1. Tumors of the transparent septum
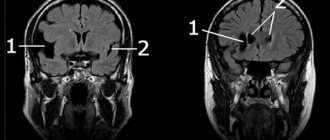
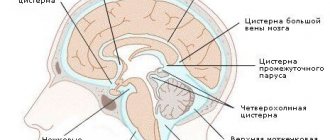
Among brain tumors localized in the area of the septum pellucidum
, the most common are ganglioneuroma and central neurocytoma.
Ganglioneuroma
, or otherwise ganglioma, gangliocytoma is a benign tumor usually reaching small sizes - up to 4 cm. Ganglioneuroma is formed mainly by glial cells and does not have a capsule. Neoplasms tend to infiltrate into the spinal canal and posterior mediastinum.
Central neurocytoma
It is also a benign tumor and is quite rare - in only half a percent of cases of the total number of brain tumors. The usual location of neurocytoma is the lumen of the lateral ventricles closer to the area of the transparent septum. Central neurocytoma is characterized by slow growth and does not have a tendency to become malignant. This pathology affects both men and women in the age range from 15 to 40 years.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes
Pathologies of the septum of the brain are rare, so there are no exact causes. However, there are assumptions:
- Chronic fetal hypoxia during pregnancy.
- Infections of the mother during pregnancy, for example, toxoplasmosis, or pneumonia.
- Injuries to the skull and brain, if the disease of the septum is of an acquired nature.
- Prematurity. In this case, the cavity of the transparent septum of the brain in a baby 100% contains a cyst.
- Maternal alcoholism.
- Acquired enlargement of the cavity can form due to prolonged boxing sessions.
- Septal cysts can be congenital or acquired. The first option occurs for the above reasons, the second – for skull injuries, hemorrhagic strokes and neuroinfections.
The septum may be absent due to:
- Disturbances in the formation of the corpus callosum.
- Holoprosencephaly is a defect due to which the hemispheres are not separated at all.
- Septo-optic dysplasia is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which the formation of the anterior structures of the brain is disrupted.
2. Symptoms of tumors of the transparent septum
The most characteristic of tumors of this localization is damage to the hippocampus, the cortical center of smell. It causes olfactory disturbances
associated with difficulty recognizing odors and olfactory hallucinations.
In addition, the general symptomatic picture is not much different from the signs that are usually characteristic of most brain tumors:
- increased intracranial pressure;
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- clouding of consciousness;
- muscle weakness, paralysis of the upper/lower limbs;
- visual disturbances;
- poor coordination of movements, unsteady gait;
- mental disorders.
Visit our Neurosurgery page
Symptoms
Non-fusion of the layers of the septum pellucidum does not develop the clinical picture. However, some American scientific publications report that plate laminae increases the risk of developing mental disorders: bipolar affective disorder, schizophrenia, dissocial personality disorder.
A septum pellucida cyst, if congenital, is considered a type of normal anatomy. The acquired variant develops a clinical picture of the general cerebral type:
- Headache. Appears due to increased intracranial pressure, which is provoked by an increase in the size of the cyst. The headache is usually bursting and aching in nature.
- Periodic disturbances of consciousness. Most often it develops as a type of somnolence - a mild variant of a disorder of consciousness in which the patient is inhibited, apathetic, drowsy and disoriented. There is also lethargy and indifference to any activity.
- Dizziness.
- Vomiting that occurs without previous nausea and is often not associated with food intake. Vomiting usually brings relief to the patient.
- Convulsive seizures. Appear when intracranial pressure increases.
The transparent septum of the brain in newborns may contain a large cyst. Then, due to irritation of the meninges, meningeal symptoms appear in the clinical picture:
- Headache.
- Excitation.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Excessive skin sensitivity, hypersensitivity to sound, photophobia.
- The child can take a specific meningeal position - the kicking dog position. Hands are pressed to the chest, legs are pulled towards the stomach, which is retracted. Also, due to hypertonicity of the muscles of the back of the head, the head is thrown back.
Absence of the septum pellucidum of the brain is rare. More often, the pathology is recorded in isolation. Does not develop a clinical picture.
3.Diagnostics and treatment
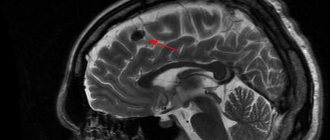
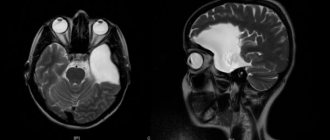
Diagnosis of tumors is carried out using both MRI and CT
, and using special methods -
electromyography and electroneurography
.
This helps assess the condition of the patient's neuromuscular system. In addition, neuro-lumbar puncture
for histological analysis.
surgery is used to remove central neurocytoma.
using transcranial access. However, this is not always possible due to the deep location of the tumor. In this case, radiation therapy is used.
Today, an innovative technique is used to remove a tumor using a cyber-knife - targeted, high-precision irradiation of a tumor with powerful beams of ionizing flux.
. It is envisaged that a high dose of radiation accumulates exclusively in tumor tissues, making them nonviable, but without affecting healthy tissues.
Regarding the diagnosis and treatment of ganglioneuroma
, then there are certain features. A clear diagnostic sign can be an increased concentration of norepinephrine, dopamine and prostaglandins in the urine and blood serum. Treatment of the tumor in most cases is carried out conservatively, or more precisely, by administering a special medicinal solution designed to cause sclerosis of the tumor. If the desired effect is not achieved, it is surgically removed. It should be noted that there are cases of random disappearance of ganglioneuroma without medical intervention.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
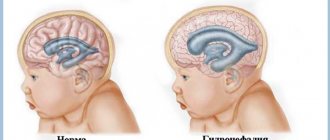
Reasons for the development of pathology
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum of the brain is a rare and abnormal disease of the central nervous system.
