Attack of VSD or vegetative crisis
Attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia occur suddenly and are accompanied by unpleasant symptoms that are provoked by disorders in the autonomic nervous system.
With frequent attacks of VSD, a person’s level of performance decreases, attention and memory deteriorate. With intense manifestations, a deterioration in mental health is observed - he becomes depressed.
VSD is not a disease, but a set of symptoms that may indicate different diseases. Diagnosis depends on the type of accompanying symptoms. In the International Classification, a vegetative crisis is classified as a panic attack.
The first manifestations of the crisis are observed at about 20 years of age. But it happens that this happens at a younger age. Women are almost 3 times more likely to suffer from this symptom complex.
The manifestations of this disorder are not always pronounced. In most cases, the manifestations are blurred or insignificant. The trigger for the syndrome to enter the active phase is severe stress, hormonal imbalance, and intense physical activity.
The most striking are the first manifestations of a crisis, and therefore are remembered for a lifetime.
Helpful information
An attack of VSD manifests itself through difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and causeless anxiety.
These and other signs lead to increased fear of death. This fear is most often caused by the fact that a person does not understand what is happening to him and cannot influence it either. Another concern is that the crisis can last from several minutes to several hours.
Actions to take during an attack at night
Often, attacks of anxiety with panic attacks can occur at night. This is the time when the body is in its most vulnerable state. As a rule, crises are a consequence of the negative impact of stress that a person experienced during the day.
The attacks usually begin around three o'clock. The patient wakes up, feels a fever, an acute lack of air, and is tormented by a severe headache, panic, and anxiety. Irregularities in the functioning of the heart and sudden jumps in blood pressure are often observed.
Despite the fact that attacks at night have a less negative impact on the physical condition of the body, their symptoms are greatly aggravated due to fear. Ultimately, this has a bad effect on psycho-emotional health. Because these attacks disrupt the natural sleep process, people often feel tired and weak during the day.
If timely treatment is not started, a person becomes increasingly afraid of falling asleep, as a result of which chronic insomnia develops. This factor only makes attacks more frequent, which can lead to depression.
Proper first aid will help relieve unpleasant symptoms and minimize negative consequences. First you need to do everything to calm down as much as possible and take a vertical position. Sedatives will help bring the cardiovascular system back to normal. Valerian extract or Novopassit is well suited for this purpose.
As soon as the first signs subside a little, you need to do a few simple breathing exercises. While sitting with your eyes closed, you need to take deep breaths and exhales. They will have a calming effect and help you fall asleep again (provided that the attack is mild).
You should call an ambulance if you experience pain in the chest area, or if your blood pressure drops or rises sharply. Under such circumstances, doctors who arrived on call will give the patient a drug that will reduce the activity of the sympathoadrenal system (for example, Verapamil, Relanium). It is not recommended to self-medicate with such means, since if misidentified, there is a risk of further aggravating the situation.
Causes of vegetative crisis
There are many reasons for the occurrence of VSD attacks. They are divided into primary and secondary. The primary factors that provoke the development of a vegetative crisis include genetic determinism. It leads to deviations in the structure and functioning of systems and organs.
Secondary causes include:
- prolonged and frequent stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- mental stress;
- hormonal imbalance;
- mental instability;
- problems with the heart and vascular system;
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- long-term medication use;
- presence of allergies;
- physically inactive lifestyle.
People with weakened nervous systems suffer from attacks more often. These individuals are generally quite impressionable and suspicious, mentally unstable, do not tolerate change well, are anxious, with constant mood swings.
Vegetative crises also provoke acute diseases, the use of psychotropic substances, and alcohol.
Symptoms of VSD with a crisis course, how to relieve an attack.
In childhood and adolescence, few people tried to fight vegetative-vascular dystonia; moreover, a dozen years ago medicine did not pay much attention to VSD. Nowadays, many modern doctors believe that dystonia is not a disease, but only a complex of hypochondriacal disorders that completely undermines the nervous system and makes a person suffer out of the blue. Be that as it may, patients with VSD really suffer.
They urgently need a friendly and serious attitude, especially from close people. Each attack of VSD (also called a “crisis”) is experienced by the patient so vividly and acutely that sometimes its terrible aftertaste haunts the person for several days. What does a VSD worker need to know about crises and how to help himself?
