Why is meningitis dangerous?
Meningitis is expressed in the rapid inflammation of the membrane of the brain, under which serous fluid accumulates. If misdiagnosed, untimely access to doctors and improper treatment, the disease can lead to cerebral edema and result in disability or even death.
Unlike purulent meningitis, serous meningitis is not accompanied by massive death of nerve cells. Therefore, the chances of recovery and a favorable outcome with the serous type of the disease are higher.
Serous and purulent types of meningitis at the cellular level are diseases of opposite nature. It is very difficult to distinguish them externally. In fact, there is only one reliable diagnostic method - lumbar puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid and its subsequent analysis.
Epidemic outbreaks and quarantine for serous meningitis
According to epidemiologists, outbreaks of this disease occur approximately once every five years.
After all, meningitis is considered an uncontrollable disease, since there is no vaccine against it yet.
Although it can be cured, complications are still possible. How many days does quarantine last?
Those preschool and educational institutions where patients with meningitis are found are closed for a two-week quarantine and work is carried out to disinfect the premises. All children in contact with sick children are given preventive measures. How dangerous is serous viral meningitis?
Where does the disease come from?
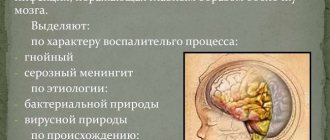
By its origin, serous meningitis can be:
- Primary – brain damage directly from a viral or bacterial attack.
- Secondary - develops against the background of another disease that causes a weakened immune system.
The causative agents of the disease can be:
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- fungi.
According to medical statistics, among childhood morbidity, viral pathogens account for 80% of cases of serous meningitis. Children of preschool age - from three to six years old - are susceptible to inflammation of the meninges. Schoolchildren and adults to a lesser extent.
Acute serous meningitis is most often caused by enteroviruses. Among them, there are two main ones: the ECHO virus and the Coxsackie virus.
In more rare cases, the reasons are:
- Epstein-Bar virus (is the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis);
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes;
- measles;
- influenza viruses (especially highly mutagenic ones).
In medicine, there are three ways of transmitting the disease:
- Contact – with a handshake and other touches by the wearer. In the latter, the virus is most often localized on the hands, skin lesions, mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes.
- Airborne - concentration of the virus in the respiratory tract. It is transmitted by inhaling air that contains saliva particles containing the pathogen in the form of an aerosol.
- Alimentary (fecal-oral) method - a susceptible organism ingests water contaminated with enteroviruses. In recent years, outbreaks of meningitis have become common in the summer, when the swimming season is in full swing. The infection, entering the child’s mouth with water, accumulates in the intestines. Later it is excreted in feces and again ends up in the water.
Enteroviruses retain their vital functions on food products for a long time. Personal hygiene, thorough washing of vegetables and fruits reduce the risk factor.
The incubation period of the disease varies from several hours (acute form) to several days. In this case, the first symptoms of serous meningitis in children may appear only a week after the direct infection.
Consequences
Despite the severe acute period of the disease, which can last up to two weeks, serous meningitis with timely treatment does not pose a serious threat to the child’s health and goes away without a trace. In this regard, the serous type is much more gentle than the purulent type.
Rarely, a consequence of serous meningitis is liquor-hypertension syndrome. frequent headaches, asthenia, emotional problems (frequent mood swings, tearfulness, moodiness), memory deterioration, and difficulty concentrating may persist As a rule, these effects finally disappear after a few weeks or months.
Tuberculous meningitis is known to have the most terrible consequences. If the diagnosis was not made on time and anti-tuberculosis drugs were not prescribed, death may occur within 3-4 weeks. If treatment was started late, relapses and complications may occur.
We invite you to watch a useful video on the topic:
Symptoms
When the incubation period ends, serous meningitis manifests itself with sharp and obvious signs, which are collectively called meningeal syndrome.
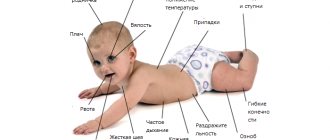
A sick child exhibits several symptoms from this list:
- Fever. An indispensable symptom of serous meningitis, occurring in two waves. First, the temperature rises to 39.5-40 degrees and usually lasts for about three days. Then it subsides and returns again in a day or two. In mild cases, the temperature may return in a “truncated” version – 37-38 degrees.
