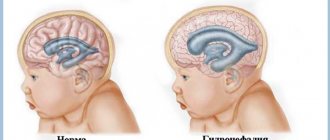
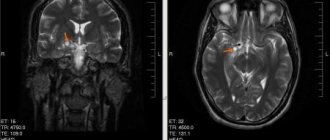
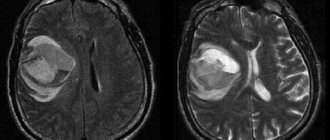
Often, even in the maternity hospital, doctors discover that the lateral ventricles of the baby’s brain are enlarged. However, this does not mean that the baby urgently needs serious treatment. What does this mean, what does it threaten and, most importantly, what to do? The consequences of enlarged cerebral ventricles in infants can be severe. More on this later.
Structure
The ventricles of a child's brain are interconnected collectors where liquor fluid is formed. Large cavities are combined, and they are located on the sides. The lateral ventricles are connected by a special system of small holes. There is also a distal medulla with an enlarged fourth ventricle.
While ensuring the functioning of the ventricles, the liquor fluid can freely penetrate into the middle of the subarachnoid space. This zone is located on the borders of the arachnoid and dura mater of the brain, maintaining an optimal volume of fluid, even in a possible pathological condition.
Usually in newborns it is determined that the lateral ventricles of the brain are enlarged. In this case, the dorsal horns of the ventricles enlarge, fluid accumulation may occur, and the cerebral ventricles also enlarge. High-quality diagnostics helps to exclude an asymmetric arrangement of brain collectors.
What are the ventricles of the brain, their role
The ventricles of the brain are strips of tissue necessary for the deposition of cerebrospinal fluid. External and internal factors can lead to their increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest. These formations are involved in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Asymmetry is a condition in which one or both cavities are enlarged to varying degrees.
- Lateral . The ventricles are the most voluminous, and they contain cerebrospinal fluid. They connect to the third ventricle via the interventricular foramina.
- Third . Located between the visual tuberosities. Its walls are filled with gray matter.
- Fourth . Located between the cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Etiology and pathogenesis
In medicine, doctors call an increase in these parts of the brain ventriculomegaly. It doesn’t matter what led to this phenomenon, what will cause the most concern is the obvious asymmetry. With symmetrical enlargement, the expansion can be considered completely normal or it can be a sign of hydrocephalus, which appeared for certain reasons.
But with asymmetric or disproportionate sizes of the ventricles, we can talk about a formation that is quite voluminous in size, as well as the results of a possible injury. Parents in such a situation need to immediately go with their baby to an urgent appointment with a neurosurgeon, since without proper treatment the consequences will be quite unpredictable. But sometimes a mild degree of asymmetry of the children's ventricles of the brain is considered quite normal. If the size of the ventricles near the foramen of Monroe differs by no more than 2 mm, there is no talk of a pathological condition. The main thing is to promptly and very carefully monitor the child’s condition.
Causes
Immediately after birth, dilated symmetrical ventricles are found in prematurely born babies. It is noteworthy that symptoms of intracranial ventricular enlargement are usually not observed. But if an increase in horns is detected, we can talk about a certain pathology.
The ventricles of the brain may enlarge in infants for the following reasons:
- A fall or head injury, which contributes to impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which begins to stagnate in the stomachs, as a result of which the child begins to show symptoms of excessive intracranial pressure.
- Fetal hypoxia, placental insufficiency and defective structure of the placenta. As a result of such conditions, the blood supply to the fetal brain is disrupted, which contributes to the expansion of the collectors inside the skull.
- Bacterial infection of a pregnant woman, since microorganisms easily reach the fetus through the placenta, causing various complications.
- Pathological birth. Damage and trauma during childbirth can cause impaired blood supply to the baby's brain and lead to increased expansion of the ventricles.
- Oncological formations in the brain. Excessive tumor growth causes increased pressure on the internal structures of the child’s brain, which causes pathological enlargement.
- Prolonged labor. If a lot of time passes between the moment of water breaking and childbirth, intrapartum hypoxia and disruption of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles may develop.
- Infectious diseases that penetrate the blood-brain barrier can form brain pathological formations.
Other reasons
Dilatation in newborn ventricles is indicated when, according to the results of neurosonography, the anterior horns in diametrical size near the foramen of Monro become more than 5 mm. The causes of this condition may be acquired or congenital. The last category includes:
- acute fetal hypoxia in the womb;
- difficult pregnancy and difficult, premature birth;
- septic complications in a child;
- birth injury;
- subarachnoid and subdural bleeding occupy a special place;
- excessive asymmetry occurs due to increased blood volume causing compression of a particular ventricle of the brain;
- developmental defects;
- intrauterine infections;
- extragenital pathology of a pregnant woman.