In childhood and adolescence, few people tried to fight vegetative-vascular dystonia; moreover, a dozen years ago medicine did not pay much attention to VSD. Nowadays, many modern doctors believe that dystonia is not a disease, but only a complex of hypochondriacal disorders that completely undermines the nervous system and makes a person suffer out of the blue. Be that as it may, patients with VSD really suffer.
Varieties
In total, there are three types of VSD attacks. Depending on the type, the number of relapses varies, as well as the severity of the condition. They also depend on the disorder of one or another part of the nervous system - sympathetic, parasympathetic. Each of them corresponds to a specific type. In total there are:
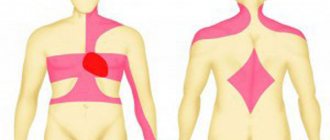
- Panic attack (sympathoadrenaline crisis), which is provoked by disorders of the sympathetic department. This variety is characterized by the release of adrenaline into the blood, which provokes a narrowing of blood vessels, overexcitation, and increased heart contractions. Pallor of the skin and headaches also appear. Nervous overexcitation leads to increased anxiety and increased fear.
- Vagoinsular syndrome, which is characterized by disorders of the parasympathetic department. With this type, there is a sharp release of insulin into the blood. A person exhibits symptoms of a hypoglycemic state. Its main symptoms include a decrease in blood pressure, constriction of the pupils, sweating, an attack of suffocation and vomiting.
- Mixed appearance, in which there are signs of sympathoadrenaline crisis and vagoinsular syndrome.
Also, attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia are divided depending on the duration of the attack. They come in light, medium and heavy. Lungs appear no longer than 15 minutes and are often accompanied by disorders of one system (for example, in the form of rapid heartbeat or asthma attacks).
The average ones last up to an hour, and after them a post-crisis state is observed, which lasts up to several days. Severe autonomic attacks are characterized by disorders of many systems simultaneously (for example, tachycardia, fear, headache, increased salivation, nausea). The duration reaches several hours, after which the unpleasant sensations may continue for the next two days.
Types of seizures
Why does the cause of VSD attacks lie in the functioning of the nervous system? Because this system is characterized by increased sensitivity to environmental changes, genetically inherent characteristics in a person, external factors, stressful situations and personal experiences.
Depending on the manifestations of dystonia, there are several types of attacks that occur:
Vegoinsular type , which has the following characteristics:
- feeling of heaviness in the head;
- fainting state;
- a noticeable decrease in blood pressure;
- the appearance of breathing problems;
- disturbances in heart rhythm, with a reduction in the number of its contractions, manifested in a feeling of “fading”.
This symptomatology is most typical for people who have problems with alcohol. The main danger of a vegoinsular attack is a feeling of acute lack of oxygen, which provokes the development of a panic attack.
The sympatho-adrenaline type is characterized by the occurrence of the following symptoms:
- headaches;
- discomfort in the chest;
- increased heart rate;
- increased blood pressure numbers;
- dilated pupils;
- numbness of hands and feet.
An increased heart rate can lead to shortness of breath, which can lead to a feeling of suffocation.
The mixed type has the following characteristics:
- trembling of limbs;
- redness of the skin;
- increased urge to urinate;
- constant thirst that cannot be quenched;
- heartache;
- loss of strength.
According to another classification, the following types of dystonia are distinguished:
- Hypertensive , characterized by a sharp increase in pressure, increased heart rate, headaches, increased temperature, and anxiety.
- Hypotensive , characterized by a sudden decrease in blood pressure, a decrease in heart rate to 45 beats per minute, weakness in the body, a feeling of lack of oxygen, dizziness, gastrointestinal disorders and loss of consciousness.
- Cardiological , having the following symptoms: lack of air, chest pain, arrhythmia, with problems with the heartbeat.
How it manifests itself
VSD attacks can manifest themselves in different ways. The symptoms of this disorder are many and can have different combinations depending on the form. The most common signs of a vegetative crisis include:
- darkening of the eyes;
- speech disorder;
- lack of concentration;
- feeling of derealization, depersonalization;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- lethargy;
- increased level of sweating;
- suffocation;
- feeling of unreasonable fear;
- increased anxiety;
- sleep problems;
- increased salivation;
- involuntary urination;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
- numbness of arms and legs.
Signs appear in different combinations and may be more intense or muted. Their severity and duration manifest themselves differently, depending on the individual characteristics of the organism. It has been noticed that the intensity of manifestations is brighter in the hot season.
