general characteristics
Trembling hyperkinesis is a common type of involuntary movements.
Although symptoms occur at any age, including childhood, higher rates occur in people over 65 years of age. Tremor feels like a rhythmic shaking. It is often observed in the hands, reminiscent of counting coins or rolling pills, but can also affect other parts of the body: the head (movements like “yes-yes” or “no-no”), torso, feet. Sometimes the chin, tongue, and vocal cords are involved in the pathological process, which interferes with eating and disrupts the function of speech formation. Isolated tremor is not life-threatening, but violent movements make daily activities significantly more difficult. Hand tremors create difficulty in writing, drawing, holding cutlery, and other activities that require fine motor skills (dressing, manual labor). Tremor limits professional and social activity, creates psychological discomfort, and reduces quality of life. Some types of hyperkinesis progress over time and are accompanied by neurological deficits, while others disappear with the elimination of the causative factor.
Preventive measures
The most important thing in old age is to avoid stressful situations and not take everything to heart. You need to understand that communicating with aggressive people has a bad effect on your quality of life. Also, don't overload yourself with excessive physical work. Alternate it with periods of proper rest.
All older people should follow the following recommendations:
- Due to your age, try to lead an active lifestyle. Take walks alone or with friends in the fresh air. Do some simple sports: swimming in the pool, aerobics, Nordic walking.
- Go to bed on time. Ensure quality sleep: close the curtains, isolate yourself from unnecessary noise and sounds, choose comfortable bedding.
- Avoid drinking alcohol, cigarettes, drugs and coffee.
- Take a course of anti-anxiety medication.
- Follow all doctor's recommendations.
- Review your diet. Include foods containing iodine, potassium, magnesium, iron and calcium.
- Do exercises with a relaxing effect (yoga, meditation, breathing exercises).
Classification
Tremor or trembling is a motor disorder, which in the structure of neurological syndromes belongs to hyperkinesis. By origin, it can be primary (essential) and secondary, which is a sign of an underlying disease, intoxication or the effects of medications. Taking into account etiopathogenetic features, two types of tremor are distinguished:
- Physiological.
Occurs in healthy individuals, is characterized by low amplitude, and is not visually detected. Physiological tremor is a normal mechanism of motor control, is enhanced by external factors, but can be consciously reduced by the patient himself. - Pathological.
Caused by various disorders in the central or peripheral parts of the nervous system. The most common variants are parkinsonian, cerebellar, and essential tremor. There are also dystonic, neuropathic, orthostatic and some other types.
Considering the clinical and morphological features, we distinguish between slow (in the range from 3 to 5 Hz) and fast tremors (6-12 Hz), low- and high-amplitude (small- or large-scale), intermittent or constant. An important criterion for systematization is the conditions of development, according to which rest tremor and action tremor are distinguished (action tremor). The latter has several varieties:
- Postural (static).
Caused by maintaining a stationary position of body parts (arms extended forward and spread to the sides, head). A type of tremor is considered to be positional tremor, characteristic of strictly defined positions. - Kinetic.
Associated with motor acts. Simple kinetic tremor occurs during any non-purposeful movements. Intentional trembling intensifies as a goal is achieved. - Kinesiospecific.
It is observed only during certain narrowly focused actions. A typical example is writing tremor, which is absent in other situations involving the same muscles. - Isometric.
Occurs under conditions of isometric muscle tension, with strong contraction without movement. Such trembling is observed when clenching a hand into a fist or holding a heavy object.
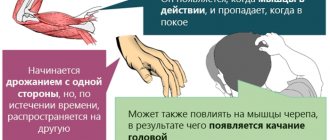
Topographic classification involves dividing tremor depending on location. Focal affects only one anatomical zone (hand, head, soft palate, etc.), segmental covers adjacent areas (bibrachial), when several areas are affected on one side, hemitremor is noted, and involuntary movements throughout the body suggest generalized tremors. When making a diagnosis, the time of first appearance of the symptom, family history, and connection with the use of certain substances are taken into account.
Our boarding houses
Golitsyno
Minsky
Treatment with water when an elderly person's hands are shaking
Hydrotherapy is useful not only for sick people, but also for healthy people. Swimming in the pool and in open water gives very good results. In addition, Charcot showers are prescribed. By alternating cold and hot water, spontaneous fluctuations can be significantly reduced.
Diet table
You need to radically change your diet. Exclude from the menu foods that are harmful to the elderly: coffee, chocolate, baked goods, pickles, marinades, smoked foods, fried foods and fast food. Try to get rid of bad habits, stop drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes. If you are unable to cope with the problem yourself, then seek help from a narcologist. Your desk should have:
- Fermented milk products: cheese, feta cheese, sour cream, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, kefir and yogurt.
- Rabbit, turkey and chicken meat.
- Beef liver.
- Nuts of all kinds.
- Oatmeal, pearl barley.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Non-carbonated drinks: herbal teas, dried fruit compotes, smoothies, juices, fruit drinks.
