The ulnar nerve belongs to the peripheral system. Ulnar nerve neuropathy is a common disorder that occurs due to human habits and traumatic factors.
The ulnar nerve passes through the joint, which is considered the least protected area. Compression lesions in this area are almost as common as carpal tunnel syndrome, which is also sometimes called carpal tunnel syndrome.
Anatomy of nerve location
The ulnar nerve begins in the C7-C8 bundle, Th1, which is located in the medial part of the brachial plexus. The ulnar structure has no branches or small roots. It passes through the inside of the shoulder, gradually forming the back.
Important! In the area of the elbow joint, the nerve is located closest to the surface of the skin, and then passes into the cubital canal.
In the canal it is surrounded by ligaments and tendons, so protection against injury and compression in this area is increased. From the elbow to the wrist, the nerve runs along the inner edge of the forearm. At the head of the bone at the bottom of the wrist, an additional branch is formed on the back of the hand, then it goes deep into the palm and again divides into 2 branches.
When disturbed, the superficial branch leads to loss of sensitivity in the little finger and partially in the ring finger. The second branch takes over the functions of the sensory organ of the rest of the palmar ligament.
Classification of elbow neuropathy
There are several types of ulnar nerve neuropathy. The classification is based on an etiological basis, that is, on the causes of damage:
- post-traumatic neuropathy - appears due to rupture or severe stretching of the nerve;
- Compressive neuropathy - associated with nerve compression syndrome, this group includes Guyon's syndrome.
The latter group is more common and is associated with characteristics of professional activity and human diseases that affect the vulnerable area of the elbow.
Symptoms: how does the lesion manifest itself?
Symptoms of subluxation of the elbow joint include:
- acute pain syndrome;
- change in the appearance of the elbow due to an elongated joint;
- temperature increase;
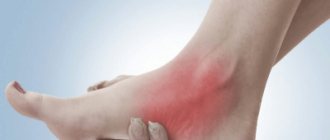
- swelling in the elbow area;
- limited joint mobility or complete inability to move;
- loss of sensation in the injured arm.
The severity of symptoms depends on the complexity of the dislocation. The more severe the damage to the joint, the more discomfort the person experiences.
Pain is the main symptom of many injuries.
It is worth noting that pain is inherent in a number of pathologies, both serious and non-serious. However, acute and unbearable pain is recorded only with serious lesions. Complex dislocations can only be corrected in a hospital setting.
Reasons for violation
The position of the ulnar nerve influences the causes of damage that lead to symptoms of neuropathy. Unlike the radial or median nerve, the ulnar nerve passes a few millimeters from the skin layer. Moreover, this area is constantly exposed to traumatic factors and pressure. The traumatic mechanism of neuropathy occurs under the following circumstances:
- dislocations, bruises of the arm and elbow area;
- fractures of various parts of the shoulder, wrist and forearm;
- wrist injuries, including sprains.
The second category of circumstances under which ulnar nerve neuropathy occurs is associated with compression-ischemic disorders due to diseases:
- deforming osteoarthritis, osteodystrophy;
- synovitis, bursitis, tendovaginitis;
- destruction of the myelin sheath of the nerve, characteristic of various sclerosis, encephalomyelitis and leukoencephalitis - the common name for such disorders is demyelinating;
- aneurysms located near joints;
- neoplasms leading to nerve compression;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Occupational habits and characteristics can cause neuropathy:
- the habit of leaning on your elbow when performing any task, or while talking on the phone;
- monotonous and monotonous work with tools with a fixed elbow position, including the use of a professional vibrating tool;
- prolonged stay under a drip – the patient’s arms are straightened, the nerve is in a state of compression;
- regularly riding a bicycle or motorcycle with tension in the elbow joints;
- resting on the elbows when working at a table, using tools, and also when driving a car.
In terms of frequency of occurrence, ulnar nerve neuropathy, caused by professional habits, occupies a leading place and can only compete with disorders such as arthrosis.
How does ulnar nerve neuropathy manifest itself or when the elbow gets an electric shock?
Among lesions of individual nerves, ulnar nerve neuropathy is the second most common and this is primarily due to its location.
Paresis, loss of sensitivity, pain - this is not a complete list of symptoms characteristic of this disease.
In this article we will look at what neuropathy (neuritis) of the ulnar nerve is, treatment and symptoms of this disease.
