Amnesia (memory loss) can be complete or partial, have different types of manifestations and vary in severity. Complete amnesia is characterized by the loss of absolutely all memories over a certain period of time. Partial memory loss allows you to save some images (vaguely) and fragments of memories, while a violation of spatio-temporal characteristics is observed.
Amnesia, depending on the duration of the lost period of active memory, can be of the following types:
- retrograde – loss of memories of circumstances immediately preceding the onset of the disease;
- antegrade – occurs after emerging from unconsciousness or coma;
- anterograde – combines retrograde and antegrade amnesia;
- retarded - loss of memories manifests itself some time after loss of consciousness.
Depending on the development and course of the disease, there are several types of memory loss:
- progressive amnesia – characterized by slow erasing of memory, the ability to remember recent events is impaired, their emotional assessment is reduced, memories are vague and confused;
- regressive amnesia - temporary memory loss with the probable subsequent restoration of lost memories;
- stationary amnesia – characterized by persistent and unchanging loss of memory for specific life events.
Reasons for failure
- Injuries
A common cause of memory loss is brain injury, ranging from a mild concussion to a severe open head injury.
Even an accidental blow to the head with a “bump” can cause a short-term loss of memory due to the displacement of brain matter, followed by local swelling and an increase in intracranial pressure. Our expert in this field:
Vasinkina Inna Yurievna
Neurologist
Call the doctor
- Alzheimer's disease
Progressive and irreversible memory loss that begins with fairly harmless forgetfulness is later diagnosed as Alzheimer's disease. In old age, dementia is common - dementia, its spectrum is diverse, and Alzheimer's disease is the most fatal and severe. If you contact a neurologist early, you can notice an incurable disease at an early stage and begin therapy that will slow down the rate of development of the disease. The neurologist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic specializes in a wide range of neurological pathologies and has passed the appropriate certification.
- Brain strokes
Atherosclerotic damage to cerebral vessels, diabetic microangiopathy and increased blood pressure cause forgetfulness, in one case, insufficient blood and oxygen enter the nerve cells - cerebral ischemia, in the second - excess, but all have a common symptom of short-term forgetfulness. The same is observed after a stroke, hemorrhagic or ischemic.
- Other pathological conditions
Depression and decreased thyroid function, menopausal disorders - all conditions are based on an imbalance in hormone production, and the clinical picture also shows a memory impairment.
- Poisoning and intoxication
Taking medications that reduce the symptoms of depression or sleep disorders can lead to forgetfulness; in this case, neurological diseases themselves are accompanied by memory impairment, and the medications aggravate the symptoms. Alcohol, drugs and carbon monoxide act in a similar way.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Cognitive problems
In most cases, patients have truly mild or moderate brain damage. After an accident, cognitive problems such as memory and concentration problems are noted. The effects of these mild forms of brain damage can affect work, family and social life. Over time, problems such as personality changes, increased irritability and decreased social behavior may also appear. “It is not uncommon for patients to show a good recovery at first glance, but over time they develop difficulties at work and in home situations,” explains Van der Naalt. At the same time, the majority of these patients resume their work activities within two months after the injury. Ultimately, 80% of them return to their old working level within six months, the rest have to change their type of activity or reduce the number of working hours. They still have residual symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and problems with memory and concentration. Van der Naalt: “To return to the old level of functioning, they need to put in significantly more effort. Another problem they may face later is the inability to do several things at once. It's stressful."
Symptoms
Memory is very individual, and its disorders are also varied. Infrequent short-term failures can occur as early as 35 years of age, become more frequent after 50 years of age, at 65 years of age it is an almost daily state of “forgetting something,” and after 70 years of age dementia often develops, the obligatory symptom of which is amnesia.
With dementia, a patient may forget everything, including himself, for several hours, but then remember what is important to him, but does not remember the very fact of memory loss: “I didn’t forget anything,” is a common phrase, and for the patient this really was the case.
Memory impairments reflect the body’s dysfunction and indicate a decrease in cognitive and intellectual abilities. Understanding the cause means finding a therapeutic way to eliminate disorders or reduce the rate of increase in signs of the disease, possibly Alzheimer's disease.
Whether forgetfulness is a consequence of fatigue, disruption of hormone production or vascular damage due to chronic diseases - only a specialist can figure this out. Specialists at the Moscow neurology clinic “Medicine 24/7” will diagnose pathology and help solve painful problems that worsen the quality of life.
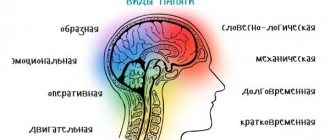
Memory impairment
Memory is a tool of the nervous system that can store, process and reproduce information. Memory deterioration is a separate criterion or symptom of serious illnesses. Both older and younger people suffer from the disorder. Memory impairment is one of the types of disorders that significantly impairs a person’s quality of life.