Leave a request for selection of a boarding house
for an elderly person with hand tremors
Another option is possible - fasting. But without consulting a doctor, performing such an action is strictly prohibited!
Treatment with bees and leeches if the hands of the elderly are shaking
Apitherapy and hirudotherapy have been used since ancient times. Modern medicine considers these methods outdated. However, so far they have brought positive results. It is not for nothing that beekeepers feel absolutely healthy for a very long time after the end of the season. And leeches have a triple positive effect:
- bloodletting can relieve the circulatory system and cleanse the blood vessels;
- installing them at biologically active points is equivalent to acupuncture;
- The secretions of the salivary glands contain valuable components that improve blood flow.
Saliva contains substances that act as thrombolytics. They dissolve blood clots, reduce blood clotting, saturate it with oxygen, and help reduce swelling. Thanks to the healing properties of bees and leeches, the immune system is stimulated, which, in turn, helps eliminate symptoms.
Why does tremor occur?
Causes of hand tremors
The most typical location of tremors is the hands. Considering the physiological mechanisms of tremor development, they note the ability to intensify with muscle fatigue, hypothermia, and the action of psychogenic factors (emotional shocks, anxiety). The range of pathological causes is very wide - the main positions in it are given to essential tremor and Parkinson's disease, but there are many other conditions that can cause hand tremors:
- Endocrinopathies
: thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, hypoglycemia, hyperparathyroidism. - Metabolic disorders
: Wilson-Konovalov disease (shaking, shaking-rigid forms), Hallervorden-Spatz disease. - Space-occupying formations
: subdural hematoma, tumors, cavernous angiomas. - Vascular brain damage
: ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. - Infectious diseases
: neurosyphilis, epidemic encephalitis. - Hereditary pathology
: fragile X-associated tremor and ataxia syndrome (FXTAS), Kennedy bulbar-spinal amyotrophy, sensory ataxia, neuropathy, dysarthria and ophthalmoplegia syndrome (SANDO). - Polyneuropathy
: metabolic (diabetic, paraproteinemic, toxic), chronic inflammatory demyelinating, hereditary motor-sensory. - Withdrawal syndrome
: withdrawal of alcohol, drugs (cocaine, heroin), medications (opioids, benzodiazepines). - Intoxication
: salts of heavy metals (mercury, arsenic, lead), carbon monoxide, carbon disulfide. - Taking tremorogenic drugs
: tricyclic antidepressants, neuroleptics, sympathomimetics.
The development of physiological tremor is largely due to mechanical factors - the weight of the limb, muscle tone, and the rigidity of the joint apparatus. The leading role in the formation of pathological tremor is played by changes in the central nervous system associated with the appearance of so-called tremor generators (central oscillators) with spontaneous or induced rhythmic activity. The second important point is the loss of control over voluntary movements by the cerebellar system.
Causes of head tremors
Rhythmic nodding and turning the head are quite common, but are usually included in the picture of mixed trembling, when involuntary motor acts cover several areas of the body. Often we are talking about parkinsonian (primary, secondary) or essential tremor. Other causes of hyperkinesis are the following diseases:
- Cervical dystonia.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Holmes tremor (mesencephalic).
- Prion diseases:
Kuru disease. - Paraneoplastic syndromes
: opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. - Metabolic encephalopathies
: hypoxic-ischemic, uremic, hepatic. - Hereditary diseases
: olivopontocerebellar atrophy, leukodystrophy (Peliceus-Merzbacher disease), ataxia with vitamin E deficiency.
Tremor of central origin is caused by damage to the neural ring of the extrapyramidal system, which contains subcortical structures - the basal, stem, and cerebellar nuclei. An important place is given to changes in the striopallidal system, rubrospinal tract, and thalamic connections. Head trembling occurs with pathology of the cervical spine, which is associated with circulatory disorders and compression of the spinal nerves.
Causes of chin tremor
Trembling of the lower jaw can be an early symptom of Parkinson's disease or neuroleptic parkinsonism (rabbit syndrome). Chin tremor is also due to other reasons that require attention when carrying out differential diagnosis. Increased alertness is traditionally caused by conditions characteristic of early childhood:
- Neonatal tremor
. - Perinatal damage to the central nervous system
: hypoxic encephalopathy, intrauterine infections, birth injuries. - Cerebral palsy
. - Hydrocephalus
. - Familial chin tremor (geniospasm)
.
Physiological tremor of the newborn period occurs against the background of crying, when undressing or taking a child out of the water, under the influence of fear or cold. Risk factors for damage to cerebral structures are infectious diseases, obstetric and somatic pathologies in a pregnant woman. The development of intoxication and withdrawal syndrome in a child cannot be ruled out when the mother uses psychoactive drugs.
Possible complications
If mental abilities are preserved, there may not be any special complications of tremor for a long period of time. When the disease reaches a severe stage, attacks of trembling lead the patient to a decrease in the quality of life in general and loss of social communication. With improper or insufficient treatment, the pathological process spreads throughout the body. Uncontrolled movements become more intense and pronounced. A person experiences difficulties not only in a professional environment, but also in the everyday sphere.