There are also acquired reasons:
- hydrocephalus;
- hemangiomas, cysts and brain tumors.
Neurosurgeons pay special attention to hydrocephalus of newborns. In the structure of the brain with such a disease, a lot of cerebrospinal fluid accumulates, which provokes the appearance of general cerebral symptoms and can cause quite complex conditions.
Hydrocephalus enlarges the cerebrospinal fluid cavities, remaining unchanged in size for a long time. But after a period of decompensation due to a sudden jump in intracranial pressure, the specialist begins to notice an expansion of the ventricles of the brain in the baby.
the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles are enlarged
Moms, who has encountered this? What awaits us? I read the Internet, forums, it’s scary.. It’s clear that there is rehabilitation, massages, medications ahead.. Share the good outcomes, otherwise I’ve read about the outcomes in the form of cerebral palsy, epilepsy, mental retardation and I’m ready to sit down and cry... These diagnoses are the fear of my life .. In two weeks we are going to the region to see a neurologist, I got a referral. We are 4 months and 10 days old. Pregnancy is healthy. Childbirth at exactly 37, lasted 28 hours, weak labor, weak pushing period, gave birth on an IV. The child was squeezed out. They cut the umbilical cord right away; they didn’t wait for it to pulsate. Tight entanglement, I couldn’t breathe myself. I lay under the hood for several hours. 4/7 Apgar. NSG at 1 month is good. Development according to age, with a slight delay. Since birth, he has been spitting up frequently and a lot (totally). He holds his head for a long time and confidently. I found my left hand at 3 months, my right hand at almost 4 months. I rolled over on my stomach twice, at 4 months, but it doesn’t happen again. He also knows how to roll back, but is lazy. Smiles, gurgles, and is active when he sees an adult. Repeats sounds after adults, tries to copy facial expressions. Loves communication, looking at bright pictures, smiles at everyone, even the reflection in the mirror and the animals in the pictures. Laughs when we play horned goat, when we tickle, and when dad teases. He began to reach for toys at 3.5 months. He grabs freely with his left hand, tries with his right, but so far it doesn’t work. I'm helping. Sometimes he simply grabs a suspended toy with two fists. Everything goes into the mouth. In general, the right hand is weaker. Often the son holds it tightly clenched into a fist and presses it to his chest. He may cling to his clothes and even pinch himself while doing so. There is a deep fold between the shoulder and elbow folds. There is no such thing on the left hand. When I give him my fingers and pull him up, sometimes he presses his head to his chest, and sometimes he throws it back. Sometimes it clings tightly with your fingers, and sometimes your fingers feel like rubber. Sometimes it groups and pulls itself up, and sometimes it hangs like a sausage. He doesn’t do the wheelbarrow, no matter how hard I try, he sticks his face into the table and his arms in different directions. In a position on his stomach, he sometimes falls to the right, while the right hand is at fault, it seems to be in good shape and he tries to press it to his side. In general, he has been standing on his elbows for a long time, sometimes he began to do an airplane, sometimes he throws his right hand forward (and grabs a toy), and lifts his left leg up. On the left foot, the toes began to be constantly curled, everything was fine before. When leaning on the table, he rests on his legs, sometimes stands on his tiptoes. Despite this, our neurologist and orthopedist had no complaints about the child. They began to be examined about the unexpectedly blue nasolabial triangle and skin around the mouth. Blue wreaths also appeared on the head and eyelids. Recently, while crying, something similar to an attack of affective-respiratory syndrome happened. On NSG at 4 months, the interhemispheric fissure and the left ventricle are slightly widened, and the anterior horns of the lateral ventricles are slightly enlarged. They prescribed Diacarb, Asparkam, Kudesan. Blood was retested, hemoglobin 127. Head and chest at 3 months 40 and 40, not measured at 4 months yet. Up to 4 months I gained a lot, but in the last month very little.
Sorry it's so long and confusing. I wanted to briefly describe everything.
Symptoms of manifestation
Not in every situation, expansion of the ventricles of the brain causes the development of unfavorable symptoms. Usually the child does not feel much discomfort, which clearly indicates the development of a rather complex pathology. But with more severe disorders, the baby may experience the following adverse effects:
- Visual disturbances manifested in the form of poor focusing or strabismus. Sometimes a child may experience double vision, and this condition intensifies when looking at small objects.
- Disturbed gait: the child stands on his heels or walks on his toes.
- Disproportional head.
- Behavioral disorders: the little patient becomes drowsy and lethargic, even somewhat apathetic, and finds it difficult to get involved in recreational activities.
