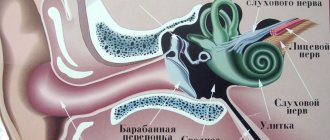
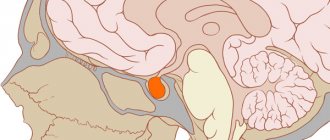
The concept of polyneutropathy includes a group of diseases, the causes of which may be different. The feature that unites these ailments is the abnormal functioning of the peripheral nervous system or individual nerve bundles.
Characteristic features of polyneutropathy are symmetrical dysfunction of the muscles of the upper and lower extremities. In this case, there is a slowdown in blood flow and deterioration in the sensitivity of the arms and legs. This disease mainly affects the lower extremities.
Polyneuropathy of toxic origin according to ICD10
One of the most common types of this disease is toxic polyneuropathy. From the name of the disease it becomes clear that it is a consequence of the effects of various toxic substances on the nervous system. Toxins can enter the body from the outside or be a consequence of a disease.
In order to make it easier to determine the type of this disease, it was proposed to consider the reasons that caused toxic polyneuropathy. ICD 10, or the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, offers a very convenient form of dividing the disease. The essence is to assign a code to one or another type of illness, based on the reasons for its occurrence. Thus, toxic neuropathies are designated according to the ICD 10 list with code G62. The following is a more refined classification:
- G62.0 – designation for drug-induced polyneuropathy with the possibility of specifying the medication;
- G62.1 – this code refers to the alcoholic form of the disease;
- G62.2 – code for polyneuropathy caused by other toxic substances (you can enter the toxin code);
- G62.8 – designation for other specified polyneuropathies, which include the radiation form of the disease;
- G62.9 – code for neuropathy unspecified (NOS).
As noted earlier, toxic polyneuropathy can be caused by two types of causes:
- Have exogenous preconditions (this type includes diphtheria, herpetic, caused by HIV infection, lead, arsenic, alcohol, caused by OPC poisoning, drug, radiation neuropathy).
- Be a consequence of endogenous factors (for example, diabetic, caused by paraproteinemia or dysproteinemia, diffuse connective tissue lesions).
Toxic neuropathy has recently become a fairly common disease due to increasing human contact with toxins of various origins. These dangerous substances surround us everywhere: they are in food, consumer goods, medicines and in the environment. Infectious diseases also often cause this disease. Microorganisms produce toxins that affect the human body and affect the nervous system.
The essence of the violation
Every day a person encounters toxic substances . This could be household chemicals, low-quality food, cheap cosmetics. People who are forced to work with pesticides and poisonous substances are at risk.
Everyone knows that harmful substances can poison the body, but not everyone knows how this happens.
When a toxic substance or low-quality food enters the body, a mechanism is launched to actively utilize them . The immune system is activated, producing special leukocyte cells that allow you to overcome toxins before they settle in the body.
When the body fails to cope, extensive intoxication develops, in which human health is at risk. Toxins are able to penetrate any cells and tissues of the body, disrupting natural biological processes, including metabolism. As a result, vital organs and entire systems begin to suffer, since the body clearly does not receive enough nutrients.
Based on the nature of toxins entering the body, toxic polyneuropathy can be divided into two large groups:
- Endogenous – intoxication occurs inside the body with toxins that are synthesized by the body itself in the presence of any disease. This includes inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, respiratory system, etc.
- Exogenous – toxins enter the body from the environment. This could be poisoning from poisons, chemicals, or stale foods.
Young children quite often develop neurotoxicosis, when, under the influence of prolonged dehydration, symptoms of neuropathy develop, the cause of which is a banal acute respiratory infection.
Diphtheria polyneuropathy
From the name of the disease it is clear that it occurs as a result of a severe form of diphtheria, accompanied by exposure to an exotoxin. Most often, this phenomenon occurs in adult patients. In this case, there is an impact on the membranes of the nerves of the skull and their destruction. Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves either in the first week (especially dangerous with cardiac arrest and pneumonia), or after the 4th week from the moment of infection.
They are expressed by damage to the functions of the eyes, speech, swallowing, difficulty breathing and tachycardia may occur. Symptoms almost always begin to disappear after 2-4 weeks or several months.
Polyneuropathy due to HIV
In two out of three cases, patients with HIV infection experience neurological complications, and most often they occur in the last stages of the disease.
