Meningitis is such a unique disease that its clinical course was noted long before its causes were identified. History has preserved the description of such a disease as meningitis, even in ancient culture.
Of course, the most characteristic was meningococcemia - a variant of meningococcal infection, with the development of high mortality and necrosis of the fingers, ears and nasal turbinates. Against this background, meningitis was a “side symptom.” If isolated serous meningitis occurred, then there was almost no information about such a disease.
And this is understandable: the difference between serous meningitis and purulent meningitis is pathomorphological, that is, it was necessary to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid or perform an autopsy. But, as we know from history, autopsies were prohibited in ancient times and the Middle Ages. Therefore, an infection such as serous meningitis remained a “dark horse” for a long time, and the diagnosis of this group of diseases began to be carried out only with the possibility of the development of such techniques as lumbar puncture, as well as in connection with the general development of microbiology and virology.
A real breakthrough in the field of research on serous meningitis was made after the accumulation of a solid base of scientific facts . First of all, about diseases such as purulent meningitis, encephalitis and other diseases of the central nervous system. The discovery by D.I. Ivanovsky of such non-cellular life forms as viruses (using the example of the tobacco mosaic virus) at the end of the 19th century allowed us to assume the viral nature of many forms of serous meningitis. Rapid advances in neurology and physiology have made it possible to accurately determine the main syndromes, understand what is characteristic of serous meningitis, and form a complete opinion about how this infection manifests itself.
Short description
Damage to the membranes of the spinal cord and brain, provoked by bacteria, viruses, fungi, is defined by official medicine as serous meningitis. Children of preschool age are mainly at risk. This is exactly the period when the baby begins to attend kindergarten, where there may be potential carriers of the virus. In schoolchildren and adults, this pathology is detected quite rarely.
The disease is characterized by symptoms that accompany meningitis of other etiologies. These are high (above 38) temperature, headache, nausea and vomiting. Such symptoms make timely diagnosis difficult, since parents often confuse the condition with colds. But the consequences are unfavorable, so the manifestation of any signs should force you to seek medical help.
Possible consequences and complications
With meningitis, the meninges are hyperemic, and the blood-brain barrier is destroyed, which causes cerebral edema.- Due to the entry of pus into the vessels of the brain, inflammation and ischemia of the brain tissue may develop.
- In case of brain damage, various types of paralysis may develop, visual impairment and hearing loss, and mental retardation may occur.
- There is a risk of bleeding in the adrenal glands. And the occurrence of sepsis can seriously threaten a person’s health and life.
Causes of the disease
The main pathogens that provoke serous meningitis are bacteria and viruses, and less often fungi. But the main cause is enterovirus. Infection of a healthy person occurs through air, contact or water. Often the disease is diagnosed as a complication after illnesses:
- pneumonia;
- flu;
- measles;
- chickenpox;
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- AIDS.
Infection often occurs from an infected person, even during a conversation with him. The greatest peak occurs in the warm season, since many reservoirs are contaminated with harmful microorganisms.
A healthy immune system allows the body to withstand the onslaught of an invading infection. Weakened immunity, unhealthy diet, and poor lifestyle allow the virus to easily penetrate and infect a weakened body. This explains the fact that serous meningitis in adults or children is a consequence of another disease. In a weakened body, the enterovirus quickly reaches the brain through the bloodstream, provoking an initial severe inflammatory process.
Etiology or causes of serous meningitis
The number of infections based on meningeal syndrome, manifested by serous inflammation, is large. Let's look at some of the causes of this disease.
Serous meningitis can be caused by both bacteria and viruses . Let us briefly list the main causes and features of these lesions.
Bacterial causes
- Tuberculosis of the central nervous system. Causes meningitis quite often. It is always secondary in nature, and appears as a complication of the tuberculosis process in the lungs, lymphatic vessels and other organs. It is characterized by a gradual onset and slow progression of symptoms. This process is characterized by a sharp decrease in sugar levels in the cerebrospinal fluid, and the formation of a delicate fibrin film on the surface of the cerebrospinal fluid, from which Mycobacterium tuberculosis is released.
