Cryptogenic epilepsy is one of the most complex chronic pathologies of the central nervous system, the development of which is due to unknown or uncertain causes. The disease is manifested by regularly recurring specific seizures. The cryptogenic form is found in almost 50% of patients suffering from epileptic seizures.
Cryptogenic epilepsy can be partial, temporal, generalized and focal. With cryptogenic focal epilepsy, patients experience frequent paroxysmal conditions (convulsive seizures). The long course of the disease threatens personality changes, the so-called “epileptic dementia.” This type of pathology is diagnosed mainly at a young age, in patients under 20 years of age, but sometimes occurs in older people. The focal form of cryptogenic epilepsy is practically untreatable, so the patient requires long-term, and most often lifelong, therapy.
What kind of disease is this
Cryptogenic epilepsy has a whole set of epileptic symptoms, the causes of which cannot be determined. The type of illness is hidden. Manifestations of cryptogenic epilepsy are not differentiated from symptoms of other types of disease. With this form, spontaneous electrical impulses occur in the cerebral cortex, causing overexcitation of nerve transmission. As a result, a convulsive focus is formed, provoking an attack.
Seizures can be focal or gradually spreading throughout the victim’s body. The first type of pathology represents limited areas of increased activity in the cerebral cortex.
The symptomatic nature of the disease is detected only with a comprehensive examination of the body. Local abnormalities are detected using magnetic resonance imaging.
Depending on the pathological focus, epilepsy can occur in such lobes as:
- frontal;
- temporal;
- occipital;
- parietal
The frontal form is often accompanied by sudden attacks that last in short series. In rare situations, secondary generalization occurs due to damage to brain cells. If the focus of epileptic activity is localized in the temporal zone, the patient, against the background of regularly manifested emotions, exhibits a phenomenon such as déjà vu. It is this subtype of the disease that is most often encountered in practical medicine. Cryptogenic frontotemporal epilepsy is diagnosed in the same way; the symptoms in this situation are combined.
Pathology is always accompanied by increased activity in the crown area, which is responsible for sensory functions. Victims experience unusual sensory sensations, such as:
- tingling on only one side of the body;
- distorted perception of one's own limbs.
Accompanied by partial seizures, it is the rarest form.
Make an appointment
What is cryptogenic epilepsy?
Cryptogenic epilepsy is a psychoneurological disease of a chronic nature, the causes of which cannot be determined. The pathology during the period of exacerbation provokes epileptic seizures (muscle cramps or convulsions). During seizures, short-term loss of consciousness, mental and autonomic disorders are noted. As cryptogenic epilepsy progresses, the patient's personality may change.
To understand the characteristics of the disease, what it is, it is necessary to turn to the mechanism of development of the pathology. Seizures occur due to brain activity in certain areas. Due to spontaneous impulses generated in the pathological focus, the excitability of the nervous system increases, as a result of which the muscles begin to contract convulsively and the flow of other processes is disrupted. After this, complete amnesia sets in: the patient does not remember the events that occurred during the attack.
An important feature of the disease is that when examining a patient, it is impossible to determine the exact location of the pathological focus in the brain.
The clinical picture of cryptogenic epilepsy is variable. The types and localization of symptoms are determined by the zone(s) of location of the pathological focus in the cerebral cortex. Moreover, some of the clinical phenomena that are troubling in the disease are not caused by cryptogenic epilepsy. In particular, the main cause of metabolic disorders in neuropsychiatric disorders is pathology of the pancreas, liver or stomach.
Despite the fact that the factors provoking the onset of the disease cannot be established, researchers have identified the following pathologies, against the background of which epilepsy often occurs:
- hereditary predisposition to diseases that provoke disorders of brain activity;
- ischemia, stroke;
- brain tumors;
- congenital diseases;
- poisoning;
- infectious brain lesion.
Epileptic seizures occur due to the influence of a wide range of factors. Seizures occur due to loud sounds, bright or flashing lights, sudden temperature changes, and stress.