The toxic effect of the virus, autoimmune reactions, secondary infection, the development of tumors and the consequences of taking drugs in combination lead to disruptions in the normal functioning of the body. The result is encephalopathy, meningitis and polyneutropathy of the cranial nerves. The latter ailment is often expressed in decreased sensitivity of the feet and pain in the lumbosacral region. They are treatable, but can have fatal complications.
Lead polyneuropathy
This type of disease occurs due to lead poisoning, which can enter the human body through breathing or through the gastrointestinal tract. It is deposited in the bones and liver. Lead toxic polyneuropathy (ICD 10 code - G62.2) is expressed in the patient in the form of lethargy, high fatigue, “dull” headache, decreased memory and attention, encephalopathy, anemia, colitis, pain in the limbs, tremor of the hands. This disease is characterized by damage to the radial and peroneal nerves. Therefore, “dangling hand” and “cock gait” syndromes often occur. In these cases, contact with lead is completely limited. The prognosis for recovery from the disease is favorable.
Prognosis and possible complications
The outcome of the disease depends on its form and duration of contact with toxic substances. The timely initiation of therapy is of no small importance for the prognosis.
With the development of acute polyneuropathy, it is most often possible to achieve a favorable outcome, which is accompanied by complete regression of symptoms. However, this is true only with a timely diagnosis and adequate treatment measures.
The chronic form of the disease with adequate therapy proceeds relatively favorably. Thanks to proper treatment, it is possible to significantly slow down the progression of the disease. People with this diagnosis can live quite a long time.
An unfavorable outcome is possible in the case of acute intoxication when a large amount of toxin enters the body. As a result, there is a risk of developing kidney or liver failure. If treatment for these conditions is not started in time, the likelihood of death is high.
Arsenic polyneuropathy
Arsenic can enter the human body along with insecticides, medicines, and paints. This disease is occupational among smelters. If the exposure to the toxic substance was single, then vascular hypotension, nausea and vomiting develop. After 2-3 weeks, polyneuropathy appears, expressed in weakness of the leg muscles. If repeated arsenic poisoning occurs, then symmetrical distal sensorimotor manifestations of the disease occur. In the case of chronic intoxication with a toxic substance, hypersalivation, trophic and vascular disorders (skin hyperkeratosis on the soles and palms, rashes, stripes on the nails, pigmentation on the abdomen in the form of drops, peeling), and ataxia are observed. Arsenic polyneuropathy is diagnosed by analyzing the composition of urine, hair and nails. The patient’s recovery after an illness lasts months.
Classification of violation
Depending on the characteristics of the origin of the disease, the following types of toxic polyneuropathy are distinguished:
- Diphtheria - this disorder is considered a typical complication of diphtheria and develops as a result of a toxic form of an infectious disease. In this case, the neuropathic syndrome is of a mixed nature, and both motor and autonomic and sensory disturbances are observed.
- Herpetic - in this case, the disorder develops in the post-infectious period. In most cases, it is caused by herpes simplex and chickenpox viruses. Also, the reason may lie in infection with cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus.
- Lead - this form of the disease is a consequence of lead poisoning and manifests itself in the form of chronic movement disorder and motor defects, which in most cases are asymmetrical in nature. At the same time, sensory disorders are not too pronounced.
- Arsenic - the cause of the development of this disease is poisoning with insecticides, including arsenic, drugs or dyes. With a single exposure to a large amount of a toxic substance, a person’s consciousness is impaired, vascular hypotension and vomiting appear. If the patient survives, polyneuropathy develops within 2-3 weeks. In this case, muscle weakness is variable in nature and is observed mainly in the lower extremities.
- Alcoholic – the mechanism of development of this form of the disease has not been well studied. The key role in this case is played by impaired thiamine resorption, which provokes the development of thiamine deficiency. Alcohol also has a toxic effect on the body. The clinical picture of this disease includes a number of sensory, motor and autonomic disorders.
Alcoholic neuropathy
In medicine, there is an opinion that toxic polyneuropathy due to alcohol has not been studied enough, and the mechanism of its development is not fully understood.
The main reason is thiamine deficiency in the body and gastroduodenitis, which occurs due to alcohol abuse. In addition, alcohol itself has a toxic effect on the nervous system.