Vegetative-vascular crises
The basis of vegetative-vascular crises is an excessive concentration in the body of substances such as adrenaline, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, steroid hormones and other biologically active substances. How a crisis manifests itself depends not only on the content of these substances, but also on the individual characteristics of the human body and its sensitivity to them. There are several types of crises.
Sympathetic-adrenal crises more often occur in people in whom the influence of the sympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system predominates over the parasympathetic. During a crisis, they experience anxiety, excitement, a feeling of anxiety that turns into fear, discomfort in the heart, head, tachycardia (rapid pulse), then blood pressure rises, chills occur, and hands and feet get cold.
Vagoinsular crises appear predominantly in patients with vagotonia (predominance of the tone of the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system over the sympathetic one). Crises begin with general weakness, dizziness, nausea, lack of air, and freezing in the heart area. The pulse becomes slower, blood pressure decreases, sweating and intestinal motility increase sharply. The condition improves somewhat with a horizontal position of the body. Sometimes at the peak of a crisis, vomiting may occur, which, however, does not bring relief.
Hyperventilation crises begin with a feeling of lack of air. The breathing rate increases (up to 25-30 or more per minute), as a result of which the body loses a significant amount of carbon dioxide. As a result, tachycardia appears, pressure increases, and so-called hyperventilation tetany develops, that is, muscle tension in the forearms and hands, as well as the legs and feet. The hands and feet become damp and cold to the touch.
Vegetative-vestibular crises are manifested by sudden dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. At the peak of the crisis, significant fluctuations in blood pressure may be observed, often towards hypotension. This type of crisis most often occurs when the body position changes or even turns the head sharply.
Vegetative-vascular crises last in mild cases from 5-10 minutes to an hour, in moderate cases - 2-4 hours, in severe cases up to 6-8 hours, sometimes up to several days.
How to cope with an attack?
Depending on what form of crisis is being dealt with, its elimination will occur in different ways. An attack of VSD can occur both during the day and at night. Patients perceive nighttime manifestations worse, as they seem more pronounced.
If we are talking about a mild form, you can cope with it at home. To do this, you should initially accept the idea that the symptoms being shown are not fatal and can be influenced.
To eliminate unpleasant manifestations, just take a walk in the fresh air, drink herbal tea, and lie down.
If this is a crisis of moderate or severe form. You can't do this without taking medications. But for this you need to seek help from specialists. After additional diagnostics, a diagnosis is established and treatment is prescribed. The most commonly prescribed drugs are tranquilizers and antidepressants.
People suffering from a constant vegetative crisis anticipate the onset of the next attack. If possible, it is worth distracting yourself with something, sometimes it really helps. But if an attack cannot be avoided, in order to alleviate the condition, you should follow some recommendations:
- unfasten the top buttons of clothes to allow fresh air to enter, if possible, open a window;
- sit on a chair, or better yet, lie down if this is an acute form of crisis, raise your legs high for blood flow to the head;
- drink a sedative;
- calm down, wait until the attack passes.
What should you not do during an attack?
If a person finds such manifestations in himself, in order to alleviate his condition, he needs to give up some actions that will only aggravate the condition.
Speaking about the disorder as a whole, it is worth considering that those suffering from VSD need to exclude:
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- use of any psychoactive substances;
- drinking coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- heavy physical exercise;
- reduce stressful situations
If we are talking about another attack, during it it is not recommended to take pills that were not prescribed by a doctor or continue physical activity. Otherwise, an attack of VSD does not require additional action.
If a person does not know anything about the disorder, it is more difficult for him to cope with the manifestations. The fear intensifies and this only intensifies the symptoms. To avoid this, it is worth learning more about the crisis, as well as how to deal with it.
First aid for VSD
People who have been diagnosed with vascular dystonia should know how to quickly relieve an attack of VSD.
You need to be able to cope with it yourself, since it can happen suddenly and there may be no one nearby.
What to do during an attack of VSD:
- First you need to try to calm down . You should not think about death because of the alarming symptoms that appear. It is necessary to understand that this is just a crisis of VSD; after a while they will disappear.
- Then you need to unfasten your tight clothes and, if possible, go out into the air . This must be done to ensure the supply of oxygen to the lungs. It is recommended to drink a sedative. For example, tincture of peony, motherwort, Chinese lemongrass, valerian. They should be used as follows: 50 grams of tincture should be dissolved in half a glass of boiled water.