Reasons for development
To date, it has not been possible to find out why epileptic activity of the cryptogenic type of brain occurs. However, scientists concluded that the development of the disease can be triggered by the following factors:
- burdened heredity;
- complications after traumatic brain injury;
- history of stroke;
- a brain tumor;
- intoxication with chemicals.
The most likely cause of the pathology is considered to be a genetic predisposition.
Diagnosis of the disease
If cryptogenic generalized epilepsy is suspected, the doctor first interviews the patient’s relatives in order to clarify the phenomena that occur during epileptic seizures and the possible causes of the development of the disorder. After this the following are carried out:
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- CT and MRI of the brain;
- electroencephalogram.
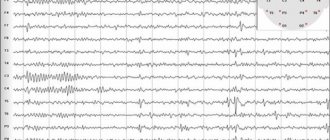
The last method is the most informative. However, an EEG shows the presence of a pathological focus, provided that the examination is carried out during an epileptic attack.
First signs
The main symptom of epilepsy is seizures. With cryptogenic epilepsy, generalized or partial seizures may occur. Before the onset of partial seizures, more typical of cryptogenic epilepsy, a so-called aura occurs. It signals that a seizure is about to occur. The appearance of the aura allows the doctor to determine the location of the brain lesion.
A motor type aura is accompanied by unexpected movements of the patient, which indicates the location of the affected part in the frontal lobe of the brain. With a rapid deterioration in visual and auditory functions, it can be assumed that the localization of the disorders is in the occipital or temporal lobe.
Expert opinion
Author: Polina Yuryevna Vakhromeeva
Neurologist
In recent years, doctors have noted an increase in the incidence of epilepsy. The exact causes of this disease have not yet been established. It is known that about 4-10 people per 1000 people suffer from seizures. Drug-resistant cryptogenic epilepsy is considered one of the most severe forms of the disease. It is difficult to select treatment for this species due to drug resistance.
A qualified team of doctors at the Yusupov Hospital takes on complex cases. Diagnosis of epilepsy in our clinic is carried out using modern medical equipment. European CT, MRI and EEG equipment are used for examination. They allow you to determine the location of the pathological focus with high accuracy. An analysis of blood and the degree of resistance of the body to drugs is carried out in a modern laboratory.
Therapy for cryptogenic epilepsy is carefully developed by experienced neurologists and epileptologists. In this case, an individual approach is used. Drugs are selected taking into account the degree of drug resistance and other associated conditions. The prescribed medications meet the latest European standards for the treatment of epilepsy.
Classification and symptoms
Cryptogenic epilepsy is divided into two types:
- Focal. This type of disease has a more pronounced clinical picture. In cryptogenic focal epilepsy, the focus of activity is often located in the temporal lobe of the brain.
- Generalized. Cryptogenic epilepsy of this type is characterized by a variable clinical picture and the presence of multiple pathological foci in the brain.
With cryptogenic epilepsy, there is no aura (a harbinger of an epileptic seizure). However, over time, some patients begin to feel the imminent onset of a seizure.
Each attack goes through several stages:
- Tonic muscle contractions, in which the patient involuntarily arches the body. At the initial stage, a short-term cessation of breathing is possible. Most patients experience blue skin on their face. It is also possible that the pulse may disappear.
- Clonic seizures. The body's condition returns to normal. At the same time, the patient begins to involuntarily twitch his limbs. A typical sign of tonic seizures is active foaming from the mouth.
- Muscle relaxation. At this stage, involuntary urination and/or fecal loss may occur. Due to muscle relaxation, the sensitivity of the body sharply decreases, and the patient temporarily loses the ability to control the body.
Typically, each attack ends in deep sleep, after which the patient experiences fatigue and headaches.
The nature of the clinical picture varies depending on the type of seizure: simple or complex. In the first, convulsive contractions are observed only on one part of the body (rarely they involve both).
