Hello, dear friends!
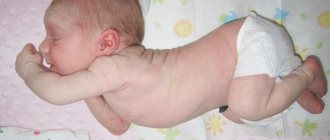
The life of a young mother is filled with surprises. Pleasant ones that the baby himself prepares for us, smiling, taking his first steps and uttering his first word. And not really. Most often, nature presents them in the form of ailments and pathologies. We will talk about one of them today. Hypoxia in a newborn. What it is? In short, this is oxygen starvation. Moreover, it is experienced not only by the brain, but also by the tissues and internal organs of the baby.
This is not a disease, but a specific, often dangerous, phenomenon that you need to know in person. After all, if a mild degree of hypoxia may not have a negative impact on the development of the baby, then severe jokes are bad. It often causes disruption of brain activity, neurological diseases, malfunction of internal organs, and even disability. In advanced cases, death is possible.
What is cerebral hypoxia called?
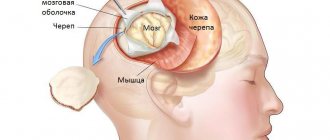
The deviation, as a result of which the baby suffers from a lack of oxygen, is called cerebral hypoxia. When there is a lack of oxygen, the brain cannot function fully, so the central nervous system and other organs are at risk. In most cases, the pathology appears during gestation.
Hypoxia can be acute or chronic. Difficult childbirth that affects children's health leads to the first type of pathology. During chronic hypoxia, the baby experiences a lack of oxygen for a long time. Oxygen starvation is not a safe deviation, as it entails many complications (one of them is the death of brain cells).
Sometimes children are given a disability because of this disorder.
Rehabilitation after discharge
Further treatment after discharge from the maternity hospital (the child’s condition is satisfactory) is carried out by a local neonatologist, who prescribes massage, therapeutic exercises, feeding regimen and explains to the woman the rules for caring for a child who has experienced hypoxia after birth.
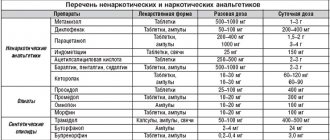
Medicines prescribed include drugs that improve blood circulation and nutrition of the brain (vinpocetine, piracetam, cerebrolysin), drugs that reduce intracranial pressure (diacarb, asparkam, potassium-containing drugs), and anticonvulsants according to indications.
The child is being monitored by a pediatrician and must be regularly examined by a neurologist.
Types of hypoxia in newborns
Both internal and external circumstances can contribute to the formation of hypoxia in infants.
Types of disease:
| Name | Short description |
| Respiratory hypoxia | Occurs as a result of difficulty breathing. The disease is often a side effect of asthma, muscle paralysis, and brain injury. |
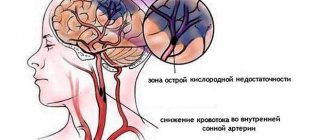
| Circulatory hypoxia | Appears in parallel with cardiovascular diseases. There may be impaired blood flow, as a result of which the central nervous system is not saturated with oxygen in the required volume. This leads to a state of shock, which can lead to ischemic stroke. |
| Hypoxic disease | It is observed when the brain does not have enough air from the outside world. |
| Tissue pathology | Occurs when body cells have difficulty absorbing oxygen. Develops with constant contact with dangerous substances (for example, drugs or poisons). |
| Hemic hypoxia | Formed when the body is damaged by gases or toxic substances. |
The consequences of hypoxia in a newborn are severe. Timely treatment will help avoid serious complications. First of all, it is necessary to undergo an examination to detect a specific disease.
Causes and consequences of oxygen starvation
The fetus experiences a lack of oxygen while in the womb of a mother suffering from:
- severe intoxication against the background of toxicosis,
- chronic diseases (heart disease, lung disease, pathology of the endocrine system, etc.),
- drug, nicotine or alcohol addiction,
- frequent stress,
- improper nutrition.
Most often, hypoxia occurs in children of young mothers and women over 35 years of age. Often the baby experiences a lack of oxygen due to Rh conflict. Sometimes acquired hypoxia occurs, caused by entanglement of the umbilical cord, difficult childbirth, immaturity of the respiratory system, multiple pregnancies, or as a result of the baby being born earlier or later than expected.
How is this violation determined?
A woman does not always know why her baby begins to show activity and becomes restless. By kicking and turning over, the fetus signals that it lacks oxygen. After active actions, the baby calms down, the tremors become weak, barely noticeable.
A movement test will help a woman understand what is happening with the child. If the fetus makes less than 3 active kicks within an hour, this is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist.