- If you don’t have the strength to go out into the air on your own, then you need to open a window in the room . After this, you should lie on your back and raise your legs. This will improve the flow of blood to the head.
- If someone is nearby, then their first aid for vegetative-vascular dystonia should be to sprinkle the patient’s face with cold water . If the latter begins to lose consciousness, then he should give him ammonia to sniff. If this is not available, use cologne or alcohol.
- Then you can drink the same Valocordin or Corvalol .
- If you have high blood pressure, you need to take a pill that should help lower it. If your blood pressure is low, you will need to take a medicine that will raise it.
- You can drink strong sweet tea or coffee.
- Immerse your feet in warm water.
- To calm your heartbeat, apply pressure to your eyeballs.
So, we found out how to relieve an attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
But how can you prevent the development of this condition?
What to do with VSD is not recommended by doctors:
- drink large quantities of alcoholic beverages, smoke;
- go on diets that require almost complete abstinence from food;
- watch films and TV series that contain scenes of violence;
- prepare yourself for the onset of a crisis;
- spend little time outdoors, a lot at the computer or TV;
- drink large amounts of coffee or energy drinks;
- engage in extreme sports.
First you need to try to just calm down
Treatment
Therapy for somatomorphic autonomic dysfunction is necessary. This allows us to reduce negative manifestations to a minimum, thereby improving a person’s quality of life.
For VSD, the following treatment methods are practiced:
- medicinal;
- traditional medicine;
- psychotherapy.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is treatable, but it will take a lot of time to achieve complete recovery. Especially when it comes to advanced complex forms.
Helpful information
Even those who have a hereditary predisposition can get rid of negative symptoms. In this case, doctors achieve long-term remission.
The most common therapy is medication. Depending on the degree of damage, sedatives, antidepressants and tranquilizers are used. The latter are prescribed only by a doctor. If there are problems with high blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
The most common drug for panic attacks is Glycine. If anxiety increases, Afobazole is prescribed. Dizziness is eliminated by Betaserc, and blood pressure is reduced by Bisoprolol. Improved metabolism occurs with the use of Vazorbalom. Vestinorm is used for sleep problems. An equally common drug is Validol, which eliminates excessive excitability and reduces the manifestation of tachycardia. Grandaxin is used to eliminate obsessive states in humans during and after an attack. Magnesia is used for attacks of somatomorphic autonomic dysfunction as an anticonvulsant drug.
Traditional medicine involves the use of herbs to prepare soothing herbal teas. Psychotherapy is also very important, but many ignore this stage, considering it useless. But in fact, it is almost the most important. The reason is that the root cause of VSD is often neurosis - a psychogenic disorder that is treated through psychotherapy. Depending on the severity of the crisis. It is recommended to contact a psychologist, psychotherapist, or psychiatrist.
Why do seizures occur?
Vegetative-vascular dystonia with a crisis course often progresses from a mild or asymptomatic form. The autonomic disorder itself can develop against the background of the following conditions:
- pathologies of the central nervous system, birth injuries and concussions;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- natural changes in the body’s hormonal levels (for example, pregnancy, menopause or puberty in adolescents);
- pathologies of the autonomic nervous system, formed against the background of infectious foci, tumors, osteochondrosis.
The first attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia does not occur only in the presence of the listed factors. Some push is needed here. The onset of the disease can be triggered by stress, psycho-emotional or physical stress, some diseases, taking medications, surgical interventions, anesthesia, etc.
Therefore, it is more advisable not to think about how to deal with a VSD crisis and what to do when it occurs, but to find out why it could have happened and eliminate the possible causes of its occurrence.
Usually the disease is not limited to just one attack. Often the understanding that a crisis can happen again leads to a feeling of fear and anticipation. The patient begins to worry because he does not know how to behave in such a situation and what should be done. He worries that he will not be able to prevent the onset of the crisis.
The result is a vicious circle: stress, exacerbation of the disease, clinical manifestation of a VSD crisis (sympatho-adrenal or any other type), fear of a recurrence of the attack, another stress and a new crisis. Moreover, each repeated attack is eliminated much more difficult than the previous one.
According to the international classification (ICD-10), VSD is classified as a disease that requires proper psychotherapeutic treatment. To achieve complete treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the conditions that cause stress and change your lifestyle. Otherwise, attacks of the disease will recur.
