Every person knows that body temperature is a stable indicator. If it constantly remains at the level of 36.6o, this indicates that there are no problems or disorders in the body. An increase in temperature, scientifically called hyperthermia, occurs when the body has to fight an infection or other pathology that requires a protective response. An increase in the thermometer mark at the time of illness indicates the active release of cells of the immune system. Some cases of hyperthermia go beyond the body's protective actions and begin to pose a threat to the health and even life of the patient. Such a case is temperature during a stroke. Why it can change the indicators, what this is connected with and how to deal with this phenomenon will be discussed further.
What temperature is considered normal in a patient after a stroke?
Experts say that if a person has suffered an ischemic or hemorrhagic attack, then in this case the general body temperature rises in almost everyone. In this case, we are talking about the fact that the body simply confirms the fact that quite recently it was forced to endure a complex shock. However, this may also be a signal that the patient has developed complications during the attack.
Doctors recommend paying attention to temperature readings. If it does not exceed the permissible 37.5 degrees, then in this case we are talking about a normal recovery process. The person is recovering and soon the lost strength will return to him.
If the temperature after a stroke is 38 degrees or more, then its level indicates how extensive or intense the hemorrhage occurred during the stroke. This means that it is much more difficult for the human body to cope with the consequences of this incident, so there is a risk of possible complications. Therefore, if there is a sharp jump in this indicator, you need to immediately seek help.
If the temperature jumps significantly after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke, the patient is first given an antipyretic drug. This is necessary in order to reduce the extent of hemorrhage and prevent possible damage to the brain structure. After this, the patient may require hospitalization and mandatory examination.
Norm and violations
Temperature during a stroke
For a doctor, all indicators are important. Hyperthermia during a stroke will tell the specialist how severely the brain cells are affected. The parameters do not change immediately. First, characteristic symptoms of the pathology appear, after which the body temperature rises. In some situations, hyperthermia is present immediately at the onset of the attack. Based on normal data or abnormalities, the doctor determines the person’s condition. Sometimes situations are too critical.
Possible deviations:
- An acceptable increase in body temperature is when the readings are not higher than 37.5°C. This is normal for the patient, but for a specialist, the ideal state of the patient is when the temperature is 37.2°C. Indicators for the human body during an attack can fluctuate within 1 degree, no more.
- With an ischemic stroke, body temperature decreases. If the mark stops at 36°C, the patient has every chance of a positive outcome.
- Increased body temperature. The mark reaches 37.5°C and above. Experts consider this condition critical. The higher the numbers, the worse. Hyperthermia indicates serious disorders that occur in the human body.
Temperature during a stroke is of great importance; using it, the doctor not only determines the patient’s condition, but also makes predictions regarding his health. If the parameters are high enough the patient has little chance of surviving and recovering from the blow. Hyperthermia complicates blood circulation. At elevated temperatures, the hematoma puts pressure on the brain tissue. Even 1 degree can play a decisive role.
The important moment is when the patient’s temperature rises. The later this happened, the less likely the patient is to have a positive prognosis. The risk of death is quite high.
Temperature readings in such patients are measured immediately after an attack. If a person is given antipyretic medications, he has every chance to avoid complications and consequences before the doctor arrives. It happens that hyperthermia occurs at the very beginning of a stroke. The doctor gives the patient antipyretics. Such a solution helps not only save the patient’s life, but also protects brain tissue from extensive damage.
Fever
If we talk about what fever indicates, then, as a rule, it is the body’s reaction to pathological processes, which can be both acceptable and pathological. In the latter case, we are talking about disorders in the functioning of the brain. With a strong increase in temperature after a stroke, metabolic processes in the body increase. Therefore, the human body needs to spend much more energy in order to maintain the vital activity of cellular material. As a rule, this leads to the fact that cells gradually begin to lose their functionality, and neurons die faster.
Restoring normal metabolic processes is necessary to ensure that cells receive the required amount of oxygen. The fact is that at the time of a stroke there is a sharp slowdown in blood circulation. If at the same time the temperature increases sharply, then brain cells begin to die 2 times faster. The appearance of fever after an attack is fraught with similar consequences.
