A person usually speaks to convey his thoughts to others. If he stops doing this, to say that he will get bored is to say nothing.
Therefore, in case of any deviation in speech, you need to seek help from specialists in order not only to correct the situation, but also to avoid serious consequences. If this is not done in time, you may stop making certain sounds or stop speaking altogether, and this is much worse than when someone simply does not pronounce the sound “r”.
Dysarthria
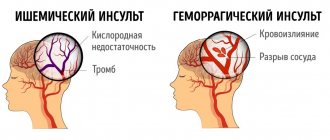
Dysarthria is a violation of pronunciation or articulation due to paralysis of the bulbar muscles, dysfunction of the facial muscles. The motor skills of speech, the pronunciation of sounds, the rhythm of breathing, and intonation coloring are impaired. It becomes difficult to understand what the person wants to say. People around you notice dysarthria. The person slurs his speech, speaks unclearly, and slurs simple words. The meaning and tempo most often do not change, and the strength of the voice is impaired. This disorder is always caused by an organic cause - impaired blood flow, infection or intoxication. In case of such a disorder in an adult, an urgent need to contact a neurologist to find out the cause. There may be a tumor of the nervous system, trauma, hemorrhage or ischemia (oxygen starvation). Dysarthria manifests itself in multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, myotonia, cerebral atherosclerosis, syringobulbia and many other nervous diseases. In healthy people, dysarthria is observed in a state of deep intoxication.
Dysarthria resulting from diseases has several forms:
- bulbar, caused by damage to the nuclei of the cranial nerves, occurs with cerebrovascular accidents, manifests itself as a single slit sound;
- pseudobulbar (damage to one side of the speech muscles), which occurs when the pathways from the cerebral cortex to the nuclei in the brain stem are damaged, manifests itself as slurred, slurred speech with the inability to pronounce hissing and whistling sounds;
- extrapyramidal, when the nerve nuclei located in the subcortex are affected, manifested by involuntary guttural cries;
- cerebellar - “chanted” speech;
- hemispheric or cortical, when lesions occur in the cortex, the use of all linguistic means becomes difficult.
Neurologists and speech therapists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of diarthria.
Favorable prognosis?
Speech disorders can be corrected if this work is started at an early age or early stage. The people around us and the efforts of the person himself play an important role in improving the condition. If the disorder is identified in a timely manner and treatment is started, speech can be normalized. Such children continue to study in regular schools and get along well with the kids.
In complex forms of the disease, achieving improved speech is not easy. You can only correct your speech function. In such situations, the range of measures is broader, and the patient needs to visit a specialized institution. It is necessary to maintain the continuity of speech therapy organizations: go to special kindergartens, correctional schools. It is also important to be treated in psychoneurological hospitals if it was prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention involves implementing effective measures from birth. The child must be protected from neutroinfection, skull and brain injuries. It should not be affected by toxic factors.
It must be taken into account that success comes with a systematic approach and comprehensive organization of events. Along with traditional treatment, unconventional methods should not be forgotten. It is important to carry out physical activity activities. Using a variety of methods can provide excellent results if used correctly.
Success in speech restoration largely depends on the patient’s attitudes, his desire and patience, and his environment. A favorable prognosis for the development of research on aphasia depends only on enthusiastic scientists. “The funding situation in the country is problematic. Because of this, some laboratories that were planning to open were unable to do so,” says Maria Ivanova.
Psychologists, linguists, and neurologists, with their own enthusiasm, are trying to develop neurolinguistics as a scientific field. For this purpose, the Summer School on Neurolinguistics was created, which this year for the third time brought together specialists from all over the country and from abroad under the roof of the Higher School of Economics. There are more and more neurolinguist students every year, the popularity of this field is growing, but the issue of funding still remains up in the air.
Aphasia
This is a violation of the structure of speech or understanding of its meaning.
Motor aphasia is a sign of damage to Broca's area or the lower parts of the frontal lobe. The person understands the spoken speech, but cannot say anything. Sometimes individual words or sounds break through, often obscene. This speech disorder is almost always accompanied by motor disorders in the form of paralysis of the right limbs. The cause is blockage of the superior branch of the middle cerebral artery.
Sensory aphasia is the inability to understand the meaning of speech, develops when the temporal gyrus of the hemispheres or Wernicke's area is damaged. The person does not understand the spoken speech, but fluently pronounces a set of words devoid of any meaning. The handwriting remains the same, but there is no essence in what is written. Often combined with visual impairments, the person is not aware of his defect. The cause is blockage of the lower branch of the middle cerebral artery by an embolus or thrombus. Conductive or conductive aphasia - a person understands speech, but cannot repeat anything or write from dictation. Speech consists of many mistakes that a person persistently tries to correct, but cannot. The white matter of the brain in the supramarginal gyrus is affected.
Acoustic-mnestic - a person cannot pronounce long complex phrases, making do with a minimal primitive set of words. It is extremely difficult to find a word. Develops with damage to the left temporal region, characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.