Toxic alcoholic polyneuropathy can be subacute, acute, but most often there is a subclinical form, detected during examination of the patient. It is expressed in a slight impairment of the sensitivity of the feet, degradation or absence of Achilles tendon reflexes, and pain in the calf muscles upon palpation. Often toxic polyneuropathy is expressed in symmetrical paresis, atrophy of the flexor muscles of the feet and fingers, decreased sensitivity of the “glove” and “sock” areas, pain in the feet and legs of a constant or shooting type, burning in the soles, swelling, the appearance of ulcers and hyperpigmentation of the skin of the extremities. Sometimes this disease can be combined with dementia, cerebellar degeneration, and a symptom of epileptiformia. The patient is recovering slowly. The success of treatment depends on the return or cessation of drinking alcohol. The ICD code for toxic polyneuropathy due to alcoholism is G62.1.
Classification
The peculiarities of the pathology are that its type and treatment method completely depend on which group of toxins provoked the polyneuropathy. If we consider toxic polyneuropathy from the point of view of the duration and frequency of exposure to the provoking factor, then we can distinguish the following classification :
- Chronic toxic polyneuropathy - develops as a result of the progression of the underlying disease, which is characterized by a chronic course.
- Acute toxic polyneuropathy - occurs as a result of poisoning with pesticides and highly toxic substances. It is characterized by an acute course and the need for emergency care, since its absence can cause death.
Based on what exactly caused the development of the disease, five types of intoxication :
- Drug intoxication occurs due to the use of a large number of medications, which, when activated in the body, adversely affect the functioning of the stomach, liver and excretory system. Usually the diagnosis is accompanied by a list of medications that could provoke drug intoxication. Children and patients suffering from chronic diseases are at risk.
- Alcohol intoxication - includes the harmful effects of ethyl alcohol toxins on the entire body. Patients who have taken a large amount of alcohol at one time, as well as people who constantly use it, are at risk.
- Radiation toxicity develops as a side effect after radiation therapy in the fight against cancer. Radiation sickness can also result from prolonged exposure to radiation at work or in research centers.
- Food intoxication - caused by poisoning with low-quality products that contain a large number of pathogenic microorganisms, for example, Shigella, Salmonella. It has an acute course with characteristic signs of dehydration.
- Intoxication with poisons and toxic substances - develops due to toxic substances entering the body. Requires the introduction of an antidote that neutralizes the poison. Otherwise, death may occur.
A particularly dangerous form of toxic polyneuropathy is alcohol-drug polyneuropathy , when a person abuses alcohol while constantly taking medications.
When combined with certain medications, alcohol can cause bradycardia and slow breathing, which can cause death in high doses.
This classification helps the doctor quickly decide on first aid methods, as well as further treatment.
Drug-induced polyneuropathy
This type of neurological disorder is caused by taking the following medications:
- When treated with Perhexilen at a dosage of 200-400 mg per day, polyneuropathy occurs after a couple of weeks. It manifests itself in decreased sensitivity, ataxia, and paresis of the limbs. In these cases, the drug is stopped and the patient's condition improves.
- Isoniazid polyneuropathy develops when there is a deficiency of vitamin B6 in people with a genetic disorder of its metabolism. In this case, pyridoxine is prescribed orally.
- Excess Pyridoxine (50-300 mg/day) leads to the formation of sensory polyneutropathy, severe headache, fatigue and irritability.
- Long-term treatment with Hydrolazine can lead to dysmetabolic polyneutropathy and requires taking vitamin B6.
- Taking the drug "Teturam" at a dose of 1.0-1.5 g/day can result in paresis, loss of sensitivity, and optic neuritis.
- Treatment with Cordarone at a dosage of 400 mg/day for a period of more than a year can cause toxic polyneutropathy.
- With a lack of vitamins B6 and E, polyneutropathies also occur, as well as with their excess.
Drug-induced toxic polyneuropathy is designated by ICD 10 code G62.0.
The influence of heredity on the disease
There is no direct inheritance of toxic polyneuropathy, but there are still some prerequisites for the development of the disease that are inherited. This includes diabetes mellitus, which itself is not inherited, but can appear in blood relatives. People with alcohol addiction are also at risk. Coding genes, in the presence of favorable conditions, can make themselves felt, which will subsequently lead to the development of polyneuropathy.
But the disease itself cannot be inherited.
Endogenous toxic polyneutropathies
This type of disease occurs in most cases due to dysfunction of the endocrine glands, as a result of a deficiency of necessary hormones, or when the functions of other internal human organs are impaired. The following types are distinguished:
- Diabetic polyneuropathy can begin acutely, progress slowly or quite rapidly. It first appears as pain and loss of sensation in the limbs.