Complex partial seizures are characterized by the following disorders:
- gestural (automatic and uncontrolled, repetitive movements);
- oralimentary (problems with swallowing);
- speech (temporary loss of ability to speak);
- visual (decreased quality of vision, hallucinations).
After the seizure, ambulatory disorders are observed, due to which the patient is half asleep.
Against the background of a simple partial attack, visceral and autonomic disorders are possible. In the first case, dysfunctions of organs located in the upper part of the body (mainly the head) are noted. In particular, after an attack, the patient complains of the presence of a foreign object (lump) in the throat. In some cases, sexual disorders are noted.
With vegetative disorders, body temperature rises, blood pressure temporarily changes and nausea bothers you.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of cryptogenic epilepsy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- a more severe course of attacks, in contrast to the classic type of disease;
- reduced effectiveness of drug treatment;
- significantly accelerated pace of personality change;
- different results of diagnostic studies with each subsequent execution.
Each type of cryptogenic epilepsy has its own characteristic features and symptomatic manifestations that make it possible to differentiate one form from another.
Partial seizures characteristic of cryptogenic focal epilepsy can be simple (without loss of consciousness), complex (with loss of consciousness) and complicated by secondary generalized seizures.
The leading symptom complex of cryptogenic focal epilepsy is repeated partial paroxysm.
The nature of simple partial seizures can be motor, sensory, autonomic, somatosensory, accompanied by auditory, visual, olfactory or gustatory hallucinations and mental disorders.
Complex partial seizures in cryptogenic focal epilepsy in rare cases begin with a simple seizure, after which the patient’s consciousness is impaired, and sometimes automatisms occur. After an attack, patients experience confusion. Secondary generalization of partial seizures is allowed. In these cases, at the beginning, an epileptic attack can be simple or complex, and as it develops, there is a diffuse spread of excitation to other parts of the cerebral cortex, after which the paroxysm becomes generalized.
With symptomatic epilepsy, in addition to seizures, other symptoms develop, corresponding to the main lesion of the cerebral cortex. In patients with this diagnosis, intelligence decreases, cognitive impairment occurs, and children experience delayed mental development.
In idiopathic epilepsy, which is characterized by benignity, neurological deficits and mental and intellectual disorders are not observed.
In addition, the disease may be accompanied by the occurrence of twilight states, in which the following occurs:
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- erratic motor and speech activity;
- clouding of reason.
Attacks of focal cryptogenic epilepsy in adults are more severe than in children. Finding effective therapy is also more difficult for them. Conventional antiepileptic drugs for this pathology have less effect and have virtually no effect in minimal dosages. During the period between attacks, patients continue to have nonspecific symptoms not associated with convulsive attacks: depression, resentment, unreasonable temper, memory impairment.
Treatment of cryptogenic focal epilepsy
The seizures of this disease are completely controllable, with the only exception being frontal lobe epilepsy, which is difficult to treat with anticonvulsants. Drug treatment for focal cryptogenic epilepsy will depend on the causes of the disease that have been investigated and discovered. The main task is not only to stop seizures, but, if possible, to eliminate the basis of the disease.
- Drug therapy . Using this method of treatment, the doctor prescribes medical anticonvulsants to the patient if the patient has more than two seizures per day. As practice has shown, in 25% of all cases this method of treatment has excellent results and leads to a cure for the patient. When the form of the disease is very severe, anticonvulsant drugs help reduce the severity of seizures and their course. Treatment is started with a minimum dose, with further increases. The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of the drug.
- Surgical intervention . This treatment is used only if it is necessary to remove tumor pathologies from the brain, a cyst, which is the root cause of the development of epilepsy.
- Dieting . The mechanism of action of diet therapy is a clear ratio of fats, carbohydrates and protein in the daily menu. The diet must consist of fatty foods: cream, fatty meats, butter. Reduce such foods as: fruits, pastas, vegetables and baked goods.
Focal cryptogenic epilepsy is not a death sentence, but only a chronic disease. Modern medicine successfully copes with attacks, stopping them with medications. And with timely treatment and the right lifestyle, in 80% of cases, adult patients and sick children can be relieved of the severity of symptoms almost forever.
