Features of left-sided stroke
The left side of the human brain is responsible for:
- control of the right side of the body;
- speech abilities;
- analysis of what is happening;
- logical thinking;
- operations with lists and numbers;
- linear representations.
Important! The presence of a left-sided stroke leads to partial or complete atrophy of these brain functions.
In all other respects, ischemia proceeds in the same way as with damage to the right hemisphere of the brain.
Motor disorders
Tactile disorders
Damage to the left side of the brain during a stroke is accompanied by a decrease in sensitivity on the right side of the body.
This is not paresis or paralysis yet. But when touching the skin and examining specific reflexes, it turns out that the patient feels external stimuli worse than on the healthy side.
If the lower extremities are affected, this is most clearly seen in the Babinski reflex.
The hand is less susceptible to deviation, but specific automatic reactions are also weakened.
With a total disruption of the motor centers of the brain, a complete lack of sensitivity is possible, while the ability for voluntary movements is formally preserved (other phenomena can occur in parallel).
Decreased functional activity and muscle controllability
The muscles become weak. This is the result of insufficient stimulation of motor structures.
Formally, the tone is preserved, but the centers of the brain are no longer able to produce a nerve impulse of sufficient strength, which leads to a decrease in the motor activity of the limbs.
A classic example that is used in diagnostic practice.
The patient is asked to raise his arms above his head. The limb on the side opposite to the affected one (in particular on the right) turns out to be lower than the other, which is due to weakness.
In the absence of high-quality rehabilitation, which consists of constant training and physical therapy, the disorder can remain for life.
Paralysis, paresis, paresthesia
In the first case, we are talking about a dual process: a total impairment of motor activity combined with a complete lack of sensitivity.
This is a common phenomenon; it occurs when the parietal or frontal lobe of the brain is predominantly affected.
Paresthesia is a partial loss of the two described functions. This does not make the consequences any easier. Motor activity, if there is any, is scant. The limb cannot perform functions.
Paresthesia develops almost immediately. It's a crawling sensation.
The lesion affects more than just the arm or leg. The entire right half of the body suffers. Including the facial muscles. The patient cannot fully control the facial muscles.
With paralysis, this ability is absent altogether.
Causes
In general, the origins of any type of ischemia are similar. Risk factors include previous history of:
- atherosclerosis of the large arteries of the brain;
- diabetes;
- compaction of the vessels of the extremities;
- hemicrania;
- atrial fibrillation;
- purulent-septic diseases;
- brain vasculitis;
- arterial hypertension and so on.
A stroke can develop against the background of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, in particular heart defects.
The occurrence of a blood clot can be provoked by pathologies in the composition of the blood, that is, its increased viscosity.
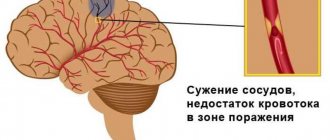
Atherothrombotic ischemic stroke in the left MCA region occurs due to the formation of a blood clot and blockage of the vessel.
This type of disease occurs against the background of coronary heart disease or arterial hypertension.
A completely healthy woman can develop a stroke due to frequent use of contraceptives.
Excessive smoking or drinking alcohol also depresses the condition of blood vessels. The result is a massive ischemic stroke.
How to diagnose
To diagnose a stroke on the left side of the brain, procedures such as:
- Comprehensive collection of samples for laboratory work. Donating blood and urine is mandatory. The blood will be checked for lipoprotein levels and a coagulogram. After receiving the results, a system of pharmacological and physical treatment is built. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms and further maintaining the body;
- X-ray of the sternum. It is carried out to identify possible complications. The most common is pneumonia;
- Blood pressure monitoring. If obvious abnormalities are detected that are similar to symptoms in the early stages of ischemia, the patient is urgently transferred to appropriate treatment;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is performed either before or immediately after a stroke attack. Gives a clear picture of the state of the brain during ischemia and is the most effective procedure for detecting thrombosis of cerebral arteries;
- CT scan. It is prescribed when several hours have passed after the ischemic crisis. Otherwise, the procedure is useless, since in photographs of horizontal sections of the brain the effects of ischemia appear only after a lapse of time;
- Consultation with a panel of specialists. The teams include a neurologist, cardiologist and neurosurgeon. After considering a specific case, doctors draw up a plan for surgical treatment of a stroke and a further program for restoring the body after an attack.