- Polyneuropathy associated with paraproteinemia and dysproteinemia occurs mainly in older people and is associated with diseases such as multiple myeloma and macroglobulinemia. Clinical manifestations are expressed in pain and paresis of the lower and upper extremities.
- Polyneuropathy also develops in diffuse type connective tissue diseases: periarthritis nodosa, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma.
- Hepatic polyneuropathy is a consequence of diabetes and alcoholism and has similar clinical manifestations.
- Neurological disorders in gastrointestinal diseases are associated with pathology of the digestive organs, leading to vitamin deficiencies. Celiac disease can provoke polyneuropathy, which is expressed in psychomotor impairment, epilepsy, visual disturbances, and ataxia.
Toxic polyneuropathies (information for patients and doctors)
Toxic polyneuropathy (information for patients and doctors) Alcoholic polyneuropathy
What is Alcoholic Polyneuropathy? “Alcoholic polyneuropathy” is a consequence of the direct toxic effect of ethanol and its metabolites on peripheral nerves with predominant damage to thin, weakly myelinated and unmyelinated fibers that conduct pain, temperature sensitivity and provide autonomic-trophic functions.
How common is this disease among the Russian population? In Russia, according to official data, about 5% of the population over the age of 18 abuses alcohol, which is about 7.5 million people. According to the WHO report, in 2021 our country was in fourth place in terms of the amount of alcohol consumed per capita (13.9 liters of pure alcohol per year), behind Lithuania, Belarus and Moldova. At the same time, in Russia they often drink strong alcoholic drinks, while in other European countries preference is given to beer and wine. In relation to polyneuropathies of other origins, the proportion of alcoholic damage to peripheral nerves is about 40%. According to the literature, 76% of patients suffering from alcohol dependence for more than 5 years have clear clinical signs of alcoholic polyneuropathy; At the same time, subclinical (“erased”, “hidden”) nerve damage according to electroneuromyography (ENMG) is detected in 97–100% of patients who chronically drink alcohol, that is, in the vast majority.
How do I know if I drink a lot of alcohol? The GAGE questionnaire will help answer this question. Answer the questions unequivocally “YES” or “NO” in the way you understand them. If you have difficulty answering, do not answer anything:
- Have you ever felt that you should cut down on your drinking?
- Did you feel irritated if someone around you (friends, relatives) told you about the need to reduce your drinking?
- Have you ever felt guilty about drinking alcohol?
- did you have the desire to drink alcohol as soon as you woke up after drinking alcoholic beverages?
Interpretation of results: for each answer “YES” - 1 point. A score of 2 or more points corresponds to SIGNIFICANT ALCOHOL ABUSE. You need to reconsider your lifestyle and eliminate the harmful effects of the toxic effects of alcohol on the body, in particular polyneuropathy. Yes, I scored more than 2 points, but what symptoms bother patients with alcoholic polyneuropathy? The first signs of the disease may not be immediately noticed by patients, since this type of polyneuropathy is characterized by a slow progression of symptoms over several years. Less commonly, the clinic can develop acutely, during or after a binge.
Depending on which nerve fibers are more involved in the pathological process, the following characteristic complaints arise:
- sensitive symptoms: numbness, tingling, “burning”, “burning”, pain, “crawling” in the feet, legs, and later in the hands; decreased sensitivity in the feet - “I don’t feel like I’m putting on shoes, I don’t feel the floor”; unsteadiness when walking, worse in the dark and with eyes closed;
- motor symptoms: weakness develops in the muscles of the feet and legs, then weakness in the muscles of the hands may develop (impaired fine motor skills); difficulty walking, “spanking” of the feet;
- autonomic symptoms: fluctuations in blood pressure; “interruptions” in the work of the heart; constipation, diarrhea; dry skin or sweating; erectile dysfunction and decreased libido;
- symptoms of concomitant damage to the central nervous system: memory impairment; confusion; decreased intelligence; disorientation; indifference to loved ones and others; inattention; drowsiness.
The clinical picture and “set” of symptoms may vary. In 42% of those diagnosed with alcoholic polyneuropathy, neuropathic pain syndrome is detected.