Treatment of male microstroke
The very first measure in treatment is to restore normal blood flow to the brain. This is done with the help of special medications:
- Means for normalizing blood pressure;
- Cardiac glycosides that help normal heart function;
- Vasoactive drugs that help improve blood circulation in brain tissue;
- Drugs that help reduce blood clotting;
- Nootropics that allow you to stimulate brain function, thought processes, and nutrition of brain cells.
- In addition to medications, the patient undergoes additional rehabilitation measures:
- Massages;
- Special exercises for breathing;
- Physiotherapy;
- If necessary, meet with a psychologist or speech therapist.
Additional Information
There are cases when some patients, on the contrary, have a drop in temperature (for example, to 36 degrees) after a stroke. The reasons for this presentation are that no major neurological deficit occurs. In this case we are talking about positive dynamics. The recovery process occurs quite quickly and the patient has every chance of recovery.
Accordingly, an increase in temperature may indicate that brain cells are not able to recover properly, but instead continue to die.
Temperature after a stroke: why does it increase?
There are very different versions depending on how much time has passed since the attack. However, most often an increase in temperature occurs due to:
- Extensive hemorrhages.
- Ischemia.
- Arterial thrombosis.
- Necrosis of brain tissue.
- Vein thrombosis or cerebral edema.
If after a stroke there are changes in the indicators of the thermoregulation center of the human body. This leads to neurogenic hyperthermia. In some situations, the causes of fever after a stroke are that the patient has an allergic reaction to a particular drug that was prescribed to him for the recovery period in order to speed up the recovery process. In this case, you must immediately stop taking it or choose funds from another group.
Temperature during stroke - causes of increase and methods of reduction
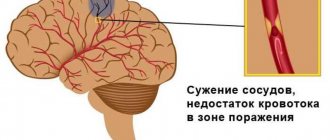
The temperature that occurs during a stroke is a reliable indicator of hemorrhage in the tissue of the brain (brain).
In other words, fever in combination with signs of neurological impairment is a symptom pathogenetic for hemorrhagic stroke. But with ischemic stroke (infarction of brain tissue), the temperature in the vast majority of cases is somewhat lower.
Acceptable norm for stroke
The temperature indicator during a stroke is an important symptom also for the reason that it quite reliably indicates the clinical severity of the general condition of a neurological patient due to the fact that it characterizes the severity of brain tissue necrosis in the patient.
Fever figures up to 37 degrees are considered to be the maximum acceptable, although numerous studies of acute stroke cases conducted in leading clinics in the world have reliably shown that the vast majority of patients with the nosology in question had an absolutely adequate average temperature at the time of admission to the clinic.
In those patients who were struck by a major stroke, febrile fever manifested itself after a few hours (4-6) and increased up to 40 degrees. In patients with moderate stroke, a rise in fever up to 40 degrees was observed 12 hours after stroke. A mild degree of necrotic tissue damage to the brain manifests itself without fever.
The temperature after a stroke can reach febrile values (up to 40 degrees), and it will be very, very difficult to stop hyperthermic syndrome.
What is most interesting is that such a high fever during a stroke cannot occur if the patient is in a coma.
Most likely, this feature is due to the fact that the increase in body temperature is caused by an inflammatory non-infectious reaction of the human body - leukocytes destroy the focus of necrosis, promoting its gradual replacement with connective tissue.
Reasons for rising temperature
In order to relieve a possible attack of febrile fever, doctors pay considerable attention to identifying the causes of the development of hyperthermic syndrome in the acute period and the increase in temperature during the recovery stage.
It is clear that different types of hemorrhagic stroke (in this case, we mean SAH and stroke of the brain parenchyma itself) correspond to fever curves that are different in characteristics, which, in turn, are the main harbingers of much more serious complications.
For example, an increase in body temperature in combination with severe neurological impairment, which reaches critical values within a few minutes, clearly indicates the manifestation of very serious clinical variants of the disease (the classic case is that persistent febrility will be achieved with extensive hemorrhage).
The pathogenetic mechanisms of temperature increase during stroke include:
- Development of edema of brain tissue after the manifestation of stroke;
- The occurrence of complications of an infectious nature (for example, pneumonia) or exacerbation of the clinical picture of concomitant chronic diseases against the background of destabilization of the general condition of the body;
- Manifestation of extensive hemorrhage, which will be considered a consequence of neurocellular necrosis, and not its root cause.