Anatomy of the ulnar nerve
The anatomy of the ulnar nerve (topography of the ulnar nerve) is not the most complex of all the nerve processes in the human body, but it also has its own characteristics.
The ulnar nerve itself performs a conductive function, like other types of nerves, but its anatomical structure is special.
So, the ulnar nerve takes its origin from the spinal nerve, and to be precise, it comes out of the medial bundle of the brachial plexus, then passes along the shoulder girdle to the human shoulder.
The structure of nerves It is worth noting that during the passage from the spinal cord to the shoulder, not a single branch departs from the nerve.
Further, from the shoulder it runs along the back side to the elbow, where it runs along the back of the arm. On the back surface of the elbow, the nerve is located as close to the skin as possible.
After the elbow bend, the nerve enters the cubital canal and it is the entry point that is one of the dangerous ones, from the point of view of pinching or compression (in the cubital groove, the nerve is located in the joint as close as possible to the ulna bones and can be compressed by muscles or the ulna bone, which will cause pain and accompanying symptoms.)
Further, after passing through the cubital canal, the nerve passes along the forearm and divides into two branches: the dorsal and palmar branches.
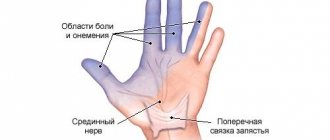
The innervation of the skin and muscles of the wrist lies on the dorsal branch. The palmar branch runs along the back of the hand and innervates the skin of the palm and the sensitivity of the little finger, ring finger and partly the middle finger.
In addition, it is divided into deep and superficial branches. The superficial one is responsible for the innervation of the skin, and the deep one is responsible for muscle sensitivity.
The deep branch enters Guyon's groove (Guyon's canal) where it can also be compressed or squeezed due to the close proximity of the small carpal bones.
The topographical feature of the nerve structure is important in determining the cause of the disease.
Classification
Neuropathy (neuropathy) of the ulnar nerve (also known as corporal tunnel syndrome of the ulnar nerve) has its own classification, which is not as extensive as other ailments. So, depending on the cause of the occurrence, inflammation of the ulnar nerve occurs:
Primary is associated with the presence of the disease, regardless of the factors that can provoke pinching or neuropathy (prolonged leaning on the elbow, etc.). Secondary, in turn, depend on the underlying disease or external factor (trauma, infectious disease, etc.).
What happens inside when pinched
Depending on the location, the disease may also vary:
- Cubital lesion.
- Pinching in the Guyon canal area.
More than 70% of all cases of pinched nerve occur either in the cubital region or in Guyon's fissure, due to the peculiarities of the nerve's passage.
Causes
Ulnar nerve entrapment can be caused by trauma (post-traumatic syndrome) or compression (compression syndrome or compression-ischemic neuropathy).
The post-traumatic variant is provoked by injury or sprain of joints, muscle rupture, soft tissue bruise, etc.
As for the compression option, it is primarily related to the patient’s lifestyle.
Cubital:
- sitting for a long time, leaning on the elbow (pupils or students in classes, office workers, thus putting pressure on the antecubital fossa);
- specifics of driving (many people, when driving, lean on their elbow, which is exposed to the window);
- long-term invasive effects (drip);
- frequent movements in the elbow joint (possible in some athletes).
Guillain's syndrome:
- regular use of a cane while walking;
- riding a motorcycle;
- working with tools that cause vibration and radiate not only into the shoulder, but also into the wrist crease.
The condition for the formation of a compression variant of neuropathy in Guillain’s canal is compression or prolonged (same type) impact on the wrist.
Which nerve is responsible for what?
In addition, the reasons for the formation of neuropathy may be:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- vascular aneurysm;
- swelling (thickening of a joint or muscle);
- tenosynovitis;
- osteodystrophy;
- osteoarthritis;
- demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, multiple encephalomyelitis);
- post-traumatic arthrosis;
- thickening (enlargement) of lymph nodes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a pinched ulnar nerve vary depending on the location of the injury or inflammation.
So, with the cubital variant of the disease:
- decreased sensitivity in the elbow;
- pain in the ulnar fossa (with prolonged exposure to the nerve, pain begins to spread to the fingers and to the surface around the elbow);
- problems with moving the little finger to the side (this action causes difficulty);
- muscle weakness;
- decreased motor activity in the hand, numbness;
- the hand takes the form of a “bird’s” or “clawed” paw.