If after a visit to the doctor there are still doubts, additional research is carried out:
- cardiotocography,
- fetal electrocardiogram,
- BFP,
- extended blood tests, etc.
What are the consequences of fetal hypoxia for the child in the future?
Due to intrauterine hypoxia, the brain does not receive enough oxygen. Encephalopathy often develops, sometimes the child cannot be saved (see also: causes of encephalopathy in children). In a baby who has suffered hypoxia during pregnancy and childbirth, the consequences of a lack of oxygen may appear within several months.
Severe oxygen deficiency does not go unnoticed. Changes in brain function can lead to serious pathologies of the nervous system, including cerebral palsy.
Severity of hypoxia
At birth, the baby is assessed according to the degree of functioning of all organs, for which the Apgar scale is used. The general situation in the first minutes after birth and the situation that developed 5 minutes later are recorded.
There are 4 forms of pathology:
- Severe hypoxia (0-3 points): absence of reflexes, including sucking, low blood pressure, depression, excessive lethargy, painful cries, convulsions, a radical change from high to low pulse. It can occur due to entanglement in the umbilical cord, obstruction of the respiratory system, short or long labor, a significant difference between the baby’s head and the mother’s pelvis, due to general diseases.
- Hypoxia of moderate severity (4-5 points): loss of strength, decreased motor activity, convulsions, incomplete paralysis, impaired sucking function.
- Mild disturbance (6-7 points): excessive agitation, restlessness of the child, trembling of the limbs, eyelids and chin, squint.
- Absence of pathology (8-10 points).
When assessing a newborn, breathing, reflexes, skin color, muscle tone and heart rate are taken into account. Mild hypoxia disappears without outside help within 5 minutes. Moderate hypoxia requires medical intervention.
After taking the medications, the baby's condition stabilizes.
A severe form of the disease requires the child to be urgently sent to intensive care, where appropriate treatment is prescribed. Here the newborn is under the supervision of specialists.
Consequences
When there is a lack of oxygen in the child’s body, severe metabolic disorders occur. Due to the influence exerted by acidosis, the permeability of the vascular walls increases, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted, edema begins, and brain tissue swells. Due to oxygen starvation, damage to nerve cells occurs, and the more severe and prolonged the starvation, the greater the damage. In addition, it leads to vascular paresis, edema and microhemorrhages. All this leads to degenerative changes in the child’s brain tissue.
All consequences of untreated hypoxia are purely individual and are entirely determined by the predispositions of the child himself. But mental and physical impairments are guaranteed to appear and become stronger by age six. By this time, the child may already experience nervousness and hypertonicity, leading to an exacerbation of hyperactivity, decreased attention and deterioration in academic performance. By this point, many parents come to their senses and begin to treat the child, turning to a neurologist and speech therapist, but with age it becomes more and more difficult to overcome the consequences of oxygen starvation.
The more time passes from the moment the child suffered hypoxia, the more difficult it is to achieve even minor results.
How is a violation determined?
Hypoxia is easy to detect immediately after birth.
Its characteristic features are:
- an increase in heart rate, followed by a slowdown in heart function;
- disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions;
- heart murmurs;
- presence of blood clots;
- pale skin;
- the limbs and nasolabial triangle are particularly blue;
- slow breathing or cessation of breathing;
- there are no reflexes or they are weakly expressed (the baby is powerless or does not move);
- intracranial pressure;
- the baby did not cry after birth;
- presence of green waters.
If the disorder is not detected immediately after birth, the child may experience increased drowsiness, moodiness, rapid freezing, flinching when touched, and other disorders. If you detect the first signs of hypoxia, you should immediately consult a doctor for timely diagnosis of the disease.
It is important to know the form of the pathology in order to identify the severity of the problem.
How to detect hypoxia?
Many pronounced symptoms indicate the disease. But most often only doctors can identify them, as well as suspect something is wrong.
Main symptoms:
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart (murmurs are heard, tachycardia, bradycardia or arrhythmia are observed);
- the appearance of meconium in the amniotic fluid;
- small volume of blood;
- the presence of blood clots in the vessels;
- lack of crying in a newly born baby.
As a rule, all of them are diagnosed in the maternity hospital. However, there are other signs that may indicate hypoxia.
A pediatrician or an experienced mother can notice them:
- constant or regular body trembling in an infant;
- convulsions;
- restless sleep;
- whims and crying for no reason;
- flinching from touch;
- crying during bathing;
- constant freezing of the baby;
- trembling of the chin, legs and arms when crying;
- muscle tone.
Most often, these factors are signs of mild hypoxia and disappear with well-chosen drug treatment.