In the event that the patient who developed a stroke, at the time of the manifestation of a cardiovascular accident, suffered from some kind of chronic inflammatory-infectious disease (for example, the same urinary tract infections, or had a chronic lung abscess), complications such as the occurrence persistent fever will definitely make themselves felt.
The temperature during a stroke (especially in old people) can rise to 37.2 - 37.5 degrees even during the rehabilitation period, due to the fact that there is a delayed reaction of the body to damage to human GM tissues.
A significantly reduced level of body temperature is also an unfavorable factor that significantly aggravates the patient’s recovery process (in this case, most likely, there is also a stem defect - damage to the medulla oblongata with its centers of unconditioned reflex activity by a necrotic process).
An extensive necrotic focus can also cause a person’s body temperature to decrease rather than increase - situations of this kind do occur, but are quite rare.
Their occurrence can be explained by different levels of activity of the human immune system.
With a sufficient amount of protective forces, the process of resorption of the necrotic lesion by leukocytes will take place without a significant increase in body temperature, and with immune deficiency, most likely, it will be necessary to state the fact of temperature jumps.
First aid
Due to some pathophysiological specifics, normalizing body temperature during the onset of stroke and at the rehabilitation stage is a very difficult task. Simple NSAIDs, used as antipyretic drugs, cannot always be prescribed, since they also have blood-thinning properties.
Accordingly, in case of stroke of hemorrhagic type, the use of drugs from this pharmacological group is strictly prohibited for the reason that it will lead to a significant increase in hemorrhage.
And with stroke of an ischemic nature, there is a high probability of hemorrhagic transformation of the ischemic focus.
Taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s condition, in the situations under consideration, in order to save life, it is advisable to use other methods. Another option is craniocerebral hypothermia.
!
In the event that an adult who has been diagnosed with stroke (namely a stroke of the brain parenchyma, and not SAH), suddenly has a temperature rise to 38.5 - 39.
5, it is allowed to administer intravenously a lytic mixture, which will include analgin and diphenhydramine in equal parts (papaverine, like any other antispasmodics, is strictly forbidden to use).
However, before this, it will be necessary to prescribe hemostatic agents, for example, dicinone (etamsylate) or aminocaproic acid.
An indicator that the treatment of hyperthermic syndrome in a patient with stroke is carried out effectively is not only the normalization of body temperature, but also the indicators of the blood coagulation system.
If its liquefaction is observed, the risk of repeated hemorrhage in the brain tissue increases significantly.
Consequences
After the manifestation of acute stroke, persistent fever often occurs due to the presence of the following complications:
- Localization of the necrotic process over a significant area of brain tissue.
- Presence of cerebral edema.
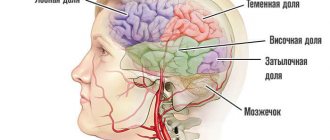
- The necrotic process caused damage to the thermoregulation center in the brain, which is located in its medulla oblongata. In this situation, there is a high probability of death, since isolated damage to this particular department is extremely rare - as a rule, it is associated with damage to other unconditioned reflex centers that are responsible for maintaining vital functions.
- An inflammatory-infectious complication that has arisen after the manifestation of a stroke, an allergic reaction to the medications used.
In situations where the increase in body temperature was of central origin, doctors performed craniocerebral hypothermia. The expediency of this method of treatment was justified by the fact that due to the pressure exerted by the extensive hematoma on some areas of the brain tissue, the likelihood of irreversible consequences of the primary hemorrhage significantly increased.
The consequence of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke can be a persistent low-grade fever that will last for several months.
This kind of condition occurs if the formed necrotic focus is subjected to long-term resorption by the human immune system, the intensity of which leaves much to be desired. A particularly low level of protective forces is observed in a bedridden patient.
Unfortunately, in all cases of the formation of a persistent fever that lasts for more than one week (in this case it will no longer matter whether it is febrile or subfebrile), the prognosis of the disease leaves much to be desired - to restore working capacity, or at least the ability to self-care, even and there is no need to hope.