Treatment methods
As each minute passes from the moment of crisis, the effectiveness of subsequent therapy expires.
That’s why they start it in the ambulance. The orderlies provide basic therapy, including:
- Suppression of headaches using pharmacological agents. Their compositions often include paracetamol, tramadol, ketaprofen and the like;
- Relief of seizures when they occur;
- Intravenous administration of 0.9% sodium chloride solution to control and stabilize water and electrolyte balance;
- Adjustment and monitoring of blood pressure and cardiovascular system activity;
- Monitor and lower, if necessary, body temperature. Produced either pharmacologically or physically;
- Oxygen therapy if absolutely necessary.
Subsequently, the patient is prescribed thrombolytic and anticoagulant therapy. The techniques restore blood flow in the vessels and prevent the occurrence of blood clots in the future, respectively.
There are several types of thrombolytic treatment, each of which is prescribed depending on the time that has passed since the onset of ischemia:
- Systemic thrombolysis. Effective in the first three hours after an attack. The principle of the method is the intravenous administration of 10% of the drug “Alteplase” at the rate of 0.9 mg per kilogram of human weight. The patient spends the next hour under a drip from the remaining medicine. "Alteplase" has no antigenic effect on the body and is considered a hypoallergenic substance;
- Intraarterial thrombolysis. It is prescribed in cases where up to 6 hours have passed since the crisis or the intravenous injection has not shown positive results. It is a surgical intervention. In its process, 1 mg of the drug is administered alternately, first in the immediate vicinity of the blood clot, then in its thickness, and then closer to the edge of the formation. This is followed by an hour-long intra-arterial injection of 17 mg of Alteplase;
- Mechanical thrombolysis. The technique is experimental and is used only in cases of unsatisfactory results from both previously described methods or after 8-12 hours after the onset of the stroke.
The essence of anticoagulant therapy comes down to the selection and intravenous administration of blood thinning drugs. In some cases, treatment with these drugs continues for 3-6 months after discharge.
Most often, administration occurs orally and is necessary to stabilize the body during a stressful period and prevent relapses.
Rehabilitation
The effectiveness of recovery measures directly depends on the timeliness of first aid. While still in the hospital, the patient undergoes an initial course of rehabilitation in the rehabilitation department, but even after discharge home, medical supervision and control are maintained. Often, stroke patients are discharged from the hospital directly to a sanatorium. This requires appropriate indications and a doctor’s referral. Sanatorium treatment is paid for under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
At home, the patient must continue to engage in exercise therapy, exercises to restore speech, sometimes with the help of a speech therapist. At the same time, the moral support of family and friends plays a decisive role here, since the treatment is long and requires strength, desire, and motivation.
A special hypocholesterol diet, as well as the DASH diet, which prevents hypertension, also plays an important role:
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Citrus | Smoked meats |
| Spinach | Pickles |
| Berries | Canned food |
| Nuts | Rich broths |
| Dried fruits | Sausages |
| Mustard and tomato paste | Dairy |
| Corn | Sweets, ice cream |
| Fresh vegetables and fruits | Bakery |
| Bran | Convenience foods, fast food |
| Seafood | Soda, strong tea, coffee |
| Fresh juices | Semolina |
A prerequisite for recovery is giving up bad habits.
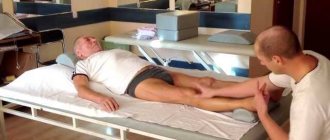
Massotherapy
To restore movements on the right side, patients after discharge from hospital or sanatorium-resort rehabilitation are prescribed a course of therapeutic massage. They start with a session of 5 minutes, maximum duration is half an hour. Massage is performed only by certified specialists. The purpose of the procedure is to reduce muscle tone, indirectly thinning the blood. If the patient is bedridden, massage is necessary to prevent bedsores.