The goals can be achieved with timely diagnosis and regular use of medications prescribed by doctors. Strictly follow the dosage of medications prescribed by your doctor. Concomitant treatment is the correct daily routine, that is, wisely distributing rest time and stress on the body, the absolute absence of negativity, various shocks and shocks, and a healthy lifestyle. Only in this way, through the efforts of doctors and the patient directly, can one, if not completely cure the disease, then at least reduce its symptoms to a minimum.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing the disease, the main criterion is to exclude organic brain damage. It is for this purpose that the following procedures are used:
- collection of family and individual anamnesis with clarification of the presence of brain injury, birth or congenital pathology;
- electroencephalogram, based on recording the biorhythms of the brain during various activities, for example, sleep, intellectual or physical activity;
- conducting magnetic resonance imaging, which helps detect impaired brain activity or localized brain damage;
- performing angiography, which allows you to study how well the blood supply to the brain flows;
- neuropsychological diagnostics, designed to study the quality of mental activity;
- a blood serum test aimed at detecting syphilis and other pathogenic microorganisms in the body.
The victim must undergo laboratory tests, including genetic diagnostics, biochemical and general blood tests, as well as a urine test. Epilepsy is diagnosed by doctors only after conducting a full range of examinations and excluding the possibility of other pathologies affecting the body.
Prevention
It makes sense to talk about prevention only in the context of acquired forms of the disease. Because for the most part the pathological process occurs in childhood, much less often in adolescence. The activities are as follows:
- Refusal of alcohol, especially drugs.
- Correction of the diet towards its fortification.
- Avoiding stress, mastering relaxation techniques.
- Get adequate sleep (at least 7 hours a day).
- Avoiding brain injury.
- Treatment of somatic diseases immediately after their detection.
You may also be interested in:
Varieties
Cryptogenic epilepsy (ICD class 10) is divided into subtypes of varying prevalence. Victims may experience multiple types of seizures, and some medical researchers view the pathology as an intermediate diagnosis requiring the use of additional diagnostic methods.
West syndrome
This variant appears in children aged 2-4 months. The main symptom of this type of neuropsychiatric disorder is spontaneous attacks that quickly arise and cease. The disease causes a child to lag in intellectual development.
When the victim reaches the age of 12 months, the disease may stop on its own or change into another type, for example, Lennox syndrome, which is accompanied by various types of seizures.
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
This type of pathology refers to the childhood form of epilepsy, which develops in a child between the ages of 2 and 8 years. The syndrome forms independently, less often transforms from a condition that occurs at an earlier age. Characterized by a sudden loss of balance or coordination, and short-term hearing loss. The patient practically does not lose consciousness. Frequent seizures can cause delays in intellectual development and also increase the likelihood of injury.
Myoclonic-astatic form
The form can be diagnosed in children aged 5 months to 5 years. The main symptom that occurs at a very early age is a generalized seizure. Children who can walk experience episodes of loss of balance and coordination.
A seizure consists of lightning-fast and sudden movements of the limbs, rapid nodding of the head, as well as the feeling of a blow to the knee area. Most often, the attack occurs in the morning, after getting up.
Myoclonic absence seizures
A type of disease is detected in the age group from 1 to 12 years. These seizures are the first type of seizure in most situations. By the time an attack is detected, more than half of children have severe mental and intellectual development delays.
The disease is often accompanied by complete or partial loss of consciousness, sudden movements of the muscles of the shoulder girdle, limbs or face with a transition to sudden short-term seizures. The duration of one episode is less than a minute, but can occur several times a day.
Partial seizures
There are several types of partial attacks, these include:
- Motor. Accompanied by cramps and contraction of muscle tissue in certain areas of the body. It occurs and goes away suddenly, without loss or clouding of consciousness.