- Changes in muscle tone, revitalization of tendon reflexes.
- Dizziness and pain in the head area.
- Vomiting may develop.
- Bulging, tension and enlargement of the fontanelles in linear dimensions.
- Optic disc congestion.
- Decreased appetite: The newborn usually does not eat well and has increased regurgitation. High cerebrospinal fluid pressure can affect the vomiting center, which is located at the bottom of the rhomboid fossa.
- Decreased sucking and swallowing reflexes.
- Disturbed sleep: the child has difficulty falling asleep and may walk in his sleep.
- Pronounced veins in the forehead, which causes obstructed blood flow from the head.
Are the ventricles of the brain enlarged in an infant? This pathology has varying degrees of severity during its course. When initial symptoms are detected, a mild course of the disease is noted. If a baby develops the above symptoms, which indicate high pressure inside the head, the illness may become more severe. If the baby’s condition generally deteriorates, it is recommended to carry out rather severe treatment, always in a hospital.
It is important to understand that all of the above symptoms do not necessarily indicate the development of brain enlargement. A slight increase in these structures and their slight asymmetry, changes in the fundus, and the presence of reflexes may not bother parents in any way. The main thing is to constantly monitor the baby’s condition and regularly perform neurosonography.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disorder
In adults, ventricular asymmetry rarely causes symptoms. However, in some cases, this anomaly can cause the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting; dizziness; headache; feeling of heaviness and fullness of the head; apathy; feeling of anxiety.
In addition to these symptoms, the picture of the disease can be supplemented by symptoms of diseases that caused ventricular asymmetry.
Such symptoms include cerebellar disorders, paresis, cognitive impairment or sensory disorders.
In infants, symptoms depend on the severity of the pathology. In addition to general discomfort, symptoms such as throwing back the head, regurgitation, increased head size and others may occur.
Symptoms of the pathology also include strabismus, refusal to breastfeed, frequent crying, anxiety, tremors, and decreased muscle tone.
However, quite often the pathology does not cause characteristic symptoms and can only be detected after an ultrasound scan.
Diagnosis of this condition
To determine the exact dimensions of the ventricles, doctors prescribe the following informative methods:
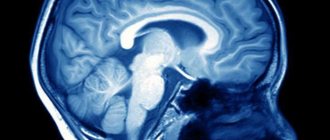
- Computed tomography makes it possible to identify the size of the ventricles, as well as their structure. This procedure does not cause any particular inconvenience to the newborn and does not harm him.
- Ultrasound examination describes the size and quantitative indicators of the ventricles of the brain, and also calculates their index. This method helps to estimate the available volume of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain collectors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is used if the diagnosis is quite difficult to establish. This procedure is performed for older children. But even for small children, MRI, if the ventricles of the brain are enlarged in an infant, is carried out after putting them into anesthesia.
- Neurosonography.
- Examination of the fundus of the eyes.
After complete closure and narrowing of the fontanelles, the doctor begins to monitor changes in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, performing MRI and X-ray CT. Magnetic resonance imaging describes the soft tissue structures of the brain as completely as possible, but, as noted above, you need to lie in the ring of the device for quite a long time, and this will be very difficult for a small child. It is also worth remembering that there are some contraindications for this procedure.
In such a situation, computed tomography, which quickly determines the size of the ventricles, will be very effective. But it is worth understanding that tomography has a small radiation dose on the newborn, and the quality of the information will be less.
Are the ventricles of the brain enlarged in an infant? This could be caused by subarachnoid or subdural hemorrhage. In this case, an MRI will detect excessive blood accumulation. Typically, pathological dilatation of parts of the brain begins with the horns at the back of the head. To examine them, screening methods are used - neurosonography, or ultrasound through the fontanel to identify the size of the ventricles and brain. If the ventricles are not examined well enough, their enlargement can be judged. But to make this diagnosis you need to see them more clearly.
Do I need treatment?
The ventricles of the brain are enlarged in infants. The question of treatment is often of interest to worried parents, since the pathology can be quite dangerous. And yet, if the baby does not have obvious clinical manifestations of the disease, if it develops quite normally, no special therapy is required.
Is the 3rd ventricle of the brain enlarged in an infant? The pathology is treated with a precisely determined excessive increase in fluid pressure. This can be determined indirectly by performing tomography, and direct examination is performed using a last resort - lumbar puncture. Basically, these procedures are carried out when meningitis is detected, which, by the way, usually does not cause an increase in the size of the ventricles of the brain.