Prevention
It is difficult to prevent the manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia if we are talking about genetic determination. More often, an attack of VSD occurs against the background of a severe stressful situation or due to significant stress. It turns out that in some cases this can be avoided. Regardless of whether a person has had attacks or not, in order to prevent or minimize them, it is necessary:
- reduce stressful situations;
- reduce or completely eliminate the consumption of coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- avoid intense physical activity;
- maintain a daily routine;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- spend more time outdoors;
- take a contrast shower;
- If you have psychological problems, seek help from a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Somatomorphic autonomic dysfunction brings a lot of inconvenience to those it affects. But you can correct the situation if you seek help from specialists. This type of disorder is treatable. To obtain a better and faster effect, an integrated approach is used.
What is VSD
VSD is not an independent disease, but a syndrome that describes autonomic dysfunction. Vascular dystonia is manifested by impaired vascular tone and the appearance of symptoms of autonomic disorder.
Reasons for violation:
- genetic predisposition;
- constant stress;
- skull injuries;
- diseases of the cervical spine;
- temperament.
The main risk group for developing attacks of VSD are people with a weak psyche, prone to irritability and fussiness. Also, exacerbation of vegetative-vascular dystonia often occurs in emotionally passive people.
Stress is also one of the fundamental factors in the development of VSD attacks. Frequent stress depletes the nervous system, as a result the body develops a specific reaction to the destructive influence of a stressful state. This reaction manifests itself as attacks of VSD.
Vegetative paroxysms (exacerbations) are not dangerous, but they can worsen the quality of life and bring a lot of trouble. The main symptoms of VSD in the acute stage:
- pain in the heart area;
- breathing problems;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- chills;
- dizziness;
- clouding of consciousness;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
Clinical manifestations of vegetative-vascular dysfunction are different for each patient. Doctors count about 150 different manifestations of this disorder.
Provoking factors
Modern medicine cannot yet explain why primary vegetative crises occur, which must be distinguished from panic attacks; these are different terms. In the course of studies of such phenomena, it was found that they are formed under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- pathological changes that have occurred in the organs of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the central nervous system that develop against the background of tumor phenomena, mechanical damage and internal hemorrhage;
- endocrine pathologies, mainly characterized by thyroid dysfunction;
- genetic factor;
- long-term course of drug therapy, involving the use of certain drugs;
- regular stress and nervous strain;
- hormonal imbalance .
Diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Even highly qualified specialists can find it difficult to recognize vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD).
An equally important role is played by the environment in which a person lives. Often, a primary panic attack occurs in children who have experienced physical violence.
According to medical research, panic attacks are more often diagnosed in people:
- living in developed regions of the country;
- possessing developed intelligence;
- characterized by increased responsibility;
- being anxious by nature.
Panic attacks are rarely reported in people who live in remote regions.
What does vegetative-vascular dystonia lead to?
Content
A panic attack can be caused by severe stress
As in the case of arterial hypertension, with vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) there are complications in the form of acute manifestations. These are so-called vegetative crises that develop quite suddenly. Their flow is fast. But they do not pose a danger to life. The following points provoke the occurrence of a crisis during VSD:
- Any emotional or traumatic situation,
- Great physical activity
- Drinking alcohol
- Premenstrual period,
- Prolonged exposure to the sun
- Sudden weather changes and other factors.
What are crises?
Alcohol is one of the causes of dystonia attacks
Autonomic crises are a fairly common consequence of vegetative-vascular dystonia. As a rule, they are extremely difficult for people to perceive. The patient himself and his relatives may consider an attack of VSD to be an extremely severe and life-threatening condition. Actually this is not true. Only the first attacks are difficult to perceive, but with their frequent repetition the patient adapts to them. But it is often impossible to completely get rid of the feeling of fear.
Panic attacks with vegetative-vascular dystonia come in three degrees of severity:
- Mild degree. With this type of attack, few symptoms of VSD appear, the duration of the crisis is about 15 minutes,
- Average. Several symptoms of VSD occur, dysfunction of the autonomic system is pronounced. Duration from half an hour to an hour. Weakness after an attack lasts about a day,
- A severe attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by the appearance of many attacks, autonomic disorders are very pronounced. Convulsions and twitching of the limbs occur. Over the next few days, the person feels very weak, which makes it difficult to lead a normal lifestyle.