- Sensory. Characterized by a sudden onset of fever, chills, tingling, burning or crawling sensations. Additionally, there is a disturbance in the functioning of the senses in the form of hallucinations.
- Mental. Characterized by a sudden disturbance in mental or speech activity, loss of balance or coordination, and hallucinations.
- Vegetative. Features include increased sweating, changes in body temperature in certain areas of the skin, increased or slowed heart rate.
Visceral and autonomic seizures
The form occurs in the form of painful sensations in the head and throat. In some cases, adolescents and adults may experience an unreasonable erection or orgasm. The disorder is accompanied by a failure of temperature regulation and surges in blood pressure. Often visceral and autonomic seizures are mixed. Both varieties have a number of features:
- the duration of the attack is 5-10 minutes;
- convulsive muscle contractions are present;
- there are no provoking factors;
- may be combined with other forms of seizures;
- after the seizure stops, a feeling of disorientation in space may occur.
Situational seizures
Several factors can trigger a seizure:
- taking narcotic drugs;
- alcohol consumption;
- use of medications;
- a history of brain injury;
- intoxication with chemicals;
- viral blood infection;
- disruption of the heart or liver.
These attacks can be caused by:
- sudden exposure to bright light, especially flashing light;
- loud sounds;
- temperature changes from extremely high to extremely low.
The above factors can trigger the underlying mechanism for the occurrence of epileptic seizures.
Prevention and prognosis
The prognosis is ambiguous, timely diagnosis and correctly selected treatment improve the patient’s well-being and return the previous rhythm of life. Among the complications, the most likely are coma, damage to the limbs during an epileptic seizure, depression of respiratory function, heartbeat, mental and emotional status disorders. When seizures appear in childhood, the process of socialization of the individual suffers; the child either avoids society himself, or society perceives him incorrectly.
Prevention of cryptogenic epilepsy has not been developed.
Treatment
Timely diagnosis of the disease will help you select an effective treatment program and reduce the risk of side effects. Therapy can be carried out in an inpatient or outpatient setting. Correction with medications is prescribed only after the final diagnosis is made and the second attack of pathology is completed. Therapeutic treatment for a disease has several goals:
- relief of pain accompanying attacks;
- preventing the occurrence of new epileptic episodes;
- reduction in the frequency of seizures;
- reducing the duration of the attack;
- reducing the likelihood of new side effects;
- restoring the functioning of the nervous system without the need to use medications.
Drug therapy for cryptogenic epilepsy involves taking medications that reduce the frequency and duration of epileptic seizures. Additionally, nootropic substances that affect nerve impulses can be prescribed. In addition, patients with a similar diagnosis are prescribed psychotropic medications.
Some patients with cryptogenic epilepsy are prescribed surgical correction, a therapeutic diet, and physiotherapeutic techniques. There is no single method to completely get rid of epileptic seizures. However, competent treatment at the Yusupov Hospital using innovative techniques helps alleviate the condition of patients in 90% of cases.
Considering the fact that the patient’s condition depends on the influence of external factors, he is recommended to lead a correct lifestyle, try to eliminate stressful situations and overwork.
The diet of a patient with epilepsy should include foods with increased amounts of protein. It is necessary to give up hot and spicy foods, coffee and tea. A dairy-vegetable diet is recommended. Due to the fact that alcohol can aggravate the course of the disease, drinking alcohol even in minimal doses should be strictly avoided.
Treatment methods
Cryptogenic epilepsy with generalized seizures is treated with medications that are used to prevent the onset of another epileptic attack and stop complications that arise.
Anticonvulsants such as ethosuximide or carbamazepine help achieve this. Drug therapy is also supplemented with GABA receptor agonists (Picamilon, Aminalon).
Depending on the nature of the attacks and the resulting consequences, the following is introduced into the treatment regimen:
- psychotropic medications (restore psychological status);
- neurotropes (inhibit the activity of the pathological focus);
- diuretic medications (eliminate swelling);
- hemodialysis (for renal pathologies).
.