Are there risk factors for developing this disease? There definitely is! The most important factor is the frequency of alcohol consumption. There are 3 cohorts of patients who abuse alcohol: occasional drinkers (a period of sobriety of more than 5 days, without binge drinking), frequent drinkers (drinking alcohol more than 3 times a week with a hangover more than 1 time a week) and constant drinkers (daily drinking, without sobriety) . It was found that patients from the groups of “frequent drinkers” and “constant drinkers” have higher rates of detection of polyneuropathy (29.6% and 29.9%, respectively) than the group of patients “occasional drinkers” (11.3%). Subjective polyneuritic symptoms developed after a relatively short duration of abuse (1-5 years), and signs of severe polyneuropathy developed after alcohol abuse for more than 10 years. Female gender increases the risk of developing more severe polyneuropathy. Such gender differences are due to a higher rate of absorption of alcohol and, as a consequence, a higher level of alcohol in the blood in women than in men. Women's addiction and full-fledged dependence on alcohol develop much faster than in men. If in men chronic alcoholism (first-second stage) develops after 6-12 months of daily drinking, then for women 3-6 months are enough. The genetic risk factor manifests itself, first of all, in a hereditary craving for alcohol, which can, from generation to generation, lead to the development of alcoholic polyneuropathy and damage to other organs and systems. Malnutrition and B vitamin deficiency often accompany alcohol abuse. It has been proven that ethanol reduces the absorption of vitamins in the small intestine, reduces their “liver” reserves, and disrupts the processes of phosphorylation and the formation of active forms of vitamins. Deficiency of B vitamins is an additional cause of peripheral nerve damage, which, together with the toxic effects of alcohol, aggravates the course of polyneuropathy. Impaired liver function is caused by a long period of alcohol intake or the addition of other concomitant diseases. As a result, fatty hepatosis occurs, which over time can transform into alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver. Liver failure is a separate cause of damage to peripheral nerves, and when caused by alcohol, it leads to severe polyneuropathy.
What type of alcohol increases the risk of developing polyneuropathy? Any type of alcohol contains ethanol and its metabolites, mainly acetaldehyde, which has a direct toxic effect on peripheral nerves. Scientists from the Maugeri Medical Detoxification Center conducted a comparative analysis of alcoholic beverages consumed by their patients. It was found that drinking wine, compared to drinking beer, causes a greater risk of developing polyneuropathy. This may be due to the presence of impurities that wine producers add to their product. No other comparative studies have been conducted on this topic.
What is the mechanism of nerve damage caused by alcohol consumption? Alcohol enters the bloodstream within 5 minutes of ingestion and reaches its peak after 30–90 minutes. Ethanol and its toxic metabolites affect the functioning of neurons. Free oxygen radicals disrupt the function of cellular structures, primarily the vascular endothelium, causing endoneurial hypoxia and leading to damage to nerve axons. In addition, ethanol reduces the synthesis and disrupts the normal configuration of nerve fiber cytoskeletal proteins and slows down axonal transport.
On what basis did the doctor diagnose “Alcoholic polyneuropathy”? The key to making a diagnosis is a history of systematic or binge drinking of alcohol, the absence of anamnestic and clinical and laboratory signs of other probable causes of polyneuropathy: diabetic, hereditary, dysimmune, etc. To confirm the diagnosis and exclude alternative causes of polyneuropathy, the doctor may order the following tests:
- electroneuromyography, which allows you to assess the functional state of motor and sensory fibers of peripheral nerves and determine the nature of their damage;
- general blood analysis;
- detailed biochemical blood test;
- glycated hemoglobin and glucose tolerance test;
- blood test for HIV, RW, hepatitis B and C;
- blood test for levels of vitamins B1, B6, B9, B12, homocysteine;
- rheumatic tests (rheumatic factor, antineuronal antibodies ANCA, antinuclear factor, antibodies to nuclear antigens ANA, antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide, antinuclear antibodies, etc.);
- antineuronal antibodies (anti-Hu, anti-CV2/CRMP-5).
- electrophoresis of serum and urine proteins with immunofixation + freelite.
To diagnose polyneuropathy with predominant damage to thin, weakly myelinated nerve fibers, additional research methods are used:
- cardiovascular tests, assessment of heart rate variability, tilt test;
- autonomic evoked potentials;
- corneal confocal microscopy;
- quantitative sensory testing;
- punch skin biopsy with assessment of the condition of intraepidermal thin nerve fibers.