Prevention
Serious and prognostically unfavorable complications that really threaten a person’s life may well manifest themselves immediately after the onset of a stroke. Complications dangerous not only to health, but also to human life include, among other things, persistent fever, which can reach febrile and subfebrile levels.
To avoid all adverse consequences, when body temperature rises above 37.5 C, a search for a possible infection and therapy with antibacterial drugs should begin.
It is imperative to re-take the entire set of tests - general clinical blood and urine, biochemical blood with determination of the renal-hepatic complex, and most importantly - it is necessary to determine the indicators that characterize the state of the blood coagulation system, since all complications arise, as a rule, due to , which increases bleeding in the brain tissue.
Conclusion
Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to prevent the development of fever with necrotic lesions of the central nervous system. All that remains is to fight the already developed symptom, and the sooner this is started, the higher the chances of success.
The prophylactic prescription of antipyretic drugs, especially those belonging to the pharmacological category of NSAIDs, is somewhat unjustified due to the possible thinning of the blood.
Stroke
Source: https://sosudoved.ru/lechenie/temperatura-pri-insulte.html
Additional reasons
If we talk about statistics, then, according to doctors, most patients suffer from fever, more precisely, hyperthermia within a month after a stroke. This often develops against the background of:
- Pneumonia.
- The appearance of bedsores.
- Inadequate care for a patient who cannot care for himself.
- Stagnation, if we are talking about lying down for too long.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases that appear against the background of infection.
- Urogenital infections.
- Tissue necrosis.
Additionally, not only a high temperature may appear after a stroke, but also increased sweating. At the same time, patients do not experience any other changes in well-being. Therefore, if during the recovery process there is only an increase in temperature, but there are no other signs of a viral or seasonal disease, then this indicates the body’s reaction to the disaster that has occurred.
When temperature jumps are possible, their causes
During a stroke, the temperature rises for the following reasons:
- cerebral edema;
- blood clots in blood vessels;
- pneumonia;
- viral infections;
- displacement of the thermoregulation center resulting from cerebral hemorrhage.
In addition, with a stroke, there is an exacerbation of other serious disorders that preceded the stroke. They include.
- cardiovascular diseases;
- pneumonia;
- genitourinary infections.
Therefore, it is extremely important that the doctor knows about all the diseases the patient has previously suffered.
What could be the consequences?
If a person has a fever after an ischemic stroke or attacks of another category, then first of all this is a sign of hemorrhages occurring in the brain.
There are a number of quite serious consequences of such a change in condition. If a person has a fever, this can lead to an acceleration of metabolic processes and subsequent oxygen starvation of cells. Against this background, damage occurs to some centers of the brain.
If the human body has not been able to fully recover, this can trigger the development of disability. There are cases when, after a stroke, people fall into a coma and die.
Clinical picture as a whole
In addition to hyperthermia, doctors include general cerebral and focal symptoms in the clinical picture of a stroke.
Includes the following features:
- dizziness and headache;
- noise in ears;
- urge to vomit;
- disturbances in consciousness - from slight disorientation in space and time to partial or complete loss of consciousness and immersion in a coma;
- convulsions.
Damage to the right hemisphere is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- paresis of the left half of the body;
- speech problems;
- conduct disorder;
- lethargy;
- memory problems.
If there is a violation in the left hemisphere, the following signs are observed:
- paresis of the right half of the body;
- problems with spatial perception;
- hot temper and aggression;
- behavioral disorders.
What to do at home
First of all, it is worth saying that if a fever persists after a stroke, the patient’s relatives should under no circumstances try to cope with the problem on their own or prescribe strong medications to the patient. In this case, there is a great risk of only further harming human health. However, it is not always possible to receive timely qualified assistance. In this case, it is allowed to give a patient with a high fever after a stroke non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These include Aspirin, Analgin, Paracetamol, and Ibuprofen. However, giving more than two tablets is prohibited.
Under no circumstances should you try to treat a patient with antibiotics and drugs belonging to the group of steroid drugs, including potent analgesics.
If the patient’s relatives are expecting the arrival of doctors, then the patient’s reflexes need to be checked. In no case should you give antipyretic tablets to a patient if he is breathing heavily or cannot swallow the medicine on his own. There is a possibility that a relapse occurred and the development of a stroke condition began.