If necessary, the patient is transferred to a specialized diet. To avoid another exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol.
Forecast
In case of cryptogenic epilepsy, it is favorable if the patient follows all medical prescriptions and there is a person next to him who can provide him with first aid. However, a long course of the disease leads to a decrease in intellectual abilities, absent-mindedness, dementia and speech disorders. That is, over time, the disease leads to irreversible changes in the patient’s personality.
But the most dangerous is epilepsy, which is characterized by frequent and prolonged (more than 5 minutes) seizures. In these cases, emergency medical care cannot be avoided, since a prolonged seizure can provoke swelling of the brain and lungs.
Changes in mental functions in epilepsy
As a rule, characteristic changes occur in memory, attention, thinking, speech, personal characteristics, and in general a significant decrease in the rate of mental processes. Already at the initial stage of the disease, there is some inertia in mental activity, for example, it is difficult for the patient to switch attention, which is easy to detect using a switching test, for example, a Schulte table with black and red numbers, where it is necessary to alternately find and name numbers from 1 to 25 in red - descending, black - ascending.
Their thinking can be characterized as sluggish, viscous, and with the increase in epileptic dementia, it becomes difficult to operate with complex logical structures. In speech, “stuckness” on unimportant details is also found, while the goal of verbal communication does not occur. In conversation, such patients tend to use diminutive suffixes: “doctor”, “little bed”, “boy”; they may even seem overly obsequious and sugary, it seems as if they are trying to please. At the same time, the other extreme in the personality of patients with epilepsy is sudden and uncontrollable outbursts of rage, even for minor reasons.
Also, a characteristic feature of these patients is an excessive tendency to order, for example, they can arrange dishes in the closet according to size and perfectly evenly, lay out clothes in the closet by color in perfectly even piles. Their speech is distinguished by a characteristic reasoning, different from schizophrenic: they can talk pathetically or in a moralizing tone for a long time about some shallow, everyday, superficial things. He also suffers, and with pronounced personality changes, there is no sense of humor.
Useful to know: Poor blood circulation in the brain, how to identify the symptoms?
to contents ^
Diagnosis and treatment
Cryptogenic focal epilepsy requires timely consultation with a doctor. In the hospital, a person will be able to undergo diagnostics, which will help confirm the presence of the disease and rule out other brain lesions. The doctor will examine the person’s lifestyle, symptoms of the disease, and past illnesses. It is important to know if any of your close relatives have had epilepsy of any type .
If a person is suspected of having epileptic seizures, they are referred for echoencephalography. It can reveal any pathology in the functioning of the brain. The device records the electrical activity of the organ. Often it is necessary to fix it precisely at the moment of a seizure. It is worth noting that this examination will reveal secondary generalization of the seizure, which is important for selecting the correct treatment.
Additionally, MRI and CT are prescribed. These studies make it possible to understand whether there are other lesions in the brain area. In their absence, a diagnosis such as cryptogenic epilepsy can be made.
Therapy consists of the use of medications, in particular anticonvulsants. Only a doctor can prescribe a specific medicine, as well as determine the duration of the course of treatment. It should be noted that the therapy itself takes a lot of time - up to about 5 years . Moreover, complete cure does not occur in all cases. In the best situation, it is possible to get rid of the negative symptoms of the disease and reduce the number of attacks.
A person is advised to reconsider his lifestyle, try not to overwork, and also avoid stressful situations. You need to get rid of bad habits if you have them, because alcohol and smoking can lead to more frequent attacks. It is important to eat right and get the required amount of sleep. In this situation, you will be able to significantly improve your well-being and tolerate the symptoms of the disease more easily.
With cryptogenic epilepsy, a person should listen to the doctor’s recommendations and also be regularly monitored by a specialist. You may have to reconsider the chosen treatment regimen and select more effective methods. It is not allowed to carry out therapy on your own, because this can significantly worsen the person’s condition. Only a good doctor can reduce the number of epileptic seizures, as well as influence their intensity.