The patient ceases to be able to work and cannot take care of himself without assistance. Tremor is a serious pathological process that requires immediate therapeutic treatment. The disease leads to dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system, curvature of the cervical spine, writing disorder, and severe speech defects. The motor amplitude gradually decreases. Against this background, unpleasant sensations arise in the cervical spine and constant headaches. The most severe complication of tremor is disability.
- Face painting for children - drawing ideas with photos. How to do face painting for a child with your own hands for beginners
- How to get out of depression
- Setting up a Beeline router. Step-by-step guide for connecting a Beeline wi-fi router with your own hands with video
Diagnostics
The diagnostic search begins with an analysis of complaints, anamnestic information and a neurological examination. The clinical tremor rating scale allows you to objectify the intensity of tremor. If a syndromic diagnosis usually does not cause difficulties, then certain difficulties may arise with the nosological verification of the pathology. Additional methods are used for differentiation:
- Lab tests.
Some causes of tremor can be determined by the results of a biochemical blood test with the determination of thyroid-stimulating hormones, glucose, calcium, kidney tests and other indicators. Toxicological tests allow you to determine the concentration of toxic substances, drugs, and medications. If hepatolenticular degeneration is suspected, ceruloplasmin levels and urinary copper excretion are examined. - Tomography.
Neuroimaging is indicated for sudden onset, rapid progression, or combination of tremor with other neurological disorders. MRI of the brain reveals atrophic, ischemic lesions or other structural damage. Functionally active zones are examined using positron emission tomography. - Computer stabilography
. A stabilometric analyzer (stabilometric platform) with biofeedback helps to assess the characteristics of postural tremor. During the study, support reactions are studied, including when performing diagnostic tests - static and dynamic. - Tremorometry.
The most widely used method for recording involuntary rhythmic vibrations is using a computer polygraph, which evaluates the frequency and amplitude of trembling. To record tremorograms, tenso-, piezo-, and accelerometric methods are used. - Electroneuromyography.
It makes it possible to indirectly judge the parameters of trembling by the tension and relaxation of individual muscles. Electromyography helps differentiate tremor from other movement disorders and identify individual causes of tremor (polyneuropathy).
Cerebral vascular pathology is detected by transcranial ultrasound and angiography. The displacement of the midline structures and the state of the ventricular system are visible on the echoencephalogram. The hereditary nature of some diseases can be confirmed using molecular genetic tests. Conditions accompanied by tremor are differentiated among themselves and with other hyperkinesis.
Occupational therapy
Psychological factors leading to hand tremors in the elderly
Emotional people are more likely to experience this phenomenon. During the experience of fear or fear, grief, or anger, convulsive trembling of the limbs occurs. In addition, it can begin from excessive physical labor, hypothermia, or sun or heatstroke.
There are several other causes of tremor:
- Depressive state. Then you just need to undergo a rehabilitation course with a psychiatrist. He will prescribe antidepressants, which in a month will already give a positive result. A person’s mood improves, anxiety disappears and self-confidence appears.
- Taking some medications may cause side effects.
- Abuse of alcohol, cigarettes, drugs and coffee.
- Intoxication of the body due to poisoning with carbon monoxide, heavy metals and toxic objects.
Select a service for your relative | |||
| Caring for bedridden people | Disability care | Elderly care | Care after a heart attack |
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Treatment of tremor is intended to reduce functional limitations and social maladaptation of patients. The basis of therapy is conservative methods, which are usually symptomatic. If secondary tremor is detected, treatment involves eliminating the causes of its occurrence and correcting the underlying pathology. Among the therapeutic measures used:
- Lifestyle optimization.
It is necessary to avoid situations that increase the intensity of trembling. In the early stages of the disease, patients are recommended to master adaptive methods - use pens and cutlery with thick handles, blunt scissors and knives, phones with voice control, etc. - Physical methods.
Methods of physical influence include the use of special orthoses that limit the mobility of the hand in the wrist joint. Assistance in mastering simple motor patterns is provided by physical therapy and occupational therapy, which are complemented by massage, reflexology and balneotherapy. - Pharmacotherapy.
Several groups of drugs are indicated for the treatment of tremor. Based on clinical feasibility, anticonvulsants (primidone, topiramate, gabapentin), antiparkinsonian drugs (levodopa, amantadine, pramipexole), beta-blockers (propranolol, atenolol, nadolol) are prescribed. For severe tremors of the head and voice, botulinum toxin A injections are performed.
How can you determine the magnitude of vibrations at home?
If the trembling of the limbs occurred as a result of a tragedy experienced, emotional, intellectual or physical overload, then no tests are necessary. The phenomenon itself will disappear after proper rest.
But if you have constant trembling, do a simple exercise before contacting a specialist. Take paper and pen. Reproduce a spiral shape on the sheet. If everything is in order, then the edges of the waves will be spherical and smooth. In another case, jagged lines indicate that it is time to get examined at the hospital.