What treatment can a neurologist prescribe? The main and main stage of treatment is a complete cessation of drinking alcohol. Observation by a narcologist will be useful. Pathogenetic therapy for alcoholic polyneuropathy has not yet been developed. A nutritious, balanced diet with sufficient amounts of vitamins and protein and other lifestyle changes (quitting smoking, normalizing body weight) themselves contribute to a significant improvement in the condition of patients with alcohol-related illness. In cases of concomitant deficiency of B vitamins, vitamins B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), B9 (folic acid), B12 (cyanocobalamin) are prescribed. In the presence of neuropathic pain syndrome, medications are prescribed according to the symptoms of its correction: antidepressants (amitriptyline, duloxetine, venlafaxine) and anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin). Restorative and rehabilitation methods of treatment (transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, myostimulation, acupuncture, biofeedback, massage, physiotherapy, balance therapy, robotic therapy) occupy an important place in the correction of polyneuritic disorders. If you have symptoms of polyneuropathy and you scored 2 or more points on the GAGE questionnaire, then you urgently need to seek specialized medical care at the Center for Diseases of the Peripheral Nervous System of the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Center for Neuroscience!
Drug-induced and chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy What do these terms mean? Drug-induced polyneuropathy is multiple, diffuse, uniform and symmetrical damage to peripheral nerves that develops while taking a drug with a high and moderate degree of neurotoxicity. Chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy that develops during or after chemotherapy is considered separately.
How common is this disease? The prevalence of all drug-induced polyneuropathies has not been reliably determined. At the same time, the prevalence of polyneuropathy among cancer patients receiving chemotherapy is 77.2%. In approximately 1/3 of patients, symptoms persist for at least 6 months after completion of chemotherapy. In addition, the severity of polyneuropathy may limit the continued use of adequate dosing of drugs, potentially increasing morbidity and risk of death from cancer.
What drugs can contribute to the development of this disease? The following is a partial list of drugs with high and moderate neurotoxicity: Vitamins: • pyridoxine (B6) • niacin (B3) Immunosuppressants: • chloroquine • gold salt drugs • leflunomide • cyclosporine Cardiovascular drugs: • amiodarone • procainamide • captopril • hydralazine Antimicrobials: • metronidazole • nitrofurans • chloramphenicol • fluoroquinolones • streptomycin Statins: • atorvastatin • lovastatin • pravastatin Psychotropic drugs: • amitriptyline • lithium salts • amphetamines Antihistamines: • cimetidine NSAIDs: • indomethacin Antigout drugs: • colchicine • allopurinol Chemotherapy drugs: • platinum-based drugs: cisplatin, carboplatin, oxaliplatin • taxane-containing drugs: paclitaxel, abraxane, docetaxel • thalidomide and its analogues: lenalidomide, revlimid, methiblastane • vinca alkaloids: vincristine, vinblastine, vinorelbine, vindesine Anesthetics: • nitrous oxide Anti-alcohol drugs: • disulfiram
IMPORTANT ! The connection between taking a drug from this list and the development of polyneuropathy can only be established by a DOCTOR! Independent withdrawal of the drug is NOT ALLOWED! Your goal is to warn your attending neurologist about taking medications from this list if you have characteristic polyneuritic complaints!
What symptoms bother patients with these types of polyneuropathies? Symptoms for drug-induced and chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy are absolutely the same as for alcoholic polyneuropathy (see above). At the same time, the symptoms of polyneuropathy can be extremely variable, which is associated with the individual response of nerve fibers to the damaging effects of drugs and chemotherapy.
How quickly does polyneuropathy develop when taking a neurotoxic drug? If we talk about drugs that do not belong to the group of chemotherapy, then the first symptoms of neurological disorders may appear after a long time from the start of taking it. Patients often do not see the connection and attribute their complaints to other possible causes and lifestyle changes. We see a different picture after a course of chemotherapy, when symptoms can increase quite quickly after just 1 course of treatment. But the development of symptoms may be delayed, 3-6 months after the end of the entire course of chemotherapy.
On what basis did I receive this diagnosis? The key to making a diagnosis is the presence of polyneuritic complaints and symptoms revealed during examination, as well as a history of constant or systematic use of a drug from a risk group or chemotherapy including drugs with moderate and high neurotoxicity. It is important that there are no anamnestic and clinical laboratory signs of other probable causes of polyneuropathy, including a negative family history. One of the criteria for the correctness of the established diagnosis includes improvement of the condition, or stopping the progression of the disease against the background of therapy. To confirm the diagnosis and exclude alternative causes of polyneuropathy, the doctor may prescribe the studies listed above, including electroneuromyography, which allows you to assess the functional state of the motor and sensory fibers of the peripheral nerves and determine the nature of their damage.