What does fetal hypoxia mean for a child in the future?
Brain hypoxia is the most common consequence of lack of oxygen. In most cases, this disorder affects the brain and not other organs. During pregnancy, it is difficult to determine what pathologies will arise as a result of disruption of brain activity. But after birth, it is realistic to assess the trauma caused.
Some pathologies will be noticeable after a considerable time (for example, speech problems), others can be identified in the maternity hospital or at the very beginning of the baby’s life. The consequences of hypoxia in a newborn can have varying degrees of severity: from minor excitability of the child to serious diseases (paresis of various dislocations, cerebral palsy).
If an acute form of hypoxia was observed during childbirth, cerebral hemorrhage, decreased blood supply, and cerebral edema quite often occur.
The consequences of hypoxia in a newborn, in severe cases, can lead to complete disability of the child.
The lesions that appear during such pathologies are irreversible and total. Acute and chronic oxygen starvation can cause various neurological disorders. In the case of prolonged hypoxia, children may experience abnormal or incomplete development of certain human organs, heart or kidney defects.
Children can often outgrow a minor form of the disease by about 7 years of age (provided that the child is registered with a neurologist and follows his recommendations).
Causes
The factors that provoke the development of hypoxia in the newborn are very numerous. Conventionally, they can be divided into 4 large groups:
Antenatal causes (acting during pregnancy)
These include:
- severe somatic diseases of the mother (cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine pathology),
- chronic intoxication of a pregnant woman (smoking, drinking alcohol, using drugs, occupational hazards, disturbed ecology).
This list also includes:
- premature and post-term pregnancy,
- gestosis,
- severe pronounced anemia,
- bleeding during pregnancy (previa, placental abruption),
- intrauterine infection of the fetus with chronic maternal infections and acute infection suffered during pregnancy,
- polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios,
- multiple pregnancy.
In addition, hypoxia may be to blame for:
- Rhesus conflict pregnancy and antiphospholipid syndrome,
- permanent threat of miscarriage and development of fetoplacental insufficiency,
- constant stress, unfavorable living conditions, poor nutrition.
Intrapartum causes (complicated labor)
This group includes:
- protracted or, conversely, rapid labor,
- birth injury to the fetus (damage to the brain or spinal cord),
- labor stimulation with oxytocin,
- surgical delivery (application of obstetric forceps, caesarean section).
This group also includes:
- drop in blood pressure during childbirth,
- preeclampsia and eclampsia during childbirth,
- placental abruption during childbirth,
- hypoxia of a woman during general anesthesia,
- uterine ruptures,
- anomalies of labor (discoordination of labor forces).
Pathology from the umbilical cord
- true nodes and their tightening of the umbilical cord,
- rupture of the umbilical vessels,
- umbilical cord entanglement,
- umbilical cord compression.
Fetal causes (from the fetus).
These reasons include:
- hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (anemia due to hemolysis of red blood cells),
- fetal malformations (anomalies of the cardiovascular and pulmonary systems),
- infectious intrauterine diseases,
- hemorrhages in the brain, adrenal glands.
Asphyxia of the newborn
Asphyxia, which subsequently turns into hypoxia of the newborn, develops as a result of blockage of the respiratory tract (ingestion of amniotic fluid and meconium by the child, blockage of mucus, tight entanglement of the umbilical cord, prolonged and problematic birth of the head, and others).
Chronic fetal hypoxia
Hypoxic syndrome is the main symptom of chronic lack of air. In this condition, the speed of blood circulation increases, the viscosity of the blood decreases, resulting in damage to the brain.
Symptoms
Hypoxia negatively affects the child’s brain, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bad feeling;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- muscle spasms (cramps);
- sleep disturbance;
- vomiting, nausea;
- problems with vision and hearing;
- lethargy;
- clumsiness;
- uncontrolled urination and bowel movements;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus.
Seizures usually begin with twitching of the muscles of the face and limbs. After some time, a convulsive posture may be observed with the head thrown back and the back arched in the shape of an arc. This pose is reminiscent of an exercise called a “bridge.”
How to diagnose pathology
If oxygen starvation is detected before the birth of the child, then treatment will be effective.
A pregnant woman must undergo a comprehensive examination, consisting of:
- ultrasound examination of the fetus;
- cardiotocography;
- a test that detects embryo movements;
- listening to a child's heart using a stethoscope.
Ultrasound results allow you to monitor the general condition of the fetus, determine the volume of amniotic fluid, and also study the baby’s organs. Using this method, the doctor determines whether the child is safe or whether there will be health problems. CHT and listening to the heart will help determine if the fetal heartbeat is abnormal.