Types of violations
Our brain works with two types of memory - short-term and long-term. The first stores a small amount of information for a short period of time. Data is not particularly important to a person. Long-term memory is the ability to retain complex information for a long time. These are all things you remember and do reflexively.
Long-term memory is divided, in turn, into two types:
- Implicit (not declarative) - skills and reflexes. You remember how to ride a bike, drive a car, roller skate. If you learn this, you will never forget.
- Explicit (declarative) - memories of studying at school, who is my president, where are my keys, what did I do yesterday. Memories related to our personal experiences.
At a certain point, the brain stops processing information in full. A person develops forgetfulness, which brings a little discomfort to life. If you do not pay attention to this phenomenon, the inability to remember leads to more serious consequences.
There are two types of memory loss:
- Transient (temporary) - characterized by temporary memory loss, which is quickly restored. Violations appear due to severe fatigue, drinking alcohol the day before, and inattention.
- Permanent (constant) - complete absence of memory. A person forgets basic things and cannot remember, even if people around him remind him. Such violations are fraught with consequences.
If your forgetfulness appears more and more often, it’s time to consult a specialist.
Types of diseases characterized by memory loss
Our brain is capable of storing a huge amount of information. At a certain time, a failure occurs, some data is lost partially or completely.
List of diseases caused by memory disorders:
- Hypomnesia is characterized by uneven memory impairment. A person is not able to remember reference data - titles, names, numbers, numbers.
- Hypermnesia is a pathological exacerbation of memory. Increased memorization of small details is often a painful factor. As a rule, it is observed in the initial stages of drug or alcohol intoxication.
- Paramnesia is characterized by false perception and processing of information. Overestimation of the influence of one’s own personality on past events.
- Amnesia is a complete loss of memory. The loss of data and skills can be temporary, and this period of time can be completely different. Recovery, if it comes, does so spontaneously.
Let's look at the main factors influencing memory loss.
Causes and symptoms
Memory loss progresses as a cognitive impairment or disorder associated with other problems:
- stressful situations;
- cerebral circulatory disorders;
- mental illness;
- hormonal disorders;
- nervous system disorders;
- vitamin deficiency;
- brain oncology;
- alcohol and drug addiction.
Symptoms of the disorder:
- chronic fatigue;
- irritation;
- decreased attention;
- headache;
- anxious state.
The ability to remember is affected by somatic diseases caused by damage to the blood vessels of the brain. As a result, circulatory disorders occur - hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis to determine what causes memory impairment.
Which doctor should I contact?
Doctors of the highest category constantly study the cognitive functions of the brain. A neurologist treats memory disorders. Possessing innovative equipment and devices, the specialist will find out the causes of memory deterioration and prescribe therapy and restorative procedures. Based on an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will develop a health restoration program.
Diagnosis and treatment
The examination is based on psychoneurological, laboratory and instrumental methods. When diagnosing memory impairment, pathopsychological tests of certain types of memory are performed to identify the causes that provoke the disorders. A general, biochemical, hormonal blood test is taken.
Among the instrumental techniques used:
- positron emission tomography;
- scanning of brain vessels;
- electroencephalogram;
- angiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment for memory loss is aimed at eliminating the causes of the disorder. If medical factors are not detected, psychocorrection methods are used. Psychological effects are exerted on patients suffering from emotional disorders.
As a supplement, a relaxation method and massage are prescribed. The main task of memory restoration is to relieve the patient of nervous and physical stress. The doctor conducts a conversation with relatives on the issue of resolving family relationships.
Physical therapy is prescribed at the same time. Light training allows you to quickly restore memory.
Expert recommendations
The first thing I recommend is to cure all kinds of diseases that in one way or another affect memory impairment. Next, we begin to train the ability to record information:
- Remember purchases, phone numbers, names. First, let's write down the data on a piece of paper. Then we restore the information without looking at the draft.
- Remember the little things when decluttering your home. Availability of keys, tools, receipts.
- Talk through the actions you intend to do, for example, hanging a raincoat in the hallway.
- Get a good night's sleep. Healthy sleep has an impact on your psycho-emotional state.
- Do breathing exercises. Exercising improves the ability to remember information.
Memory will be restored if it is not associated with severe disorders such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease.
Prevention
Walking in the fresh air, moderate physical activity, and the opportunity to get more rest will help compensate for memory impairment. Try not to burden yourself emotionally, avoid stress, look at life calmer! Schedule a visit to a specialist once every six months. Stay healthy always!
Treatment
Based on ongoing examinations by specialists, we can conclude that a balanced diet can help you get rid of memory problems. To maintain normal brain functioning, you need to include vegetables, fruits, fish, and cereals in your diet. Alcohol and fatty foods aggravate the condition.