Hirudotherapy
Quite often, to prevent stroke recurrence, treatment with leeches is used, which, together with saliva, when biting the skin, deliver many biologically active substances into the blood. The basis of stroke prevention is hirudin, which is an anticoagulant, improves blood flow, and normalizes blood pressure. Leeches are placed in the coccyx area or in the behind-the-ear area.
Consequences
Paralysis and disturbance of spatial perception
Due to the fact that the left side of the brain controls the sequence of perception of the world and allows one to analyze what is happening, it is more difficult for the patient to rehabilitate after the onset of paralysis.
This happens because a person cannot be aware of his body, as a result of which he does not notice motor dysfunctions.
Without realizing the problem, it is impossible to solve it, therefore, to recover from a left-sided stroke, sometimes it is necessary to work with a psychotherapist.
Treatment includes physiotherapy, exercises, massages and medications.
Behavior disorder
From time to time there are such manifestations of atypical behavior as:
- apathy;
- unmotivated anger;
- hysterical laughter or crying;
- insomnia and sleep phase disorder;
- attacks of excessive psychomotor agitation, etc.
For adjustments, a visit to a psychiatrist is necessary. Depending on the situation, the patient is prescribed psychotherapy and a course of antidepressants.
Memory impairment and weakening of mental abilities
After a stroke you may experience:
- Hypomnesia - weakening of memory functions;
- Hypermnesia is the inability to filter out unimportant information, which subsequently completely ends up in the long-term memory department;
- Paramnesia is a distortion of memories or their complete replacement with false ones;
- Amnesia is the complete loss of some memories.
Rehabilitation requires constant training both with specialists in centers and at home.
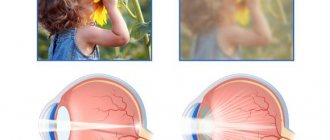
Visual impairment
The peculiarity of getting rid of ophthalmological problems after an attack is the uselessness of drug treatment without an integrated approach to recovery. In addition to taking medications, you must:
- follow a diet rich in vitamin A;
- systematic moisturizing of mucous membranes with gels and drops;
- performing a special program to strengthen the eye muscles;
- taking a course of vitamins for vision.
We invite you to watch an interesting video on the topic:
Mental emotional sphere
Depression
A type of post-traumatic disorder. In this case, the source is a severe condition. Accompanied by classic signs of a pathological process.
Anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure), inhibition of mental activity, decreased background of emotions.
Additional points are also highlighted: weakness, drowsiness, apathy, bowel movements, pessimism, suicidal thoughts.
Depressive syndrome is especially pronounced in patients with severe, irreversible types of neurological deficit, which is caused by a fundamental change in living conditions, apparent inferiority, and disability.
Treatment is prescribed in extreme cases; in general, the disorder fades into the background as rehabilitation progresses. Improvement or addiction.
Strictly speaking, a stroke on the left side and brain nutritional disorders in general do not provoke depression on their own. This is a normal reaction to traumatic events.
Phobic disorders
Most patients develop fears: becoming a burden, repeating the episode, disability and inferiority.
These moments may appear implicitly. A person does not always openly express his own concerns.
There are frequent cases of destructive behavior and latent auto-aggression. This can manifest itself in frequent drinking of alcohol, refusal to use medications, non-compliance with specialist recommendations (while formally maintaining loyalty to the doctor, the so-called high compliance).
Recovery requires long-term psychotherapy. Pills won't help matters.
Behavioral disorders
They can be part of depression or an independent problem when, for example, the frontal lobes of the brain are damaged.
In the first case, the patient is angry, pessimistic, whiny, and aggressive. This is the result of awareness of acquired limitations, fears of becoming a burden, and other issues. A complex emotional complex is formed in all patients without exception.
In the second situation we are talking about psychopathological products. Affective disorders are the result of damage to the frontal lobes, which are partially responsible for the behavioral component.
Typical options are unmotivated aggression, inappropriate gaiety, foolishness and other moments. Much depends on the patients’ personal attitudes and propensity for violence.
If there is a history of mental disorders, they worsen. Character traits are emphasized even more.
Insomnia
Occurs during the early rehabilitation period or as a symptom of depression. Accompanied by frequent night awakenings.
As a result of such “rest,” the patient becomes even more irritable and lethargic. Feels overwhelmed and tired. Medication correction is required, but using gentle methods.