How to independently determine deviations in the development of a baby in the first weeks of his life:
The main sign of hypoxia is an excess of generally accepted standards of heart rate: 160-170 beats per minute.
Treatment options
Treatment of oxygen starvation in infants depends on how severe its symptoms are, how long it was in conditions of lack of air, and which organs are affected. Hypoxia in infants is highly treatable. But the duration of the lack of air directly affects the severity of the deviations.
Cerebral palsy is often a consequence of oxygen deprivation. Delayed psychomotor development in newborns may also occur. But this disease is easy to cure. If a lack of oxygen is detected during childbirth, treatment will begin with restoring breathing. The baby may end up in intensive care.
If prenatal hypoxia is detected, delivery by cesarean section is possible.
Lack of oxygen can be treated with medications, as well as with massage . Children suffering from this disease should be registered with a neurologist. Medicines may be prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure and improve blood supply to the brain and blood flow in the body.
To normalize muscle tone, massages, therapeutic exercises, and water treatments are prescribed. By adhering to the correct methods of treating hypoxia, by the age of one and a half years the child can completely get rid of this pathology.
Consequences
The consequences of hypoxia in a newborn most often negatively affect the child’s brain. It is responsible for the normal functioning of the entire body. The consequences of oxygen starvation can manifest themselves in the most unexpected forms.
If the umbilical cord is damaged and the child cannot breathe on his own during childbirth, this indicates that the baby’s body stops receiving blood, blood pressure drops, and venous pressure becomes higher. The baby's blood supply decreases, swelling and accumulations of spilled blood appear in the tissues and cavities of the body.
Sometimes there are seizures and vision problems.
Cerebral palsy is one of the most serious consequences of hypoxia. The birth of a huge number of children with this disease is attributed to the regular use of drugs that affect rapid delivery. At an older age, the child will need to be shown to a psychologist. And, if necessary, a speech therapist.
Therapeutic tactics of hypoxia
If fetal hypoxia occurs during the period of pushing or during contractions (decrease in heartbeat), a decision is made to complete the labor as soon as possible: a cesarean section or the application of obstetric forceps (in the case of labor stimulation with oxytocin, the administration of the drug is stopped). After the birth of the child, immediate medical care begins:
- clearing the respiratory tract from mucus, meconium and water (suction with a special aspirator);
- supplying a mixture of oxygen with air or pure humidified oxygen through a mask, nasal catheter or mechanical ventilation device (in case of severe hypoxia, the newborn is placed in an incubator, intubated and mechanical ventilation is started);
- heating the baby with radiant heat (on a special changing table), and in case of severe hypoxia, placing the baby in an incubator;
- administration of drugs that stimulate blood circulation and increase blood pressure (camphor, dopamine) and drugs that stimulate the respiratory center (etimizole);
- intravenous infusions solution, sodium bicarbonate (neutralization of carbon dioxide in the blood), glucose to restore the reduced volume of the vascular bed;
- transfusion of blood products if necessary (hemolytic disease of the newborn);
- prescribing antibiotics to prevent pulmonary infections in case of severe hypoxia or intrauterine infection of the fetus, as well as in respiratory distress syndrome during premature birth;
- prescription of anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, phenazepam);
- To reduce intracranial pressure, administration of diacarb and veroshpiron (diuretics with the effect of reducing cerebrospinal fluid production) is indicated.
Acute hypoxia in newborns
A few hours after birth, the baby may experience acute oxygen starvation. Often, a woman in labor cannot influence the occurrence of a hypoxic condition in the child. In some cases, incompetent health care workers are responsible for the suffocation of a newborn.
Causes of the pathological condition
The main factors that influence the formation of hypoxia in a child:
- Intrapartum , that is, occurring during childbirth. Such reasons include labor that is too long or too fast, umbilical cord prolapse (the supply of oxygen to the baby is cut off if the umbilical cord is squeezed between the birth canal and the fetus), compression of the baby’s head in the birth canal for too long, and weak labor.
- Antenatal (reasons that appear before the birth of the child). They occur if the placenta detaches prematurely or the uterus spontaneously ruptures during pregnancy. This also includes polyhydramnios and multiple pregnancies. These disorders are typical for women who are not giving birth for the first time, or who suffer from inflammation of the genital organs after an abortion.
Early contact with a specialist will help reduce the risk of complications of hypoxia.
Signs
Lightning hypoxia occurs rapidly, and within a few minutes the child dies. An acute lack of oxygen occurs a couple of hours after the baby is born.