In the case of Guillain's syndrome:
- paresis of the fingers (little finger, ring finger and part of the middle finger), palms, limbs may become swollen or numb;
- paralysis;
- The above mentioned fingers may hurt from the palm side.
Basically, the symptoms in the above cases are identical, with the only exception that the lesion does not affect the back of the hand if we are talking about a pinched nerve in the Guillain's canal.
It is worth noting that the symptoms of the disease often intensify in the morning, after the patient awakens (or the symptoms can cause awakening), since many patients unconsciously put their hand under their head, which leads to numbness and the formation of these symptoms.
Fingers with ulnar nerve neuropathy
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this disease is carried out using a comprehensive test. Which, in addition to standard neurological tests, also includes instrumental diagnostics.
The study of the disease is carried out by a neurologist, who, at the first visit, clarifies with the patient what is bothering him and the nature of the unpleasant sensations.
Neurological tests include:
- test for bending the fingers into a fist (negative result - if all fingers come together in a fist, and positive if the little finger protrudes slightly);
- test to assess range of motion (the hand is placed on a flat surface and the patient tries to scratch this surface with the little finger and spread the pressed fingers to the sides. If there is a nervous position, this will be quite problematic);
- image of the Okay sign with your hand (a sick person will not be able to complete this test).
Since the patient has quite a lot of different nerves in the arm (radial, median, etc.), the doctor must differentiate inflammation of the ulnar nerve from neuralgia of other nerve endings and roots. For this, the patient is shown instrumental diagnostics that can show not only the cause of inflammation, but also distinguish it from other diseases.
Thus, instrumental diagnostics may include:
- radiography of the elbow joint;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography of the forearm;
- radiography of the wrist joint;
- computed tomography of joints;
- testing nerve conduction velocity;
- physical examination of the elbow joint;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- histological examination.
Treatment
Inflammation of the ulnar nerve can be treated on an outpatient basis, since this disease does not require inpatient observation, with the exception of surgical intervention.
Treatment methods are as follows:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- folk
Conservative treatment involves the use of medications, which, in turn, include:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticosteroids, diclofenac, ketorolac);
- painkillers (metamizole sodium, anesthetics);
- anticholinesterase drugs (ipidacrine, neostigmine);
- vasoactive drugs (nicotinic acid, pentoxifylline);
- metabolites (B vitamins, alpha lipolic acid).
The greatest effect is caused by injections of the above drugs, as the absorption of the active substance increases.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe a compress with dimexide and cold on the painful area.
At the acute stage, when the pain syndrome has just appeared, it is important to perform a motor blockade of the arm and elbow joint, especially at night.
The patient is recommended to have a fixing bandage, in most cases using a splint made from improvised materials (a needle or a strong stick).
In addition to drug treatment with tablets, physiotherapy is prescribed, which includes:
- UHF;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
An excellent way to eliminate the unpleasant consequences of inflammation (muscle atrophy) is massage and electrical myostimulation.
Surgical intervention (operation) is indicated in case of lack of effect from medications, the presence of a hematoma, tumor, and also in the case of the development of tunnel-type neuropathy.
Types of surgical intervention:
- nerve decompression;
- neurolysis;
- removal of adhesions;
- nerve transposition;
- tumor removal;
- scar removal;
- removal of hematoma.
Any operation, especially one performed on nerves, is performed under anesthesia. Pain relief can be performed using either general or local anesthesia.
Surgical option
Naturally, home remedies are used to treat ulnar nerve neuropathy, which in most cases are aimed at eliminating the pain symptom.
Before you start using traditional medicine, we strongly recommend that you consult your doctor for advice and obtain his permission to use a particular recipe.
Horse sorrel tincture:
Soak the roots of horse sorrel in vodka in a ratio of 1 to 1. Namely, half a jar of roots and half a liter of vodka are used for a liter jar. Infuse the root for at least 10 days and apply as a compress to the sore spot. The effect is enhanced if the compress is done at night.
Bay leaf ointment:
Mix 200 grams of vegetable oil and 4 tbsp. l. finely chopped bay leaf. Leave the ointment for a week. Rub the resulting product into the area that hurts until the pain stops.
Horseradish compress:
Horseradish is ground with raw potatoes in a ratio of 1 to 1 and 1 tbsp is added to the resulting mixture. l. honey The resulting mixture is wrapped in thick cloth and applied to the left or right hand, depending on the location of the pain syndrome, for an hour. Horseradish acts as an anesthetic, and potatoes compensate for its burning effect.