Panic attacks, general anxiety
They arise independently or are separated from depression during the development of the latter. Accompanied by moments of unmotivated strong fear, in the most advanced cases.
As for other options, everything is limited by constant excitement.
Usually the point of “application” of mental reflection is one’s own health. In extreme situations, it is possible to form overvalued ideas and fragments of hypochondriacal delirium. These are unstable disorders, they are treated simply.
Forecast for life
Although it is not always possible to predict the course of a person’s recovery, even in personal consultation with highly qualified specialists, there are a number of aggravating factors:
- advanced age;
- living in a place with poor ecology;
- remoteness from places where they can provide timely assistance in case of a new attack;
- mental illness;
- presence of bad habits.
If any point is applicable to the patient, then the likelihood of a recurrent stroke increases by 5-10%. The basic risk percentage can be calculated using the table below:
| Index | Description | Points |
| Age | Over 60 years | 1 point |
| HELL | Systolic blood pressure more than 140 mm Hg. Art. Diastolic blood pressure more than 90 mm Hg. Art. | 1 point |
| Symptoms | Numbness in one part of the body Slurred speech Other | 2 points 1 point 0 points |
| Duration of symptoms | More than an hour 10-59 minutes Less than 10 minutes | 2 points 1 point 0 points |
| Scoring: 0-4 points - 0.4%, 5 points - 12.1%, 6 points 31.4% | ||
Rehabilitation period
As stated above, even with a high chance of survival, recovery will take quite a long time.
It is important that the patient himself wants to return to his previous life and does everything possible for this in his situation
The recovery period includes a number of activities:
- physiotherapy;
- various types of massage;
- physiotherapy;
- visiting a speech therapist;
- alternative medicine (acupuncture, hirudotherapy);
- teaching reading and writing skills;
- conversations with a psychologist.
At this time, a loved one should be near the patient. Only with support can you cope with complications after brain damage.
How long do you live after a stroke?
35% of patients die 3 days after the incident, and 50% do not survive 1 year (does not depend on whether they belong to the male or female part of the population). The average lifespan of survivors ranges from 1 to 10 years. It is influenced by many factors:
- number of damaged cells;
- type of complications;
- age;
- quality of restoration;
- balanced diet;
- compliance with doctor's orders;
- presence of bad habits.
Left-sided ischemic stroke is a complex disease. Its main danger is the loss of important body functions. The chance of surviving and returning to a full life is small. It will not be possible to fully recover. In addition, after a stroke you will periodically have to undergo special treatment. However, if you strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, you can regain motor activity, the ability to communicate and self-care.
How long do they live?
About 75% of victims survive an ischemic stroke. About 15-25% of patients die in the first month. Only 35% of patients live more than a year. In order to get into this percentage, you must constantly be registered with a cardiologist and strictly follow his instructions.
The most common cause of death after a stroke is the development of complications. Cerebral edema, pneumonia, kidney failure, etc.
Monitor your body, and at the first symptoms similar to pathological abnormalities due to ischemia, immediately call an ambulance. The most important thing when treating a stroke is time, which is important not to waste by procrastinating in the hope that it will go away on its own.
Possible complications
It often happens that people who have suffered a stroke die immediately or die within the next year. Also, this pathology can provoke complete or partial disability of the victim, which seriously affects the quality of human life and his emotional health. In addition, there are also the following consequences of an ischemic stroke on the left side:
- complete or partial paralysis of one part of the human body;
- incorrect perception of external stimuli;
- speech dysfunction;
- loss of many skills: a person cannot write or read, is not able to correctly navigate in space;
- complete or partial memory loss;
- loss of abilities for logical thinking and adequate assessment of current situations;
- deterioration in the performance of the visual system (loss or deterioration of vision, strabismus, etc.);
- chronic facial deformation (muscle paralysis);
- the occurrence of all kinds of psychological disorders (they can be either minor or serious);
- Epileptic illness may occur.
Most often, such complications occur due to poor quality or untimely treatment. That is why you need to know the existing symptoms of the disease and immediately contact specialized medical institutions in order to prevent the development of irreversible complications in time.