During the specified period of time, the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath, trouble breathing;
- slow heartbeat;
- low blood pressure;
- a state of coma accompanied by the death of the baby (if the child is not given first aid).
Diagnostics
Acute fetal hypoxia can be detected using an obstetric stethoscope (irregularities in heart rhythm, too frequent or infrequent heart contractions, poor audibility of heart sounds). Phono- and electrocardiography, which will help assess the functioning of the child’s heart. They are used to confirm the results obtained.
An ultrasound will record disturbances in the motor functions of the embryo (it should make approximately 5 movements in half an hour), as well as changes in breathing rate. Hypoxia of the newborn is indicated by turbid amniotic fluid having a green color.
They may contain particles of meconium (the baby's first stool).
Treatment methods
The consequences of hypoxia in a newborn require mandatory treatment. If acute oxygen starvation is detected, the expectant mother must be hospitalized immediately. Doctors prescribe taking ascorbic acid, glucose, and inhaling oxygen-air mixtures.
Medicines are also prescribed that have a positive effect on the respiratory system of a pregnant woman. Considering the causes of hypoxia, in some cases caesarean section and the use of obstetric forceps are recommended.
Treatment of infantile hypoxia should begin as soon as possible. If a newborn has swallowed amniotic fluid, the newborn's airway must be cleared using special equipment. To restore breathing, an oxygen mask is put on the child.
A mild type of oxygen starvation does not require serious treatment. Therapeutic exercises, physical procedures, and massage are prescribed.
Moderate hypoxia requires taking medications that improve blood circulation in the brain. In severe cases of the disease, the baby is sent to the intensive care unit. In case of cerebral edema, urinary medications are prescribed. Anticonvulsant medications will help relax the muscles and also relieve the child from seizures.
Posthypoxic changes
Often post-hypoxic changes provoke developmental delays in children. The baby's weight stays the same. Such children begin to speak their first words later than their peers, and they suffer from neurological diseases. Often oxygen starvation is the cause of mental disorders.
Diagnosis and treatment
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to undergo an examination. Even during pregnancy, a woman will need to perform an ultrasound of the fetus, a movement test, and also listen to the heartbeat. Based on the results of the research, it will be possible to understand whether there is a threat to the baby.
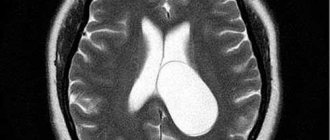
After birth, the baby undergoes an ultrasound of the brain and a neurological examination. If deviations are noticed, then the presence of hypoxia can be suspected.
During treatment, breathing is first restored using aspiration, then artificial ventilation can be used. A solution of glucose and cocorboxylase is injected into the umbilical cord. For bardycardia, a heart massage is performed, and adrenaline and other medications are injected into a vein. After this, the child will need to be given vitamins, undergo infusion treatment, and also undergo oxygen therapy.
Forecast
Timely treatment of chronic lack of oxygen, gestation of the fetus under normal conditions, as well as a successful birth process will make a favorable prognosis in the future. The consequences of acute hypoxia depend on the factors of occurrence, timing of disease progression and regular use of medications.
The consequences of a lack of oxygen are fraught with dangerous complications for the newborn. To avoid hypoxia in a baby, a pregnant woman needs to spend more time in the fresh air, undergo medical examinations on time, and carefully choose a gynecologist.
Author: Ekaterina Pisarenko
Article design: E. Chaikina
Prevention
Prevention of hypoxia in a child is one of the primary tasks that faces a pregnant woman. To avoid having to undergo long-term treatment for the effects of oxygen starvation, the expectant mother should follow the following recommendations:
- Spend time outdoors. It is important not just to sit, but to take walks. This way the body will receive enough oxygen.
- To refuse from bad habits. Alcohol and tobacco smoke negatively affect the condition of the fetus.
- Do special gymnastics for pregnant women.
- Regularly see a gynecologist and follow his recommendations.
- Get tested on time.
- Eat properly. The menu must include fresh fruits and vegetables, eggs, herbs, seafood, and liver. It has been proven that anemia contributes to the development of fetal hypoxia.
- Stick to a daily routine.
- All extragenital infections must be treated before the baby is born.
Immediately after contractions begin, you must call an ambulance and go to a medical facility. Only in a maternity hospital can a newborn be provided with quality care. Home birth is dangerous. Very often such events end with serious consequences for the woman and child.
In order to prevent hypoxia, obstetricians should immediately remove the umbilical cord from the baby's neck. It is important to quickly clear his airways of mucus and other impurities that interfere with normal breathing. Compliance with obstetric care during childbirth is the main prevention of hypoxia in a maternity hospital.