- Severe headache. It starts from the temples and smoothly moves to the back of the head. Bright light and noise increase pain.
- A characteristic symptom of childhood serous meningitis is limb cramps.
- Lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting (without relief), diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Intoxication, which entails joint pain, general weakness, moodiness and irritability of the child.
- In children, meningitis is often accompanied by standard symptoms of respiratory diseases - runny nose and sore throat. Therefore, parents sometimes mistake it for acute respiratory infections and do not sound the alarm.
- Sick children from three years of age try to take a characteristic position: lying on their side, pressing their hands to their chest and knees to their stomach. The head is thrown back towards the back.
- The acute form of meningitis may be accompanied by impaired motor functions (partial paralysis and paresis).
- Double vision and strabismus are another symptom of the so-called reactive meningitis, which develops over a few hours.
- An attentive parent may notice increased tension in the neck muscles.
- Disorders of consciousness: from stupor and absent-mindedness to coma (in advanced acute form).
These signs can manifest themselves to a greater or lesser extent, singly, in groups or complexly.
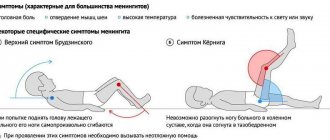
For an accurate diagnosis, we check for the presence of certain types of meningeal syndromes:
- Kernig syndrome, when a child cannot straighten a leg bent at an angle of 90 degrees.
- Brudzinski syndrome is a reflex flexion of one leg while bending the other (or flexion of the legs simultaneously with flexion of the head).
- Lesage syndrome (for infants): when you hold a baby by the armpits, he bends his legs and pulls them towards his stomach. Swelling of the fontanelle is also observed.
- Mondonesi syndrome is a severe headache with light pressure on the eyeballs covered by the eyelids.
Some of the symptoms of serous meningitis are similar to those of the meningeal form of tick-borne encephalitis. Because this parasite is active during the summer (as are meningitis outbreaks), the diseases can be confused.
Prevention
Following preventive measures reduces the chances of developing meningitis. As is known, the virus is transmitted by airborne droplets and through contact with personal objects of the virus carrier. The following rules will help prevent the development of the disease:
- You should always wash your hands with soap before eating;
- no need to use other people’s personal hygiene items and cutlery;
- If a disease outbreak has been declared in a city, public places should be avoided (especially, avoid swimming in local rivers and lakes).
There is also a vaccine that can protect against the infection that causes meningitis. Vaccinations are recommended for young children and freshmen who want to live in a dormitory.
Enteroviral meningitis can lead to serious complications, so self-medication is dangerous to health and life. Symptoms can develop quickly, but in some situations they are mild and vague, which can lead to a delay in determining the diagnosis. The sooner you see a doctor, the higher the chances of effective treatment.
How to fight the disease
Parents who suspect that their child has inflammation should first call an ambulance. Diagnosis and treatment of serous meningitis in children should be carried out by specialists.
For mild meningitis, doctors usually limit themselves to a blood test and scraping of mucus from the nasopharynx. Acute and reactive forms are accompanied by lumbar puncture - examination of the cerebrospinal fluid. The method allows you to differentiate the serous or purulent type of meningitis.
Doctor's advice
To relieve pain, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, and Ketoprofen are used. As an antipyretic therapy, preference should be given to Paracetamol as the drug of choice in children.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
If you suspect meningitis, you should not get carried away with antibiotics - they are ineffective, since the disease is viral in nature. But antiviral drugs, on the contrary, will slow down the development of inflammation of the lining of the brain. Immunostimulating therapy is also used in combination.
The doctor's prescription will depend on the type of infection that caused the disease, as well as on the symptoms manifested:
- If the causative agent is an esterovirus, Internoferon is often prescribed. In case of herpes infection or the presence of the Epstein-Bar virus - Acyclovir.
- To relieve intracranial pressure and migraines, a course of dehydration is carried out. The child should be given diuretics (Furosemide, Lasix, Diacarb).
- Children with weakened immune systems are prescribed intravenous immunoglobulin.
- To relieve intoxication, a saline solution with ascorbic acid is administered intravenously.
- During a fever, the child is given antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen).
- To improve immunity, vitamins C, B2, B6 are prescribed.
- If a child has spasms and convulsions, he is prescribed Seduxen and antispasmodics - “No-shpu” or “Drotaverine” (they contain the same active ingredient, the drugs differ only in cost).