To eliminate short-term amnesia, you can perform exercises, take vitamins and medications to stimulate brain activity. In case of memory loss, consultation with a specialist is required to determine the cause of the pathology and the appropriate therapeutic technique.
To prevent amnesia, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are required. You need to understand that if you pay attention to your own health, the higher the chances that memories will be transferred to the area of long-term memory.
When the first signs of memory deterioration appear, you should stop using psychotropic drugs. Record events that occur so you can play them back if necessary. You need to spend at least 8 hours a day sleeping.
Classification of pathological conditions
Amnesia is the inability to remember events and recall necessary information in memory. This condition may appear suddenly or gradually.
Let's list the forms of amnesia:
- Retrograde . Memories that preceded a certain event are erased. Such a period may last a long time or a short time. Memories of what is happening are gradually resumed, starting with the most distant processes. There is likely to be a complete loss of information about what occurred before the injury.
- Anerograde . Difficulties in the processes of memorization and reproduction begin from the period when the pathology begins to develop; events that occur before this are not affected. There is likely to be a complete loss of information about what happened before such a trauma.
- Kogradnaya . When the patient loses consciousness, no information is recorded.
- Completely transient . Expressed in the lack of ability to remember specific events. During such an attack, a person’s behavior may not differ from usual; gradually he is asked questions about what happened a couple of minutes ago. Problems with self-identity often arise.
- Psychogenic . Occurs as a result of alcohol intoxication, violence, schizophrenia, and trauma during a natural disaster. It is difficult for the patient to reproduce data about himself. Often patients at a young age are susceptible to the disease.
- Transient global . Refers to elderly patients; attacks can last up to several hours and occur up to 5 times a year. The reasons have not been fully studied. During the attack, the ability to orientate deteriorates; the same question is asked to the person several times in a row.
- Progressive . Occurs in various types of dementia, Alzheimer's disorder. Memory deteriorates gradually and completely. At the first stages, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness occur, after which the patient forgets what has happened recently, then does not remember processes that took place a long time ago.
- Dissociative is a defensive reaction of the psyche; problems arise with memory from the recent past, caused by a stressful situation. It is difficult to reproduce individual biographical facts.
- Korsakoff's syndrome with characteristic long-term memory loss that develops against the background of alcoholism after regular stress to the vessels of the nervous system.
Treatment of amnestic syndrome in Moscow
The goal of helping a patient with memory loss is to restore it or stabilize the condition and achieve long-term remission. Amnestic syndrome does not have a specific treatment regimen. Each patient receives an individual care plan. It depends on the cause of the development of the disorder and the characteristics of its manifestation. For the organic form, medications or surgery are used primarily, and for the psychogenic form, psychotherapy is used. The most commonly used drugs are:
- vascular agents to reduce blood viscosity and expand the microvasculature and improve cerebral blood flow;
- neuroprotectors, nootropics and antioxidants to improve metabolism in brain cells, reduce their sensitivity to ischemia, and normalize cognitive functions;
- anticholinesterase drugs and ginko biloba preparations for dementia in order to reduce the progression of dementia in the elderly and increase daily activity;
- In Alzheimer's disease, memantines are used to improve mnestic functions.
For patients with mental disorders, antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers, and mood stabilizers are used. They help normalize behavior, restore control over the biological rhythm, improve mood during depression, and eliminate anxiety, phobia, and anxiety.
Dr. Isaev’s clinic uses only proven, certified drugs with minimal side effects. They must be taken strictly according to the course prescribed by the doctor.
If a tumor, hematoma or cyst is detected in the brain, it is surgically removed. Methods of psychotherapy allow, in combination with medication, to accelerate the recovery of the patient’s memory. In the absence of organic disorders, hypnotherapy helps to restore memories. These patients use a cognitive-behavioral technique that allows them to identify negative mental dogmas and replace them with positive ones. With its help, a person relates to his problem more easily and this helps him speed up his recovery.
With the psychogenic form of amnesia, the goal of treatment is not so much to restore memory, but to help the patient accept its loss. The method of psychoanalysis eliminates psychotraumas coming from early childhood, and family therapy improves relationships between loved ones and helps optimize the prognosis for amnestic syndrome. For people with a lack of inclination to demonstrate their feelings and experiences, creative types of treatment in the form of art therapy and fairy tale therapy help. Help for alcoholics with amnesia is provided in the form of the use of vitamins and means for detoxifying the body.
Critical stage dementia
It is the final stage of the disease. During this period, patients completely lose the ability to self-care, are unable to move independently, eat, dress, or even cover themselves with a blanket. Speech becomes fragmentary and difficult to understand. However, patients remain conscious and respond to clear and emotional appeals to them from loved ones.