Hand rehabilitation exercises
Additionally, during the recovery stage, the patient is shown physical therapy exercises (PT), as well as classes on specialized equipment.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis of this disease in most cases is favorable and leaves no consequences, unlike some other ailments. However, an important condition for the absence of consequences is timely treatment.
The disease can be cured in a short time, the main thing is not to delay it.
Regarding the prevention of this disease, the following recommendations can be noted:
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- refusal or reduction of monotonous movements in the elbow joint;
- upper limb gymnastics is excellent for preventing pinching or inflammation of the ulnar nerve;
- regular intake of vitamins;
- visit a massage once every six months (or more often);
- monitor your health and be careful to avoid bone fractures, sprains or bruises of the upper extremities;
- Visit your doctor regularly for routine preventive examinations.
So, ulnar nerve neuropathy is a harmless but unpleasant disease, the course of which is difficult to predict. If symptoms reminiscent of this disease appear, you should not delay contacting a doctor. Get treatment on time and don’t joke with your health, especially when it comes to the nervous system.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/595f61ded7d0a69b431e48f9/5db12b856d29c100add480db
Symptoms of a neuropathic disorder
Peripheral nerve disease is caused by different causes, but the manifestations boil down to the same symptoms:
- muscle weakness appears and sensitivity in the area of the injured elbow decreases;
- the ulnar fossa begins to hurt, the discomfort spreads to the fingers and covers the area around the elbow;
- in patients with neuropathy, the little finger cannot move away from the other fingers even 10 degrees;
- as it develops, a symptom of “clawed paw” appears, when the fingers are twisted and it is difficult for a person to move the hand;
- numbness gradually develops and motor activity on the injured elbow decreases.
Guillain's syndrome is slightly different from classical neuropathy in that it has increased symptoms: the fingers hurt on the side of the palm, and paralysis of the little and ring fingers is possible. In some cases, paresis, swelling and numbness affect part of the middle finger.
The symptoms of the disease are sometimes confused with arthrosis, since they occur mainly in the morning, immediately after waking up. However, unlike arthrosis, the pain is stronger and does not go away after a short rest.
Symptoms of upper limb neuropathy
As it develops, neuropathy of the upper extremities gives various symptoms, which can manifest themselves in the form of pain, paresthesia, impaired sensitivity and motor activity. The first signs are very difficult to notice, since they are hidden behind the sensations of rapid muscle fatigue, weakness, and inaccuracy in performing finger movements. Most patients attribute these manifestations to fatigue, increased physical activity, incorrectly chosen position for night rest, etc.
After some time, the symptoms of neuropathy of the upper extremities become more typical for this disease:
- pain appears first after performing certain operations (for example, after prolonged work at the computer), then unpleasant sensations are present almost constantly;
- pain and tension in the muscles of the upper limbs intensify in the evening, reach their peak during bedtime, and may be completely absent in the morning;
- numbness of certain areas is combined with paresthesia (a feeling of crawling);
- decreased muscle strength;
- increased fatigue of the arm muscles when performing habitual physical work;
- impairment of motor activity;
- development of contractures in the joints of the fingers at a late stage.
With prolonged development of neuropathy of the upper extremities, paresis, plegia, and muscle paralysis may occur. It will be very difficult to restore their functionality later. Therefore, it is necessary to start treatment in the early stages of the disease.
Methods for diagnosing pathology
Ulnar nerve neuropathy can be detected without complex and expensive examinations. First, the patient needs to contact a neurologist or therapist. Next, the doctor will conduct a diagnosis using the Froman method:
- You need to press the paper sheet against the table with your thumbs so that the rest of your palm is perpendicular to the surface. If there is neuropathy, the thumb will bend when pressure is applied, and it becomes impossible to straighten it.
- To confirm the pathology, you need to strike with the edge of your palm or your fingers in the place of the cubital canal. The pain will intensify in this case, as will the numbness or tingling sensation.
- By pinching and tingling, the doctor determines the degree of loss of sensitivity in the patient’s parts of the hand.
Of the instrumental examination methods, ultrasound is most often used to confirm the diagnosis. The device reflects changes in the structure of the trunk well.