- Syphilis. Likewise, this reason for the development of meningitis is secondary. Symptoms increase slowly, and most often the process occurs in the secondary stage of syphilis, against the background of a fresh rash. The tertiary stage, with gummous lesions, is characterized by involvement of the oculomotor nerves and severe headaches at night. Syphilitic lesions are characterized by the appearance of epileptic seizures.
- Brucellosis. It is a zoonotic disease and is sourced from sick animals and milk. Meningitis occurs for a secondary reason, due to the generalization of the process. Its development is preceded by damage to the joints and connective tissue: bursitis, arthritis, tendovaginitis. The disease often occurs in the form of acute serous meningitis, and even in the form of meningoencephalitis.
- Leptospirosis. In this case, the cause is advanced leptospirosis, with damage to the liver, muscles, and also in the presence of hemorrhagic syndrome. The disease often begins acutely, with stunning chills, and can significantly worsen the course of the underlying disease.
- Listerellosis. An acute process also begins, with severe fever, chills, the appearance of a rash, enlargement of the liver, spleen and lymph nodes. If meningitis is not treated, or treated incorrectly, then from serous it becomes purulent, with high mortality;
- Psittacosis. This meningitis occurs due to ornithosis pneumonia, and then the pathogens disseminate hematogenously into the central nervous system. The course is also acute; the pathogen, as in previous cases, is isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid and when sputum is cultured.
Viral causes
The number of viruses that cause serous meningitis is very large: this is the causative agent of mumps (mumps), these are intestinal viruses (enteroviruses), Coxsackie, ECHO, the causative agent of lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Serous inflammation on the membranes is caused by influenza and parainfluenza viruses, arboviruses and herpes viruses of various types.
In addition, the meningeal form can occur when infected with the tick-borne encephalitis virus. In the case of a presumably viral etiology, certain difficulties arise in diagnosis due to the lack of isolation of the pathogen.
Classification of the disease
Modern medicine identifies several types of serous meningitis. It depends on the type of pathogen or agent of the disease:
- serous meningitis caused by the Coxsackie or Echo virus;
- bacterial, where the agent is bacteria that cause tuberculosis and syphilis;
- fungal, caused by parasites such as Candida, Coccidioides immitis.
Depending on the severity of the disease at the time of its detection, several more types are determined - primary or secondary degree.
Symptoms of the disease
Once the body is infected, the disease may appear within 2-6 days. This is precisely the incubation period for pathology. The treatment is long-term, requiring a hospital stay. Recovery is possible in at least two weeks.
The disease manifests itself with meningeal specific signs:
- high body temperature;
- fever;
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the eyes when looking at bright light;
- pain in the ears even with slight noise;
- lack of appetite;
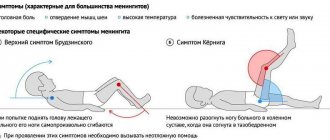
- Brudzinski's or Kernig's sign.
Meningeal signs are the presence of several symptoms at once. When Brudzinski's symptoms are detected, the patient cannot turn his head or bend his neck. When you try to bend one leg, the other bends spontaneously. When determining Kernig's symptom, the patient is asked to raise his leg vertically from a lying position. If he has a disease, he will not be able to do this. The condition is often accompanied by loss of consciousness.
Main symptoms and signs of the disease
Often, the signs of meningitis go unnoticed and then gradually increase over the course of several weeks.
- The development of aseptic meningitis may be preceded by attacks of fever, which can last several days. The disease can manifest itself as headaches and hyperesthesia; in young children, irritability and constant crying appear.
- Nausea and vomiting, convulsions do not occur as often.
- An exanthema may appear, which is present with Coxsackie virus infections and echoviruses.
- Rigidity of the neck and back muscles is also characteristic, but there are no designated neurological disorders of a local nature.
- Fever, sensitivity to bright light, feeling of lethargy, muscle pain, chills, sore throat, abdominal pain, hallucinations, body rash, spinal symptoms, Brudzinski's and Kernig's signs.