Expert: Galina Filippova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, General Practitioner Author: Natalya Dolgopolova
The material uses photographs belonging to shutterstock.com
Cognitive amnesic syndrome
The word “amnesia” itself, translated from Greek, means memory loss, which greatly affects a person’s cognitive abilities. Memorizing events and information is the basis of learning and the emotional coloring of what happened. That is why amnestic syndrome is very traumatic; it not only reduces the patient’s quality of life, but also affects his loved ones.
This condition is considered as a complex of symptoms under various diagnoses. But clinical medicine allows it to be indicated as an independent disease if the cause of the disorder cannot be identified. Typically, amnestic syndrome has two characteristic features:
- loss of memory for past events (retrograde amnesia);
- inability to remember current information (anterograde amnesia).
Other functions of cognition in this case are rarely affected, but may be impaired because they depend on the patient’s memory:
- ability to concentrate;
- organization in space;
- abstraction (visual or auditory).
A person ceases to show initiative and independence, and is almost always in a complacent state. Immediate memory with repetition of just spoken phrases or series of numbers is retained. Some patients in the acute phase of the disease develop a tendency to invent answers or events. With dementia, the patient sometimes replaces lost information about himself with information that he once saw or read. At the same time, adventures are presented to them as their own, but this is done unconsciously.
Advanced stage of Alzheimer's disease
- A decrease in motor memory leads to a loss of skill in performing familiar actions: writing, using a spoon and fork, etc. Speech is significantly impaired; a person selects incorrect synonyms for forgotten words.
- Violations of visual memory lead to the fact that the patient ceases to recognize friends and relatives. Sometimes the ability to recognize one's own face in a mirror or in a photograph is lost.
- Disorientation occurs in space and time. A person can easily get lost not only on the street, but also in his own home; he cannot remember when an event happened: yesterday, today, or maybe 10 years ago. The patient becomes vulnerable because he does not remember the last time he ate, slept, saw relatives, or took medications.
- Reproduction of long-term memory episodes is impaired. Together with a violation of time orientation, this leads to the patient being “stuck” in the past. A person, replaying episodes from his youth in his memory, seems to remain in them. He may incorrectly state his age, marital status, place of residence, and so on.
- At this stage, grumpiness, untidiness, and suspicion may appear. People suffering from Alzheimer's disease begin to show unreasonable aggression towards relatives. Visual hallucinations may appear (a friend who is no longer alive came, scenes from past professional activities, etc.).
- Dysfunctions of somatic organs are manifested: urinary and fecal incontinence, dyspepsia, hearing impairment, smell impairment, muscular dystrophy, immobility.
Psychogenic amnesia
Conditions that lead to the loss of memory of a certain part of data about one’s personality are called psychogenic. These types of amnesia include:
- Katathimnaya. The patient forgets only those data that are in some way related to psycho-emotional experiences.
- Hysterical. Often observed in hysterical psychopathic syndrome. In this case, the person cannot remember only the traumatic moment.
- Post-hypnotic. The patient is unable to reproduce what happened to him in a trance state. This is usually part of the suggestion.
- Dissociative. Refers to the body's protective reactions that do not allow the destruction of mental functions. Memory for events that cause severe stress is erased. It differs from other types of psychogenic amnesia in that the loss itself is a treatment and relief from further problems.
- Dissociative fugue. Also refers to defense mechanisms, but at the same time a person escapes from a difficult situation by moving to another city and forgetting about his past life and his personality. At the same time, he retains his basic skills completely. After some time, events are restored, usually this happens suddenly and immediately.
Manifestations of amnestic syndrome
A classic sign of amnesia is the inability of a person to recall a certain period of time in his life. Most often, recent events are forgotten first, and then more distant ones. In a regressing process, recovery is observed in the reverse order. Some types of disorder involve false, fictitious memories, or confabulations. With their help, the body tries to fill the gaps. At the same time, the person sincerely believes in the truth of his “memories.”
Amnestic syndrome after a stroke is characterized by hypo- and paramnesia (general memory loss and confusion of present and past events). At the same time, speech impairment and movement deficits are noted. Memory loss occurs in psychoorganic syndrome, and cognitive dysfunction is also observed. A person loses the ability to assimilate new information, his attention decreases, and his thought processes slow down. With dissociative amnesia, the patient becomes absent-minded, begins to wander, and often experiences affective disorders. Transient global loss of memories is characterized by complete disorientation. With Korsakoff's syndrome, several types of amnesia are often combined.
With a stationary disorder, a person often suffers and worries about his condition, is tormented by a feeling of guilt, and becomes depressed. Progressive amnestic syndrome leads to complete helplessness; a person can leave home and get lost in a familiar area. There is a gradual loss of skills and knowledge. At the end there is complete disorientation and constant care is required.