Sometimes X-rays and MRIs are required to identify the causes of the disorder if they were not known in advance. If these methods fail to identify the factors of ulnar nerve neuropathy, electromyography is prescribed. Using this method, impulse conduction disturbances are determined.
It is not necessary to donate blood and urine for testing in all cases of diagnosing neuropathy. However, with their help it is possible to exclude infections and inflammatory processes, as well as some other diseases.
Symptoms and treatment of neuralgia
The origin of ulnar neuralgia can be different - somatic and infectious pathologies, trauma, prolonged compression.
The inflammatory process affects the fibers of the peripheral nerves and manifests itself:
- pain syndrome;
- numbness of the upper limb (impaired passage of nerve impulses to the brain);
- disruption of the functional activity of the arm muscles.
Treatment of neuralgia of the elbow joint is complex and consists of the use of medication and physiotherapeutic methods:
- using a plaster splint, the arm is fixed in a half-bent position and suspended in a special bandage - in this way, the cause that caused the neuralgia is most often eliminated;
- in case of an inflammatory reaction, antibacterial agents are prescribed, in case of an acute infectious disease - antiviral agents;
- to relieve swelling, it is necessary to take potassium-sparing diuretics;
- B vitamins are considered an effective means for improving cellular metabolism;
- Papaverine is strongly recommended to improve trophism and blood circulation in tissues;
- to maintain the physiological tension of nerve and muscle tissues, electrophoresis, ampli-pulse and UHF are prescribed;
- The patient can carry out massage sessions independently, starting with rubbing the fingertips, flexion and extension of the joints of the phalanges and hands.
Treatment of the disease
It is necessary to begin treatment for ulnar nerve neuropathy after confirming the diagnosis. The doctor determines the therapy, taking into account the accompanying circumstances, symptoms and main causes of the disease. In most cases, drug therapy is used, as well as traditional medicine. In rare cases, for example, with severe injuries and mechanical clamping of the fiber, surgery is prescribed.
The objectives of therapy are reduced to solving one goal - restoring the conductivity of a nerve damaged by external factors. If it is ischemic, compression syndrome, then an integrated approach is required. In case of injuries and fractures, long-term fixation of the damaged structure is usually sufficient.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy for ulnar nerve neuropathy is mainly limited to eliminating pain. To do this, take drugs from the NSAID group: Nimesulide, Meloxicam, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac and products with similar active ingredients.
Diuretic drugs are also used if the patient has severe swelling. Be sure to use complex vitamins and injections with B vitamins - they have the best effect on the recovery process in diseases such as neuropathy.
Important! Neuromidin is a potent drug for restoring neuronal conductivity.
Antispasmodics are used if there is severe muscle hypertonicity and spasm that does not allow the limb to relax normally. In severe cases, they resort to lidocaine or novocaine blockade with the use of antibacterial substances or glucocorticosteroids.
Physiotherapeutic methods
This group includes therapeutic techniques that make ulnar nerve neuropathy go away faster. Physiotherapy relieves swelling, normalizes blood circulation, and helps with pain. Some methods help get rid of destructive and atrophic processes. Physiotherapy affects metabolism and increases the benefits of medications.
Important! Physiotherapeutic treatment can only be performed during the period of rehabilitation or remission; it is prohibited during the acute phases of the disease.
Acupuncture - acupressure - massage gives good results in restoring the pinched ulnar nerve. Additionally, doctors recommend taking courses of therapeutic exercises.
Acupuncture is also an acupuncture technique and is highly effective. Electrical discharges stimulate the nerve well and relieve spasms, so ulnar nerve neuropathy can be treated using electrophoresis and other methods using current.
Home treatment with traditional recipes
Any natural recipes can be taken only after consultation with the doctor. There are many effective folk remedies that have been used for many years for neuropathy:
- Orange peels . Decoction of 1 tsp. dried orange peels and 1 tsp. dry lemon balm perfectly relieves inflammation. Pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and leave for 10 minutes. Then it is filtered, mixed with valerian tincture and taken a glass a day for a month, dividing the portion into 3-4 doses.
- Alcohol tinctures. They help relieve pain and are especially effective if ulnar nerve neuropathy is caused by compression. For tinctures you can use celandine, lilac and other medicinal herbs.
- Heat compresses. Heat can be used for treatment only if the neuropathy is not caused by an inflammatory process. Compresses are made from warm sand or cereal. You can use a heating pad filled with boiling water.