In the initial stages of the disease, an abundant presence of granulocytes is often found in the cerebrospinal fluid , especially in the case of an illness caused by the herpes simplex virus. High pleocytosis (1000-3000/3 elements) is characteristic and very often occurs with meningitis, which arose due to complications of mumps and lymphocytic choreomeningitis.
Mild hypoglycorrhachia may occur. This type of meningitis has pronounced similarities and differences with other types of this disease.
Often, it is not so scary and has fewer negative consequences, unlike purulent meningitis of bacterial, fungal or protozoal origin.
Diagnostics
A pathology such as serous meningitis is diagnosed quite simply based on the listed symptoms. But this is only enough for the doctor to draw up an anamnesis. The patient will have to undergo a full laboratory and instrumental examination. Serological diagnosis involves:
- general blood analysis;
- bacteriological analysis;
- spinal tap;
- Ultrasound, MRI of the brain.
Patients often feel significant relief after spinal cord retrieval. This is further evidence that there is serous meningitis in children or adults. The relief is temporary, since after the fluid is taken, the intracranial pressure drops sharply. Treatment is complex and lengthy. This must be done, as the consequences are quite sad.
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease. And since serous meningitis is a viral disease and is transmitted by a simple handshake, disease prevention includes:
- ban on swimming in open waters;
- ban on drinking untreated tap water;
- a ban on eating food without prior heat treatment;
- compliance with all hygiene rules - hand washing should be done after every trip to the toilet and outside, as well as before eating;
- maintaining cleanliness in the room where the child is located - daily wet cleaning, cleaning toys from dirt, etc.;
- avoiding crowded places;
- sport and healthy eating.
The development of serous meningitis can lead to dire consequences. Therefore, it is very important to teach your child a healthy lifestyle and compliance with all the rules of personal hygiene. Only comprehensive preventive measures will help you prevent the development of this disease in your child.
Treatment
The appearance of these symptoms should cause concern, especially for parents. You should not wait for the local pediatrician to arrive. The course of the disease is rapid, so it is better to call an ambulance.
If at a high temperature the patient cannot bend his legs or turn his head, serous meningitis can be suspected. In this situation, emergency hospitalization is required.
It is not advisable to lower the temperature or give antibiotics on your own. This will give a temporary effect and complicate the diagnosis. Treatment of serous meningitis does not involve the use of antibacterial drugs at all. After a diagnostic examination, the doctor usually prescribes:
- antiviral drugs, often interferon;
- immunoglobulin is prescribed to strengthen the immune system;
- to reduce intracranial pressure - diuretics (Furosemide, Lasix);
- antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine);
- droppers with prednisolone and ascorbic acid;
- colloidal preparations are prescribed in the absence of cardiac pathologies;
- antipyretics only when the temperature is above 38 ° C;
- Seduxen, Domosezan to prevent seizures;
- vitamin therapy.
The patient was placed on bed rest for several days. It is advisable to eliminate unnecessary movements. The etiology of the disease is not fully understood. Therefore, it is better to strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions and recommendations. This is the only way to quickly achieve complete recovery without sad consequences.
Symptoms
The main sign of serous meningitis is the child’s behavior. Doctors pay attention to the stiffness of the neck muscles. If you ask your baby to pull his chin to his chest, he will not be able to do this.
Doctors carry out a number of specific actions that help them identify the problem and make an accurate diagnosis:
- The child's leg is bent at a right angle. If this manipulation fails, then the diagnosis is serous meningitis.
- When bending one leg, the other follows. Reflex flexion is a sure sign of the disease. Also, when you bend your head, your legs also reflexively bend.
All symptoms in a particular child appear to a greater or lesser extent. Some are obvious, some are subtle. To speak with confidence about the disease, you need to be examined by a doctor. Only after passing certain tests and a specialized examination can we talk about the reasons that led to the deterioration of the baby’s health.
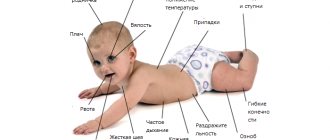
Obvious signs that a child is sick are the following:
- increase in body temperature up to 39 degrees;
- aching pain in the forehead, closer to the temples;
- when the eyes suddenly move from one object to another, pain appears;
- gagging mixed with painful nausea;
- fear of bright and even weak light;
- headaches and dizziness up to fainting.