A child with meningitis is advised to rest and go to bed. Parents are advised to consider photophobia and auditory stimuli. Your child will do best in a quiet, darkened room.
How is the treatment carried out?
Enteroviral meningitis is characterized by a sluggish course, but despite this, all patients with suspected such a disease are urgently hospitalized. Treatment depends on the symptoms and underlying cause.
Unfortunately, there are no drugs yet that could destroy enterovirus . Therefore, the patient is prescribed medications to eliminate the symptoms. Such therapy is aimed at reducing inflammation and intracranial pressure.
Treatment involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics – inhibit the processes of inflammation that occur in the soft tissues of the brain;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - relieve inflammation, tone blood vessels and eliminate pain;
- sedatives - prescribed if the patient has poor sleep, increased excitability or convulsive syndromes;
- antiemetics - needed if the patient is bothered by frequent vomiting.
In more complex cases, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticoids. The drugs have a stronger anti-inflammatory effect; they also tone the blood vessels of the brain and reduce their permeability. Thanks to this, there is a decrease in the manifestations of the disease.
You should take this medicine only after the recommendations of your doctor, because it has a large number of contraindications. The dosage and duration of treatment are selected depending on age, weight and severity of symptoms.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, positive results can be seen within 6-8 days. However, the consequences of the illness may linger for several weeks. Most often this is hearing loss, mild headache and decreased vision clarity. The complications are temporary and after a certain period they will disappear on their own.
How to protect yourself from illness
All parents should pay attention to the prevention of serous meningitis in children. In the summer, you should listen to local news - if an outbreak of meningitis follows after visiting open water, you should not allow your child to swim there.
Measures to combat the disease are generally reduced to maintaining hygiene rules:
- Drink boiled or specially purified water. This rule should be taken especially seriously by those who live in low-lying areas where wastewater may enter the water intake.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene - be sure to wash your hands after visiting the toilet and before eating.
- Wash vegetables and fruits before eating (especially in the summer). Products can additionally be doused with boiling water - enteroviruses are afraid of high temperatures.
- Meningitis can develop against the background of other viral diseases - measles, mumps, influenza and even common ARVI. Therefore, be attentive to the follow-up treatment and recovery of your child after any such illness.
- If a baby has a weak immune system, he should not come into contact with rodents (even domestic ones), as they are considered carriers of serous meningitis pathogens.
Meningitis is a complex disease. Due to the carelessness of parents, the disease often has the most disastrous consequences. But if you raise the alarm in time and go to a medical facility, serous meningitis will go away quite quickly - in 10-12 days. And don’t forget about prevention – it’s better not to get sick at all.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, contact an infectious disease specialist online or at a good infectious diseases hospital.
For more information about meningitis in children, watch the video:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://niidi.ru/dotAsset/e3e1899f-a522-4aa4-acd2-f28dedca3bc0.pdf
Rate how useful this article was
5 Voted by 1 person, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Consequences of serous meningitis in children
As a rule, this disease can be successfully dealt with.
But some children experience headaches and asthenic phenomena upon completion of treatment. In this case, you cannot do without consulting a neurologist.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the consequences are much worse:
- Complete or partial hearing loss.
- Problems with the functions of the speech apparatus.
- Partial or complete loss of visual acuity.
- Malfunction of the brain.
- Delay in psychomotor development.
- Rarely - comatose state up to death.
- Children should not swim in open water.
- Eat only thoroughly washed vegetables and fruits.
- Eat with clean hands.
- Use only high-quality water for drinking.
Memo to parents
- Routes of transmission and infection of serous meningitis: contact, airborne, waterborne.
- If you have high body temperature, convulsions, vomiting, or diarrhea, call a doctor immediately.
- Do not try to treat enteroviral serous meningitis in your child on your own.
- Strictly follow all doctor's instructions to avoid any complications.
- Quarantine for serous meningitis lasts two weeks
- Monitor your child’s lifestyle: do not allow him to eat unwashed food with dirty hands or swim in the river.
- Carry out hardening procedures to strengthen the immune system.
Video
Elena Malysheva clearly shows and talks about how to protect a child from enteroviral meningitis:
Why does a child hiccup often? To answer this question, you need to understand the nature of hiccups and where they occur. Then it will be possible to find out ways to relieve children from prolonged bouts of hiccups. Get into it and apply it!
