disorders, ischemia.
Mexidol increases the content of Dopamine in the brain, improves metabolic processes in brain tissue, its blood supply and oxygen supply to cells. Under the influence of the drug, the level of cholesterol in the blood decreases.
Under the influence of the drug, the therapeutic effect of tranquilizers, antidepressants, antipsychotics, sleeping pills and anticonvulsants is enhanced, which makes it possible to significantly reduce their daily dose, as well as reduce the likelihood of developing side effects.
The drug improves the condition of the heart muscle against the background of ischemia, restores myocardial contractility and normalizes blood supply to the ventricles.
Mexidol activates the following enzymes: superoxide dismutase, calcium independent phosphodiesterase, acetylcholinesterase.
This improves the transmission of nerve impulses at synapses and binding to ligands. Mexidol increases the formation of neurotransmitters, in particular dopamine.
The drug triggers glycolytic reactions and ensures the oxidative processes of the Krebs cycle during tissue hypoxia, which supports the formation of ATP and creatine phosphate at the required level.
Tumor cells are poor in mitochondria (produce energy) and rich in lysosomes (contain a complex of highly active enzymes). These enzymes are capable of digesting proteins, and their uncontrolled release into the cytoplasm of cells leads to self-digestion and cell death.
Vitamin C is not involved in the metabolism of cancer cells, but together with vitamins A and E it serves as good protection for healthy cells (the mechanism of natural death of cancer cells in the presence of antioxidants is not considered in official oncology).
Cancer patients and doctors should know that the complex of vitamins A, E and C has a clear direct anti-cancer effect, which manifests itself within 7-10 days after the start of their use. In cancer patients, the amount of vitamins A and E is reduced by 70%, and vitamin C by 60%.
When using antioxidants after surgery, the relapse rate decreases from 80% to 5.7%. With a 15-day course of treatment with antioxidants, the condition of cancer patients, blood tests, and pain disappear significantly.
Former cancer patients, and healthy people as well, should take antioxidants constantly and throughout their lives.
Patented antioxidant complexes produced in the form of dietary supplements are noteworthy.
- Vitamin B15 (Puritans pride, USA)
- B50 (NowFoods, USA)
- E-400 (NowFoods, USA)
- S-500 (NowFoods, USA)
- Zinc NowFoods, USA)
- Superantioxidants NowFoods, USA)
- Selenium NowFoods, USA)
- Chlorophyll NowFoods, USA)
- Omega 3-6-9 (NowFoods, USA)
- Glutathione (NowFoods, USA)
- ANSS (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin A (NowFoods, USA)
The drugs are used with meals, at the same time.
- Novomin (Siberian Health)
- Zinc (NowFoods, USA)
- Selenium (NowFoods, USA)
- Indole-3-carbinol (for hormone-dependent tumors) (NowFoods, USA)
- Grape seed extract (NowFoods, USA)
- Resveratol (NowFoods, USA)
- Quercetin (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin C-500 (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin A (NowFoods, USA)
- Vitamin E-400 (NowFoods, USA)
- Pine bark extract (NowFoods, USA)
- Coenzyme Q10 (NowFoods, USA)
- Alpha lipoic acid (NowFoods, USA) or berlithion (Berlin Hemi)
- Pycnogenol 100 mg (NowFoods, USA)
- Hemp oil (Russia)
special instructions
Combined with pharmaceuticals used in therapeutic practice. In pediatrics, it is not used for special indications, since there is no evidence of safety.
While taking it, you should not drive a car or other vehicles that require quick reactions.
Available in pharmacies with a prescription.
Mexidol tablets are prescribed to patients for the treatment and prevention of the following conditions:
- The period of rehabilitation of the patient after an ischemic stroke or with frequent transient ischemic attacks;
- Traumatic brain injuries or consequences after them;
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia with frequent attacks of panic attacks;
- Brain dysfunctions of various origins - after injuries associated with metabolic processes;
- Impaired functioning of the brain and coronary vessels caused by the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques;
- Coronary heart disease as part of complex treatment;
- Neuroses and various psycho-emotional disorders;
- Withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism with severe disturbances in the psycho-emotional state;
- The rehabilitation period after poisoning with tranquilizers or antipsychotic drugs;
- Prevention of the development of heart and vascular disease in patients at risk or with excessive physical exertion;
- Chronic stress.
The tablets have some restrictions for use, so before starting therapy you should carefully read the accompanying instructions. The following conditions are contraindications:
- Severe liver failure;
- Acute liver dysfunction;
- Individual intolerance to the components included in the tablets;
Since there are no clinical data on the effect of the drug Mexidol on the intrauterine development of the fetus, treatment with this drug is contraindicated in pregnant women.
It is not known whether the drug is excreted in breast milk and how this can affect the child’s body, therefore, due to the lack of information, treatment with the drug is not carried out among nursing mothers. If a course of therapy is necessary, a woman should think about ending the lactation process.
Mexidol: when is it used?