Each membrane of the brain performs a specific function. The septum pellucidum is the medulla and consists of two plates.
Agenesis is one of the components of most congenital brain defects. The absence of a septum is due to improper formation or underdevelopment of the corpus callosum.
Agenesis of the cavity of the transparent septum is classified as an anomaly of the central nervous system and is quite rare. This pathology is characterized by the complete or partial absence of the cavity of the transparent septum. This anomaly has not been sufficiently studied. The defect develops already in the second week after conception.
Predisposing factors to the development of agenesis:
- Heredity
- Mutations
- Intrauterine infections
- Insufficient supply of nutrients to the fetus
The development of pathology is also influenced by toxic substances and medications that the woman took during pregnancy. The use of drugs such as Trimethadione, Phenytoin, Isotretinoin and some others can contribute to congenital brain abnormalities. These drugs, used in the first trimester of pregnancy, affect the formation of the brain and can lead to developmental defects.
If the expectant mother drank alcohol, the child developed fatal alcohol syndrome. This also predisposes to congenital pathology. Infections in the mother or injuries sustained during the 12th to 22nd weeks of pregnancy can lead to disturbances in the development of the fetal brain.
Most often, this pathology is inherited or occurs due to spontaneous mutations.
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum does not occur in isolation. Typically, the pathology is part of various cerebral anomalies: agenesis of the corpus callosum, porencephaly, hydranencephaly, septo-optic dysplasia, holoprosencephaly, etc.
Clinical manifestations
Signs of pathology appear in the first years of a baby’s life
Severe symptoms appear in childhood during the first two years of life. At birth, children with agenesis appear healthy and develop normally until three months of age. At this stage of development, the first signs of pathology appear.
With agenesis, the following symptoms are observed:
- The appearance of porencephaly
- Microencephaly
- Insufficient formation of the gyrus
- Aicardi syndrome
- Atrophy of the optic and auditory nerves
Also, against the background of the pathology, early puberty, seizures and seizures can be observed. Pathology can manifest itself in different ways. With partial agenesis, these signs may not be observed in the child and may not affect development, but will need to be regularly monitored by a neurologist. Sometimes agenesis can occur without clinical manifestations for several years.
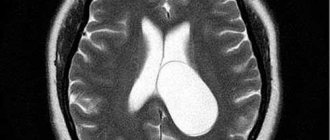
Septum pellucida cyst
If we talk about transparent septa (Verga's cyst), then these are two thin plates of the medulla with a gap, which, in fact, will be separated. This fissure is located in the area between the fornix and the anterior part of the corpus callosum. In some people, the diameter of the cyst is 1-2 mm, while in other cases the cysts grow to several centimeters. Today there are many classifications of this pathology. To begin with, it must be said that a septum pellucida cyst can be congenital (formed in the fetal brain during intrauterine development) or acquired (formed after birth, in children or adults). In addition, cysts are divided based on their location. For example, in some patients the cyst is located in the anterior zone of the interventricular septum. Sometimes it is located in the cerebellum. These factors, of course, must be taken into account when treating a cyst.
A cyst of the transparent septum mainly forms during fetal development. According to statistics, about 60% of babies (and 100% of premature babies) are born with a cyst in the brain.
As for the reasons, they look approximately the same, regardless of whether the cyst appears in adulthood or during fetal development:
- diseases accompanied by inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- injuries and diseases accompanied by cerebral hemorrhages;
- varying degrees of concussion;
- diseases of infectious origin, especially those affecting the meninges.
In fact, in most cases, the presence of a septum pellucida cyst in the brain is not clinically evident—the patient is not even aware of the problem. Moreover, a cyst of the transparent septum of the brain, the size of which is not too large, is usually discovered by chance during the diagnosis of another disease. Sometimes a cyst
begins to compress neighboring parts of the brain, from time to time blocking the foramen of Monroe. What symptoms should you look out for? Patients typically complain of the following:
- severe headaches that appear suddenly and disappear just as suddenly;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- disruption of the hearing aid - patients note a decrease or deterioration in hearing, the appearance of tinnitus;
- some patients complain of a feeling of squeezing in the head area.
Naturally, when treating a cyst, it is important to determine the primary disease and carry out appropriate treatment, be it an infection or an inflammatory process. When intracranial pressure increases, patients are prescribed drugs that normalize the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The treatment regimen usually includes osmotic diuretics (remove excess fluid), agents to improve blood circulation in brain tissue, and nootropic drugs. The rapid growth of a cyst if left untreated is a threat. In the end, the cyst compresses blood vessels and tissues; disruption of neuron nutrition causes degradation of certain brain structures, which is why cells gradually lose their functions. As a rule, stabilization of intracranial pressure and treatment of the primary disease is sufficient - the cyst gradually decreases and sometimes even disappears on its own. Unfortunately, this does not always happen and some patients require surgery. To begin with, using a special probe, a hole is formed in the wall of the cyst through which the fluid exits into the cerebral ventricle. In 80% of cases, this procedure allows you to get rid of tumors. Sometimes the hole between the walls of the cyst is still closed, and the doctor may decide that bypass surgery is necessary.