And if the baby hiccups in your stomach even before birth, then here we tell you why this happens. The main thing is don't worry!
What do you know about low hemoglobin in children? https://bo-bo-bo.ru/bolezni/krovi/nizkijj-gemoglobin-u-rebenka-prichiny-simptomy.html It definitely needs to be raised!
Did you like this article?
Tell your friends! Like us using the floating button bar on the left. You will support our work and tell your friends on your favorite social network about this useful article.
We have new materials coming out almost every day! To keep abreast of updates, subscribe to our RSS channel or follow updates on social networks: VKontakte, Facebook, Odnoklassniki, Google Plus or Twitter.
We can even send all updates straight to your inbox:
The entry was published on December 16, 2013 by admin in the Infectious category.
Incubation period and modes of transmission of serous meningitis in children: 4 comments
- Anton
July 1, 2021 at 11:57 amPlease call me back at Anton's number.
Reply ↓
- Jeremymal
March 11, 2021 at 5:18 amhttps://clck.ru/F7nBP — Smartphone holder with wireless charging function A unique car holder for a smartphone with wireless charging. The device is securely mounted in the car thanks to double fixation. Automatically charges your smartphone when you're on the go.
Reply ↓
- Vika
January 6, 2014 at 11:07 pmI recently decided to vaccinate my child against infectious meningitis. I think I did the right thing. There have been too many cases of infection in children, especially of school age. Although I didn’t make the decision right away - I was afraid of complications. Fortunately, everything was fine. As I was warned, the injection site in my shoulder was noticeably sore for one day, but then everything returned to normal. I hope the vaccination will help the child not get sick.
Reply ↓
- nata
January 4, 2014 at 2:20 pmI heard that in the last stage of this disease, red spots appear all over the body. Is it so? And how long does it usually take from a sharp increase in temperature to the appearance of these spots? Yes...and is it possible to save a person if at this stage he is taken to the hospital? There was such a case in our city. The girl was not saved. She was 17 years old.
Reply ↓
Diagnostics
It is possible to assume that a patient has serous meningitis based on the characteristic clinical picture, especially the following signs:
- “cooper dog pose”;
- positive symptoms of Brudzinsky, Kerneg;
- muscle stiffness in the back of the neck;
- positive Lesage sign (in children of the first years of life).
To establish the cause that caused the development of the inflammatory process in the meninges, it is necessary to collect an anamnesis, paying attention to the characteristics of the onset of the disease and the presence of contact with sick individuals.
In a general blood test for serous meningitis, signs of an inflammatory process are revealed, namely leukocytosis, a shift in the leukocyte count to the left and an increase in ESR.
To identify the pathogen, virological studies are carried out using ELISA, RIF, PCR methods, and bacterial culture of discharge from the nose and throat is also performed.
Confirmation of the diagnosis of serous meningitis is possible based on the results of laboratory testing of cerebrospinal fluid. A sign of serous inflammation is an increased content of protein in the cerebrospinal fluid. With tuberculous and fungal meningitis, a decrease in glucose concentration is observed in the cerebrospinal fluid. The predominance of neutrophils in the cerebrospinal fluid is characteristic of bacterial serous meningitis, but if the disease has a viral etiology, then lymphocytes predominate.
Confirmation of the diagnosis of “serous meningitis” is based on the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid
In syphilitic and tuberculous serous meningitis, pathogens are identified by microscopy of cerebrospinal fluid smears stained in a special way.
Additional diagnostic methods include ophthalmoscopy, RPR test (diagnosis of syphilis), tuberculin tests, ECHO-EG, MRI of the brain, and electroencephalography.
Serous meningitis must be differentiated from subarachnoid hemorrhage, arachnoiditis, tick-borne encephalitis, purulent meningitis of meningococcal, pneumococcal or any other etiology.
Symptoms
| Occurrence (how often a symptom occurs in a given disease) | |
| Intolerance to bright light (photophobia, light sensitivity) | 90% |
| General weakness (fatigue, tiredness, weakness of the body) | 90% |
| Vomiting of various types, including indomitable | 90% |
| Severe headache spreading over the entire head | 80% |
| General increase in body temperature (fever, fever) | 70% |
| Increased skin sensitivity to pain | 70% |
| Spasms in the leg muscles | 40% |
| Pain in the muscles of the extremities (pain in the legs, pain in the arms, pain in the muscles) | 30% |