Treatment of the disease
A neurologist monitors the treatment process for this pathological condition. If this condition is caused by the consequences of cranial or brain injuries, as well as space-occupying formations, a pediatric neurosurgeon may join the therapy.
To eliminate the fact that the ventricle of the brain is enlarged in a newborn, the following treatment methods are used:
- Nootropic drugs are prescribed to improve brain function and better blood supply to blood vessels.
- Diuretics reduce intracranial pressure, normalize the formation of cerebrospinal fluid, and also improve the child’s overall well-being.
- Sedative medications eliminate increased anxiety in the newborn.
- Multivitamin complexes compensate for all microelements that are involved in quite important processes. Multivitamins strengthen the body and improve the body's resistance to disease.
- Potassium preparations have a positive effect on the process of urine excretion and reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
- Massage reduces muscle tone and relaxes the nervous system. Special gymnastics will normalize the outflow of excess fluid, preventing it from stagnating.
- Antiviral and antibacterial agents are prescribed for certain indications and are used if the disease is caused by bacteria or viruses. They are usually prescribed in courses.
- Surgical treatment is performed for space-occupying formations and to eliminate existing bone fragments after a fracture.
Forecast
Are the ventricles of the child's brain enlarged? If the pathology is treated in time, the disease will have a favorable prognosis. Symptoms of ventriculomegaly quickly pass without disturbing the child in the future. Intracranial pressure normalizes.
Older children tolerate this condition somewhat more difficult. A prolonged course of the disease without effective treatment can lead to the development of hearing and vision impairment. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, persistent disorders are usually detected in the infant, which undoubtedly negatively affect the further development of the child. As you can see, the consequences of enlarged cerebral ventricles in infants are completely different.
Health care
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain itself does not require treatment. It is prescribed only in the presence of symptoms characteristic of the pathology. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the disease that is causing the dilatation.
The following drugs are used to treat ventricular asymmetry:
- diuretics; nootropic substances; anti-inflammatory drugs; vasoactive drugs; neuroprotectors sedatives; if the disease is caused by infections, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
If the pathology is caused by a cyst or tumor, their removal is required. If the patient's condition quickly deteriorates, an operation is performed to form a new connection of the ventricular system, which will bypass the anomaly.
Most often, ventricular dilatation occurs in infants. In the absence of timely and competent therapy, dilatation may persist and even worsen. With mild dilatation and the absence of obvious symptoms, the condition does not require special treatment. All that is needed is constant monitoring of the size of the asymmetry, as well as the general condition of the child.
If the disease is caused by injury, intrauterine development disorder, infection or tumor, constant monitoring of the patient, treatment of symptoms, and, if possible, elimination of the causes of the pathology are required.
The child is treated by a neurologist together with a neurosurgeon. To minimize the risk of complications, a child with this diagnosis should be constantly monitored by doctors. Most often, diuretics are prescribed for treatment, which promote the production of cerebrospinal fluid, which puts pressure on the lateral ventricles.
Additionally, it requires taking medications to improve blood supply to the brain, and sedatives are prescribed.
Massage, therapeutic exercises and other methods of physiotherapy are required. Infants with this diagnosis are observed on an outpatient basis. Treatment of the pathology may take several months.
Older children are treated depending on the cause of the pathology. Antimicrobial drugs are prescribed if the cause of the asymmetry is a brain infection. In case of tumors, cysts and other formations, surgery is prescribed.
Mild pathology most often does not cause any symptoms. In rare cases, a slight delay in the motor sphere may occur, but this also goes away completely over time. A severe form of the pathology can lead to cerebral palsy as a result of high intracranial pressure.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain is not the most dangerous, but it requires attention pathology that occurs in people of any age.
If this problem is detected, you should visit an experienced specialist who will prescribe the appropriate tests to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of dilatation, as well as reducing intracranial pressure.
Bottom line
It is important to note that, according to doctors, the left ventricle of the brain in an infant may be enlarged due to heredity. Asymptomatic enlargement that occurs in infants can be passed on from parents, and they may not be aware of such an important feature of their body. In this case, we are talking about balance on the boundaries of the norm.
Parents should be calm: the mere presence of enlarged cerebral ventricles in a fetus or infant does not at all mean the development of a serious illness. The diagnosis should not be considered a signed “sentence”.
The size of the ventricles is normal
In infants, the ventricles are often dilated. This condition does not at all mean that the child is seriously ill. The dimensions of each ventricle have specific values. These indicators are shown in the table.
First and second ventricles (lateral)
To assess normal indicators, the determination of all structural elements of the lateral ventricles is also used. The lateral cisterns should be less than 4 mm deep, the anterior horns between 2 and 4 mm, and the occipital horns between 10 and 15 mm.