Features of choosing medications
When a person has suffered a serious attack, it is very important to control his body temperature. If the temperature after a stroke does not rise above 37.5 degrees, then serious measures should not be taken. However, it is important to monitor any changes in these indicators. If the temperature rises above 38.6 degrees, then the patient can be given Paracetamol. It is difficult to calculate the dosage yourself. It is important not to harm the patient further. Experts recommend giving the patient approximately 325-1000 mg of the drug every 5-6 hours. However, the dose of the medicine should not exceed 4 g per day. It is necessary to evaluate not only the patient’s condition, but also his weight and age. If we are talking about an elderly person, then you should not experiment. It's better to call a doctor.
Specialists are taking the necessary measures to lower the temperature. Today there are two methods of such therapy.
Preventive actions
Prevention refers to a set of measures aimed at preventing the development of brain strokes, their relapses, and subsequent complications. Necessary:
- Conduct courses of treatment in a timely manner for existing chronic pathologies.
- If you experience frequent pain in the heart area, be sure to check with a cardiologist.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Eat properly.
- To refuse from bad habits
Stroke is one of the most dangerous diseases, often resulting in lifelong disability and even death. A timely, competent response to the first symptoms of the disease, an accurate assessment of the patient’s condition, as well as correctly prescribed treatment will facilitate recovery and improve the prognosis.
Acute cerebrovascular accident is an extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate treatment, especially if a fever occurs during a stroke. After a stroke, people often remain disabled, especially if assistance was provided untimely or unqualified. Currently, the development of new methods of treatment and recovery after stroke continues.
This indicates the high social significance of this problem for our country. Specialists pay no less attention to studying the causes of cerebrovascular accidents. The stroke itself can occur in different ways, and accordingly, the consequences for a person can be very diverse. It is worth noting that a stroke does not always immediately put a person to bed, and the lack of timely treatment makes its further course more difficult.
It is not recommended to use independent or traditional methods for treatment or subsequent recovery after a stroke - they can complement therapy, but only as an adjunct, and if prescribed by a doctor.
Invasive method
When using this method, doctors inject the patient intravenously with a specialized physiological solution, which has a cooling effect. He considers this method to be the most effective, as it allows you to quickly reduce and correct the patient’s temperature.
However, the invasive method also has a drawback. It lies in the fact that such manipulations can provoke certain complications. For example, thrombosis or hemorrhage in blood vessels may develop as a side effect.
Non-invasive method
In this case, it is possible to lower the patient’s body temperature by acting on his skin. Usually, regular ice is used for this, which is packed in special bags. After this, cold lotions are applied to the patient's head. This method allows you to minimize the effect on the condition of blood vessels, but there is a risk of frostbite. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the patient’s condition. If you allow hypothermia to occur, it can cause serious problems.
Both of these methods are not suitable for those people who are not doctors. Without proper preparation, it is very easy to harm the patient. Although doctors allow the use of a non-invasive method at home, you need to be extremely careful. It is necessary to monitor the patient's temperature every minute and not apply ice for too long.
Prevention
It is important to prevent the patient from developing a fever after a stroke. To do this, it is necessary to perform several preventive measures. The patient must be turned over periodically. This is necessary in order to prevent the development of bedsores. This is especially important for paralyzed patients, as stagnation occurs in their body.
At home, it is recommended to use specialized anti-bedsore mattresses. In addition, you need to turn over in bed in order to counter the likely development of pneumonia. It wouldn't hurt to use a massage. Such measures are also useful if the patient is diagnosed with pneumonia. Massage procedures promote better removal of phlegm.
It is very important to monitor the patient's hygiene. If he does not undergo daily procedures, this can lead to infectious diseases. You need to understand that the body is greatly weakened after receiving a blow. Its protective and other functions do not work properly. Therefore, it is also worth excluding possible contacts with people suffering from viral pathologies.
The room where the patient is located must be periodically ventilated. However, the patient should not be allowed to be in a draft. In addition, the ward or room must be wet cleaned daily. If the patient suffers from allergies, then it is important to exclude any contact with irritants.