What treatment options are there? After the diagnosis is made, together with specialized specialists, drug therapy is reviewed: the “neurotoxic” drug is replaced with another one. If necessary, symptomatic therapy for neuropathic pain syndrome (antidepressants, anticonvulsants) is prescribed. Prescribing “neurometabolic” drugs is not advisable due to the lack of evidence. Restorative and rehabilitation treatment is important in the correction of neurological disorders in polyneuropathy: transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, acupuncture, biofeedback, interventional methods, massage, physiotherapy, balance therapy, robotic therapy. But we must remember that some methods are contraindicated in the presence of a concomitant history of cancer.
What are the prognosis for this disease? Life expectancy does not differ from that of people who do not have this disease. Recovery depends on the course of the underlying disease for which the “neurotoxic” drug is prescribed. It is extremely important for the prognosis to make a timely correct diagnosis, drug treatment and careful monitoring of the patient.
If you have symptoms of polyneuropathy and are taking “neurotoxic” drugs, then you urgently need to seek specialized medical care at the Center for Diseases of the Peripheral Nervous System of the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Center for Neuroscience.
Employees of the Center for Peripheral Nervous System Diseases provide consultations to patients on an outpatient basis within the framework of compulsory medical insurance and on a commercial basis.
MAKING AN APPOINTMENT AND ENMG/iEMG BY MULTI-CHANNEL PHONE +7 +7
Polyneuropathy after chemotherapy
Toxic polyneuropathy after chemotherapy is classified as a separate group of diseases, since it can be a side effect of taking medications or result from the breakdown of tumor cells. It causes systemic inflammation and damages nerve cells and pathways. This phenomenon can be complicated by the presence of diabetes, alcoholism, liver and kidney dysfunction. This disease is expressed in impaired sensitivity and movement disorders, decreased tone of the muscles of the extremities. Polyneuropathy after chemotherapy, the symptoms of which are described above, can also cause motor dysfunction. Disorders of the autonomic and central nervous systems are less common.
Treatment of this type of disease is reduced to symptomatic therapy. The patient may be prescribed anti-inflammatory, painkillers, immunosuppressants, hormonal drugs, Neuromultivit and Thiamine vitamins.
Treatment
Therapy is carried out in several stages :
- Resuscitation - consists of removing toxins from the body as quickly as possible, as well as maintaining vital functions.
- Basic therapy helps to overcome the negative effects of intoxication, as well as remove all toxins.
- Maintenance therapy – normalizes metabolic processes and corrects the functioning of the body.
Several groups of medications can be used, including:
Article on the topic: Treatment of leg pain
Vitamins – help normalize metabolic processes in the body, helping to restore all processes. Most often, vitamin complexes with a predominance of B vitamins are prescribed.
They help strengthen the nerve fiber, normalize conductivity and restore sensitivity.
The most common of them are:
Neurobion - contains neurotropic vitamins that help strengthen axonal connections and restore the conductivity of nerve impulses. Suitable for long-term use, as it causes virtually no adverse reactions. Not prescribed in case of individual intolerance. Price – 230-260 rubles.
Neurobex - normalizes metabolism, which leads to the acceleration of metabolic processes and the natural restoration of neural connections. Strictly contraindicated in the presence of acute thromboembolism, as well as erythremia. Price – 240-280 rubles.
Preparations for improving the conductivity of nerve impulses - help restore the conductivity of nerve impulses by activating natural regeneration processes, as well as reducing the need of cells for oxygen.
The most effective of them are:
Mexidol - has a complex effect, normalizing metabolic processes and increasing cell resistance to hypoxia. Not used for pathologies of the liver and kidneys. Price – 280-310 rubles.
Trental - normalizes blood counts and also strengthens nerve fibers in the periphery.
Not prescribed for hemorrhagic stroke or increased tendency to bleed. Price – 310-350 rubles. Glucocorticoids are necessary to reduce pain, swelling and discomfort, which is achieved by blocking the body's immune reactions and reducing the synthesis of pain mediators. Most often, they are administered in the first hours after intoxication is detected, which helps reduce the manifestation of an allergic reaction. It can be:
Prednisolone - affects the synthesis of hormones of the adrenal cortex, having an antihistamine and moderate analgesic effect. Not used for hypertension, arrhythmia and kidney inflammation. Price – 280-350 rubles.