Additional symptoms of serous meningitis are hallucinations, obvious auditory delirium, in very infants the fontanel on the head swells, very often fainting is accompanied by convulsions.
Consequences of serous meningitis
If the patient received timely medical care, the consequences of the disease are favorable. The fever disappears on the 3-4th day, complete recovery is possible in two weeks. If the visit to a medical institution was untimely, treatment was carried out at home using improvised means, then liquor-hypertension syndrome may occur. This is increased intracranial pressure caused by a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain.
The situation is serious, provoking:
- loss of consciousness;
- defective mental and physical development;
- impairment of the organs of hearing and vision, up to complete loss;
- kidney pathologies;
- to whom;
- sudden infant death syndrome or death in adults.
The consequences caused by the tuberculosis pathogen are especially dangerous. This form of the disease requires the use of anti-tuberculosis drugs. If this was not done, then the patient's death may occur on the 22-25th day after the onset of the disease. Incomplete or incomplete treatment provokes relapse.
Disease phases and risk factors
The aseptic form has three phases of its development.
Prodromal phase
The patient begins to feel soreness in the muscle tissue, throat, malaise, and constant fatigue. A rash appears on the body, diarrhea. The phase lasts for a week. At this time, treatment measures must be taken.
The most common misconception about meningitis is that you can get it by walking without a hat in winter.
In fact, you cannot get sick without contact with the pathogen. However, during such contact, the chances of becoming infected increase with weak immunity.
Neurologist, reflexologist, hirudotherapist
Kislitsyna Ekaterina Nikolaevna
10 years of experience
Waiting phase
It occurs without symptoms. Duration ranges from 2 to 5 days.
Neuroinfection
The patient experiences headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, meningeal signs and photophobia. Recovery occurs after fourteen days.
In certain cases, meningitis occurs without obvious symptoms or with only one phase. If you consult a doctor during the first phase of the disease and receive timely treatment, recovery occurs seven days after the start of therapy and strengthening of the immune system.
Factors that significantly increase the risk of developing the disease include:
- Work in medical institutions as a nanny or caregiver.
- Weakened immunity.
- Susceptibility to viruses.
- Taking certain medications.
- Age.
CSF analysis for meningitis
Neurosurgeons, neurologists and infectious disease specialists often have to perform a lombal puncture, which is the collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from a patient.
Adults get meningitis much less frequently than children and adolescents. Weakened immunity is often the root cause of the development of various diseases and the penetration of infections into the body.
Certain groups of medications can provoke the occurrence of aseptic meningitis if they are not taken as prescribed by a doctor or in cases of incorrect calculation of the daily dose.
Preventive actions
Treatment of any form of meningitis does not begin at the time of discharge from the hospital. A whole range of preventive measures will be recommended, some of which will have to be observed and carried out for 4 years. Prevention will not hurt those who have been in contact with the patient.
The best prevention is considered to be a strong immune system, which can be easily maintained with a healthy diet and vitamin supplements. Adults need to give up alcohol and smoking, children and their parents need to ensure a healthy lifestyle. Vaccination against tuberculosis may be recommended. This procedure should not be ignored. This guarantees no relapse.
In addition, it is recommended:
- do not visit polluted water bodies;
- regularly do wet cleaning and ventilate the room;
- wash your hands after going outside and before eating;
- wash fruits and vegetables before eating;
- do not drink tap water;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Principles of nutrition
Not only ready-made vitamin complexes, but also recommendations from alternative medicine will help strengthen the immune system. Children need to be taught from early childhood the dangers of eating unhealthy foods. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude carbonated sweet drinks, spicy, fried, fatty foods, reduce salt and sugar to a minimum, and avoid visiting fast foods. The menu of a person who has had meningitis should include:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- dairy products;
- hard cheeses;
- lean meats (boiled, steamed);
- sea fish and seafood;
- nuts;
- buckwheat, cheese;
- dried fruits.