Indications for the use of Mexidol are as follows:
- Residual effects after strokes, as well as during transient cerebral ischemia to prevent exacerbation;
- Concussion, consequences of head injuries;
- Acute and chronic encephalopathies;
- Autonomic dysfunction;
- Neurosis-like conditions;
- Panic attacks;
- Cognitive impairment due to cerebrosclerosis;
- Acute coronary circulatory disorders, as an additional therapy;
- In surgery after surgical interventions, purulent inflammation of the peritoneum and pancreatitis;
- Psychopathy, withdrawal syndrome;
- Acute intoxication with psychotropic drugs;
- Neurasthenic conditions after strong physical exertion;
- For prevention before extreme stress.
- End-stage liver failure;
- Anuria;
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance.
The drug is non-toxic. Does not affect coordination, blood pressure and breathing.
Possible side effects from the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
An allergic reaction such as urticaria or Quincke's edema is possible.
Daily dose and method of administration
Mexidol tablets are prescribed at 375-750 mg/day.
First day – 1-2 tablets (125-250 mg).
Then the dose is increased to the maximum effective, but not more than 800 mg/day.
Symptoms of overdose include increased drowsiness.
Mexidol in ampoules
The drug is prescribed for intravenous jet, slow (5-7 min) administration, and drip – 60 drops/min. Before jet administration, dilute in an isotonic solution.
Intramuscular injection is made deep into the tissue of the upper outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle.
- For the treatment of dementia - 0.1-0.3 g/day is administered intramuscularly.
- For alcohol withdrawal – intravenous drip – 0.5 g/day.
- Poisoning with neuroleptics – 0.3 g/day.
- In surgical practice, for the treatment of peritonitis, pancreatitis - 0.2 g 3 times / day.
- For severe necrotizing pancreatitis - 0.8 g twice the first two days, then 0.5 2 times a day by drip.
- For acute strokes and dyscirculatory encephalopathies - 500 g drip 4 times a day for two weeks.
- The drug is discontinued gradually after achieving positive clinical and laboratory results.
- For preventive purposes – 200 mg 2 times a day, course – 14 days.
- In hospital settings, Mexidol is prescribed to children for the treatment of neuroinfection at a dose of 0.1 mg. intramuscularly.
- A 5% Mexidol solution is used to rinse the mouth for stomatitis, gingivitis and purulent inflammation in the periodontal pocket. Apply 3 times a day.
Mexidol is broken down in the liver and excreted in the urine. Action time – 4 hours.
Interaction with other drugs
Meskidol potentiates the effect of anticonvulsants, benzodiazepines, and antidepressants. Reduces the toxicity of ethyl alcohols.
Tablets of 125-250 mg are prescribed orally 3 times a day. The dose of Mexidol should be increased gradually. The course of treatment ranges from 14 days to 6 weeks and depends on the type and severity of the disease.
After collecting tests and determining a sustainable positive effect, Mexidol is gradually discontinued. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated after 1-3 months.
Important: Mexidol and instructions
Often, to enhance the therapeutic effect, as prescribed by a doctor, the drug is prescribed together with nootropics, herbs with a sedative effect, tranquilizers, Actovegin, Piracetam and their analogues. Such therapy can only be prescribed by the attending physician, because It is he who determines the benefits and harms of complex treatment, the degree of its effectiveness.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter
The tablets are intended to be taken orally, without chewing, with water or any other liquid. Treatment begins with 1 tablet 3 times a day, if necessary increasing the single dose to 2 tablets. The duration of drug therapy depends on the diagnosis, but is at least 2 weeks.
To eliminate and prevent signs of ischemia, patients with coronary heart disease are recommended to take this drug for at least 6 weeks. During periods of probable exacerbations (autumn and spring), the course is repeated.
If the dose recommended in the instructions is exceeded, the patient may experience drowsiness, lethargy, and dizziness.
The drug Mexidol, when used simultaneously with ethanol, reduces the toxic effect of the latter.
When tablets are used simultaneously with nootropics, antipsychotics, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, their therapeutic effect is enhanced, so patients require dose adjustment.
Analogues of Mexidol tablets
In pharmacies you can select medications that are similar in their therapeutic effect to Mexidol tablets. These include:
- Medomexy;
- Mexiprim;
- Mexidant;
- Mexipridol;
- Mexicofin;
- Neurox;
- Cerecard.
The drug Mexidol can be bought in pharmacies in Moscow at a price of 270 rubles per pack.
Source: https://MoyaTravma.net.ru/simptomy/meksidol-onkologii-mozhno/
Analogues of Mexidol tablets
In pharmacies you can select medications that are similar in their therapeutic effect to Mexidol tablets. These include:
- Medomexy;
- Mexiprim;
- Mexidant;
- Mexipridol;
- Mexicofin;
- Neurox;
- Cerecard.
Before replacing the prescribed drug with one of the listed analogues, you should definitely check with your doctor about the daily dose, age restrictions and contraindications.
The drug Mexidol can be bought in pharmacies in Moscow at a price of 270 rubles per pack.
Source: onkoloz.ru