- White clay. Compresses of white clay mixed with water stimulate relaxation of the nerve and restore it.
You can do massage at home using unrefined natural oils: camphor, olive, turpentine.
In case of intense pain, doctors recommend immediately contacting a doctor rather than using traditional medicine. Often, when the pain is unbearable and other methods do not work, surgery is prescribed.
Surgery for neuropathy
Surgical intervention is required for advanced forms of the disease. To do this, they use the neurolysis method - it helps eliminate pinched nerves. The channel in which the fiber is located is also changed, or a new channel is formed. Additionally, dissection of the palmar ligament is required.
After the procedure, the patient undergoes rehabilitation: exercise therapy, massage and medication. The recovery period can last up to 6 months, since surgery in 90% of cases is prescribed for already neglected areas of the elbow.
Exercise therapy
Ulnar nerve neuropathy will not go away completely unless the patient engages in physical therapy. The complex can include special exercises for the arms and shoulder girdle:
- you need to work out the phalanges of all fingers, doing straightening and pressing exercises;
- you also need to warm up your elbow, making amplitude movements up and down;
- it is necessary to perform movements with the hand to restore all motor capabilities.
The doctor issues a referral to a physiotherapist or exercise therapy trainer, and the specialist selects the optimal set of exercises for the patient.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massage treatments
The doctor should prescribe therapeutic exercises, this will help to quickly cure hand neuritis. It is necessary to bend the limb at the elbow and lean on the table. In this case, you need to lower your thumb and raise your index finger with it. Such exercises must be done about ten times.
The following will need to be done in a filled bath. Apply pressure in the middle of your fingers about fifteen times until they are straight. Next, you will need to release and lift each finger with your healthy limb at least ten times. Therapeutic gymnastics makes it possible to develop hand mobility.
The attending physician must select certain exercises for each patient. There may be physical activity with a tennis ball or other objects. After a person has the opportunity to hold the elements, the exercises are transferred to the wall bars. The patient must come to the exercise therapy room almost every day. Some of the above exercises can be done at home.
Massage procedures can be performed by a specialist and special massagers. During this time, the skin, nerves, and blood vessels are captured, therefore blood flow and metabolism improves. The average massage lasts about fifteen minutes. If no methods help cure radial neuritis, then surgery is prescribed.
Prevention and prognosis
It will take 3 to 6 months to treat neuropathy; if surgery is required, the rehabilitation period will take another 6 months. The patient's condition improves within the first 2-3 days after starting medication.
If the patient comes in when the first symptoms appear, the prognosis is favorable; you can count on the elimination of pain and partial limitation of mobility during the first 2-3 weeks.
If the patient consults a doctor when muscle atrophy has begun, it will be more difficult to restore motor function. Most often, it is in this case that surgical intervention is required.
To prevent relapses, the patient must adhere to the following rules:
- You should not put any weight on the affected limb for 12 months, then only moderate exercise is allowed;
- you should not engage in work that requires monotonous movements of the injured elbow;
- during office work, it is necessary to constantly do gymnastics designed to change the position of the elbow joint;
- you need to take vitamins and strengthen your immune system;
- also, people who already have a history of ulnar nerve neuropathy need to visit a massage therapist at least once a year to complete the course;
- it is necessary to treat infections and prevent sprains, fractures and bruises of the damaged area;
- Once every 6-12 months you need to visit a neurologist to exclude relapse.
Neuropathy of the ulnar, as well as the femoral nerve - compression or traumatic - requires the participation of a doctor in the treatment process. However, in most cases, patients can hope for a positive outcome from therapy. To quickly eliminate the disorder, you need to use all available means, discussing them with your doctor. In the future, care must be taken to prevent relapses.
How to provide first aid?
If there is a suspicion of displacement or subluxation in the elbow area, the following steps must be taken:
- Ensure complete immobility of the joint.
- Apply a cold object to the injured area.
- Take one painkiller tablet.
Immobilization can be performed using a sling bandage
After this, you need to get an appointment with a specialist at the emergency room as quickly as possible. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug tablet can be used as an analgesic. The symptoms of injury will go away completely only after the joint is realigned. Discomfort may persist for several days after the dislocation is repaired.
You should not delay visiting a specialist, even if there are no external signs and mobility in the elbow is preserved. Due to improper actions, the injury can be aggravated (for example, a subluxation can develop into a full-fledged dislocation with rupture of the joint capsule and ligaments).