Optical-mnestic - a person recognizes objects, but cannot name or describe them. The loss of simple concepts from everyday life impoverishes both speech and thinking. Develops in toxic and dyscirculatory encephalopathies, as well as brain tumors.
Total aphasia - there is no ability to understand speech, nor to say or write anything. Characteristic of cerebral infarctions in the middle cerebral artery basin, often accompanied by paralysis, visual impairment and sensitivity. When blood flow through the middle cerebral artery is restored, speech may be partially restored.
Diagnostic features
It is necessary to analyze the complaints expressed by the patient. The medical history is also taken into account. Experts usually ask when the slurred speech appeared and whether there are any relatives suffering from such an illness. You definitely need to visit a neurologist and get examined by him. The doctor will check the mandibular and pharyngeal reflexes, examine the pharynx, and make sure there is atrophy of the tongue muscles.
The reflexes of the lower and upper extremities are checked. You should be examined by a speech therapist. The doctor evaluates speech indicators, identifies tempo disturbances and difficulties. An examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary, which will protect against processes in the mouth such as ulcers and tumors, which can cause problems.
A computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scan of the head is performed, which will help identify the cause of slurred speech. The causes in adults and children are determined in consultation with a neurosurgeon. Only after a complete diagnosis are treatment methods prescribed.
Neurological diseases in children
Slurred speech in a child is associated with various ailments. The main ones include:
- The external design of an utterance is a pronunciation disorder.
- Internal design – systemic speech disorder.
Most often, neurological diseases in children and newborns are the result of:
- — intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- - exposure to teratogenic factors on the fetus during pregnancy (taking certain medications, drinking alcohol, smoking, HIV infection, syphilis, etc.);
- — birth injury (pinched nerve or damage to brain structures);
- - hereditary predisposition (presence of a disease gene in the genotype of one or both parents), genetic diseases;
- - past infection.
Characteristic symptoms of neurological diseases in children:
- - delayed physical and neuropsychic development;
- - absence or weakening of congenital reflexes;
- - visual or hearing impairment;
- - muscle wasting;
- — violation of the formation of voluntary movements.
Nerve diseases in children can appear at any age, but more often they are observed from birth.
Stuttering or logoneurosis
Develops in adults after severe fright or unbearable stress against the background of congenital insufficiency of the speech apparatus. The reasons may be outwardly harmless, but affect concepts that are important to a person - love, affection, family feelings, career aspirations.
The basis is a neurotic disorder. Logoneurosis often intensifies in situations of tension - at crucial moments, when speaking in public, during an exam, during a conflict. Several unsuccessful attempts or tactless behavior of others can lead to a fear of speech, when a person literally “freezes” and cannot utter a word.
Logoneurosis manifests itself as long pauses in speech, repetitions of sounds, syllables or entire words, as well as spasms of the lips and tongue. Trying to “skip” a difficult place dramatically increases stuttering. At the same time, there are no specific words or sounds on which a person stumbles; speech may stop on any word.
Stuttering is always accompanied by respiratory neurosis, when respiratory spasms occur. Almost always, along with the fear of speech, a person is worried about anxiety, decreased self-esteem, internal tension, sweating, and sleep disorders. Additional movements in the form of tics of the facial muscles, movements of the arms and shoulder girdle are common. Successful treatment of stuttering is possible at any stage; it is important to consult a doctor in time.
Prevention
It is impossible to say with 100% certainty that there are certain ways to prevent pronunciation problems. If you have risk factors, you should undergo regular examination at a medical facility. The specificity of defects in the articulatory apparatus does not make it possible to make a forecast for the future. If you have vascular problems, you need to control your blood pressure and lead a healthy lifestyle. Remember that sitting in front of a computer monitor will not get rid of the problem. You need to communicate more with friends and family, take walks in the fresh air.
Speech impairment in adults is not a death sentence; a large role is played by its early diagnosis and an integrated approach to therapy. Treatment should not be symptomatic, but aimed at eliminating or suppressing the cause. Of course, some age-related changes are irreversible. So, with senile dementia, the dynamics will only worsen over time. However, through drug treatment, doctors are able to slow down the development of the disease and the transition to the terminal stage. Do not forget that great importance is given to the patient’s mental state. A positive attitude will help and give confidence not only to him, but also to his relatives.
Symptoms
Speech disorders appear immediately after stress. The patient may be in shock and not understand what is happening to him. When he tries to speak, he discovers that his voice has disappeared. Sometimes the patient refuses communication itself and withdraws into himself.
It is possible to lose not only the verbal ability to communicate, but also the person is unable to express his thoughts in writing. Due to nervous shock, the patient may experience clouding of consciousness, tremors of the limbs and other disorders.
If the voice does not recover within several hours after the incident, this is not yet a pathology. The next 2-3 days will be decisive. If a person does not speak during this time, his muteness is already defined as mutism. Silence lasting 2 weeks or more can be considered chronic mutism.