Dexamethasone is an adrenal hormone that affects the metabolic processes of proteins and carbohydrates.
Blocks the growth of the immune response to an irritant. Not used in case of individual intolerance. Price – 20-25 rubles for 1 ampoule. Other medications – the following first aid medications may be used:
- isotonic solution;
- sodium thiosulfate;
- anti-diphtheria serum (for diphtheria);
- tetacin-calcium (for lead intoxication);
- atropine sulfate (for FOS poisoning);
- dimercaprol (for mercury poisoning);
- unithiol (for arsenic poisoning).
Diagnosis of the disease
Toxic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is diagnosed through the following studies:
- Ultrasound and x-ray of internal organs;
- cerebrospinal fluid analysis;
- study of reflexes and the speed of its passage along nerve fibers;
- biopsy.
The success of treatment of polyneuropathy depends on the accuracy and timeliness of diagnosis.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of a disorder, safe working conditions must be observed.
To do this, you should use protective equipment and stay in conditions of exposure to toxic substances for no longer than the permitted period. As for endogenous factors, it is very important to promptly treat diseases that can provoke the development of this complication. In addition, it is recommended to visit your local physician at least once a year.
Toxic polyneuropathy is a rather serious disease that requires timely assistance. Therefore, if any symptoms of this disorder appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor who will select adequate therapy.
Features of treatment of the disease
Toxic polyneuropathy, the treatment of which primarily comes down to eliminating the causes of its occurrence, should be considered comprehensively.
Depending on the type of disease and the severity of its course, the following medications are prescribed:
- "Tramadol" and "Analgin" - for severe pain.
- "Methylprednisolone" - for particularly severe cases of the disease.
- “Pentoxifylline”, “Vazonit”, “Trental” - to increase blood flow in the vessels of nerve fibers.
- B vitamins.
- "Piracetam" and "Mildronate" - to enhance the absorption of nutrients by tissues.
The following physiotherapeutic methods can be used:
- electrical stimulation of the nervous system;
- massotherapy;
- magnetic stimulation of the nervous system;
- indirect effects on organs;
- hemodialysis, blood purification.
- Exercise therapy.
It is up to the doctor to decide which method of treating polyneuropathy is most appropriate in a particular case. It is absolutely impossible to ignore the symptoms of the disease. Acute polyneuropathy can become chronic, which threatens loss of sensation in the limbs, muscle atrophy and complete immobility.
Diagnosis and treatment
To correctly diagnose the disease, you need to collect anamnesis. For this purpose, the doctor determines the patient’s working conditions, possible interactions with chemical components, and how often alcohol is consumed. Taking an anamnesis is of great importance, especially in a situation where the patient has recently changed several jobs.
During neurological studies, it is not always possible to obtain comprehensive information regarding the etiology of the disease. A person can only determine damage to peripheral nerve endings. Using special equipment and tools, it is necessary to determine the process of disruption of the transmission of bioelectric impulses. But the causes of polyneuropathy cannot be determined.
In some situations, doctors prescribe a peripheral nerve biopsy . Thanks to this, it will be possible to become familiar with the structural transformations that occur in neurons.
Therapeutic techniques are determined to obtain the following results:
- Renewal of the structure of nerve fibers.
- Increasing bioelectric activity in problem areas.
- Normalization of motor activity of arms and legs.
- Preventing the development of the disorder.
For therapy to be successful, you need to get rid of different types of interaction with the provoking agent. When the cause is a disorder of the endocrine system, you need to be more careful in treatment.
Many medications are used to stabilize the peripheral nerves. To begin with, specialists prescribe medications that help restore the myelin sheath of the nerve trunks. Vitamin B is used for these purposes.
A good effect can be achieved due to the action of drugs that help strengthen the conductivity of impulses. Ipigrix is often prescribed for this purpose.
In the acute form of the disorder, the use of glucocorticoids is justified. Of the medications included in this list, you need to consider Dexamethasone. If autoimmune activity develops during the disease, plasmapheresis should be used. When patients respond well to physical therapy techniques, electrical stimulation can be used.
Thanks to this, it will be possible to improve the condition of peripheral nerves and restore the conduction of signals.