General manifestations
Vegetative crisis is the most striking manifestation of VSD. A crisis is also called a panic attack, because the main role in this is played by emotional factors in the form of anxiety and fear, since it seems that the attack is life-threatening. If a person knows how to control his emotions, then the manifestations of the attack are significantly reduced. After all, the emotional factor is the main one.
The most common signs of a crisis with VSD are the following:
- Feeling of lack of air, fear of suffocation, shortness of breath. breathing becomes shallow, rapid, inhalation is intermittent. The man seems to be gasping for air,
- The heart beats quickly, pulsation and trembling are felt throughout the body,
- The person sweats excessively, feels chills and trembling limbs,
- It seems that goosebumps are crawling all over the body, especially on the face, arms and legs,
- There is a feeling of weakness throughout the body, darkness in the eyes, tinnitus, dizziness,
- Unpleasant sensations in the chest. If they occur in the left half, then the person worries that he has a serious cardiac pathology, from which he could lose his life, although in fact there is no such thing with VSD,
- Convulsive twitching of the muscles of the limbs appears,
- The stomach growls, pain can occur in any part of the abdomen,
- The feeling of nausea bothers me, sometimes vomiting may occur,
- Severe headache, even migraine,
- The emotional response changes greatly: a person feels fear of death, inexplicable anxiety, and may be overly irritating and aggressive.
Types of attacks
- Sympathoadrenal crisis
With this option, the sympathetic department of the autonomic system is activated. This type of VSD crisis most often develops in the afternoon or at night. There is a strong throbbing pain in the head, palpitations or interruptions in the functioning of the heart in the chest. Hands and feet go numb. The person feels chills and the whole body trembles. There is a strong feeling of fear and anxiety about health and life.
Blood pressure rises, but not for long. It immediately returns to normal after the end of the vegetative crisis. Often this type of VSD crisis can be expressed in an increase in body temperature. An attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia ends as quickly and suddenly as it begins. At the end there is profuse urination. After a crisis, a person feels tired and overwhelmed.
- Vagoinsular crisis
With this option, the parasympathetic part of the nervous system is activated. It begins with an unexpected sensation of interruptions or freezing in the heart area. The person lacks air, there is severe weakness, dizziness, and a feeling of hunger. The patient may feel “as if he was falling through somewhere.” The skin becomes red and moist with sweat. Intestinal contractions may intensify, abdominal pain, increased gas formation, and a feeling that you want to go to the toilet may occur. Sometimes there may be diarrhea. During an attack of VSD, blood pressure drops and cardiac activity slows down. Arrhythmia may occur. After the end of the crisis of vegetative-vascular dystonia, a person feels severe weakness, fatigue, and weakness.
- Mixed vegetative crisis
This type of crisis in vegetative-vascular dystonia combines a combination of symptoms of the previous types: sympathoadrenal and vagoinsular crises.
- Hysterical type
It is also called a fainting convulsive attack. It is characterized by the appearance of darkening before the eyes, flickering of spots and loss of consciousness. A person faints, the muscles of the arms and legs twitch convulsively. If you find yourself close to such a person, make sure that the person does not get hurt if they fall, as some injuries can be life-threatening.
- Vestibule-like
This crisis in vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by the appearance of severe dizziness and tinnitus.
- Migraine-like
Characterized by the occurrence of severe migraines. Pseudoaddisonic vegetative crisis. A sudden, severe weakness, a feeling of nausea, and vomiting appears. Blood pressure drops significantly.
What to do
During an attack, you should take a horizontal position, lie down and try to calm down. You should take some herbal sedative (valerian, motherwort, peony, hawthorn) or Corvalol, Valocordin. If your blood pressure is low, you can drink coffee, tea or Citramon. More serious drugs that affect the cardiovascular and nervous systems should be used strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
It must be remembered that VSD, together with the consequence in the form of a crisis, is a functional disorder that is caused by emotions with subsequent “increasing” of oneself or from relatives. To avoid the consequences of vegetative-vascular dystonia, you should take care of your health. To do this, it is recommended to normalize your daily routine, give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, and engage in physical activity.
In general, many people know what and how it should be, but only a few implement it in their lives. Whether a person strives for health or, on the contrary, destroys himself - in any case, this is his choice and sooner or later he will have to pay. But what if it’s not just dystonia, but also serious illnesses?