Silence for 2-3 days after a traumatic event is considered normal
Treatment
After severe stress, it will take a long time to recover. Speech loss will have to be treated comprehensively, using medications and psychotherapy. Only a doctor can select medications that will reduce the load on the nervous system and help a person cope with the situation. The effect of tablets alone is not enough. Due to prolonged silence, the speech apparatus, like the engine of a car that has been parked for a long time in the garage, needs to be “warmed up.” To restore your voice, it is useful to do special gymnastics. You can choose a set of exercises together with a speech therapist.
Art therapy helps to recover from speech loss. You need to draw your fears, emotions, impressions in order to give them an outlet. Hidden experiences often cause complications with mutism.
After stressful situations, it is important to ensure a stable environment in the family. A person needs additional attention from loved ones. You need to constantly communicate with him, despite the fact that he cannot answer. If his communication style before his illness did not involve close contacts, then you cannot insist on them. Peace and tranquility contributes to the rapid return of the voice.
Classification of disorders in adults
Similar to childhood dysfunctions, pathology is divided into types according to its manifestations and symptoms. Experts identify the following expressive speech disorders:
- aphasia;
- alalia;
- bradyllalia;
- dysarthria;
- dysorthography, dysgraphia;
- dyslexia, dyslalia;
- stuttering;
- delayed speech development, or SRD.
The characteristics of aphasia are the same as in childhood. Speech impairment is caused by damage to various parts of the brain. Depending on the location of the pathological process, various symptoms come to the fore. Each type of aphasia has common and individual characteristics. To one degree or another, writing and reading impairments always appear. If pathological changes are associated with age-related changes, already formed speech skills disappear.
Correction
Health care
Therapeutic tactics depend on the etiology of the speech perception disorder. For organic brain lesions, drug therapy with neuroprotectors, neuropeptides, vitamins, and cerebral circulation correctors is necessary. Physical methods of rehabilitation are used: physiotherapy (darsonvalization, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy), therapeutic exercises, mechanotherapy.
For patients with dementia, pharmacotherapy is prescribed by a psychiatrist. Most often, nootropics, antidepressants, antioxidants, cholinesterase inhibitors, and antipsychotics are used to correct mental disorders.
For patients with congenital hearing loss, various types of hearing restoration may be recommended: electroacoustic correction (selection of a hearing aid), cochlear implantation. In the future, to develop understanding of speech and active expression, patients need classes with a teacher of the deaf.
Neuropsychological support
Methods of neuropsychological correction are used in complex therapy of alalia, aphasia, mental retardation, and autistic disorders. As part of cognitive rehabilitation, work is being done to develop HMF; sensorimotor correction involves the formation of a body diagram, spatial representations, non-verbal expression of one’s needs, etc. Various methods are used: neurogymnastics, exercises for interhemispheric interaction, cerebellar stimulation, sand therapy, various types of sensory integration. ABA therapy is recommended for autism.
Speech therapy correction
Speech therapy classes aimed at activating auditory perception play an important role in correcting speech understanding disorders. Main directions of logotherapy:
- development of perception of non-speech sounds (recognition of natural sounds, animal voices, musical instruments, household noises);
- consolidating the objective image of a word (pronouncing a word, showing the object it denotes and writing it);
- work on understanding situational speech (affirmative and negative answers, assimilation of short oral instructions);
- development of phonemic processes (differentiation of phonemes, sound-letter analysis);
- work on the semantic side of speech (working on the understanding of non-situational issues, complex sentences and grammatical phrases, developing the skill of meaningful reading).
A positive effect on restoring speech understanding was noted from the use of finger games, mnemonics, and auditory training using the Tomatis method. In children with ASD, the choice may be made in favor of developing verbal or alternative communication (using gestures, PECS cards).
Forms of speech impairment
| Name of disorder | Main symptoms |
| Acoustic-mnestic aphasia | Speech is confused and slurred. Pauses between phrases. |
| Efferent-motor form of aphasia | There is a displacement of phonemes and a violation of articulation. |
| Alalia | Verbal communication is almost impossible. The vocabulary is insufficient, division into syllables is difficult. |
| Bradylalia | Slowing down the rate of speech is also reflected in writing and reading. Characterized by monotony. |
| Dysarthria | Complex disorders affect motor skills, breathing, timbre and strength of the voice. |
| Dysorphography | The patient makes mistakes when writing, but they are not associated with awareness of the rules of writing or pronunciation. |
| Dysgraphia | Partial spelling disorders due to insufficient control of written speech. |
| Dyslexia | Loss of reading skills, the patient has difficulty mastering the material read. |
| Dislalia | Against the background of normal hearing and correct articulation, a violation of the pronunciation of sounds is noted. A dentist is hired for diagnosis. |
| ZRR | More often found in childhood: a poor vocabulary, monotonous speech without intonation. |
| Stuttering | The tempo is interrupted cyclically when certain sounds are repeated. |